A DNA Barcode-Based RPA Assay (BAR-RPA) for Rapid Identification of the Dry Root of Ficus hirta (Wuzhimaotao)
Abstract
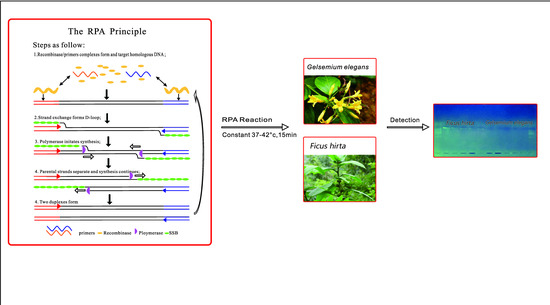
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Optimal Reaction Temperature and Time for BAR-RPA
2.2. Specificity and Sensitivity Assessment of BAR-PRA
2.3. Authenticity Identification of Wuzhimaotao in the Market
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. DNA Extraction
4.2.2. Primer Design
- RPA-ITS-F: 5′-TCAAGGAAAGACAACGAGACGATCCCAGCC-3′;
- RPA-ITS-R: 5′-CGACTACCTGTTGCCAAGACGACGTGACAG-3′.
4.2.3. Amplification and Purification
4.2.4. Optimization of BAR-RPA Reaction Temperature and Time
4.2.5. Specificity and Sensitivity Assessment of the BAR-RPA Assay
4.2.6. Identification of Wuzhimaotao Crude Drugs Using BAR-PRA
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berg, C.C. Flora Malesiana precursor for the treatment of Moraceae 3: Ficus subgenus Ficus. Blumea 2003, 48, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.K.; Gilbert, M.G. Ficus. In Flora of China (English Edition), 5th ed.; Flora of China Editorial Committee, Science Press: Beijing, China; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2003; pp. 37–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rujjanawate, C.; Kanjanapothi, D.; Panthong, A. Pharmacological effect and toxicity of alkaloids from Gelsemium elegans Benth. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, D.T.; Wu, J.L.; Jiang, Z.H.; Chen, H.B.; Lu, G.H.; Zhao, Z.Z. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used by Hakka in Guangdong, China. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Editorial Committee of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1992; Volume 61, p. 251. [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga, T.; Chikuni, K.; Tanabe, R.; Muroya, S.; Yamada, K.; Shinmura, Y. A quick and simple method for the identification of meat species and meat products by PCR assay. Meat Sci. 1999, 51, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; Dewaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.L.; Yao, H.; Song, J.Y.; Li, X.W. Use of DNA barcoding to identify Chinese medicinal materials. World Sci. Technol./Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Med. 2007, 9, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sperling, F. DNA Barcoding: Deus ex machina. Newsl. Biol. Surv. Can. (Terr. Arthropods) 2003, 22, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.L.; Yao, H.; Han, J.P.; Liu, C.; Song, J.Y.; Shi, L.C.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Ma, X.Y.; Gao, T.; Pang, X.H.; et al. Validation of the ITS2 region as a novel DNA barcode for identifying medicinal plant species. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Song, J.Y.; Liu, C.; Luo, K.; Han, J.; Li, Y.; Pang, X.H.; Xu, H.X.; Zhu, Y.J.; Xiao, P.G.; et al. Use of ITS2 region as the universal DNA barcode for plants and animals. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.H.; Du, C.Y. Research advances of Loop-mediated isothermal amplification method, LAMP. J. Nanchang Univ. 2013, 5, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Ffatanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, P.; Ghaemi, A. Nucleic acid isothermal amplification technologies: A review. Nulcleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2008, 27, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, B.; Cheng, H.R.; Yan, Q.F.; Huang, Z.J.; Shen, G.F.; Zhang, Z.F.; Li, Y.N.; Deng, Z.X.; Lin, M.; Cheng, Q. Recombinase-aid amplification: A novel technology of in vitro rapid nucleic acid amplification. Sci. Sin. Vitae 2010, 40, 983–988. [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi, N.; Nakajima, C.; Harunari, T.; Tanikawa, T.; Tokiwa, T.; Uchimura, E.; Furuya, T.; Mingala, C.N.; Villanueva, M.A.; Ohnishi, M.; et al. A new loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for rapid, simple, and sensitive detection of Leptospira spp. in urine. J. Clin. Microb. 2012, 50, 2072–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yan, J.; Yan, J. Application of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the detection of pathogenic Leptospira. Diagn. Microl. Infect. Dis. 2009, 63, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.L.; Yao, H.; Han, J.P.; Xin, T.Y.; Pang, X.H. Principles for molecular identification of traditional Chinese materia medica using DNA barcoding. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 38, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Yohei, S.; Kastsuko, K.; Seiji, N. Rapid detection of Panax ginseng by loops-mediated isothermal amplification and its application to authentication of Ginseng. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 1806–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.Z.I. Studies On The Gamma Radiation Antiseptic Dose Of Polygoni Multiflori Radix II.Studies On Molecular Identification Of Taraxacum Formosanum And Distinguishing From Its Adulterants. Ph.D. Thesis, China Medical University, Taizhong, Taiwan, 2011. Available online: http://ir.cmu.edu.tw/handle/310903500/41248 (accessed on 17 October 2011).
