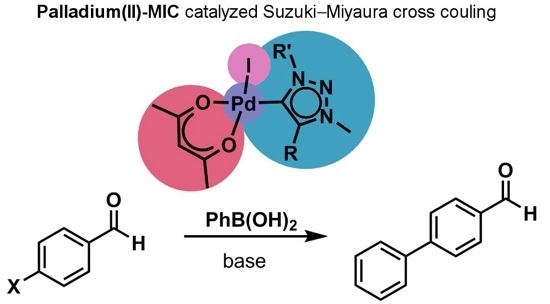
Palladium(ii)-Acetylacetonato Complexes with Mesoionic Carbenes: Synthesis, Structures and Their Application in the Suzuki-Miyaura Cross Coupling Reaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Palladium(ii) Complexes
2.2. Structural Characterization
2.3. Catalysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Procedures, Materials and Instrumentations
3.2. X-ray Crystallography
3.3. Synthesis
3.3.1. General Procedure for the Preparation of the Palladium(ii) 1,2,3-Triazolylidene Complexes 1–3
3.3.2. Suzuki-Miyaura Cross Coupling Reactions
3.3.3. Buchwald-Hartwig Amination
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Frémont, P.; Marion, N.; Nolan, S.P. Carbenes: Synthesis, properties, and organometallic chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 862–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbert, J.D.; Cazin, C.S.J.; Nolan, S.P. Copper N-heterocyclic carbene complexes in catalysis. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 912–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantchev, E.A.; O’Brien, C.J.; Organ, M.G. Palladium complexes of N-heterocyclic carbenes as catalysts for cross-coupling reactions—A synthetic chemist’s perspective. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 2768–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, C.C.; Enders, D. Merging organocatalysis and gold catalysis–a critical evaluation of the underlying concepts. Eur. J. Chem. 2012, 18, 10212–10225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, F.E.; Jahnke, M.C. Heterocyclic carbenes: Synthesis and coordination chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3122–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guisado-Barrios, G.; Bouffard, J.; Donnadieu, B.; Bertrand, G. Crystalline 1H-1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidenes: New stable mesoionic carbenes (MICs). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4759–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez-González, S.; Marion, N.; Nolan, S.P. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes in Late Transition Metal Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3612–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, W.A. N-heterocyclic carbenes: A new concept in organometallic catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1290–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalrempuia, R.; McDaniel, N.D.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Bernhard, S.; Albrecht, M. Water oxidation catalyzed by strong carbene-type donor-ligand complexes of iridium. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9765–9768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercs, L.; Albrecht, M. Beyond catalysis: N-heterocyclic carbene complexes as components for medicinal, luminescent, and functional materials applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaram, H.; Tan, J.; Huynh, H.V. Syntheses, characterizations, and a preliminary comparative cytotoxicity study of gold(I) and gold(III) complexes bearing benzimidazole- and pyrazole-derived N-heterocyclic carbenes. Organometallics 2012, 31, 5875–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, J.L.; Ruhayel, R.A.; Barnard, P.J.; Baker, M.V.; Berners-Price, S.J.; Filipovska, A. Mitochondria-targeted chemotherapeutics: The rational design of gold(I) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes that are selectively toxic to cancer cells and target protein selenols in preference to thiols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12570–12571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, R.; Rit, A.; Schulte to Brinke, C.; Daniliuc, C.G.; Hahn, F.E. Metal center dependent coordination modes of a tricarbene ligand. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 1011–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejuto, C.; Guisado-Barrios, G.; Gusev, D.; Peris, E. First homoleptic MIC and heteroleptic NHC-MIC coordination cages from 1,3,5-triphenylbenzene-bridged tris-MIC and tris-NHC ligands. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 13914–13917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidtendorf, M.; Pape, T.; Hahn, F.E. Stepwise preparation of a molecular square from NR,NR- and NH,O-substituted dicarbene building blocks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2195–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, J.D.; Lee, A.-L.; Kilpin, K.J. 1,3,4-Trisubstituted-1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene ‘click’ carbene ligands: Synthesis, catalysis and self- assembly. Aust. J. Chem. 2011, 64, 1118–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweinfurth, D.; Deibel, N.; Weisser, F.; Sarkar, B. Mit Klick zu neuen Liganden. Nachr. Chem. 2011, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabtree, R.H. Abnormal, mesoionic and remote N-heterocyclic carbene complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, K.F.; Petronilho, A.; Albrecht, M. Application of 1,2,3-triazolylidenes as versatile NHC-type ligands: Synthesis, properties, and application in catalysis and beyond. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizpurua, J.M.; Fratila, R.M.; Monasterio, Z.; Pérez-Esnaola, N.; Andreieff, E.; Irastorza, A.; Sagartzazu-Aizpurua, M. Triazolium cations: From the “click” pool to multipurpose applications. