Novel N-Substituted 2-(2-(Adamantan-1-yl)-1H-Indol-3-yl)-2-Oxoacetamide Derivatives: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Evaluation
2.2.1. Cytotoxicity in Human Tumor Cell Lines
2.2.2. Growth Inhibitory Activity of 5r in HepG2
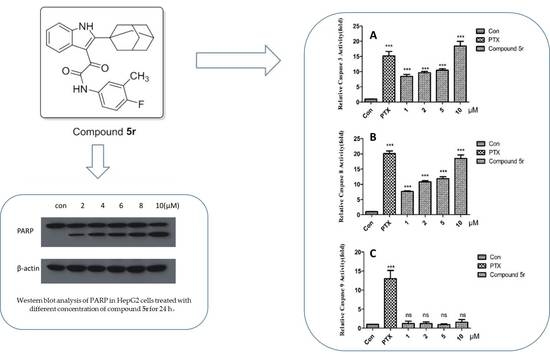
2.2.3. Inducing Apoptosis in HepG2 Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Synthesis of N-o-Tolylcycloadamantanecarboxamide (2)
3.3. Synthesis of 2-Adamantane-1H-indole (3)
3.4 General Procedure for Synthesis of 5a–y [23,46]
3.5. Cell Culture
3.6. Cytotoxicity against Cancer Cell Lines
3.7. Western Blot Analysis
3.8. A Flow Cytometry Assay
3.9. Colony Formation Assay
3.10. Caspase Activity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2013, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.A.; Schuchter, L.M. Chemotherapy for Melanoma. In Melanoma; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 209–229. [Google Scholar]
- Viaccoz, A.; Lekoubou, A.; Ducray, F. Chemotherapy in low-grade gliomas. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2012, 24, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venur, V.A.; Peereboom, D.M.; Ahluwalia, M.S. Current medical treatment of glioblastoma. Springer Cancer Treat Res. 2015, 163, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Proctor, S.; Lennard, A.; Jackson, G.; Jones, G.; Lewis, J.; Wilkinson, J.; White, J.; Sieniawski, M.; McKay, P.; Culligan, D.; et al. The role of an all-oral chemotherapy containing lomustine (CCNU) in advanced, fs progressive Hodgkin lymphoma: A patient-friendly palliative option which can result in long-term disease control. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampling, R.; Sanson, M.; Gorlia, T.; Lacombe, D.; Lai, C.; Gharib, M.; Taal, W.; Stoffregen, C.; Decker, R.; van den Bent, M.J. A phase I study of LY317615 (enzastaurin) and temozolomide in patients with gliomas (EORTC trial 26054). Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szakács, G.; Paterson, J.K.; Ludwig, J.A.; Booth-Genthe, C.; Gottesman, M.M. Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, J.-P.; Gottesman, M.M. Advances in the molecular detection of ABC transporters involved in multidrug resistance in cancer. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Xu, J.Q.; Ward, E. Cancer Statistics, 2010. Ca-Cancer J Clin. 2010, 60, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, S.; J Snape, T. 2-Arylindoles: A Privileged Molecular Scaffold with Potent, Broad-Ranging Pharmacological Activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 4828–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Dudley, E.; Plummer, S.; Tang, J.; Newton, R.P.; Brenton, A.G. Fingerprint profile of Ginkgo biloba nutritional supplements by LC/ESI-MS/MS. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, P.; Siddiqui, N. Anticonvulsant evaluation of clubbed indole-1,2,4-triazine derivatives: A synthetic approach. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 80, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-Z.; Mulholland, N.; Beattie, D.; Irwin, D.; Gu, Y.-C.; Chen, Q.; Yang, G.-F.; Clough, J. Synthesis and antifungal activity of 3-(1,3,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)-indoles and 3-(1,3,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)methyl-indoles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 63, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-Z.; Chen, Q.; Yang, G.-F. A review on recent developments of indole-containing antiviral agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, M.A.A.; Ragab, E.A.; Sabry, N.M.; El-Shenawy, S.M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new 3-substituted indole derivatives as potential anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 3832–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, R.; Puebla, P.; Díaz, J.F.; Bento, A.C.; García-Navas, R.; de la Iglesia-Vicente, J.; Mollinedo, F.; Andreu, J.M.; Medarde, M.; Peláez, R. Endowing Indole-Based Tubulin Inhibitors with an Anchor for Derivatization: Highly Potent 3-Substituted Indolephenstatins and Indoleisocombretastatins. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2813–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, A.; Parrino, B.; Vita, G.; Attanzio, A.; Spanò, V.; Montalbano, A.; Barraja, P.; Tesoriere, L.; Livrea, M.; Diana, P.; et al. Synthesis and Antiproliferative Activity of Thiazolyl-bis-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridines and Indolyl-thiazolyl-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridines, Nortopsentin Analogues. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 460–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, A.; Pennati, M.; Barraja, P.; Montalbano, A.; Parrino, B.; Spanò, V.; Lopergolo, A.; Sbarra, S.; Doldi, V.; Zaffaroni, N.; et al. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of substituted 3 [2-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1, 3-thiazol-4-yl]-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridines, marine alkaloid nortopsentin analogues. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 1654–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diana, P.; Carbone, A.; Barraja, P.; Montalbano, A.; Parrino, B.; Lopergolo, A.; Pennati, M.; Zaffaroni, N.; Cirrincione, G. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity of 3-(2-Phenyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-1H-indoles and 3-(2-Phenyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-1H-7-azaindoles. Chemmedchem 2011, 6, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppens, I.E. Current state of the art of new tubulin inhibitors in the clinic. Curr. Clin. Pharm. 2006, 1, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacher, G.; Beckers, T.; Emig, P.; Klenner, T.; Kutscher, B.; Nickel, B. New small-molecule tubulin inhibitors. Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 73, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaack, M.; Emig, P.; Bats, J.W.; Kiesel, M.; Müller, A.; Günther, E. Synthesis and Characterization of the Biologically Active 2-[1-(4-Chlorobenzyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]-2-oxo-N-pyridin-4-yl Acetamide. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 3843–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.J.; Borsenberger, V.; Louth, J.C.; Judd, K.E.; Chen, B. Design, Synthesis, and Structure-Activity Relationship of Indole-3-glyoxylamide Libraries Possessing Highly Potent Activity in a Cell Line Model of Prion Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7503–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takhi, M.; Singh, G.; Murugan, C.; Thaplyyal, N.; Maitra, S.; Bhaskarreddy, K.; Amarnath, P.; Mallik, A.; Harisudan, T.; Trivedi, R.K.; et al. Novel and potent oxazolidinone antibacterials featuring 3-indolylglyoxamide substituents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 5150–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Han, Y.-R.; Park, W.; Nam, S.-H.; Oh, K.-B.; Lee, H.-S. Synthetic analogs of indole-containing natural products as inhibitors of sortase A and isocitrate lyase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6882–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Bender, J.A.; Yang, Z.; Johnson, G.; Yang, Z.; Zadjura, L.M.; D’Arienzo, C.J.; Parker, D.D.; et al. Inhibitors of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) Attachment. 5. An Evolution from Indole to Azaindoles Leading to the Discovery of 1-(4-Benzoylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-(4,7-dimethoxy-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-3-yl) ethane-1, 2-dione (BMS-488043), a Drug Candidate That Demonstrates Antiviral Activity in HIV-1-Infected Subjects. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7778–7787. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taliani, S.; Trincavelli, M.L.; Cosimelli, B.; Laneri, S.; Severi, E.; Barresi, E.; Pugliesi, I.; Daniele, S.; Giacomelli, C.; Greco, G.; et al. Modulation of A 2B adenosine receptor by 1-Benzyl-3-ketoindole derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 69, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houlihan, W.J.; Parrino, V.A.; Uike, Y. Lithiation of N-(2-alkylphenyl)alkanamides and related compounds. A modified Madelung indole synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 4511–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.W.; Overmeyer, J.H.; Young, A.M.; Erhardt, P.W.; Maltese, W.A. Synthesis and Evaluation of Indole-Based Chalcones as Inducers of Methuosis, a Novel Type of Nonapoptotic Cell Death. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1940–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Brauer, C.; Thu, K.L.; Mason, J.M.; Blaser, H.; Bray, M.R.; Mak, T.W. Targeting Mitosis in Cancer: Emerging Strategies. Mol Cell. 2015, 60, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, B.A. How Taxol/paclitaxel kills cancer cells. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2014, 25, 2677–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M. Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malumbres, M. Physiological relevance of cell cycle kinases. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 973–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strebhardt, K. Multifaceted polo-like kinases: Drug targets and antitargets for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, M.D.; Weil, M.; Raff, M.C. Programmed cell death in animal development. Cell 1997, 88, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P. Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, J.F.; Winterford, C.M.; Harmon, B.V. Apoptosis. Its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer 1994, 73, 2013–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg-Lerner, A.; Bialik, S.; Simon, H.; Kimchi, A. Life and death partners: Apoptosis, autophagy and the cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finckenberg, P.; Eriksson, O.; Baumann, M.; Merasto, S.; Lalowski, M.M.; Levijoki, J.; Haasio, K.; Kytö, V.; Muller, D.N.; Luft, F.C.; et al. Caloric restriction ameliorates angiotensin II–induced mitochondrial remodeling and cardiac hypertrophy. Hypertension 2012, 59, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Abrams, J.; Alnemri, E.; Baehrecke, E.; Blagosklonny, M.; Dawson, T.; Dawson, V.; El-Deiry, W.; Fulda, S.; et al. Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; El-Deiry, W.S. Overview of cell death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oral, O.; Akkoc, Y.; Bayraktar, O.; Gozuacik, D. Physiological and pathological significance of the molecular cross-talk between autophagy and apoptosis. Histol. Histopathol. 2016, 31, 479–498. [Google Scholar]
- Green, D.R.; Llambi, F. Cell Death Signaling. Cold Spring Harbor Perspec. Biol. 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrik, I.; Golks, A.; Krammer, P.H. Death receptor signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Węsierska-Gądek, J.; Gueorguieva, M.; Wojciechowski, J.; Tudzarova-Trajkovska, S. In vivo activated caspase-3 cleaves PARP-1 in rat liver after administration of the hepatocarcinogen N-nitrosomorpholine (NNM) generating the 85 kDa fragment. J. Cell Biochem. 2004, 93, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.J.; Louth, J.C.; Ferrara, S.; Jackson, M.P.; Sorrell, F.J.; Cochrane, E.J.; Gever, J.; Baxendale, S.; Silber, B.M.; Roehl, H.H.; et al. Discovery of 6-substituted indole-3-glyoxylamides as lead antiprion agents with enhanced cell line activity, improved microsomal stability and low toxicity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4125–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of all compounds are available from the authors.





