Introducing Thermal Wave Transport Analysis (TWTA): A Thermal Technique for Dopamine Detection by Screen-Printed Electrodes Functionalized with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Batch Rebinding Experiments
2.2. Cyclic Voltammetry Measurements
2.3. Heat-Transfer Method (HTM) Measurements on Dopamine in Buffer Solutions with MIP-SPE
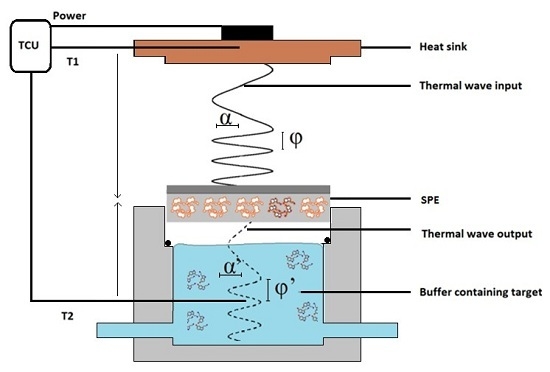
2.4. Thermal Wave Transport Analysis (TWTA) Measurements on Dopamine in Buffer Solutions with MIP-SPE
2.5. Thermal Wave Transport Analysis (TWTA) Measurements on Dopamine in Food Sample with MIP-SPE
3. Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of a MIP for Dopamine
3.3. Batch Dopamine Binding Experiments: Analysis by UV-vis
3.4. Preparation of MIP Bulk Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes (MIP-SPEs)
3.5. Cyclic Voltammetry Measurements of SPEs
3.6. Design of Set up for Thermal Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wulff, G. Enzyme-like catalysis by molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, K.; Mosbach, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in biomimetic sensors. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, J.; Nicholls, I.A.; Takeuchi, T.; Mosbach, K.; Karube, I. Molecularly-imprinted polymeric logic gates selective for predetermined chemical input species. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 10, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, A.; Bonini, F.; Turner, A.P.F.; Piletsky, S.A. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the recognition of proteins: The state of the art. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, K.; Karube, I. Molecularly imprinted polymers for biosensor applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 1999, 18, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Haupt, K. Moleclarly imprinted polymers as antibody and receptor mimics for assays, sensors and drug discovery. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietzryk, A.; Suriyanarayanan, S.; Kutner, W.; Maligaspe, E.; Zandler, M.E.; D’Souza, F. Molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) based piezoelectric microgravimetry chemosensor for selective determination of adenine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 80, 62–72. [Google Scholar]
- Maouche, N.; Ktari, N.; Bakas, I.; Fourati, N.; Zerrouki, C.; Seydou, M.; Maurel, F.; Chehimi, M.M. A surface acoustic wave sensor functionalized with a polypyrrole molecularly imprinted polymer for selective dopamine recognition. J. Mol. Recognit. 2015, 28, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, J.; Akamatsu, K.; Hara, N.; Miyoshi, D.; Nawafune, H.; Tamaki, K.; Sugimoto, N. SPR sensor chip for detection of small molecules using molecularly imprinted polymer with embedded gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 4282–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.; Csipai, P.; Geerets, B.; Weustenraed, A.; van Grinsven, B.; Gruber, J.; de Ceuninck, W.; Cleij, T.J.; Troost, F.J.; Wagner, P. Heat-transfer-based detection of l-nicotine, histamine, and serotonin using molecularly imprinted polymers as biomimetic receptors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 6453–6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Grinsven, B.; Vanden Bon, N.; Strauven, H.; Grieten, L.; Murib, M.; Jiménez-Monroy, K.L.; Janssens, S.D.; Haenen, K.; Schöning, M.J.; Vermeeren, V.; et al. Heat-transfer resistance at solid-liquid interfaces: A tool for the detection of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in DNA. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2712–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Grinsven, B.; Eersels, K.; Peeters, M.; Losada-Pérez, P.; Vandenryt, T.; Cleij, T.J.; Wagner, P. The heat-transfer method: A versatile low-cost, label-free, fast, and user-friendly readout platform for biosensor applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 13309–13318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bers, K.; Eersels, K.; van Grinsven, B.; Daemen, M.; Bogie, J.; Hendriks, J.; Bouwmans, E.; Püttmann, C.; Stein, C.; Barth, S.; et al. Heat-transfer resistance measurement method (HTM)-based cell detection at trace levels using progressive enrichment approach with highly