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, B.; Schubert, U.S. Beyond click chemistry–supramolecular interactions of 1,2,3-triazoles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 2522–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, P.; Neels, A.; Albrecht, M. 1,2,3-Triazolylidenes as versatile abnormal carbene ligands for late transition metals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13534–13535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huisgen, R.; Knorr, R.; Möbius, L.; Szeimies, G. 1.3-Dipolare Cycloadditionen, XXIII. Einige Beobachtungen zur Addition organischer Azide an CC-Dreifachbindungen. Chem. Ber. 1965, 98, 4014–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisgen, R.; Szeimies, G.; Möbius, L. 1.3-Dipolare Cycloadditionen, XXXII. Kinetik der Additionen organischer Azide an CC-Mehrfachbindungen. Chem. Ber. 1967, 100, 2494–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.C.; Finn, M.G.; Sharpless, K.B. Click chemistry: Diverse chemical function from a few good reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2004–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostovtsev, V.V.; Green, L.G.; Fokin, V.V.; Sharpless, K.B. A stepwise Huisgen cycloaddition process: Copper(I)-catalyzed regioselective “ligation” of azides and terminal alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2596–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornøe, C.W.; Christensen, C.; Meldal, M. Peptidotriazoles on solid phase: [1,2,3]-Triazoles by regiospecific copper(I)-catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions of terminal alkynes to azides. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilpin, K.J.; Paul, U.S.; Lee, A.L.; Crowley, J.D. Gold(I) “click” 1,2,3-triazolylidenes: Synthesis, self-assembly and catalysis. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohloch, S.; Su, C.-Y.; Sarkar, B. Copper(I) complexes of normal and abnormal carbenes and their use as catalysts for the Huisgen [3+2] cycloaddition between azides and alkynes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 3067–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohloch, S.; Sarkar, B.; Nauton, L.; Cisnetti, F.; Gautier, A. Are Cu(I)-mesoionic NHC carbenes associated with nitrogen additives the best Cu-carbene catalysts for the azide–alkyne click reaction in solution? A case study. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 1808–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohloch, S.; Scheiffele, D.; Sarkar, B. Activating azides and alkynes for the click reaction with [Cu(aNHC)2I] or [Cu(aNHC)2]+(aNHC = triazole-derived abnormal carbenes): Structural characterization and catalytic properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 3956–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohloch, S.; Duecker, F.L.; van der Meer, M.; Sarkar, B. Copper(I) complexes of mesoionic carbene: Structural characterization and catalytic hydrosilylation reactions. Molecules 2015, 20, 7379–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohloch, S.; Suntrup, L.; Sarkar, B. Exploring potential cooperative effects in dicopper(I)-di-mesoionic carbene complexes: applications in click catalysis. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidal, Y.D.; Lesieur, M.; Melaimi, M.; Nahra, F.; Cordes, D.B.; Athukorala Arachchige, K.S.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Bertrand, G.; Cazin, C.S.J. Copper(I) complexes bearing carbenes beyond classical N-heterocyclic carbenes: Synthesis and catalytic activity in “click chemistry”. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 3155–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canseco-Gonzalez, D.; Petronilho, A.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Ohmatsu, K.; Ooi, T.; Albrecht, M. Carbene transfer from triazolylidene gold complexes as a potent strategy for inducing high catalytic activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13193–13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.R.; Young, P.C.; Lucas, N.T.; Lee, A.L.; Crowley, J.D. Gold(I) and palladium(II) complexes of 1,3,4-trisubstituted 1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene “click” carbenes: Systematic study of the electronic and steric influence on catalytic activity. Organometallics 2013, 32, 7065–7076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettmanczyk, L.; Manck, S.; Hoyer, C.; Hohloch, S.; Sarkar, B. Heterobimetallic complexes with redox-active mesoionic carbenes as metalloligands: Electrochemical properties, electronic structures and catalysis. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10949–10952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Espinosa, D.; González-Olvera, R.; Negrón-Silva, G.E.; Angeles-Beltrán, D.; Suárez-Castillo, O.R.; Álvarez-Hernández, A.; Santillan, R. Phenoxy-linked mesoionic triazol-5-ylidenes as platforms for multinuclear transition metal complexes. Organometallics 2015, 34, 4529–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Espinosa, D.; González-Olvera, R.; Osornio, C.; Negrón-Silva, G.E.; Santillan, R. Versatile O- and S-functionalized 1,2,3-triazoliums: Ionic liquids for the Baylis–Hillman reaction and ligand precursors for stable MIC-transition metal complexes. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 1587–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolentino, D.R.; Liqun, J.; Melaimi, M.; Bertrand, G. Mesoionic carbene-gold(I) catalyzed bis-hydrohydrazination of alkynes with parent hydrazine. Chem. Asian J. 2015, 10, 2139–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretorius, R.; Fructos, M.R.