- Piepenburg, O.; Williams, C.H.; Stemple, D.L.; Armes, N.A. DNA Detection Using Recombination Proteins. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, D.S.; McNerney, R.; Teng, L.H.; Leader, B.T.; Pérez-Osorio, A.C.; Meyer, J.C.; O’Sullivan, D.M.; Brooks, D.G.; Piepenburg, O.; Forrest, M.S. Rapid Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersting, S.; Rausch, V.; Bier, F.F.; Von Nickisch-Rosenegk, M. Rapid detection of Plasmodium falciparum with isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification and lateral flow analysis. Malaria 2014, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euler, M.; Wang, Y.; Otto, P.; Tomaso, H.; Escudero, R.; Anda, P. Recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of Francisella tularensis. J. Clin. Microb. 2012, 50, 2234–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euler, M.; Wang, Y.; Heidenreich, D.; Patel, P.; Strohmeier, O.; Hakenberg, S. Development of a panel of recombinase polymerase amplification assays for detection of biothreat agents. J. Clin. Microb. 2013, 51, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collard, B.; Das, A.; Virk, P.S.; Mackill, D.J. Evaluation of ‘quick and dirty’ DNA extraction methods for marker-assisted selection in rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Breed. 2007, 126, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Kawasaki, S.; Fujimura, T.; Wang, C.T. A protocol for high-throughput extraction of DNA from rice leaves. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2005, 23, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Huang, L.Q.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, M.; Lin, S.F.; Wu, Z.G. Rapid extraction of DNA from Chinese medicinal materials by alkaline lysis. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2013, 33, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, C.Y.; Hou, H.S.; Tong, S.M. Comparison of DNA extraction methods from four Chinese traditional medical herbs. Chin. J. Biochem. Pharm. 2015, 7, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.H.; Yang, Z.L.; Yang, X.; Tan, Z.F.; Su, X.; Liu, R.N. Advances in studies on ITS sequence of medicinal plants germplasm resources. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2010, 41, 491–496. [Google Scholar]
- TwistDx. Appendix to the TwistAmpTM Reaction Kit Manuals. Available online: http://www.twistdx.co.uk/images/uploads/docs/Appendix.pdf (accessed on 14 August 2014).
- Xu, C.; Li, L.; Jin, W.J.; Wan, Y.S. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) of CaMV-35S Promoter and nos Terminator for Rapid Detection of Genetically Modified Crops. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18197–18205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C. The Application of Recombinase Mediated Isothermal Amplification Technology in Transgenic Detection. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2014. Available online: http://kreader.cnki.net/Kreader/CatalogViewPage.aspx?dbCode=cdmd&filename=1014326375.nh&tablename=CMFD201402&compose=&first=1&uid=WEEvREcwSlJHSldRa1FhdkJkcGp4dXFpSzdwaHlhQ2VrbzdRUlJhRXNwRT0=$9A4hF_YAuvQ5obgVAqNKPCYcEjKensW4ggI8Fm4gTkoUKaID8j8gFw!! (accessed on 1 May 2014).
