Transesterification Synthesis of Chloramphenicol Esters with the Lipase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
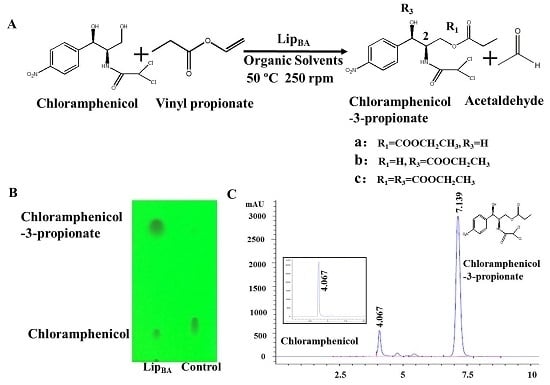
2.1. Synthesis of Chloramphenicol Propionate Esters
2.2. Transesterification of Chloramphenicol with Different Acyl Donors
2.3. Effect of Different Solvents
2.4. Effect of Reaction Temperature
2.5. Effect of Reaction Time
2.6. Effect of Enzyme Loading
2.7. Influence of the Water Content
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Enzymatic Synthesis of Cinnamyl Acetate and Single Factor Experiment
3.3. Analysis Method
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ellis, G.P.; Epstein, C.; King, J. The antibacterial activities of some esters of chloramphenicol. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 26, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebstock, M.C.; Crooks, H.M.; Controulis, J.; Bartz, Q.R. Chloramphenicol (chloromycetin)1 IV.1a chemical studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1949, 71, 2458–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, D.R.; Alhajoj, A.M.; Elattar, K.M.; Kheder, N.A.; Fadda, A.A. Synthesis and evaluation of curcuminoid analogues as antioxidant and antibacterial agents. Molecules 2017, 22, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siti Hajar, M.; Mahiran, B.; Masoumi, H.R.F.; Roghayeh Abedi, K.; Emilia Abd, M.; Hamidon, B.; Ahmad Fuad, S. Formulation optimization of palm kernel oil esters nanoemulsion-loaded with chloramphenicol suitable for meningitis treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Maillard, J.Y. Biocide Use and Antibiotic Resistance; Springer: Boston, MA USA, 2005; pp. 465–489. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaszewski, T. Side-effects of chloramphenicol and aureomycin. Br. Med. J. 1951, 1, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckarift, H.R.; Nadeau, L.J.; Spain, J.C. Continuous synthesis of aminophenols from nitroaromatic compounds by combination of metal and biocatalyst. Chem. Commun. 2005, 3, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizerra, A.M.C.; Montenegro, T.G.C.; Lemos, T.L.G.; Oliveira, M.C.F.D.; Mattos, M.C.D.; Lavandera, I.; Gotor-Fernández, V.; Gonzalo, G.D.; Gotor, V. Enzymatic regioselective production of chloramphenicol esters. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 2858–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Lu, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z. Lipase nanogel catalyzed transesterification in anhydrous dimethyl sulfoxide. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.G.; Jin, H.D.; Chang, H.N. Regioselective enzymatic acylation of multi-hydroxyl compounds in organic synthesis. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2003, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.; Poveda, A.; Jimenez-Barbero, J.; Ballesteros, A.; Plou, F.J. Regioselective lipase-catalyzed synthesis of 3-O-acyl derivatives of resveratrol and study of their antioxidant properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daugs, E.D. The preparation and isolation of chloramphenicol palmitate in toluene. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2000, 4, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Lu, D.; Ge, J.; Liu, Z. Substrate imprinted lipase nanogel for one-step synthesis of chloramphenicol palmitate. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottolina, G.; Carrea, G.; Riva, S. Synthesis of ester derivatives of chloramphenicol by lipase-catalyzed transesterification in organic solvents. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 2366–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Ma, J.; Wei, D.Z.; Lin, J.P.; Wei, W. Functional expression of a novel alkaline-adapted lipase of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens from stinky tofu brine and development of immobilized enzyme for biodiesel production. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2014, 106, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Wang, W.; Lin, L.; He, D.; Shen, Y.; Wei, W.; Wei, D.Z. Cinnamyl esters synthesis by lipase-catalyzed transesterification in a non-aqueous system. Catal. Lett. 2017, 147, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.S.; Xue, X.T.; Wang, N.; Wu, Q.; Lin, X.F. Enzyme catalyzed synthesis of some vinyl drug esters in organic medium. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2004, 34, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, K.; Itatani, Y.; Tsuda, Y. 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance (nmr) spectra of O-acylglucoses. Additivity of shift parameters and its application to structure elucidations. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1980, 28, 2065–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kersh, T.A.; Plourde, J.R. Biotransformation of antibiotics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1980, 10, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.D.; Devendran, S. Lipase catalyzed synthesis of cinnamyl acetate via transesterification in non-aqueous medium. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, K.E.; Dijkstra, B.W.; Reetz, M.T. Three-dimensional structures, and biotechnologicalapplications of lipases. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1999, 53, 315–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brault, G.; Shareck, F.; Hurtubise, Y.; Lépine, F.; Doucet, N. Short-chain flavor ester synthesis in organic media by an e. Coli whole-cell biocatalyst expressing a newly characterized heterologous lipase. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichardt, C. Solvents and solvent effects: An introduction. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2007, 11, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priego, J.; Ortíz-Nava, C.; Carrillo-Morales, M.; López-Munguía, A.; Escalante, J.; Castillo, E. Solvent engineering: An effective tool to direct chemoselectivity in a lipase-catalyzed michael addition. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, C. Solvatochromic dyes as solvent polarity indicators. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkeldam, R.W.; Tor, Y. To D or not to D? On estimating the microenvironment polarity of biomolecular cavities. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelens, S. Organotin-mediated synthesis of macrocyclic polyesters: Mechanism and selectivity in the reaction of dioxastannolanes with diacyl dichlorides. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1988, 8, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Rebsdorf, M.; Engelrud, U.; Xu, X. Enzymatic production of monoacylglycerols containing polyunsaturated fatty acids through an efficient glycerolysis system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klibanov, A.M. Improving enzymes by using them in organic solvents. Nature 2001, 409, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Mangas-Sánchez, J.; Feng, F.; Adlercreutz, P. Acyl migration in enzymatic interesterification of triacylglycerols: Effects of lipases from thermomyces lanuginosus and rhizopus oryzae, support material, and water activity. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlhoff, C.W.; Kirby, B.M.; Zyl, L.V.; Mutepfa, D.L.R.; Casanueva, A.; Huddy, R.J.; Bauer, R.; Cowan, D.A.; Tuffin, M. An unusual feruloyl esterase belonging to family viii esterases and displaying a broad substrate range. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2015, 118, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds chloramphenicol propionate and chloramphenicol were available from the authors. |





| Chloramphenicol Esters | Enzyme | Resource | Concentration | t (h) | Solvent | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloramphenicol acetate | CAL-B | C. antarctica lipase | 0.15 M | 40 | 1,4-dioxane, | [8] |