selective cell-binding surface imprints. Langmuir 2014, 30, 3631–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.; Kobben, S.; Jiménez-Monroy, K.L.; Modesto, L.; Kraus, M.; Vandenryt, T.; Gaulke, A.; van Grinsven, B.; Ingebrandt, S.; Junkers, T.; et al. Thermal detection of histamine with a graphene oxide based molecularly imprinted polymer platform prepared by reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2014, 203, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoelen, R.; Vansweevelt, R.; Duchateau, J.; Horemans, F.; D’Haen, J.; Lutsen, L.; Vanderzande, D.; Ameloot, M.; vandeVen, M.; Cleij, T.J.; et al. A MIP-based impedimetric sensor for the detection of low-MW molecules. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 18, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honeychurch, K.C.; Hart, J.P. Screen-printed electrochemical sensors for monitoring metal pollutants. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2003, 7, 456–469. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, R.; Turner, A.P.F. Glucose oxidase: An ideal enzyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1992, 7, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metters, J.P.; Kadara, R.O.; Banks, C.E. New directions in screen printed electroanalytical sensors: An overview of recent developments. Analyst 2011, 136, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreescu, S.; Barthelmebs, L.; Marty, J.-L. Immobilization of acetylcholinesterase on screen-printed electrodes: Comparative study between three immobilization methods and applications to the detection of organophosphorus insecticides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 464, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croux, D.; Vangerven, T.; Broeders, J.; Boutsen, J.; Peeters, M.; Duchateau, S.; Cleij, T.J.; Deferme, W.; Wagner, P.; Thoelen, R.; et al. Molecular imprinted polymer films on RFID tags: A first step towards disposable packaging sensors. Phys. Status Solidi A 2013, 210, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, S.; Turner, A.P.F.; Mosbach, K.; Haupt, K. Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensor System for Herbicides Using Differential-Pulse Voltammetry on Screen-Printed Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 3698–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicer, C.; Gomez-Caballero, A.; Unceta, N.; Aranzazu Goicolea, M.; Barrio, R.J. Using a portable device based on a screen-printed sensor modified with a molecularly imprinted polymer for the determination of the insecticide fenitrothion in forest samples. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, D.; Yan, M.; Ge, S.; Ge, L.; Yu, J. A disposable simultaneous electrochemical sensor array based on a molecularly imprinted film at a NH2-graphene modified screen-printed electrode for determination of psychotropic drugs. Analyst 2013, 138, 2704–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, N.; Hart, J.P.; Bird, D.J.; Luxton, R.W.; McCalley, D.V. Towards the development of molecularly imprinted polymer based screen-printed sensors for metabolites of PAHs. Analyst 2001, 126, 1936–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lulínski, P.; Maciejewska, D.; Bamburowicz-Klimkowska, M.; Szutowski, M. Dopamine-imprinted polymers: Template-monomer interactions, analysis of template removal and application to solid phase extraction. Molecules 2007, 12, 2434–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suedee, R.; Seechamnanturakit, V.; Suksuwan, A.; Canyuk, B. Recognition properties and competitive asays of dual dopamine/serotonin selective molecularly imprinted polymer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 2333–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fienberg, A.A.; Hiroi, N.; Mermelstein, P.G.; Song, W.-J.; Snyder, G.L.; Nishi, A.; Cheramy, A.; O’Callaghan, J.P.; Miller, D.B.; Cole, D.G.; et al. DARPP-32: Regulator of the efficacy of dopaminergic neurotransmission. Science 1998, 281, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, K.L.; Kahn, R.S.; Ko, G.; Davidson, M. Dopamine in schizophrenia: A review and reconceptualization. Am. J. Psychiatry 1991, 148, 1474–1486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Javitt, D.C.; Zukin, S.R. Recent advances in the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 1991, 148, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wuyts, N.; Lognay, G.; Verscheure, M.; Marlier, M.; de Waele, D.; Swennen, R. Potential physical and chemical barriers to infection by the burrowing nematode Radopholus similis in roots of susceptible and resistant banana (Musa spp.). Plant Pathol. 