Desorption of Lipases Immobilized on Octyl-Agarose Beads and Coated with Ionic Polymers after Thermal Inactivation. Stronger Adsorption of Polymers/Unfolded Protein Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
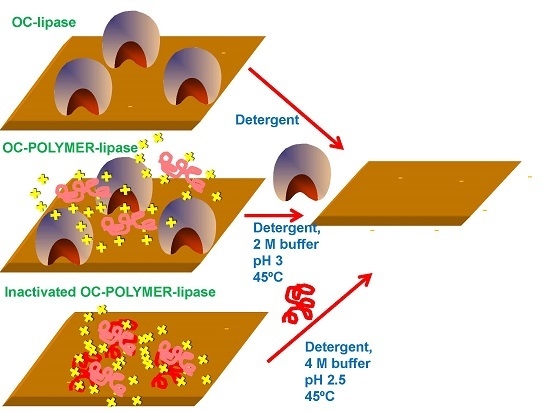
2.1. Recovery of Octyl-Agarose from OC-CALB and OC-RML Preparations
2.2. Recovery of Octyl-Agarose from OC-CALB-PEI-DS and OC-RML-PEI-DS Preparations
2.3. Reuse of Octyl-Agarose to Immobilize Lipase
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Assay of Lipase Activity
3.3. Immobilization of Lipases on Octyl-Agarose
3.4. Preparation of Coated Lipase-Octyl-Agarose Derivatives
3.5. Thermal Inactivation of Coated Lipase-Octyl-Agarose Derivatives
3.6. Enzyme Desorption from Octyl-Agarose Support
3.7. Electrophoretic Analysis
3.8. Determination of the Residual Content of Polyethylenimine from Coated Lipase Derivatives
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheldon, R.A.; van Pelt, S. Enzyme immobilisation in biocatalysis: Why, what and how. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6223–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, C.; Palomo, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Improvement of enzyme activity, stability and selectivity via immobilization techniques. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, P.V.; Ananthanarayan, L. Enzyme stability and stabilization—Aqueous and non-aqueous environment. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Torres, R.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Modifying enzyme activity and selectivity by immobilization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6290–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, D.; Jordaan, J. Advances in enzyme immobilization. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adlercreutz, P. Immobilisation and application of lipases in organic media. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6406–6436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, K.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Control of protein immobilization: Coupling immobilization and site-directed mutagenesis to improve biocatalyst or biosensor performance. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2011, 48, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, E.T.; Gu, M.B. Enzyme stabilization by nano/microsized hybrid materials. Eng. Life Sci. 2013, 13, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiCosimo, R.; McAuliffe, J.; Poulose, A.J.; Bohlmann, G. Industrial use of immobilized enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6437–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantone, S.; Ferrario, V.; Corici, L.; Ebert, C.; Fattor, D.; Spizzo, P.; Gardossi, L. Efficient immobilisation of industrial biocatalysts: Criteria and constraints for the selection of organic polymeric carriers and immobilisation methods. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6262–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guzik, U.; Hupert-Kocurek, K.; Wojcieszyńska, D. Immobilization as a strategy for improving enzyme properties—Application to oxidoreductases. Molecules 2014, 19, 8995–9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liese, A.; Hilterhaus, L. Evaluation of immobilized enzymes for industrial applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6236–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.; Yoo, Y.J. Recent progress in nanobiocatalysis for enzyme immobilization and its application. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2014, 19, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, O.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Torres, R.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Strategies for the one-step immobilization—Purification of enzymes as industrial biocatalysts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 435–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcão, V.M.; Vila, M.M.D.C. Structural and functional stabilization of protein entities: State-of-the-art. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 93, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Galan, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Rodrigues, R.C. Potential of different enzyme immobilization strategies to improve enzyme performance. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 2885–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.C.S.D.; Barbosa, O.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Importance of the support properties for immobilization or purification of enzymes. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 2413–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Stabilization of multimeric enzymes: Strategies to prevent subunit dissociation. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2009, 45, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Mateo, C.; Fuentes, M.; Palomo, J.M.; Ortiz, C.; Fernández-Lafuente, R.; Guisan, J.M. Reversible immobilization of invertase on sepabeads coated with polyethyleneimine: Optimization of the biocatalyst’s stability. Biotechnol. Prog. 2002, 18, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, J.C.S.; Rueda, N.; Sanchez, A.; Villalonga, R.; Goncalves, L.R.B.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Versatility of divinylsulfone supports permits the tuning of CALB properties during its immobilization. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 35801–35810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, J.C.S.; Rueda, N.; Torres, R.; Barbosa, O.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Evaluation of divinylsulfone activated agarose to immobilize lipases and to tune their catalytic properties. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoel, E.A.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; Freire, D.M.G.; Rueda, N.