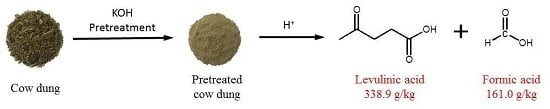
High-Yield Production of Levulinic Acid from Pretreated Cow Dung in Dilute Acid Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphology Change of Cow Dung before and after Pretreatment
2.2. Catalytic Production of Levulinic Acid from Pretreated Cow Dung by Different Liquid Acids
2.3. Catalytic Production of LA from Crude and Pretreated Cow Dung in HCl Aqueous Solutions
2.4. Effect of the Reaction Temperature on the Production of LA from Pretreated Cow Dung
2.5. Effect of Loading Substrate Amount on the Production of LA from Cow Dung
2.6. Effect of Acid Concentration on the Production of LA from Cow Dung
3. Experimental Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Pretreatment of Cow Dung
3.3. Catalytic Treatment of Cow Dung and Products Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yabushita, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Fukuoka, A. Catalytic transformation of cellulose into platform chemicals. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2014, 145, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, S.; Agarwal, B.; Sangwan, R.S. Thermo-chemical pretreatment of rice straw for further processing for levulinic acid production. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Wang, W.; Yan, Y.; Deng, A.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, L. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal treatment of corncob using tin(IV) chloride as catalyst for furfural production. Cellulose 2016, 23, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonetti, C.; Bonari, E.; Licursi, D.; Di Nasso, N.N.O.; Galletti, A.M.R. Hydrothermal Conversion of Giant Reed to Furfural and Levulinic Acid: Optimization of the Process under Microwave Irradiation and Investigation of Distinctive Agronomic Parameters. Molecules 2015, 20, 21232–21253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Dumont, M.-J.; Raghavan, V. Review: Sustainable production of hydroxymethylfurfural and levulinic acid: Challenges and opportunities. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 72, 143–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Long, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Ma, L. Production of Levulinic Acid from Pennisetum alopecuroides in the Presence of an Acid Catalyst. Bioresources 2016, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavilà, L.; Constantí, M.; Medina, F. d-Lactic acid production from cellulose: Dilute acid treatment of cellulose assisted by microwave followed by microbial fermentation. Cellulose 2015, 22, 3089–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabasso, S.; Grillo, G.; Carnaroglio, D.; Gaudino, E.C.; Cravotto, G. Microwave-Assisted gamma-Valerolactone Production for Biomass Lignin Extraction: A Cascade Protocol. Molecules 2016, 21, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pileidis, F.D.; Titirici, M.-M. Levulinic Acid Biorefineries: New Challenges for Efficient Utilization of Biomass. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 562–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Xue, L.F.; Wang, S.T.; Wang, X.H.; Shi, J.Y. Single step conversion of cellulose to levulinic acid using temperature-responsive dodeca-aluminotungstic acid catalysts. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannelly, T.; Lopes, M.; Kupiainen, L.; Dooley, S.; Leahy, J.J. Non-stoichiometric formation of formic and levulinic acids from the hydrolysis of biomass derived hexose carbohydrates. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 5797–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.T. Production of levulinic acid from glucosamine by dilute-acid catalyzed hydrothermal process. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 62, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingarten, R.; Conner, W.C.; Huber, G.W. Production of levulinic acid from cellulose by hydrothermal decomposition combined with aqueous phase dehydration with a solid acid catalyst. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7559–7574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Thomas, J.; Smet, M.; Dehaen, W.; Sels, B.F. Molecular design of sulfonated hyperbranched poly(arylene oxindole)s for efficient cellulose conversion to levulinic acid. Green Chem. 2015, 18, 1694–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonetti, C.; Licursi, D.; Fulignati, S.; Valentini, G.; Raspolli Galletti, A. New Frontiers in the Catalytic Synthesis of Levulinic Acid: From Sugars to Raw and Waste Biomass as Starting Feedstock. Catalysts 2016, 6, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachri, B.A.; Abdilla, R.M.; van de Bovenkamp, H.H.; Rasrendra, C.B.; Heeres, H.J. Experimental and Kinetic Modeling Studies on the Sulfuric Acid Catalyzed Conversion of d-Fructose to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural and Levulinic Acid in Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3024–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilaqua, D.B.; Rambo, M.K.D.; Rizzetti, T.M.; Cardoso, A.L.; Martins, A.F. Cleaner production: Levulinic acid from rice husks. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 47, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.S.; Zodge, A.D.; Pandare, K.V.; Kulkarni, B.D. Efficient conversion of cellulose to levulinic acid by hydrothermal treatment using zirconium dioxide as a recyclable solid acid catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 18796–18805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upare, P.P.; Yoon, J.W.; Kim, M.Y.; Kang, H.Y.; Hwang, D.W.; Hwang, Y.K.; Kung, H.H.; Chang, J.S. Chemical conversion of biomass-derived hexose sugars to levulinic acid over sulfonic acid-functionalized graphene oxide catalysts. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2935–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, S.; Agarwal, B.; Runge, T.M.; Sangwan, R.S. Integrated two-stage chemically processing of rice straw cellulose to butyl levulinate. Carbohydr. Poly. 2016, 150, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.G.; Kang, H.Y.; Guo, Y.F.; Zhuang, G.Q.; Bai, Z.H.; Zhang, H.X.; Feng, C.X.; Dong, Y.P. Dilute-acid conversion of cotton straw to sugars and levulinic acid via 2-stage hydrolysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 46, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.C.; Lin, L.