Development of Houttuynia cordata Extract-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery: High Drug Loading Efficiency and Controlled Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Particle Size, PDI and EE of H-SLNs
2.2. DSC Analysis of H-SLNs
2.3. FT-IR Analysis of H-SLNs
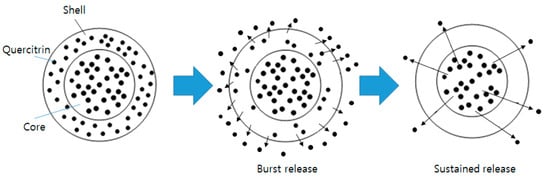
2.4. In Vitro Release Study
2.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Cell Cultures
3.3. Extraction of H. cordata
3.4. Preparation of H-SLNs
3.5. Measurement of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index (PDI) of H-SLNs
3.6. Encapsulation Efficiency (EE) of H. cordata Extracts in H-SLNs
3.7. Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC) Analysis of H-SLNs
3.8. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Analysis of H-SLNs
3.9. In Vitro Release Study
3.10. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Study
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lau, K.M.; Lee, K.M.; Koon, C.M.; Cheung, C.S.; Lau, C.P.; Ho, H.M.; Lee, M.Y.; Au, S.W.; Cheng, C.H.; Lau, C.B.; et al. Immunomodulatory and anti-SARS activities of Houttuynia cordata. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 118, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.R.; Shim, S.M. Inhibitory effect of polyphenols in Houttuynia cordata on advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) by trapping methylglyoxal. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.Y.; Bae, J.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Oh, K.Y.; Park, K.H.; Bae, Y.S. Caffeic acid and quercitrin purified from Houttuynia cordata inhibit DNA topoisomerase I activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekita, Y.; Murakami, K.; Yumoto, H.; Mizuguchi, H.; Amoh, T.; Ogino, S.; Matsuo, T.; Miyake, Y.; Fukui, H.; Kashiwada, Y. Anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory effects of ethanol extract from Houttuynia cordata poultice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.S.; Kim, B.S.; Puri, A.; Kumar, K.; Cho, C.W. Stability of paclitaxel-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in the presence of 2-hydoxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.S.; Cho, C.W. Surface modification of solid lipid nanoparticles for oral delivery of curcumin: Improvement of bioavailability through enhanced cellular uptake, and lymphatic uptake. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.S.; Cho, C.W. A multifunctional lipid nanoparticle for co-delivery of paclitaxel and curcumin for targeted delivery and enhanced cytotoxicity in multidrug resistant breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30369–30382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Lee, S.G.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, S.K.; Choi, Y.W. Surface modification of lipid-based nanocarriers for cancer cell-specific drug targeting. J. Pharm. Investig. 2017, 47, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, T.; Guo, W.; Bao, X.; Wang, D.; Ren, B.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Anticancer Effects of Resveratrol-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles on Human Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigon, R.B.; Fachinetti, N.; Severino, P.; Santana, M.H.; Chorilli, M. Skin Delivery and In Vitro Biological Evaluation of Trans-Resveratrol-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Skin Disorder Therapies. Molecules 2016, 21, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Cho, C.W. Modification of paclitaxel-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin enhances absorption and reduces nephrotoxicity associated with intravenous injection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 5397–5405. [Google Scholar]
- Jackman, J.A.; Yoon, B.K.; Li, D.; Cho, N.J. Nanotechnology Formulations for Antibacterial Free Fatty Acids and Monoglycerides. Molecules 2016, 21, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelidari, H.R.; Saeedi, M.; Akbari, J.; Morteza-Semnani, K.; Gill, P.; Valizadeh, H.; Nokhodchide, A. Formulation optimization and in vitro skin penetration of spironolactone loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 128, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, R.A.; Abass, H.A.; Attia, M.A.; Heikal, O.A. Formulation and evaluation of metoclopramide solid lipid nanoparticles for rectal suppository. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyanka, K.; Hasan, S.A.A. Preparation and evaluation of montelukast sodium loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Young Pharm. 2012, 4, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandita, D.; Ahllia, A.; Velpandian, T.; Lather, V.; Dutta, T.; Khar, R.K. Characterization and in vitro assessment of paclitaxel loaded lipid nanoparticles formulated using modified solvent injection technique. Pharmazie 2009, 64, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butani, D.; Yewale, C.; Misra, A. Topical amphotericin B solid lipid nanoparticles: Design and development. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 139, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ausborn, M.; Nuhn, P.; Schreier, H. Stabilization of liposomes by freeze-thaw and lyophilization techniques: Problems and opportunities. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1992, 38, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Strauss, G.; Schurtenberger, P.; Hauser, H. The interaction of saccharides with lipid bilayer vesicles: Stabilization during freeze-thawing and freeze-drying. