Production and Anti-Melanoma Activity of Methoxyisoflavones from the Biotransformation of Genistein by Two Recombinant Escherichia coli Strains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
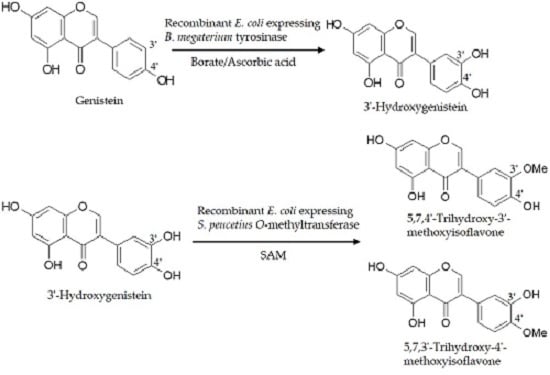
2.1. Biotransformation of Genistein by the Two Recombinant E. coli Strains and Purification and Identification of the Biotransformation Products
2.2. Anti-Melanoma Activity of the Biotransformation Products
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microorganisms, Animal Cells, and Chemicals
4.2. Preparation of Biocatalyst
4.3. Biotransformation of Both Hydroxylation and Methylation
4.4. UPLC Analysis
4.5. Purification and Identification of Biotransformation Products
4.6. Determination of Cell Viability
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franke, A.A.; Custer, L.J.; Cerna, C.M.; Narala, K.K. Quantitation of phytoestrogens in legumes by HPLC. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, M. A brief historical overview of the past two decades of soy and isoflavone research. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1350S–1354S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, D.C.; Piazza, C.; Melilli, B.; Drago, F.; Salomone, S. Isoflavones: Estrogenic activity, biological effect and bioavailability. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 38, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-S. Isolation, bioactivity, and production of ortho-hydroxydaidzein and ortho-hydroxygenistein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5699–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spohner, S.C.; Muller, H.; Quitmann, H.; Czermak, P. Expression of enzymes for the usage in food and feed industry with Pichia pastoris. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 202, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Baek, K.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, B.G. Using tyrosinase as a monophenol monooxygenase: A combined strategy for effective inhibition of melanin formation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.-M.; Wang, D.-S.; Chang, T.-S. Improving free radical scavenging activity of soy isoflavone glycosides daidzin and genistin by 3′-hydroxylation using recombinant Escherichia coli. Molecules 2016, 21, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.-M.; Ding, H.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Chang, T.-S. Production of two novel methoxy-isoflavones from biotransformation of 8-hydroxydaidzein by recombinant Escherichia coli expressing O-methyltransferase SpOMT2884 from Streptomyces peucetius. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 27816–27823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosny, M.; Rosazza, P.N. Microbial hydroxylation and methylation of genistein by Streptomycetes. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, J.G.L.; Silveira, E.R.; Pessoa, O.D.L. NMR spectral assignments of a new [C–O–C] isoflavone dimer from Andira surinamensis. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2008, 46, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.S. An updated review of tyrosinase inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 2440–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.S. Natural melanogenesis inhibitors acting through the down-regulation of tyrosinase activity. Materials 2012, 5, 1661–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.Y.; Chiang, C.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Chang, T.S. Identification of 3′-hydroxygenistein as a potent melanogenesis inhibitor from biotransformation of genistein by recombinant Pichia pastoris. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 1614–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Morikawa, T.; Xu, F.; Ninomiya, K.; Yoshikawa, M. New isoflavones and pterocarpane with hepatoprotective activity from the stems of Erycibe expansa. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Record, I.R.; Broadbent, J.L.; King, R.A.; Dreosti, I.E.; Head, R.J.; Tonkin, A.L. Genistein inhibits growth of B16 melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro and promotes differentiation in vitro. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 72, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, L.P.; Yu, X.Y.; Zhang, R.Q. Effects of genistein and daidzein on the cell growth, cell cycle, and differentiation of human and murine melanoma cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnuolo, C.; Russo, G.L.; Orhan, I.E.; Habtemariam, S.; Daglia, M.; Sureda, A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Devi, K.P.; Loizzo, M.R.; Tundis, R.; et al. Genistein and cancer: Current status, challenges, and future directions. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walle, T. Methylation of dietary flavones increases their metabolic stability and chemopreventive effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 5002–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernini, R.; Crisante, F.; Ginnasi, M.C. A convenient and safe O-methylation of flavonoids with dimethyl carbonate (DMC). Molecules 2011, 16, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koirala, N.; Pandey, R.P.; Parajuli, P.; Jung, H.J.; Sohng, J.K. Methylation and subsequent glycosylation of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 184, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 5,7,4′-trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone and 5,7,3′-trihydroxy-4′-methoxyisoflavone are available from the authors.


| Cells | Melanoma | Fibroblast | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isoflavone | Genistein | 1 | 2 | Genistein | 1 | 2 |
| Control | 100 ± 3.21 | 100 ± 4.48 | 100 ± 6.64 | 100 ± 4.12 | 100 ± 3.41 | 100 ± 0.22 |
| 11 μM | 102.41 ± 4.52 | 99.15 ± 7.42 | 92.67 ± 2.27 | 97.81 ± 4.67 | 103.68 ± 3.57 | 102.42 ± 4.97 |
| 22 μM | 77.55 ± 3.55 * | 80.77 ± 4.53 * | 83.57 ± 4.43 * | 102.33 ± 3.76 | 102.09 ± 3.86 | 99.28 ± 0.42 |
| 44 μM | 55.28 ± 2.99 * | 57.9 ± 5.18 * | 82.79 ± 3.39 * | 98.91 ± 3.41 | 94.69 ± 3.71 | 93.58 ± 2.43 * |
| 88 μM | 44.41 ± 1.92 * | 40.38 ± 1.69 * | 81.72 ± 2.78 * | 96.7 ± 2.89 | 97.69 ± 2.28 | 89.77 ± 1.18 * |
| 175 μM | 41.72 ± 3.11 * | 32.05 ± 0.9 * | 74.19 ± 0.29 * | 92.11 ± 3.12 | 102.09 ± 3.86 | 84.26 ± 1.16 * |
| 350 μM | 39.81 ± 1.91 * | 33.54 ± 2.89 * | 53.86 ± 3.00 * | 85.77 ± 1.98 * | 89.21 ± 4.99 | 71.70 ± 1.00 * |
| IC50 2 (μM) | 70.3 | 68.1 | 420.3 | N.D. 3 | N.D. | N.D. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiang, C.-M.; Chang, Y.-J.; Wu, J.-Y.; Chang, T.-S. Production and Anti-Melanoma Activity of Methoxyisoflavones from the Biotransformation of Genistein by Two Recombinant Escherichia coli Strains. Molecules 2017, 22, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010087
Chiang C-M, Chang Y-J, Wu J-Y, Chang T-S. Production and Anti-Melanoma Activity of Methoxyisoflavones from the Biotransformation of Genistein by Two Recombinant Escherichia coli Strains. Molecules. 2017; 22(1):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010087
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiang, Chien-Min, Yu-Jhe Chang, Jiumn-Yih Wu, and Te-Sheng Chang. 2017. "Production and Anti-Melanoma Activity of Methoxyisoflavones from the Biotransformation of Genistein by Two Recombinant Escherichia coli Strains" Molecules 22, no. 1: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010087
APA StyleChiang, C. -M., Chang, Y. -J., Wu, J. -Y., & Chang, T. -S. (2017). Production and Anti-Melanoma Activity of Methoxyisoflavones from the Biotransformation of Genistein by Two Recombinant Escherichia coli Strains. Molecules, 22(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010087