Halogen Bonding Involving CO and CS with Carbon as the Electron Donor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. CO and CS Monomers
3.2. OC:ClY Complexes
3.2.1. Structures, Binding Energies, Charge-Transfer Energies, and Bonding Properties
3.2.2. Spectroscopic Properties
3.3. SC:ClY Complexes
3.3.1. Structures, Binding Energies, Charge-Transfer Energies, and Bonding Properties
3.3.2. Spectroscopic Properties
4. Conclusions
- CO forms complexes with ClY molecules that are stabilized by traditional halogen bonds. SC:ClY complexes stabilized by traditional halogen bonds are found on all surfaces except SC:ClF, where only an ion-pair SC–Cl+:−F complex exists. Both traditional halogen-bonded and ion-pair complexes are found on the SC:ClNC and SC:ClCl surfaces.
- The binding energies of the OC:ClY complexes range from 4 to 16 kJ.mol−1 while the binding energies of the SC:ClY complexes with traditional halogen bonds are between 7 and 22 kJ.mol−1. Ion-pair complexes have binding energies between 23 and 115 kJ.mol−1.
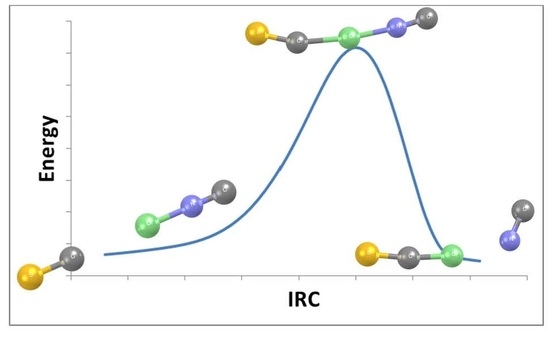
- The transition structures which connect the complex and the ion pair on the SC:ClNC and SC:ClCl surfaces provide the barriers for inter-converting these structures. Converting the complex to the ion pair requires 10 kJ.mol−1 while the reverse reaction requires 41 kJ.mol−1 on the SC:ClCl surface. The barriers for these two reactions on the SC:ClNC surface are about 33 kJ.mol−1 since the complex and ion pair have similar binding energies.
- Charge-transfer from the lone pair on C to the σ-hole on Cl is the primary charge-transfer interaction stabilizing OC:ClY and SC:ClY complexes with traditional halogen bonds. A secondary charge-transfer occurs from the lone pairs on Cl to the in-plane and out-of-plane antibonding π orbitals of ClY. This secondary interaction assumes increased importance in the SC:ClNH2 complex, and is a factor leading to its unusual structure.
- C–O and C–S stretching frequencies and 13C chemical shieldings increase upon complex formation with ClY molecules. These two spectroscopic properties clearly differentiate between SC:ClY complexes and SC–Cl+:−Y ions pairs.
- Spin–spin coupling constants 1xJ(C–Cl) for OC:ClY complexes increase with decreasing distance. For SC:ClY systems, 1xJ(C–Cl) provides a fingerprint of the evolution of the halogen bond as a function of the C–Cl distance, from a traditional halogen bond in complexes, to a chlorine-shared halogen bond in transition structures, to a covalent bond in ion pairs. 1xJ(Cl–A) is the coupling constant across the new halogen bond in the ion-pair complexes. It is significantly reduced relative to 1J(Cl–A) in the corresponding monomers.