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Gossage, R.A.; Perez, P.J.; Albrecht, M. Synthesis and catalytic applications of 1,2,3-triazolylidene gold(I) complexes in silver-free oxazoline syntheses and C-H bond activation. Dalton Trans. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petronilho, A.; Rahman, M.; Woods, J.A.; Al-Sayyed, H.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Don MacElroy, J.M.; Bernhard, S.; Albrecht, M. Photolytic water oxidation catalyzed by a molecular carbene iridium complex. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 13074–13080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandaru, S.; English, N.J.; MacElroy, J.M.D. Density functional theory calculations of catalytic mechanistic pathways for the formation of O2 involving triazolylidene iridium complexes. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 4060–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petronilho, A.; Woods, J.A.; Bernhard, S.; Albrecht, M. Bimetallic iridium-carbene complexes with mesoionic triazolylidene ligands for water oxidation catalysis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 2014, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, J.A.; Lalrempuia, R.; Petronilho, A.; McDaniel, N.D.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Albrecht, M.; Bernhard, S. Carbene iridium complexes for efficient water oxidation: Scope and mechanistic insights. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2316–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohloch, S.; Suntrup, L.; Sarkar, B. Arene–ruthenium(II) and −iridium(III) complexes with “click”-based pyridyl-triazoles, bis-triazoles, and chelating abnormal carbenes: Applications in catalytic transfer hydrogenation of nitrobenzene. Organometallics 2013, 32, 7376–7385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohloch, S.; Hettmanczyk, L.; Sarkar, B. Introducing potential hemilability into “click” triazoles and triazolylidenes: Synthesis and characterization of d6-metal complexes and oxidation catalysis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 3164–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, R.; Hohloch, S.; Su, C.Y.; van der Meer, M.; Sarkar, B. Cyclometalated mono- and dinuclear Ir(III) complexes with “click”-derived triazoles and mesoionic carbenes. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 9952–9961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolje, A.; Hohloch, S.; van der Meer, M.; Kosmrlj, J.; Sarkar, B. Ru(II), Os(II), and Ir(III) complexes with chelating pyridyl-mesoionic carbene ligands: Structural characterization and applications in transfer hydrogenation catalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 6756–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolje, A.; Hohloch, S.; Kosmrlj, J.; Sarkar, B. RuII, IrIII and OsII mesoionic carbene complexes: Efficient catalysts for transfer hydrogenation of selected functionalities. Dalton Trans. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohloch, S.; Kaiser, S.; Dücker, F.L.; Bolje, A.; Maity, R.; Kosmrlj, J.; Sarkar, B. Catalytic oxygenation of sp3 “C-H” bonds with Ir(III) complexes of chelating triazoles and mesoionic carbenes. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernet, L.; Lalrempuia, R.; Ghattas, W.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Vigara, L.; Llobet, A.; Albrecht, M. Tunable single-site ruthenium catalysts for efficient water oxidation. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 8058–8060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prades, A.; Peris, E.; Albrecht, M. Oxidations and oxidative couplings catalyzed by triazolylidene ruthenium complexes. Organometallics 2011, 30, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canseco-Gonzalez, D.; Albrecht, M. Wingtip substituents tailor the catalytic activity of ruthenium triazolylidene complexes in base-free alcohol oxidation. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 7424–7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, K.; Inomata, S.; Fukuzawa, S.-I. Position-selective intramolecular aromatic C-H bond activation of 1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene (tzNHC) ligands in (p-cymene)ruthenium(II) complexes. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 2362–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagh, B.; McKinty, A.M.; Lough, A.J.; Stephan, D.W. 1,2,3-Triazolylidene ruthenium(II)(eta(6)-arene) complexes: Synthesis, metallation and reactivity. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 12807–13146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolje, A.; Hohloch, S.; Urankar, D.; Pevec, A.; Gazvoda, M.; Sarkar, B.; Košmrlj, J. Exploring the scope of pyridyl- and picolyl-functionalized 1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidenes in bidentate coordination to ruthenium(II) cymene chloride complexes. Organometallics 2014, 33, 2588–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Rebollo, M.; Canseco-Gonzalez, D.; Hollering, M.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Albrecht, M. Synthesis and catalytic alcohol oxidation and ketone transfer hydrogenation activity of donor-functionalized mesoionic triazolylidene ruthenium(II) complexes. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 4462–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinn, S.; Schulze, B.; Friebe, C.; Brown, D.G.; Jager, M.; Altuntas, E.; Kubel, J.; Guntner, O.; Berlinguette, C.P.; Dietzek, B.; Schubert, U.S. Physicochemical analysis of ruthenium(II) sensitizers of 1,2,3-triazole-derived mesoionic carbene and cyclometalating ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 2083–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, V.; Ghattas, W.; Lalrempuia, R.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Pryce, M.T.; Albrecht, M. Synthesis, photo-, and electrochemistry of ruthenium bis(bipyridine) complexes comprising a N-heterocyclic carbene ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 5395–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinn, S.; Schulze, B.; Friebe, C.; Brown, D.G.; Jager, M.; Kubel, J.; Dietzek, B.; Berlinguette, C.P.; Schubert, U.S. A heteroleptic bis(tridentate) ruthenium(II) platform featuring an anionic 1,2,3-triazolate-based ligand for application in the dye-sensitized solar cell. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Kjaer, K.S.; Fredin, L.A.; Chabera, P.; Harlang, T.; Canton, S.E.; Lidin, S.; Zhang, J.; Lomoth, R.; Bergquist, K.E.; et al. A heteroleptic ferrous complex with mesoionic bis(1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene) ligands: Taming the MLCT excited state of iron(II). Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 3628–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naziruddin, A.R.; Lee, C.S.; Lin, W.J.; Sun, B.J.; Chao, K.H.; Chang, A.H.; Hwang, W.S. Platinum complexes bearing normal and mesoionic N-heterocyclic carbene based pincer ligands: Syntheses, structures, and photo-functional attributes. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 5848–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soellner, J.; Tenne, M.; Wagenblast, G.; Strassner, T. Phosphorescent platinum(II) complexes with mesoionic 1H-1,2,3-triazolylidene ligands. Chem. Eur.J. 2016, 22, 9914–9918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, R.; van der Meer, M.; Sarkar, B. Redox-active multinuclear Pd(II) complexes with bis- and tris-mesoionic carbenes. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulain, A.; Canseco-Gonzalez, D.; Hynes-Roche, R.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Schuster, O.; Stoeckli-Evans, H.; Neels, A.; Albrecht, M. Synthesis and tunability of abnormal 1,2,3-triazolylidene palladium and rhodium complexes. Organometallics 2011, 30, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keske, E.C.; Zenkina, O.V.; Wang, R.; Crudden, C.M. Synthesis and structure of palladium 1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene mesoionic carbene PEPPSI complexes and their catalytic applications in the Mizoroki–Heck reaction. Organometallics 2012, 31, 6215–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Ogata, K.; Fukuzawa, S.-I. Synthesis of dichlorobis(1,4-dimesityl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene)palladium [PdCl2(TMes)2] and its application to Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reaction. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 920–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, T.; Sankararaman, S. Palladium complexes with abnormal N-heterocyclic carbene ligands derived from 1,2,3-triazolium ions and their application in Suzuki coupling. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 5834–5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canseco-Gonzalez, D.; Gniewek, A.; Szulmanowicz, M.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Trzeciak, A.M.; Albrecht, M. PEPPSI-type palladium complexes containing basic 1,2,3-triazolylidene ligands and their role in Suzuki-Miyaura catalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 6055–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terashima, T.; Inomata, S.; Ogata, K.; Fukuzawa, S.-I. Synthetic, structural, and catalytic studies of well-defined allyl 1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene (tzNHC) palladium complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2012, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohloch, S.; Frey, W.; Su, C.Y.; Sarkar, B. Abnormal carbenes derived from the 1,5-cycloaddition product between azides and alkynes: structural characterization of Pd(II) complexes and their catalytic properties. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 11355–11358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik, J.B.; Ramkumar, V.; Varghese, B.; Sankararaman, S. Synthesis and structure of trans-bis(1,4-dimesityl-3-methyl-1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene)palladium(II) dichloride and diacetate. Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of polybromoarenes with high catalytic turnover efficiencies. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guchhait, S.; Ghosh, K.; Sureshbabu, B.; Ramkumar, V.; Sankararaman, S. C2-Symmetric normal and mesoionic bis-N-heterocyclic carbenes with biphenyl backbone. A comparison of bis(1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene) and bis(imidazol-2-ylidene) ligands. J. Organomet. Chem. 2014, 768, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, R.; Mekic, A.; van der Meer, M.; Verma, A.; Sarkar, B. Triply cyclometalated trinuclear iridium(III) and trinuclear palladium(II) complexes with a tri-mesoionic carbene ligand. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15106–15109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Huynh, H.V. Hetero-dicarbene complexes of palladium(II): Syntheses and catalytic activities. Organometallics 2014, 33, 6033–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, T.; Sugihara, M.; Tokoro, Y.; Fukuzawa, S.