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Immobilization of lipases on hydrophobic supports involves the open form of the enzyme. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2015, 71, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, K.-E.; Dijkstra, B.W.; Reetz, M.T. Bacterial biocatalysts: Molecular biology, three-dimensional structures, and biotechnological applications of lipases. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 1999, 53, 315–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzozowski, A.M.; Derewenda, U.; Derewenda, Z.S.; Dodson, G.G.; Lawson, D.M.; Turkenburg, J.P.; Bjorkling, F.; Huge-Jensen, B.; Patkar, S.A.; Thim, L. A model for interfacial activation in lipases from the structure of a fungal lipase-inhibitor complex. Nature 1991, 351, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochulski, P.; Li, Y.; Schrag, J.D.; Bouthillier, F.; Smith, P.; Harrison, D.; Rubin, B.; Cygler, M. Insights into interfacial activation from an open structure of Candida rugosa lipase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 12843–12847. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.K.; Song, H.K.; Shin, D.H.; Hwang, K.Y.; Suh, S.W. The crystal structure of a triacylglycerol lipase from Pseudomonas cepacia reveals a highly open conformation in the absence of a bound inhibitor. Structure 1997, 5, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derewenda, Z.S.; Derewenda, U.G.; Dodson, G. The crystal and molecular structure of the Rhizomucor miehei triacylglyceride lipase at 1.9 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 227, 818–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verger, R. ‘Interfacial activation’ of lipases: Facts and artifacts. Trends Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelle, M.; Holmquist, M.; Hult, K. On the interfacial activation of Candida antarctica lipase A and B as compared with Humicola lanuginosa lipase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Lipids Lipid Metab. 1995, 1258, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, A.M.; Savage, H.; Verma, C.S.; Turkenburg, J.P.; Lawson, D.M.; Svendsen, A.; Patkar, S. Structural origins of the interfacial activation in Thermomyces (Humicola) lanuginosa lipase. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 15071–15082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, O.G.; Cajal, Y.; Butterfoss, G.L.; Grey, R.L.; Alsina, M.A.; Yu, B.-Z.; Jain, M.K. Interfacial activation of triglyceride lipase from Thermomyces (Humicola) lanuginosa: Kinetic parameters and a basis for control of the lid. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 6615–6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, R.D.; Verger, R. Lipases: Interfacial enzymes with attractive applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 1608–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.; Holmberg, K.; Watzke, H.; Leser, M.E.; Miller, R. Lipases at interfaces: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147–148, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastida, A.; Sabuquillo, P.; Armisen, P.; Fernández-Lafuente, R.; Huguet, J.; Guisán, J.M. A single step purification, immobilization, and hyperactivation of lipases via interfacial adsorption on strongly hydrophobic supports. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1998, 58, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Armisén, P.; Sabuquillo, P.; Fernández-Lorente, G.; Guisán, J.M. Immobilization of lipases by selective adsorption on hydrophobic supports. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1998, 93, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, G.H.; Olsen, O.H.; Svendsen, A.; Wade, R.C. Theoretical investigation of the dynamics of the active site lid in Rhizomucor miehei lipase. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Production, purification, characterization, and applications of lipases. Biotechnol. Adv. 2001, 19, 627–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, K.-E.; Eggert, T. Lipases for biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, K.-E.; Reetz, M.T. Microbial lipases form versatile tools for biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reetz, M.T. Lipases as practical biocatalysts. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2002, 6, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, N.; dos Santos, J.C.S.; Torres, R.; Ortiz, C.; Barbosa, O.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Improved performance of lipases immobilized on heterofunctional octyl-glyoxyl agarose beads. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 11212–11222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgen-Ortíz, J.; Tacias-Pascacio, V.G.; Hirata, D.B.; Torrestiana-Sanchez, B.; Rosales-Quintero, A.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Relevance of substrates and products on the desorption of lipases physically adsorbed on hydrophobic supports. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2017, 96, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peirce, S.; Tacias-Pascacio, V.; Russo, M.; Marzocchella, A.; Virgen-Ortíz, J.J.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Stabilization of Candida antarctica lipase B (CALB) immobilized on octyl agarose by treatment with polyethyleneimine (PEI). Molecules 2016, 21, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Lopez, L.; Virgen-Ortíz, J.J.; Pedrero, S.G.; Lopez-Carrobles, N.; Gorines, B.C.; Otero, C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Optimization of the coating of octyl-CALB with ionic polymers to improve stability and decrease enzyme leakage. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Lopez, L.; Pedrero, S.G.; Lopez-Carrobles, N.; Virgen-Ortíz, J.J.; Gorines, B.C.; Otero, C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Physical crosslinking of RML immobilized on octyl agarose via coating with ionic polymers. Avoiding enzyme release from the support. Process Biochem. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Virgen-Ortíz, J.J.; Peirce, S.; Tacias-Pascacio, V.G.; Cortes-Corberan, V.; Marzocchella, A.; Russo, M.E.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Reuse of anion exchangers as supports for enzyme immobilization: Reinforcement of the enzyme-support multiinteraction after enzyme inactivation. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirce, S.; Virgen-Ortiz, J.J.; Tacias-Pascacio, V.G.; Rueda, N.; Bartolome-Cabrero, R.; Fernandez-Lopez, L.; Russo, M.E.; Marzocchella, A.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Development of simple protocols to solve the problems of enzyme coimmobilization. Application to coimmobilize a lipase and a β-galactosidase. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 61707–61715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacias-Pascacio, V.G.; Peirce, S.; Torrestiana-Sanchez, B.; Yates, M.; Rosales-Quintero, A.; Virgen-Ortiz, J.J.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Evaluation of different commercial hydrophobic supports for the immobilization of lipases: Tuning their stability, activity and specificity. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 100281–100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, R. The rapid determination of amino groups with TNBS. Meth. Enzymol. 1972, 32, 464–468. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, X. Immobilization and Characterization of a Thermostable Lipase. Mar. Biotechnol. 2013, 15, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, M.L.; Puri, M.; Barrow, C.J. Recent trends in nanomaterials immobilised enzymes for biofuel production. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipolatti, E.P.; Valério, A.; Henriques, R.O.; Moritz, D.E.; Ninow, J.L.; Freire, D.M.G.; Manoel, E.A.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; de Oliveira, D. Nanomaterials for biocatalyst immobilization-state of the art and future trends. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 104675–104692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdarta, J.; Wysokowski, M.; Norman, M.; Kołodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Moszyński, D.; Maciejewski, H.; Ehrlich, H.; Jesionowski, T. Candida antarctica lipase B immobilized onto chitin conjugated with POSS® compounds: Useful tool for rapeseed oil conversion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomo, J.M.; Ortiz, C.; Fuentes, M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Use of immobilized lipases for lipase purification via specific lipase-lipase interactions. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1038, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomo, J.M.; Ortiz, C.; Fernández-Lorente, G.; Fuentes, M.; Guisán, J.M.; Fernández-Lafuente, R. Lipase-lipase interactions as a new tool to immobilize and modulate the lipase properties. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2005, 36, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansorge-Schumacher, M.B.; Thum, O. Immobilised lipases in the cosmetics industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6475–6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; van Langen, L.; Sheldon, R.A. Immobilised enzymes: Carrier-bound or carrier-free? Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesionowski, T.; Zdarta, J.; Krajewska, B. Enzyme immobilization by adsorption: A review. Adsorption 2014, 20, 801–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: No samples are available from the authors.






| Treatment | OC-CALB-PEI-DS (Without Inactivation) | OC-CALB-PEI-DS (Inactivated) | OC-RML-PEI-DS (Without Inactivation) | OC-RML-PEI-DS (Inactivated) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without treatment | 0.86 ± 0.09 | 0.58 ± 0.09 | 0.75 ± 0.07 | 0.50 ± 0.06 |
| 2% SDS (pH 7, 25 °C) | 0.56 ± 0.07 | 0.51 ± 0.08 | 0.42 ± 0.08 | 0.45 ± 0.06 |
| 2% SDS in 2 M sodium phosphate (pH 7, 25 °C) | 0.39 ± 0.05 | 0.45 ± 0.09 | 0.29 ± 0.05 | 0.38 ± 0.07 |
| 2% SDS in 2 M sodium phosphate (pH 3, 25 °C) | 0.25 ± 0.06 | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.25 ± 0.05 |
| 2% SDS in 2 M sodium phosphate (pH 3, 45 °C) | 0 | 0.12 ± 0.04 | 0 | 0.16 ± 0.03 |
| 2% SDS in 4 M sodium phosphate (pH 2.5, 45 °C) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Virgen-Ortíz, J.J.; Pedrero, S.G.; Fernandez-Lopez, L.; Lopez-Carrobles, N.; Gorines, B.C.; Otero, C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Desorption of Lipases Immobilized on Octyl-Agarose Beads and Coated with Ionic Polymers after Thermal Inactivation. Stronger Adsorption of Polymers/Unfolded Protein Composites. Molecules 2017, 22, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010091
Virgen-Ortíz JJ, Pedrero SG, Fernandez-Lopez L, Lopez-Carrobles N, Gorines BC, Otero C, Fernandez-Lafuente R. Desorption of Lipases Immobilized on Octyl-Agarose Beads and Coated with Ionic Polymers after Thermal Inactivation. Stronger Adsorption of Polymers/Unfolded Protein Composites. Molecules. 2017; 22(1):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010091
Chicago/Turabian StyleVirgen-Ortíz, Jose J., Sara G. Pedrero, Laura Fernandez-Lopez, Nerea Lopez-Carrobles, Beatriz C. Gorines, Cristina Otero, and Roberto Fernandez-Lafuente. 2017. "Desorption of Lipases Immobilized on Octyl-Agarose Beads and Coated with Ionic Polymers after Thermal Inactivation. Stronger Adsorption of Polymers/Unfolded Protein Composites" Molecules 22, no. 1: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010091
APA StyleVirgen-Ortíz, J. J., Pedrero, S. G., Fernandez-Lopez, L., Lopez-Carrobles, N., Gorines, B. C., Otero, C., & Fernandez-Lafuente, R. (2017). Desorption of Lipases Immobilized on Octyl-Agarose Beads and Coated with Ionic Polymers after Thermal Inactivation. Stronger Adsorption of Polymers/Unfolded Protein Composites. Molecules, 22(1), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010091