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pimentel, G.C.; McClellan, A.L. The Hydrogen Bond; Reinhold Publishing Corp.: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Metrangolo, P.; Resnati, G. Halogen Bonding. Fundamentals and Applications; Structure and Bonding (Book 126); Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Metrangolo, P.; Resnati, G. (Eds.) Halogen Bonding I. Impact on Materials Chemistry and Life Sciences; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; Volume 358. [Google Scholar]
- Faraday Discussions: Halogen Bonding in Supramolecular and Solid State Chemistry. Available online: http://www.rsc.org/events/detail/20585/halogen-bonding-in-supramolecular-and-solid-state-chemistry-faraday-discussion (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Minyaev, R.M.; Minkin, V.I. Theoretical Study of O → X (S, Se, Te) Coordination in Organic Compounds. Can. J. Chem. 1998, 76, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, P.; Yáñez, M.; Mó, O. Resonance-Assisted Intramolecular Chalcogen-Chalcogen Interactions? Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 4548–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleiholder, C.; Werz, D.B.; Köppel, H.; Gleiter, R. Theoretical investigations on chalcogen-chalcogen interactions: what makes these nonbonded interactions bonding? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2666–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Sanz, G.; Trujillo, C.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Intermolecular weak interactions in HTeXH dimers (x=O, S, Se, Te): hydrogen bonds, chalcogen-chalcogen contacts and chiral discrimination. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheiner, S.A. New Noncovalent Force: Comparison of P⋯N Interaction with hydrogen and halogen bonds. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, 094315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahn, S.; Frank, R.; Hey-Hawkins, E.; Kirchner, B. Pnicogen bonds: A new molecular linker? Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 6034–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Bene, J.E.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. The pnicogen bond in review: Structures, binding energies, bonding properties, and spin−spin coupling constants of complexes stabilized by pnicogen bonds. In Noncovalent Forces; Challenges and Advances in Computational Chemistry and Physics; Scheiner, S., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 19, pp. 191–263. [Google Scholar]
- Alkorta, I.; Rozas, I.; Elguero, J. Molecular Complexes between Silicon Derivatives and Electron-Rich Groups. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauzá, A.; Mooibroek, T.J.; Frontera, A. Tetrel-bonding interaction: rediscovered supramolecular force? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12317–12321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, S.J. Tetrel bond-σ-hole bond as a preliminary stage of the SN2 reaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 1824–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.S.; Lane, P.; Politzer, P. Expansion of the σ-hole concept. J. Mol. Model. 2009, 15, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S.; Clark, T. Halogen bonding and other σ-hole interactions: A perspective. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 11178–11189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desiraju, G.R.; Ho, P.S.; Kloo, L.; Legon, A.C.; Marquardt, R.; Metrangolo, P.; Politzer, P.; Resnati, G.; Rissanen, K. Definition of the halogen bond (IUPAC Recommendations 2013). Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 1711–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legon, A.C. Prereactive complexes of dihalogens XY with lewis bases B in the gas phase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 2686–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, W.; Xu, Y.; Gerry, M.C.L. Microwave spectroscopic investigation of the weakly bound dimer carbon monoxide-chlorine, OC:Cl2. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 3685–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waclawik, E.R.; Thumwood, J.M.A.; Lister, D.G.; Fowler, P.W.; Legon, A.C. Geometry, strength of binding and Br2 charge redistribution in the complex OC⋯Br2 determined by rotational spectroscopy. Mol. Phys. 1999, 97, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, K.; Holloway, J.H.; Legon, A.C. The complex OC⋯ClF identified as a pre-chemical intermediate by rotational spectroscopy of carbon monoxide-chlorine monofluoride mixtures. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1995, 242, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, S.; Legon, A.C.; Thorn, J.C. Rotational spectrum of the gas-phase dimer OC⋯BrCl. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1994, 90, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, J.B.; Legon, A.C.; Waclawik, E.R. Inter- and intramolecular electron transfer in the complex OC⋯ICl determined from iodine and chlorine nuclear quadrupole hyperfine structure in its rotational spectrum. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 3097–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, R.M.; Downs, A.J. Matrix-isolated van der waals complexes formed between CO and dihalogen molecules, XY with X, Y = Cl, Br, or I. J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 107, 5298–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkorta, I.; Rozas, I.; Elguero, J. Charge-transfer complexes between dihalogen compounds and electron donors. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 9278–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, F.; Alkorta, I.; Solimannejad, M.; Elguero, J. Theoretical study of the 1:1 complexes between carbon monoxide and hypohalous Acids. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 3237–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yan, C.X.; Yang, F.; Zhou, D.G.; Zhou, P.P.; Liu, S.B. Linear sigma-hole bonding dimers and trimers between dihalogen molecules XY (X, Y = Cl, Br) and carbon monoxide. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 2687–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, F.; Wu, R.