-I. Synthesis of adamantyl substituted 1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene ligands and their PEPPSI-type palladium complexes. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, S.; Gangwar, M.K.; Nageswar Rao, M.; Madasu, M.; Kalita, A.; Dorcet, V.; Shejale, M.A.; Butcher, R.J.; Ghosh, P. Fluoride-free Hiyama coupling by palladium abnormal N-heterocyclic carbene complexes. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 17617–17628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Espinosa, D.; González-Olvera, R.; Osornio, C.; Negrón-Silva, G.E.; Álvarez-Hernández, A.; Bautista-Hernández, C.I.; Suárez-Castillo, O.R. Structural diversity of phenoxy functionalized triazol-5-ylidene palladium(II) complexes and their application in C–N bond formation. J. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 803, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, R.; Verma, A.; van der Meer, M.; Hohloch, S.; Sarkar, B. Palladium complexes bearing mesoionic carbene ligands: Applications in α-arylation, α-methylation and Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Ramkumar, V.; Sankararaman, S. Synthesis and structures of (−) menthyl and (+) neomenthyl substituted enantio pure bis(1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene)PdI2 complexes and PEPPSI type (1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene) (pyridine)PdI2complexes. Comparison of catalytic activities for C–C coupling. J. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 799–800, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hong, J.-T.; Hong, S.H. Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction catalyzed by PEPPSI-type 1,4-di(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)-1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidene (tzIPr) palladium complex. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 6630–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureshbabu, B.; Ramkumar, V.; Sankararaman, S. A mild and efficient method for the synthesis of structurally diverse 1,2,3-triazolylidene palladium(II) diiodo complexes. Comparison of catalytic activities for Suzuki–Miyaura coupling. J. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 799–800, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, O.; Marion, N.; Scott, N.M.; González, J.; Amoroso, D.; Bell, A.; Nolan, S.P. Synthesis of novel (NHC)Pd(acac)Cl complexes (acac = acetylacetonate) and their activity in cross-coupling reactions. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 9716–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, N.; Ecarnot, E.C.; Navarro, O.; Amoroso, D.; Bell, A.; Nolan, S.P. (IPr)Pd(acac)Cl: An easily synthesized, efficient, and versatile precatalyst for C-N and C-C bond formation. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 3816–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion, N.; de Frémont, P.; Puijk, I.M.; Ecarnot, E.C.; Amoroso, D.; Bell, A.; Nolan, S.P. N-heterocyclic carbene–palladium complexes [(NHC)Pd(acac)Cl]: Improved synthesis and catalytic activity in large-scale cross-coupling reactions. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 2380–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.E.M.N.; Holzwarth, M.S.; Hohloch, S.; Sarkar, B.; Plietker, B. Redox-active triazolium-derived ligands in nucleophilic Fe-catalysis–reactivity profile and development of a regioselective O-allylation. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 6310–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Deng, H.; Cheng, J.-P. An acidity scale of 1,3-dialkylimidazolium salts in dimethyl sulfoxide solution. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 7790–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, E.M.; Sherwood, J.A.; Lindsay, A.G.; Armstrong, J.; Massey, R.S.; Alder, R.W.; O’Donoghue, A.C. pKas of the conjugate acids of N-heterocyclic carbenes in water. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1559–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dröge, T.; Glorius, F. The measure of all rings—N-heterocyclic carbenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6940–6952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouffard, J.; Keitz, B.K.; Tonner, R.; Lavallo, V.; Guisado-Barrios, G.; Frenking, G.; Grubbs, R.H.; Bertrand, G. Synthesis of highly sTable 1,3-diaryl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-5-ylidenes and their applications in ruthenium-catalyzed olefin metathesis. Organometallics 2011, 30, 2617–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckenroth, M.; Kluser, E.; Neels, A.; Albrecht, M. Palladation of diimidazolium salts at the C4 position: access to remarkably electron-rich palladium(II) centers. Dalton Trans. 2008, 6242–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortman, G.C.; Nolan, S.P. N-Heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligands and palladium in homogeneous cross-coupling catalysis: A perfect union. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5151–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion, N.; Nolan, S.P. Well-defined N-heterocyclic carbenes–palladium(II) precatalysts for cross-coupling reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXS-97; Program for Crystal Structure Solution and Refinement; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- SAINT+. Data Integration Engine, Version 8.27b©, Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1997–2012.