- Xia, X.; Yu, Y.; Weidmann, M.; Pan, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y.J. Rapid detection of shrimp white spot syndrome virus by real-time, isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification assay. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.H.; Yi, X.F.; Cui, Z.H.; Lan, X.P. Detection for Aspergillus fumigatus by recombinase polymerase amplification assay. Chin. J. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 33, 214–218. [Google Scholar]
- Krõlov, K.; Frolova, J.; Tudoran, O.; Suhorutsenko, J.; Lehto, T.; Sibul, H.; Mager, I.; Laanpere, M.; Tulp, I.; Langel, U. Sensitive and Rapid Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis by Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Directly from Urine Samples. J. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 16, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaroenram, W.; Owens, L. Separation of endogenous viral elements from infectious Penaeus stylirostris densovirus using recombinase polymerase amplification. Mol. Cell. Probes 2014, 28, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D67–D72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, R.H.; Tedersoo, L.; Abarenkov, K.; Ryberg, M.; Kristiansson, E.; Hartmann, M.; Schoch, C.L.; Nylander, J.A.A.; Bergsten, J.; Porter, T.M.; et al. Five simple guidelines for establishing basic authenticity and reliability of newly generated fungal ITS sequences. MycoKeys 2012, 4, 37–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, S.; Skaletsky, H.J. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In Bioinformatics Methods and Protocols: Methods in Molecular Biology; Krawetz, S., Misener, S., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 365–386. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the Ficus hirta and Gelsemium elegans are available from the authors. |



| Name of Medicinal Herb | Sources | Code | Location | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuzhimaotao | Ficus hirta | WZS-1 | Conghua, Guangdong | P |
| Wuzhimaotao | Ficus hirta | WZS-2 | Conghua, Guangdong | P |
| Wuzhimaotao | Ficus hirta | WZS-3 | Conghua, Guangdong | P |
| Wuzhimaotao | Ficus hirta | WZS-4 | Conghua, Guangdong | P |
| Wuzhimaotao | Ficus hirta | WZS-5 | Conghua, Guangdong | P |
| Duanchangcao | Gelsemium elegans | GW-1 | Conghua, Guangdong | N |
| Duanchangcao | Gelsemium elegans | GW-2 | Conghua, Guangdong | N |
| Duanchangcao | Gelsemium elegans | GW-3 | Wanning, Hainan | N |
| Duanchangcao | Gelsemium elegans | GW-4 | Conghua, Guangdong | N |
| Duanchangcao | Gelsemium elegans | GW-5 | Conghua, Guangdong | N |
| Code | Places of Production | Results of Identification |
|---|---|---|
| Sha-1 | Shaxian, Fujian | + |
| Sha-2 | Shaxian, Fujian | + |
| JX-1 | Jinggangshan, Jiangxi | + |
| JX-2 | Jinggangshan, Jiangxi | + |
| DHS-1 | Dinghushan, Guangdong | + |
| DHS-2 | Dinghushan, Guangdong | + |
| ND-1 | Ningde, Fujian | + |
| ND-2 | Ningde, Fujian | + |
| WN-1 | Wanning, Hainan | + |
| WN-2 | Wanning, Hainan | + |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, E.; Liu, Q.; Ye, H.; Li, F.; Chao, Z. A DNA Barcode-Based RPA Assay (BAR-RPA) for Rapid Identification of the Dry Root of Ficus hirta (Wuzhimaotao). Molecules 2017, 22, 2261. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122261
Tian E, Liu Q, Ye H, Li F, Chao Z. A DNA Barcode-Based RPA Assay (BAR-RPA) for Rapid Identification of the Dry Root of Ficus hirta (Wuzhimaotao). Molecules. 2017; 22(12):2261. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122261
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Enwei, Qianqian Liu, Haoting Ye, Fang Li, and Zhi Chao. 2017. "A DNA Barcode-Based RPA Assay (BAR-RPA) for Rapid Identification of the Dry Root of Ficus hirta (Wuzhimaotao)" Molecules 22, no. 12: 2261. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122261
APA StyleTian, E., Liu, Q., Ye, H., Li, F., & Chao, Z. (2017). A DNA Barcode-Based RPA Assay (BAR-RPA) for Rapid Identification of the Dry Root of Ficus hirta (Wuzhimaotao). Molecules, 22(12), 2261. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122261