-Z.; Yan, C.-X.; Zhou, D.-G.; Zhou, P.-P.; Yao, X. Linear σ-hole⋯CO⋯σ-hole intermolecular interactions between carbon monoxide and dihalogen molecules XY (X, Y=Cl, Br). J. Mol. Graph. Modell. 2017, 76, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Habibi, M.; Masoodi, H.R. Comparison between standard and counterpoise-corrected optimization using some hydrogen and halogen bonded systems. Mol. Phys. 2007, 105, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, M.; Dichiarante, V.; Esterhuysen, C.; Szell, P.M.J. Highlights from the faraday discussion: Halogen bonding in supramolecular and solid state chemistry, July 10–12th 2017, Ottawa, Canada. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 11615–11621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Bene, J.E.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Do traditional, chlorine-shared, and ion-pair halogen bonds exist? An ab initio investigation of FCl:CNX Complexes. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 12958–12962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Bene, J.E.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. An ab initio study of cooperative effects in ternary complexes X:CNH:Z with X, Z = CNH, FH, ClH, FCl, and HLi: Structures, binding energies, and spin-spin coupling constants across intermolecular bonds. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 13951–13961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S. Halogen bonding and beyond: Factors influencing the nature of CN–R and SiN–R complexes with F–Cl and Cl2. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2012, 131, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Cheng, J. Cooperative and substitution effects in enhancing strengths of halogen bonds in FCl⋯CNX complexes. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 084314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Del Bene, J.E. Characterizing traditional and chlorine-shared halogen bonds in complexes of phosphine derivatives with ClF and Cl2. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 4222–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoso-Tauda, O.; Jaque, P.; Elguero, J.; Alkorta, I. Traditional and ion-pair halogen-bonded complexes between chlorine and bromine derivatives and a nitrogen-heterocyclic carbene. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 9552–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Mó, O.; Yáñez, M.; Del Bene, J.E. Using beryllium bonds to change halogen bonds from traditional to chlorine-shared to ion-pair bonds. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 2259–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Cheng, J.; Li, Q.; Li, W. Some measures for making a traditional halogen bond be chlorine-shared or ion-pair one in FCl·NH3 complex. Mol. Phys. 2016, 114, 3643–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bene, J.E.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Using one halogen bond to change the nature of a second bond in ternary complexes with P…Cl and F…Cl halogen bonds. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 203, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pople, J.A.; Binkley, J.S.; Seeger, R. Theoretical models incorporating electron correlation. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1976, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Pople, J.A. Approximate fourth-order perturbation theory of the electron correlation energy. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1978, 14, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, R.J.; Silver, D.M. Many-body perturbation theory applied to electron pair correlation energies. I. Closed-shell first row diatomic hydrides. J. Chem. Phys. 1975, 62, 3258–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, R.J.; Purvis, G.D. Many-body perturbation theory, coupled-pair many-electron theory, and the importance of quadruple excitations for the correlation problem. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1978, 14, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bene, J.E. Proton affinities of ammonia, water, and hydrogen fluoride and their anions: A quest for the basis-set limit using the dunning augmented correlation-consistent basis sets. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, T.H. Gaussian basis sets for use in correlated molecular calculations. I. the atoms boron through neon and hydrogen. J. Chem. Phys. 1989, 90, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woon, D.E.; Dunning, T.H. Gaussian Basis Sets For Use In Correlated Molecular Calculations. V. Core-valence basis sets for boron through neon. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 4572–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, K. The path of chemical reactions—The IRC approach. Acc. Chem. Res. 1981, 14, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hratchian, H.P.; Schlegel, H.B. Using hessian updating to increase the efficiency of a hessian based predictor-corrector reaction path following method. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2005, 1, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian09, Revision D.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Yeole, S.D.; Gadre, S.R.; López, R.; Rico, J.F.; Ramírez, G.; Ema, I.; Zorrilla, D. DAMQT 2.1.0. A new version of the DAMQT package enabled with the topographical analysis of electron density and electrostatic potential in molecules. J. Comput. Chem. 2015, 36, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, R.F.W. A Quantum theory of molecular structure and its applications. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 893–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. Atoms in Molecules, A Quantum Theory; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Popelier, P.L.A. Atoms in Molecules. An Introduction; Prentice Hall: Harlow, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Matta, C.F.; Boyd, R.J. The Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules: From Solid State to DNA and Drug Design; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, T.A. AIMAll, version 16.10.31; TK Gristmill Software: Overland Park, KS, USA, 2011.