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruker. APEX2, Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2012.
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXL Version 2014/7, Program for crystal structure solution and refinement; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 2014.
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS, Ver. 2008/1; Program for Empirical Absorption Correction; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–3 are available from the authors.





| Atoms | 1 | 3 |
|---|---|---|
| C1-C2 | 1.37 (2) | 1.387 (6) |
| C1-N3 | 1.36 (1) | 1.376 (6) |
| C2-N1 | 1.37 (1) | 1.354 (6) |
| N1-N2 | 1.32 (1) | 1.304 (6) |
| N2-N3 | 1.32 (1) | 1.351 (6) |
| Pd1-C1 | 1.98 (1) | 1.957 (5) |
| Pd1-I1 | 2.561 (1) | 2.560 (1) |
| Pd1-O1 | 2.027 (7) | 2.054 (4) |
| Pd1-O2 | 2.060 (7) | 2.046 (4) |
| O1-C23 | 1.27 (1) | 1.264 (6) |
| O2-C21 | 1.27 (1) | 1.281 (7) |
| C23-C22 | 1.39 (2) | 1.398 (8) |
| C21-C22 | 1.42 (2) | 1.379 (8) |
| C1-C2-N1 | 106 (1) | 107.5 (4) |
| C2-C1-N3 | 103 (1) | 103.3 (4) |
| C1-N3-N2 | 114.9 (8) | 112.0 (4) |
| C2-N1-N2 | 112.5 (9) | 111.9 (4) |
| N1-N2-N3 | 103.1 (8) | 105.4 (4) |
| C23-C22-C21 | 127 (1) | 127.0 (5) |
| O1-C23-C22 | 127 (1) | 126.8 (5) |
| O2-C21-C22 | 125 (1) | 127.0 (5) |
| C1-Pd1-I1 | 90.4 (3) | 88.9 (1) |
| C1-Pd1-O1 | 89.1 (4) | 88.7 (2) |
| C1-Pd1-O2 | 177.1 (4) | 178.4 (2) |
| I1-Pd1-O1 | 175.3 (2) | 177.4 (1) |
| I1-Pd1-O2 | 88.8 (2) | 90.5 (1) |
| O1-Pd1-O2 | 91.9 (3) | 91.9 (2) |
| trz-Ar (Ctrz) * | 46.7 | 86.0 |
| trz-Ar (Ntrz) * | 47.5 | 71.1 |
| trz–acac * | 57.1 | 82.7 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hettmanczyk, L.; Schmid, B.; Hohloch, S.; Sarkar, B. Palladium(ii)-Acetylacetonato Complexes with Mesoionic Carbenes: Synthesis, Structures and Their Application in the Suzuki-Miyaura Cross Coupling Reaction. Molecules 2016, 21, 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111561
Hettmanczyk L, Schmid B, Hohloch S, Sarkar B. Palladium(ii)-Acetylacetonato Complexes with Mesoionic Carbenes: Synthesis, Structures and Their Application in the Suzuki-Miyaura Cross Coupling Reaction. Molecules. 2016; 21(11):1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111561
Chicago/Turabian StyleHettmanczyk, Lara, Bianca Schmid, Stephan Hohloch, and Biprajit Sarkar. 2016. "Palladium(ii)-Acetylacetonato Complexes with Mesoionic Carbenes: Synthesis, Structures and Their Application in the Suzuki-Miyaura Cross Coupling Reaction" Molecules 21, no. 11: 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111561
APA StyleHettmanczyk, L., Schmid, B., Hohloch, S., & Sarkar, B. (2016). Palladium(ii)-Acetylacetonato Complexes with Mesoionic Carbenes: Synthesis, Structures and Their Application in the Suzuki-Miyaura Cross Coupling Reaction. Molecules, 21(11), 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111561