The Apoptotic Effect of Ursolic Acid on SK-Hep-1 Cells is Regulated by the PI3K/Akt, p38 and JNK MAPK Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cytotoxic Effect of UA on SK-Hep-1 Cells
2.2. Immunocytochemical Analysis
2.3. UA Induces Expression of TNF-α, Fas, FADD, Bax, Bcl-xL and Inhibits Expression of Mcl-1, TCTP, and Bcl-2 Proteins in SK-Hep-1 Cells
2.4. Effect of UA on Activation of Caspases and PARP
2.5. UA Induces Apoptosis in SK-Hep-1 Cells by Upregulating the PI3K/Akt, ERK1/2, JNK1/2 and p38 MAPK Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Preparation of UA
4.4. Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.6. Immunocytochemical Staining
4.7. DAPI Staining Analysis
4.8. Cell Lysis and Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PARP | poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| p38 | p38 MAP kinase |
References
- Szakiel, A.; Paczkowski, C.; Pensec, F.; Bertsch, C. Fruit cuticular waxes as a source of biologically active triterpenoids. Phytochem. Rev. Proc. Phytochem. Soc. Eur. 2012, 11, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borras-Linares, I.; Stojanovic, Z.; Quirantes-Pine, R.; Arraez-Roman, D.; Svarc-Gajic, J.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A. Rosmarinus officinalis leaves as a natural source of bioactive compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20585–20606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidpour, M.; Hamidpour, R.; Hamidpour, S.; Shahlari, M. Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Medicinal Property of Sage (Salvia) to Prevent and Cure Illnesses such as Obesity, Diabetes, Depression, Dementia, Lupus, Autism, Heart Disease, and Cancer. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2014, 4, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.H.; Jeong, S.J.; Kwon, H.Y.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.H.; Yoo, D.Y. Ursolic acid from Oldenlandia diffusa induces apoptosis via activation of caspases and phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta in SK-OV-3 ovarian cancer cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woźniak, Ł.; Skąpska, S.; Marszałek, K. Ursolic Acid—A Pentacyclic Triterpenoid with a Wide Spectrum of Pharmacological Activities. Molecules 2015, 20, 20614–20641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Nascimento, P.G.; Lemos, T.L.; Bizerra, A.M.; Arriaga, A.M.; Ferreira, D.A.; Santiago, G.M.; Braz-Filho, R.; Costa, J.G. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of ursolic acid and derivatives. Molecules 2014, 19, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johann, S.; Oliveira, F.B.; Siqueira, E.P.; Cisalpino, P.S.; Rosa, C.A.; Alves, T.M.A.; Zani, C.L.; Cota, B.B. Activity of compounds isolated from Baccharis dracunculifolia D.C. (Asteraceae) against Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. Med. Mycol. 2012, 50, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Chen, Y.; Wei, L.; Hong, Z.; Sferra, T.J.; Peng, J. Ursolic acid inhibits colorectal cancer angiogenesis through suppression of multiple signaling pathways. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, J. Evolution in Medicinal Chemistry of Ursolic Acid Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 92, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.-Q.; Ding, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.-M. Protective effects of ursolic acid in an experimental model of liver fibrosis through Nrf2/ARE pathway. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2015, 39, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Yadav, V.R.; Sung, B.; Gupta, S.C.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Ursolic acid inhibits the growth of human pancreatic cancer and enhances the antitumor potential of gemcitabine in an orthotopic mouse model through suppression of the inflammatory microenvironment. Oncotarget 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.; Tan, Z.J.; Hu, Y.P.; Shu, Y.J.; Bao, R.F.; Jiang, L.; Wu, X.S.; Li, M.L.; Ding, Q.; Wang, X.A.; et al. Ursolic acid induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of gallbladder carcinoma cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.S.; Moon, A. Ursolic acid inhibits the invasive phenotype of SNU-484 human gastric cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-H.; Ryu, H.G.; Lee, J.; Shin, J.; Harikishore, A.; Jung, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Lyu, H.-N.; Oh, E.; Baek, N.-I.; et al. Ursolic acid exerts anti-cancer activity by suppressing vaccinia-related kinase 1-mediated damage repair in lung cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, K.K.; Yu, Z.; Chen, F.L.; Li, F.; Li, W.Y.; Guo, Y.H. Synthesis and evaluation of ursolic acid derivatives as potent cytotoxic agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 2488–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Chi, T.; Tang, Q.; Yang, X.; Ou, M.; Chen, X.; Yu, X.; Chen, J.; Ho, R.J.Y.; Shao, J.; et al. A pentacyclic triterpene natural product, ursolic acid and its prodrug US597 inhibit targets within cell adhesion pathway and prevent cancer metastasis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 9295–9312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Qi, H.; Li, X.; Xiao, X.; Gao, J. Ursolic