- Reed, A.E.; Curtiss, L.A.; Weinhold, F. Intermolecular interactions from a natural bond orbital, donor-acceptor viewpoint. Chem. Rev. 1988, 88, 899–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glendening, E.D.; Badenhoop, J.K.; Reed, A.E.; Carpenter, J.E.; Bohmann, J.A.; Morales, C.M.; Landis, C.R.; Weinhold, F. NBO 6.0; Theoretical Chemistry Institute, University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, UAS, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- London, F. The quantic theory of inter-atomic currents in aromatic combinations. J. Phys. Radium 1937, 8, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditchfield, R. Self-consistent perturbation theory of diamagnetism. 1. Gauge-invariant LCAO method for N.M.R. chemical shifts. Mol. Phys. 1974, 27, 789–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, S.A.; Nooijen, M.; Bartlett, R.J. Electron correlation effects on the theoretical calculation of nuclear magnetic resonance spin−spin coupling constants. J. Chem. Phys. 1996, 104, 3290–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, S.A.; Sekino, H.; Bartlett, R.J. Coupled-cluster calculations of indirect nuclear coupling constants: The importance of non−fermi-contact contributions. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 101, 2186–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, A.; Horn, H.; Ahlrichs, R. Fully optimized contracted gaussian basis sets for atoms Li to Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 2571–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, J.F.; Gauss, J.; Watts, J.D.; Nooijen, M.; Oliphant, N.; Perera, S.A.; Szalay, P.S.; Lauderdale, W.J.; Gwaltney, S.R.; Beck, S.; et al. ACES II; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Knop, O.; Boyd, R.J.; Choi, S.C. Sulfur-sulfur bond lengths, or can a bond length be estimated from a single parameter? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 7299–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, G.V.; Hill, F.C.; Boisen, M.B.; Downs, R.T. Power law relationships between bond length, bond strength and electron density distributions. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1998, 25, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkorta, I.; Barrios, L.; Rozas, I.; Elguero, J. Comparison of models to correlate electron density at the bond critical point and bond distance. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 2000, 496, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, O.; Rankin, K.N.; Boyd, R.J. Coming to grips with N−H⋯N Bonds. 1. Distance relationships and electron density at the bond critical point. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 6552–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, O.; Rankin, K.N.; Boyd, R.J. Coming to grips with N−H⋯N Bonds. 2. Homocorrelations between parameters deriving from the electron density at the bond critical point1. J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 107, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, E.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Molins, E. From weak to strong interactions: A comprehensive analysis of the topological and energetic properties of the electron density distribution involving X−H⋯F−Y systems. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 5529–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Fluorine-fluorine interactions: NMR and AIM analysis. Struct. Chem. 2004, 15, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.H.; Deretey, E.; Knak Jensen, S.J.; Csizmadia, I.G. Hydrogen bonds: Relation between lengths and electron densities at bond critical points. Eur. Phys. J. D 2006, 37, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkorta, I.; Solimannejad, M.; Provasi, P.; Elguero, J. Theoretical study of complexes and fluoride cation transfer between n2f+ and electron donors. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 7154–7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Del Bene, J.E. Pnicogen bonded complexes of PO2X (X = F, Cl) with nitrogen bases. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 10497–10503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Del Bene, J.E. Boron as an electron-pair donor for B⋯Cl halogen bonds. ChemPhysChem 2016, 17, 3112–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Bene, J.E.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Halogen bonding with carbene bases. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 685, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |









| ClY | −ΔE | R(C–Cl) | Clp → σ*Cl–A a | Cllp → π*C–O b | δυ | Δδ13C | 1xJ(C–Cl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ClF | 15.6 | 2.662 | 43.7 | 10.3 | 16.4 | 4.23 | 65.9 |
| ClNC | 10.9 | 2.997 | 14.3 | 2.6 | 13.8 | 3.45 | 31.7 |
| ClCl | 8.4 | 3.020 | 11.9 | 2.5 | 8.0 | 2.65 | 28.7 |
| ClOH | 8.0 | 3.002 | 13.7 | 2.8 | 6.8 | 2.19 | 27.9 |
| ClCN | 7.7 | 3.225 | 6.0 | 1.0 | 8.1 | 2.27 | 16.7 |
| ClCCH | 5.5 | 3.288 | 4.1 | 0.9 | 4.3 | 1.26 | 13.7 |
| ClNH2 | 4.4 | 3.247 | 5.4 | 1.2 | 2.1 | 0.94 | 14.1 |
| SC:ClY, ClY = | −ΔE | R(C–Cl) | Clp → σ*Cl–A a | Cllp → π*C–S b | Sym |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ClNC | 22.4 | 2.795 | 26.9 | 14.7 | C∞v |
| ClCl | 16.8 | 2.768 | 26.4 | 16.0 | C∞v |
| ClCN | 15.3 | 3.092 | 8.2 | 5.6 | C∞v |
| ClOH | 14.8 | 2.772 | 25.6 | 16.9 | Cs |
| ClCCH | 9.4 | 3.183 | 5.6 | 0.9 | C∞v |
| ClNH2 | 6.9 | 3.097 | 5.1 | 6.9 | Cs |
| Y = | −ΔE | R(C–Cl) | R(Cl–A) a | −ETS | R(C–Cl)TS | E‡f b | E‡r b | Sym |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fc | 114.7 | 1.613 | 1.917 d | C∞v | ||||
| Cl | 47.7 | 1.619 | 2.379 e | 6.6 | 2.114 | 10.2 | 41.1 | Cs |
| NC | 23.3 | 1.600 | 2.209 f | −10.9 | 1.979 | 33.3 | 34.2 | Cs |
| ClY = | Δν a | Δδ13C b | 1xJ(C–Cl) | R(S–C) c | 1J(S–C) c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ClNC | 22.5 | 21.0 | 60.2 | 1.538 | −35.6 | ||
| ClCl | 15.9 | 18.6 | 62.6 | 1.539 | −36.7 | ||
| ClCN | 11.9 | 12.4 | 28.3 | 1.540 | −36.7 | ||
| ClOH | 12.8 | 14.0 | 53.1 | 1.540 | −37.1 | ||
| ClCCH | 6.0 | 6.8 | 21.7 | 1.541 | −37.5 | ||
| ClNH2 | 2.2 | 4.2 | 18.0 | 1.542 | −38.4 | ||
| SCCl+:−Y, Y = | 1J(C–Cl) | 1xJ(Cl–A) d | R(Cl–A) d | ||||
| F | 159.9 | 186.1 | −77.1 | 449.3 e | 1.917 | 1.540 | −31.0 |
| Cl | 128.1 | 162.3 | −61.9 | 50.7 f | 2.379 | 1.533 | −24.9 |
| NC | 217.3 | 191.6 | −93.1 | −48.6 g | 2.209 | 1.556 | −39.8 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Del Bene, J.E.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Halogen Bonding Involving CO and CS with Carbon as the Electron Donor. Molecules 2017, 22, 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111955
Del Bene JE, Alkorta I, Elguero J. Halogen Bonding Involving CO and CS with Carbon as the Electron Donor. Molecules. 2017; 22(11):1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111955
Chicago/Turabian StyleDel Bene, Janet E., Ibon Alkorta, and José Elguero. 2017. "Halogen Bonding Involving CO and CS with Carbon as the Electron Donor" Molecules 22, no. 11: 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111955
APA StyleDel Bene, J. E., Alkorta, I., & Elguero, J. (2017). Halogen Bonding Involving CO and CS with Carbon as the Electron Donor. Molecules, 22(11), 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111955