2007, 56, 878–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liao, C.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Gong, F.; Yan, F. High-performance dopamine sensors based on whole graphene solution-gated transistors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpleby, R.J.; Baxter, S.C.; Rampey, A.M.; Rushton, G.T.; Chen, Y.Z.; Shimizu, K.D. Characterization of the heterogeneous binding site affinity distributions in molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2004, 804, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spivak, D.A. Optimization, evaluation, and characterization of molecularly imprinted polymers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1779–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randviir, E.P.; Brownson, D.A.C.; Metters, J.P.; Kadara, R.O.; Banks, C.E. The fabrication, characterization and electrochemical investigation of screen-printed graphene electrodes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 4598–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdino, F.E.; Foster, C.W.; Bonacin, J.A.; Banks, C.E. Exploring the electrical wiring of screen-printed configurations utilised in electroanalysis. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadara, R.O.; Jenkinson, N.; Banks, C.E. Screen printed recessed microelectrode arrays. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 2410–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, M.; Kadara, R.O.; Kampouris, D.K.; Banks, C.E. Electroanalytical sensing of nitrite at shallow recessed screen printed microelectrode arrays. Electroanalysis 2012, 22, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Grinsven, B.; Vandenryt, T.; Duchateau, S.; Gaulke, A.; Grieten, L.; Thoelen, R.; Ingebrandt, S.; de Ceuninck, W.; Wagner, P. Customized impedance spectroscopy device as possible sensor platform for biosensor applications. Phys. Status Solidi A 2010, 207, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.







| Detection Method | LOD Buffer Solutions (nM) | LOD Food Sample Spiked with Dopamine (nM) | Sample Preparation Time (min) | Sample Measurement Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclic voltammetry | 4700 ± 50 | - | 1 | 2 |
| Heat-transfer method (HTM) | 350 ± 30 | 500 ± 50 nM | 45 | 15–20 |
| Thermal wave transport analysis | 260 ± 35 | 150 ± 40 nM | 1 | 3–5 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peeters, M.M.; Van Grinsven, B.; Foster, C.W.; Cleij, T.J.; Banks, C.E. Introducing Thermal Wave Transport Analysis (TWTA): A Thermal Technique for Dopamine Detection by Screen-Printed Electrodes Functionalized with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Particles. Molecules 2016, 21, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050552
Peeters MM, Van Grinsven B, Foster CW, Cleij TJ, Banks CE. Introducing Thermal Wave Transport Analysis (TWTA): A Thermal Technique for Dopamine Detection by Screen-Printed Electrodes Functionalized with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Particles. Molecules. 2016; 21(5):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050552
Chicago/Turabian StylePeeters, Marloes M., Bart Van Grinsven, Christopher W. Foster, Thomas J. Cleij, and Craig E. Banks. 2016. "Introducing Thermal Wave Transport Analysis (TWTA): A Thermal Technique for Dopamine Detection by Screen-Printed Electrodes Functionalized with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Particles" Molecules 21, no. 5: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050552
APA StylePeeters, M. M., Van Grinsven, B., Foster, C. W., Cleij, T. J., & Banks, C. E. (2016). Introducing Thermal Wave Transport Analysis (TWTA): A Thermal Technique for Dopamine Detection by Screen-Printed Electrodes Functionalized with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Particles. Molecules, 21(5), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050552