acid induces apoptosis through mitochondrial intrinsic pathway and suppression of ERK1/2 MAPK in HeLa cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 125, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.W. Autophagy inhibition enhances ursolic acid-induced apoptosis in PC3 cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achiwa, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Udagawa, Y. Regulation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways by ursolic acid in human endometrial cancer cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liang, X.; Yang, X. Ursolic acid inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in gemcitabine-resistant human pancreatic cancer via the JNK and PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionisi, F.; Amichetti, M. Proton Therapy Results in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma According to the Barcelona-Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) Staging System. Int. J. Med. Phys. Clin. Eng. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2012, 379, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koff, J.; Ramachandiran, S.; Bernal-Mizrachi, L. A Time to Kill: Targeting Apoptosis in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Watari, H.; AbuAlmaaty, A.; Ohba, Y.; Sakuragi, N. Apoptosis and Molecular Targeting Therapy in Cancer. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millimouno, F.M.; Dong, J.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Li, X. Targeting Apoptosis Pathways in Cancer and Perspectives with Natural Compounds from Mother Nature. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 1081–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases and Their Role in Radiation Response. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewthawee, N.; Brimson, S. The effects of ursolic acid on cytokine production via the MAPK pathways in leukemic T-cells. EXCLI J. 2013, 12, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.S.; Wang, W.J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zheng, L. Ursolic acid inhibits the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.Y.; Xue, X.W.; Shi, Z.M.; Wang, P.Y.; Wu, X.R.; Wang, X.J. Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid inhibit proliferation in transformed rat hepatic oval cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, X.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, G.; Dong, C.; Zhang, W.; Song, X.; Jin, T. Osthole induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, G.; Yao, F.; He, Y.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, H. Growth Inhibition and Apoptosis Induced by Osthole, A Natural Coumarin, in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, F.T.; Zhou, T.T.; Liu, B.; Bao, J.K. Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldoveanu, T.; Follis, A.V.; Kriwacki, R.W.; Green, D.R. Many players in BCL-2 family affairs. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, F.; ten Dijke, P. Signaling interplay between transforming growth factor-beta receptor and PI3K/AKT pathways in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Wang, J.; Xiao, H.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. MAPK signaling pathways regulate mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis induced by isoorientin in human hepatoblastoma cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2013, 53, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, W.J.; Lehmann, P.Z.; Li, W. Nuclear PI3K signaling in cell growth and tumorigenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Zhu, G.; Liao, S.; Yi, W.; Luo, G.; He, J.; Pei, Z.; Li, G.; Zhou, Y. Dysregulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway affects cell cycle and apoptosis of side population cells in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
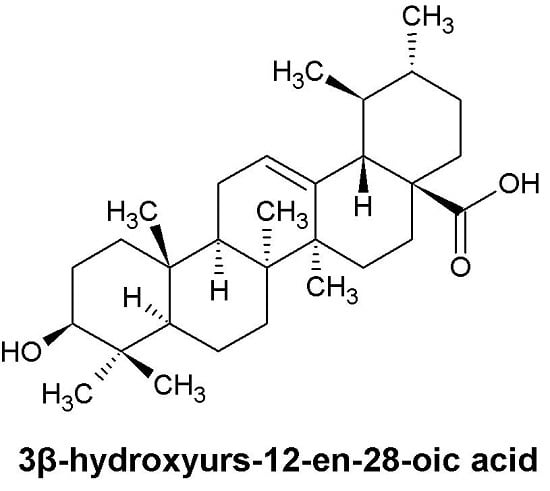
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 3β-hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid are available from the authors.








© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuang, W.-L.; Lin, P.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-L. The Apoptotic Effect of Ursolic Acid on SK-Hep-1 Cells is Regulated by the PI3K/Akt, p38 and JNK MAPK Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2016, 21, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040460
Chuang W-L, Lin P-Y, Lin H-C, Chen Y-L. The Apoptotic Effect of Ursolic Acid on SK-Hep-1 Cells is Regulated by the PI3K/Akt, p38 and JNK MAPK Signaling Pathways. Molecules. 2016; 21(4):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040460
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuang, Wan-Ling, Ping-Yi Lin, Hui-Chuan Lin, and Yao-Li Chen. 2016. "The Apoptotic Effect of Ursolic Acid on SK-Hep-1 Cells is Regulated by the PI3K/Akt, p38 and JNK MAPK Signaling Pathways" Molecules 21, no. 4: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040460
APA StyleChuang, W. -L., Lin, P. -Y., Lin, H. -C., & Chen, Y. -L. (2016). The Apoptotic Effect of Ursolic Acid on SK-Hep-1 Cells is Regulated by the PI3K/Akt, p38 and JNK MAPK Signaling Pathways. Molecules, 21(4), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040460