| CAT | S. aureus | 0.0015 M | 12 | phosphate buffer | [19] | |
| Chloramphenicol propionate | CAL-B | C. antarctica lipase | 0.15 M | 6 | 1,4-dioxane, | [8] |
| CAT | S. aureus | 0.0015 M | 12 | phosphate buffer | [19] | |
| Chloramphenicol butyrate | CAT | S. aureus | 0.0015 M | 12 | phosphate buffer | [19] |
| Chloramphenicol succinate | NR | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Chloramphenicol pivalate | NR | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Chloramphenicol decanoate | NR | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Chlor5amphenicol laurate | CAL-B | C. antarctica lipase | 0.15 M | 24 | 1,4-dioxane | [8] |
| Chloramphenicol cinnamate | NR | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Chloramphenicol palmitate | CAL-B | C. antarctica lipase | 0.15 M | 24 | 1,4-dioxane | [8] |
| nanogel | T. lanuginosus | 0.15 M | 20 | acetonitrile | [13] | |
| lipase | -- | 70 mM | 120 | toluene | [17] | |
| Chloramphenicol propionate | LipBA | B.amyloliquefaciens | 0.25 M | 8 | 1,4-dioxane | -- |
| Compound | Chemical Structure | Ratio | Time (h) | Conversion a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl acetate |  | 5:1 | 4 | 55% |
| Vinyl propionate |  | 5:1 | 4 | 81% |
| Vinyl butyrate |  | 5:1 | 4 | 30% |
| Vinyl neononanoate |  | 5:1 | 4 | 23% |
| Vinyl decanoate |  | 5:1 | 4 | 20% |
| Vinyl laurate |  | 5:1 | 4 | 8% |
| Vinyl propionate |  | 5:1 | 4 | 69% |
| Vinyl propionate |  | 10:1 | 4 | 82% |
| Vinyl propionate |  | 15:1 | 4 | 84% |
| Factor | Solvent | ET(30) | Temperature | Time | Conversion b (%) | Purity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solvent | Control | - | 40 °C | 4 h | 0 | 0 |
| Toluene | 33.9 | 40 °C | 4 h | 50 ± 1.2 | 50 ± 0.7 | |
| 1,4-Dioxane | 36.0 | 40 °C | 4 h | 89 ± 2.1 | 95 ± 2.5 | |
| THF | 37.4 | 40 °C | 4 h | 70 ± 2.3 | 85 ± 2.6 | |
| Dichloromethane | 40.7 | 40 °C | 4 h | 60 ± 1.5 | 70 ± 1.5 | |
| Acetone | 42.2 | 40 °C | 4 h | 72 ± 0.7 | 75 ± 1.2 | |
| Acetonitrile | 45.6 | 40 °C | 4 h | 80 ± 1.4 | 85 ± 0.9 | |
| Ethanol | 51.9 | 40 °C | 4 h | 81 ± 0.9 | 87 ± 0.5 | |
| Temperature | 1,4-Dioxane | 36.0 | 20 °C | 4 h | 85 ± 1.7 | 93 ± 1.3 |
| 1,4-Dioxane | 36.0 | 30 °C | 4 h | 87 ± 2.3 | 95 ± 2.1 | |
| 1,4-Dioxane | 36.0 | 40 °C | 4 h | 89 ± 1.5 | 95 ± 2.8 | |
| 1,4-Dioxane | 36.0 | 50 °C | 4 h | 91 ± 2.2 | 99 ± 1.9 | |
| 1,4-Dioxane | 36.0 | 60 °C | 4 h | 90 ± 1.9 | 93 ± 2.4 | |
| Time | 1,4-Dioxane | 36.0 | 50 °C | 8 h | 98 ± 0.6 | 99 ± 1.5 |
| 1,4-Dioxane | 36.0 | 50 °C | 12 h | 96 ± 1.8 | 90 ± 1.2 | |
| 1,4-Dioxane | 36.0 | 50 °C | 16 h | 92 ± 2.1 | 85 ± 0.7 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, F.; Li, L.; Lin, L.; He, D.; Chen, J.; Wei, W.; Wei, D. Transesterification Synthesis of Chloramphenicol Esters with the Lipase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Molecules 2017, 22, 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091523
Dong F, Li L, Lin L, He D, Chen J, Wei W, Wei D. Transesterification Synthesis of Chloramphenicol Esters with the Lipase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Molecules. 2017; 22(9):1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091523
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Fengying, Lingmeng Li, Lin Lin, Dannong He, Jingwen Chen, Wei Wei, and Dongzhi Wei. 2017. "Transesterification Synthesis of Chloramphenicol Esters with the Lipase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens" Molecules 22, no. 9: 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091523
APA StyleDong, F., Li, L., Lin, L., He, D., Chen, J., Wei, W., & Wei, D. (2017). Transesterification Synthesis of Chloramphenicol Esters with the Lipase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Molecules, 22(9), 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091523