Phaseolus acutifolius Lectin Fractions Exhibit Apoptotic Effects on Colon Cancer: Preclinical Studies Using Dimethilhydrazine or Azoxi-Methane as Cancer Induction Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
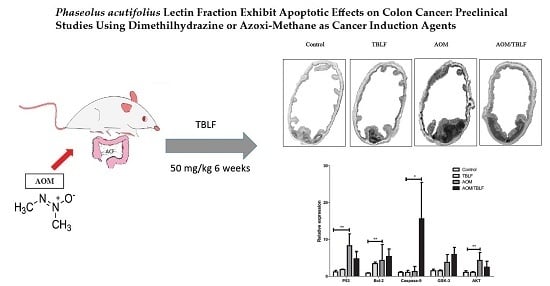
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Tepary Bean Lectin Fraction (TBLF) Extraction
3.2. Confirmation of the Cytotoxic Role of Lectins in the TBLF
3.3. Experimental Animals and Cancer Induction
3.4. Histopathology Analyses
3.5. Immunohistochemical Analyses for Proliferation and Apoptosis
3.6. Gene Expression Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breitenbach Barroso Coelho, L.; Marcelino dos Santos Silva, P.; de Menezes Lima, V.L.; Viana Pontual, E.; Guedes Paiva, P.M.; Napoleao, T.H.; dos Santos Correia, M.T. Lectins, interconnecting proteins with biotechnological/pharmacological and therapeutic applications. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. 2017, 2017, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Damme, E.J.M. History of plant lectin research. In Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.); Hirabayashi, J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1200, pp. 3–13. ISBN 9781493912919. [Google Scholar]
- Timoshenko, A.V.; Gorudko, I.V.; Gabius, H.-J. Lectins from Medicinal Plants: Bioeffectors with Diverse Activities. In Phytochemicals. Biosyntehsis, Function and Application; Jetter, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 43–57. ISBN 978-3-319-04044-8. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Zhou, C.; Yao, S.; Yu, J.; Liu, B.; Bao, J. Plant lectins: Targeting programmed cell death pathways as antitumor agents. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 1442–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, J. Lectin-based Glycomics: How and When Was the Tecnology Born. In Lectins Methods and Protocols; Hirabayashi, J., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1200, pp. 225–242. ISBN 978-1-4939-1291-9. [Google Scholar]
- Duranti, M.; Gius, C. Legume seeds: Protein content and nutritional value. Field Crop. Res. 1997, 53, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González De Mejía, E.; Prisecaru, V.I. Lectins as bioactive plant proteins: A potential in cancer treatment. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.-Y.; Hong, C.-E.; Kim, H.-G.; Lyu, S.-Y. Anti-cancer effects of enteric-coated polymers containing mistletoe lectin in murine melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 408, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagarda-Diaz, I.; Guzman-Partida, A.M.; Vazquez-Moreno, L. Legume lectins: Proteins with diverse applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fardini, Y.; Dehennaut, V.; Lefebvre, T.; Issad, T. O-GlcNAcylation: A new cancer hallmark? Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2013, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, M.N.; Chik, J.; Lee, L.; Anugraham, M.; Abrahams, J.L.; Packer, N.H. Cell surface protein glycosylation in cancer. Proteomics 2014, 14, 525–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakomori, S. Tumor Malignancy Defined by Aberrant Glycosylation and Sphingo (glyco) lipid Metabolism. Cancer Res. 1996, 5309–5318. [Google Scholar]
- Holst, S.; Wuhrer, M.; Rombouts, Y. Glycosylation characteristics of colorectal cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2015, 126, 203–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.L.; Zhang, S.; Tian, M.; Zhang, S.Y.; Xie, T.; Chen, D.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; He, J.; Liu, J.; Ouyang, L.; et al. Plant lectins, from ancient sugar-binding proteins to emerging anti-cancer drugs in apoptosis and autophagy. Cell Prolif. 2015, 48, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepa, M.; Sureshkumar, T.; Satheeshkumar, P.K.; Priya, S. Purified mulberry leaf lectin (MLL) induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer and colon cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2012, 200, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadez-Vega, C.; Morales-González, J.A.; Sumaya-Martínez, M.T.; Delgado-Olivares, L.; Cruz-Castañeda, A.; Bautista, M.; Sánchez-Gutiérrez, M.; Zuñiga-Pérez, C. Cytotoxic and antiproliferative effect of tepary bean lectins on C33-A, MCF-7, SKNSH, and SW480 cell lines. Molecules 2014, 19, 9610–9627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Gasca, T.; García-Cruz, M.; Hernandez-Rivera, E.; López-Matínez, J.; Castañeda-Cuevas, A.L.; Yllescas-Gasca, L.; Rodríguez-Méndez, A.J.; Mendiola-Olaya, E.; Castro-Guillén, J.L.; Blanco-Labra, A. Effects of Tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) protease inhibitor and semipure lectin fractions on cancer cells. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, R.; Zhang, S.; Tian, M.; Xie, T.; Liu, B.; He, G. Polygonatum odoratum lectin induces apoptosis and autophagy via targeting EGFR-mediated Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Lyu, S.Y.; Park, W.B. Mistletoe lectin induces apoptosis and telomerase inhibition in human A253 cancer cells through dephosphorylation of Akt. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Ji, N.; Zhou, J.; Bian, H.J.; Li, C.Y.; Chen, F.; Bao, J.K. A novel sialic acid-specific lectin from Phaseolus coccineus seeds with potent antineoplastic and antifungal activities. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Wu, J.M.; Li, J.; Liu, J.J.; Li, W.W.; Li, C.Y.; Xu, H.L.; Bao, J.K. Polygonatum cyrtonema lectin induces murine fibrosarcoma L929 cell apoptosis and autophagy via blocking Ras-Raf and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways. Biochimie 2010, 92, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostanska, K.; Vuong, V.; Rocha, S.; Soengas, M.S.; Glanzmann, C.; Saller, R.; Bodis, S.; Pruschy, M. Recombinant mistletoe lectin induces p53-independent apoptosis in tumour cells and cooperates with ionising radiation. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 1785–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadez-Vega, C.; Guzmán-Partida, A.M.; Soto-Cordova, F.J.; Alvarez-Manilla, G.; Morales-González, J.A.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.; Villagómez-Ibarra, J.R.; Zúñiga-Pérez, C.; Gutiérrez-Salinas, J.; Becerril-Flores, M. A Purification, biochemical characterization, and bioactive properties of a lectin purified from the seeds of white tepary bean (phaseolus acutifolius variety latifolius). Molecules 2011, 16, 2561–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynoso-Camacho, R.; González De Mejía, E.; Loarca-Piña, G. Purification and acute toxicity of a lectin extracted from tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriz-Martínez, R.; García-García, K.; Torres-Arteaga, I.; Rodriguez-Mendez, A.J.; de Jesús Guerrero-Carrillo, M.; Moreno-Celis, U.; Ángeles-Zaragoza, M.V.; Blanco-Labra, A.; Gallegos-Corona, M.A.; Robles-Álvarez, J.P.; et al. Tolerability assessment of a lectin fraction from Tepary bean seeds (Phaseolus acutifolius) orally administered to rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres Arteaga, I.; Castro Guillen, J.L. Characterization of Two Non-Fetuin-Binding Lectins from Tepary Bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) Seeds with Differential Cytotoxicity on Colon Cancer Cells. J. Glycobiol. 2016, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, M.; Ravula, S.; Tatishchev, S.F.; Wang, H.L. Colorectal carcinoma: Pathologic aspects. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2012, 3, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saini, H. Legume seed oligosaccharides. In Recent Advances of Research in Antinutritional Factors in Legume Seeds; Van Der Poel, T.F.B., Huisman, J., Lienr, I.E., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 329–341. [Google Scholar]
- Campion, B.; Perrone, D.; Galasso, I.; Bollini, R. Common bean ( Phaseolus vulgaris L.) lines devoid of major lectin proteins. Plant Breed. 2009, 128, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-da-Silva, G.; Carvalho, C.F.; Roque-Barreira, M.C. Neutrophil Activation Induced by Plant Lectins: Modulation of Inflammatory Processes. Inflamm. Allergy - Drug Targets 2012, 11, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daprà, F.; Gai, F.; Palmegiano, G.B.; Prearo, M.; Sicuro, B. Histological and physiological changes induced by Red Kidney Bean lectins in the digestive system of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). Ittiopatologia 2005, 2, 241–258. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; An, N.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Huang, K.; Bao, J. Antitumor effects of concanavalin A and Sophora flavescens lectin in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, Y.; Sugahara, T.; Ueno, M.; Fukuta, Y.; Ochi, Y.; Akiyama, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Masuda, S.; Kawakubo, A.; Kato, K. The anti-tumor effect of Euchema serra agglutinin on colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Anticancer Drugs 2006, 17, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, T.; Burbage, C.; Tagge, E.P.; Brothers, T.; Willingham, M.C.; Frankel, A.E. Ricin toxin contains three lectin sites which contribute to its in vivo toxicity. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1996, 18, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Bian, H.; Bao, J. Plant lectins: potential antineoplastic drugs from bench to clinic. Cancer Lett. 2010, 287, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorelik, E.; Galili, U.; Raz, A. On the role of cell surface carbohydrates and their binding proteins (lectins) in tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2001, 20, 245–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.Q.; Lindsley, C.W.; Cheng, G.Z.; Yang, H.; Nicosia, S.V. The Akt/PKB pathway: Molecular target for cancer drug discovery. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7482–7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, H.K.; Olusola, B.F.; Clemens, D.L.; Karolski, W.J.; Ratashak, A.; Lynch, H.T.; Smyrk, T.C. AKT proto-oncogene overexpression is an early event during sporadic colon carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollereau, B.; Ma, D. The p53 control of apoptosis and proliferation: Lessons from Drosophila. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jope, R.S.; Johnson, G.V.W. The glamour and gloom of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Wakabayashi, K. Gene mutations and altered gene expression in azoxymethane-induced colon carcinogenesis in. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Yang, W.; Koeffler, H.P. Mouse models of colorectal cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2011, 30, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, D.W.; Giardina, C.; Tanaka, T. Mouse models for the study of colon carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Panda, P.K.; Das, D.N.; Sinha, N.; Behera, B.; Maiti, T.K.; Bhutia, S.K. Abrus agglutinin suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo by inducing caspase-mediated cell death. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentin-Vega, Y.A.; Okano, H.; Lozano, G. The intestinal epithelium compensates for p53-mediated cell death and guarantees organismal survival. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Li, F.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Shi, W.; Liu, F.-F.; O’Sullivan, B.; He, Z.; Peng, Y.; Tan, A.-C.; et al. Caspase 3-mediated stimulation of tumor cell repopulation during cancer radiotherapy. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.H.; Yan, Q.J.; Kopparapu, N.K.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Sun, Y. Astragalus membranaceus lectin (AML) induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in human leukemia cells. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khil, L.-Y.; Kim, W.; Lyu, S.; Park, W.-B.; Yoon, J.-W.; Jun, H.-S. Mechanisms involved in Korean mistletoe lectin-induced apoptosis of cancer cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 2811–2818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lyu, S.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Park, W.B. Korean mistletoe lectin-induced apoptosis in hepatocarcinoma cells is associated with inhibition of telomerasevia mitochondrial controlled pathway independent of p53. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2002, 25, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, J.E.; Martinez-Gallardo, N.; Mendiola-Olaya, E.; Blanco-Labra, A. Purification and partial characterization of a proteinase inhibitor from tepary bean (phaseolus acutifolius) seeds. J. Food Biochem. 1997, 21, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffé, W.G.; Levy, A.; González, D.I. Isolation and partial characterization of bean phytohemagglutinins. Phytochemistry 1974, 13, 2685–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Armenta, E.; Téllez-Medina, D.I.; Alamilla-Beltrán, L.; Arana-Errasquín, R.; Hernández-Sánchez, H.; Gutiérrez-López, G.F. Multifractal breakage patterns of thick maltodextrin agglomerates. Powder Technol. 2014, 266, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, G.R.; Ferreira, S.C.; Ferreira, J.E.; Siqueira, S.A.C.; Pereira, J. Comparison of two methods of RNA extraction from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue specimens. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not available. |










© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreno-Celis, U.; López-Martínez, J.; Blanco-Labra, A.; Cervantes-Jiménez, R.; Estrada-Martínez, L.E.; García-Pascalin, A.E.; Guerrero-Carrillo, M.D.J.; Rodríguez-Méndez, A.J.; Mejía, C.; Ferríz-Martínez, R.A.; et al. Phaseolus acutifolius Lectin Fractions Exhibit Apoptotic Effects on Colon Cancer: Preclinical Studies Using Dimethilhydrazine or Azoxi-Methane as Cancer Induction Agents. Molecules 2017, 22, 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101670
Moreno-Celis U, López-Martínez J, Blanco-Labra A, Cervantes-Jiménez R, Estrada-Martínez LE, García-Pascalin AE, Guerrero-Carrillo MDJ, Rodríguez-Méndez AJ, Mejía C, Ferríz-Martínez RA, et al. Phaseolus acutifolius Lectin Fractions Exhibit Apoptotic Effects on Colon Cancer: Preclinical Studies Using Dimethilhydrazine or Azoxi-Methane as Cancer Induction Agents. Molecules. 2017; 22(10):1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101670
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreno-Celis, Ulisses, Josué López-Martínez, Alejandro Blanco-Labra, Ricardo Cervantes-Jiménez, Laura Elena Estrada-Martínez, Alejandro Eduardo García-Pascalin, María De Jesús Guerrero-Carrillo, Adriana Jheny Rodríguez-Méndez, Carmen Mejía, Roberto Augusto Ferríz-Martínez, and et al. 2017. "Phaseolus acutifolius Lectin Fractions Exhibit Apoptotic Effects on Colon Cancer: Preclinical Studies Using Dimethilhydrazine or Azoxi-Methane as Cancer Induction Agents" Molecules 22, no. 10: 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101670
APA StyleMoreno-Celis, U., López-Martínez, J., Blanco-Labra, A., Cervantes-Jiménez, R., Estrada-Martínez, L. E., García-Pascalin, A. E., Guerrero-Carrillo, M. D. J., Rodríguez-Méndez, A. J., Mejía, C., Ferríz-Martínez, R. A., & García-Gasca, T. (2017). Phaseolus acutifolius Lectin Fractions Exhibit Apoptotic Effects on Colon Cancer: Preclinical Studies Using Dimethilhydrazine or Azoxi-Methane as Cancer Induction Agents. Molecules, 22(10), 1670. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101670