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhuang, J.P.; Zhang, B.X.; Gong, Y. Catalytic Conversion of Cellulose to Levulinic Acid by Metal Chlorides. Molecules 2010, 15, 5258–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Wang, L.Z.; Yan, T. Methane emission inventories for enteric fermentation and manure management of yak, buffalo and dairy and beef cattle in China from 1988 to 2009. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 195, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhou, S.F.; Runge, T. Dairy manure as a potential feedstock for cost-effective cellulosic bioethanol. Bioresources 2016, 11, 1240–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollehon, N.; Caswell, M.; Ribaudo, M.; Kellogg, B.; Lander, C.; Letson, D. Confined animal production and manure nutrients. Neuropharmacology 2001, 27, 519–527. [Google Scholar]
- Stowe, E.J.; Coats, E.R.; Brinkman, C.K. Dairy manure resource recovery utilizing two-stage anaerobic digestion—Implications of solids fractionation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arikan, O.A.; Mulbry, W.; Rice, C. The effect of composting on the persistence of four ionophores in dairy manure and poultry litter. Waste Manag. 2016, 54, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.J.; Hanna, M.A.; Jones, D.D. Thermogravimetric characterization of dairy manure as pyrolysis and combustion feedstocks. Waste Manag. Res. 2012, 30, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Chao, Z. Anaerobic codigestion of pretreated wheat straw with cattle manure and analysis of the microbial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 186, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wen, Z.; Chen, S. Acid hydrolysis of fibers from dairy manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runge, T.; Zhang, C. Two-Stage Acid-Catalyzed Conversion of Carbohydrates into Levulinic Acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 3265–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y. Direct production of levulinic acid in high yield from cellulose: Joint effect of high ion strength and microwave field. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 39131–39136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, L.; Pan, X. Hydrolysis of cellulose by cellulase-mimetic solid catalyst. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6889–6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Wang, J.; Xi, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, G.; Wang, Y. High-yield production of levulinic acid from cellulose and its upgrading to γ-valerolactone. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3846–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.K.; Nannaware, A.D.; Prakash, O.; Kalra, A.; Rajasekharan, R. Synthesis of hydroxymethylfurfural from cellulose using green processes: A promising biochemical and biofuel feedstock. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 142, 318–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.B.; Fu, Y. Hydrolysis of cellulose to glucose by solid acid catalysts. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 1095–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Lin, L.; Zhou, S.Y. Catalytic hydrolysis of microcrystalline and rice straw-derived cellulose over a chlorine-doped magnetic carbonaceous solid acid. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 84, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabolcs, A.; Molnar, M.; Dibo, G.; Mika, L.T. Microwave-assisted conversion of carbohydrates to levulinic acid: An essential step in biomass conversion. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-delaRosa, S.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Optimization of the process of chemical hydrolysis of cellulose to glucose. Cellulose 2014, 21, 2397–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.X.; Zhu, L.F.; Shen, F.; Qi, X.H. Black liquor-derived carbonaceous solid acid catalyst for the hydrolysis of pretreated rice straw in ionic liquid. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidarian, P.; Behzad, T.; Karimi, K. Isolation and characterization of bagasse cellulose nanofibrils by optimized sulfur-free chemical delignification. Wood Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1071–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspolli Galletti, A.M.; Antonetti, C.; de Luise, V.; Licursi, D.; Nassi, N. Levulinic acid production from waste biomass. Bioresources 2012, 7, 1824–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not Available.







| Components | Crude Cow Dung | Pretreated Cow Dung |
|---|---|---|
| Cellulose, % | 27.2 | 58.9 |
| Hemicellulose, % | 17.2 | 10.8 |
| Lignin (acid insoluble), % | 20.6 | 8.5 |
| Ash, % | 7.6 | 6.0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, J.; Shen, F.; Qiu, M.; Qi, X. High-Yield Production of Levulinic Acid from Pretreated Cow Dung in Dilute Acid Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2017, 22, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020285
Su J, Shen F, Qiu M, Qi X. High-Yield Production of Levulinic Acid from Pretreated Cow Dung in Dilute Acid Aqueous Solution. Molecules. 2017; 22(2):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020285
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Jialei, Feng Shen, Mo Qiu, and Xinhua Qi. 2017. "High-Yield Production of Levulinic Acid from Pretreated Cow Dung in Dilute Acid Aqueous Solution" Molecules 22, no. 2: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020285
APA StyleSu, J., Shen, F., Qiu, M., & Qi, X. (2017). High-Yield Production of Levulinic Acid from Pretreated Cow Dung in Dilute Acid Aqueous Solution. Molecules, 22(2), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020285