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 858, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grit, M.; Crommelin, D.J.A. The effect of aging on the physical stability of liposome dispersions. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1992, 62, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siri, M.; Grasselli, M.; Alonso, S.D.V. Albumin-based nanoparticle trehalose lyophilisation stress-down to preserve structure/function and enhanced binding. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 126, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Date, P.V.; Samad, A.; Devarajan, P.V. Freeze thaw: A simple approach for prediction of optimal cryoprotectant for freeze drying. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovačević, A.B.; Müller, R.H.; Savić, S.D.; Vuleta, G.M.; Keck, C.M. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) stabilized with polyhydroxy surfactants: Preparation, characterization and physical stability investigation. Colloids Surf. A 2014, 444, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, H.A.; Javadzadeh, Y.; Hamidi, M.; Jalali, M.B. Repaglinide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Effect of using different surfactants/stabilizers on physicochemical properties of nanoparticles. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 23, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MuÈller, R.H.; MaÈder, K.; Gohla, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—A review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatabadi, J.E.N.; Valizadeh, H.; Hamishehkar, H. Solid lipid nanoparticles as efficient drug and gene delivery systems: Recent breakthroughs. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, G.H.; Lee, B.J.; Cho, C.W. Mechanisms of drug release from advanced drug formulations such as polymeric-based drug-delivery systems and lipid nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Investig. 2017, 47, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandagi, P.M.; Rath, S.P.; Gadada, A.P.; Mastiholimath, V.S. Taste Masked Quinine Sulphate Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Flexible Pediatric Dosing. Indian J. Pharm. Edu. Res. 2014, 48, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaerts, K.; Renes, J.; Bouwman, F.G.; Noben, J.P.; Robben, J.; Smit, E.; Mariman, E.C. Arginine deficiency in preconfluent intestinal Caco-2 cells modulates expression of proteins involved in proliferation, apoptosis, and heat shock response. Proteomics 2007, 7, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, C.J.; Medina, S.H.; ElSayed, M.E. Effect of rhamnolipids on permeability across Caco-2 cell monolayers. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, M.; Robine-Leon, S.; Appay, M.D.; Kedinger, M.; Triadou, N.; Dussaulx, E.; Lacroix, B.; Simon-Assman, P.; Haffen, K.; Fogh, J.; et al. Enterocyte-like differentiation and polarization of the human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2 in culture. Biol. Cell 1983, 47, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B.; Silva, A.M. Nanotoxicology applied to solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers—A systematic review of in vitro data. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |






| Formulation | Poloxamer 188 (%) | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | EE (%) |
| F1 | 0.5 | 419.1 ± 12.0 | 0.060 ± 0.035 | 91.3 ± 1.4 |
| F2 | 1 | 396.6 ± 14.2 | 0.184 ± 0.011 | 89.2 ± 2.3 |
| F3 | 1.5 | 221.4 ± 13.7 | 0.232 ± 0.011 | 93.1 ± 4.6 |
| F4 | 2 | 202.9 ± 1.1 | 0.216 ± 0.014 | 91.2 ± 4.4 |
| F5 | 2.5 | 209.0 ± 14.8 | 0.206 ± 0.23 | 93.0 ± 2.6 |
| F6 | 3 | 231.0 ± 35.6 | 0.223 ± 0.27 | 94.3 ± 2.5 |
| Formulation | Poloxamer 407 (%) | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | EE (%) |
| F7 | 0.5 | 195.2 ± 11.4 | 0.096 ± 0.037 | 96.3 ± 2.3 |
| F8 | 1 | 191.3 ± 9.6 | 0.154 ± 0.021 | 93.3 ± 3.6 |
| F9 | 1.5 | 164.1 ± 7.7 | 0.169 ± 0.012 | 97.0 ± 4.0 |
| F10 | 2 | 159.6 ± 22.3 | 0.166 ± 0.013 | 91.3 ± 5.1 |
| F11 | 2.5 | 160.7 ± 9.7 | 0.087 ± 0.010 | 92.8 ± 2.0 |
| F12 | 3 | 159.6 ± 22.3 | 0.233 ± 0.015 | 95.5 ± 2.2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-H.; Baek, J.-S.; Park, J.-K.; Lee, B.-J.; Kim, M.-S.; Hwang, S.-J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Cho, C.-W. Development of Houttuynia cordata Extract-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery: High Drug Loading Efficiency and Controlled Release. Molecules 2017, 22, 2215. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122215
Kim J-H, Baek J-S, Park J-K, Lee B-J, Kim M-S, Hwang S-J, Lee J-Y, Cho C-W. Development of Houttuynia cordata Extract-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery: High Drug Loading Efficiency and Controlled Release. Molecules. 2017; 22(12):2215. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122215
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ju-Heon, Jong-Suep Baek, Jin-Kyu Park, Bong-Joo Lee, Min-Soo Kim, Sung-Joo Hwang, Jae-Young Lee, and Cheong-Weon Cho. 2017. "Development of Houttuynia cordata Extract-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery: High Drug Loading Efficiency and Controlled Release" Molecules 22, no. 12: 2215. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122215
APA StyleKim, J. -H., Baek, J. -S., Park, J. -K., Lee, B. -J., Kim, M. -S., Hwang, S. -J., Lee, J. -Y., & Cho, C. -W. (2017). Development of Houttuynia cordata Extract-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery: High Drug Loading Efficiency and Controlled Release. Molecules, 22(12), 2215. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122215