| Compound | Structure | MTT (IC50, μM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | Hela | MCF7 | HepG2 | |
| 5a |  | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 5b |  | 62.13 ± 3.45 | >100 | 56.46 ± 2.71 |
| 5c |  | 43.21 ± 1.67 | 46.12 ± 2.15 | 37.87 ± 0.87 |
| 5d |  | 42.14 ± 2.61 | 46.19 ± 1.34 | 35.67 ± 1.69 |
| 5e |  | >100 | >100 | 61.12 ± 2.54 |
| 5f |  | 17.65 ± 1.54 | 24.24 ± 1.09 | 20.89 ± 0.87 |
| 5g |  | 42.12 ± 1.94 | 40.67 ± 1.48 | 35.65 ± 1.02 |
| 5h |  | 41.21 ± 1.54 | 38.91 ± 1.04 | 25.69 ± 2.01 |
| 5i |  | 28.23 ± 1.16 | 26.11 ± 0.98 | 25.14 ± 0.61 |
| 5j |  | >100 | 29.25 ± 1.90 | 21.34 ± 0.98 |
| 5k |  | 45.61 ± 1.67 | 36.15 ± 1.23 | 36.75 ± 1.85 |
| 5l |  | 65.43 ± 1.15 | 68.21 ± 2.78 | 43.21 ± 1.45 |
| 5m |  | 85.34 ± 1.54 | 76.34 ± 1.25 | 57.17 ± 2.15 |
| 5n |  | 54.32 ± 1.15 | 41.24 ± 1.12 | 40.13 ± 2.54 |
| 5o |  | 35.13 ± 1.98 | 45.13 ± 2.32 | 43.12 ± 2.32 |
| 5p |  | 40.14 ± 1.56 | 37.45 ± 0.67 | 22.24 ± 1.68 |
| 5q |  | 36.56 ± 1.12 | 35.65 ± 1.41 | 38.65 ± 1.63 |
| 5r |  | 16.12 ± 1.54 | 12.54 ± 1.15 | 10.56 ± 1.14 |
| 5s |  | 34.35 ± 1.45 | 45.83 ± 2.41 | 35.67 ± 1.14 |
| 5t |  | 37.32 ± 1.78 | 49.32 ± 2.16 | 36.76 ± 0.79 |
| 5u |  | 47.32 ± 1.78 | 56.14 ± 2.38 | 42.15 ± 2.53 |
| 5v |  | 78.34 ± 0.56 | 56.34 ± 1.56 | 41.22 ± 2.19 |
| 5w |  | 32.15 ± 2.21 | 43.12 ± 2.10 | 46.14 ± 1.45 |
| 5x |  | 42.15 ± 2.23 | 53.12 ± 2.16 | 41.14 ± 1.92 |
| 5y |  | 31.47 ± 1.24 | 29.25 ± 1.90 | 21.34 ± 0.98 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, H.-Y.; Yu, X.-D.; Wang, F.; Lin, C.-R.; Zeng, J.-Z.; Qiu, Y.-K.; Fang, M.-J.; Wu, Z. Novel N-Substituted 2-(2-(Adamantan-1-yl)-1H-Indol-3-yl)-2-Oxoacetamide Derivatives: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Molecules 2016, 21, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050530
Hu H-Y, Yu X-D, Wang F, Lin C-R, Zeng J-Z, Qiu Y-K, Fang M-J, Wu Z. Novel N-Substituted 2-(2-(Adamantan-1-yl)-1H-Indol-3-yl)-2-Oxoacetamide Derivatives: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Molecules. 2016; 21(5):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050530
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Hong-Yu, Xu-Dong Yu, Fei Wang, Chun-Rong Lin, Jin-Zhang Zeng, Ying-Kun Qiu, Mei-Juan Fang, and Zhen Wu. 2016. "Novel N-Substituted 2-(2-(Adamantan-1-yl)-1H-Indol-3-yl)-2-Oxoacetamide Derivatives: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation" Molecules 21, no. 5: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050530
APA StyleHu, H. -Y., Yu, X. -D., Wang, F., Lin, C. -R., Zeng, J. -Z., Qiu, Y. -K., Fang, M. -J., & Wu, Z. (2016). Novel N-Substituted 2-(2-(Adamantan-1-yl)-1H-Indol-3-yl)-2-Oxoacetamide Derivatives: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Molecules, 21(5), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050530