Modulation of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in LPS-Stimulated BV-2 Microglia by Prenylated Chalcones from Cullen corylifolium (L.) Medik. through Inhibition of I-κBα Degradation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
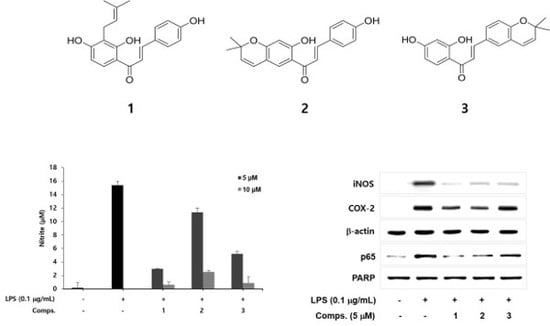
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Plant Material, Extraction and Isolation
3.3. Cell Culture
3.4. Measurement of Nitric Oxide Production
3.5. Peroxynitrite (ONOO−) Scavenging Assay
3.6. Prostagandin E2 Assay
3.7. Western Blot Analysis
3.8. Reverse Transcription and Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Analysis
3.9. Statistical Anaylsis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dheen, S.T.; Kaur, C.; Ling, E.A. Microglial activation and its implications in the brain diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, V.; Boyd-Kimball, D.; Scapagnini, G.; Butterfield, D.A. Nitric oxide and cellular stress response in brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders: The role of vitagenes. In Vivo 2004, 18, 245–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blaylock, R.L. Parkinson’s disease: Microglial/macrophage-induced immunoexcitotoxicity as a central mechanism of neurodegeneration. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2017, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forstermann, U.; Schmidt, H.H.; Pollock, J.S.; Sheng, H.; Mitchell, J.A.; Warner, T.D.; Nakane, M.; Murad, F. Isoforms of nitric oxide synthase. Characterization and purification from different cell types. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1991, 42, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, B.J. Nitric oxide in physiology and pathology. Histochem. J. 1995, 27, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebicke-Haerter, P.J. Microglia in neurodegeneration: Molecular aspects. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2001, 54, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, A.I.; Romanovsky, A.A. Prostaglandin E2 as a mediator of fever: Synthesis and catabolism. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 1977–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, K.J.; Jabbour, H.N. Cyclooxygenase enzymes and prostaglandins in pathology of the endometrium. Reproduction 2003, 126, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.W. Feeding the beast: Can microglia in the senesent brain be regulated by diet? Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Plastina, P.; Vincken, J.P.; Jansen, R.; Balvers, M.; Ten Klooster, J.P.; Gruppen, H.; Witkamp, R.; Meijerink, J. N-docosahexaenoyl dopamine, an endocannabinoid-like conjugate of dopamine and the n-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid, attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of microglia and macrophages via COX-2. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, B.; Dhingra, A.K.; Dhar, K.L. Psoralea corylifolia L. (Buguchi)—Folklore to modern evidence: Review. Fitoterapia 2013, 90, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Ryu, J.H. Prenylflavones from Psoralea corylifolia inhibit nitric oxide synthase expression through the inhibition of I-kappaB-alpha degradation in activated microglial cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 2253–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronikowska, J.; Szliszka, E.; Jaworska, D.; Czuba, Z.P.; Krol, W. The coumarin psoralidin enhances anticancer effect of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). Molecules 2012, 17, 6449–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Sarada, D.V. Antifungal activity of phenyl derivative of pyranocoumarin from Psoralea corylifolia L. seeds by inhibition of acetylation activity of trichothecene 3-o-acetyltransferase (Tri101). J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 310850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Z.; Hong, S.S.; Cai, X.F.; Dat, N.T.; Nan, J.X.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, D. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitory meroterpene analogues of bakuchiol, a constituent of the seeds of Psoralea corylifolia. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 2619–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, D.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Su, Y.F.; Fan, G.W.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, X.M. Phytoestrogens from Psoralea corylifolia reveal estrogen receptor-subtype selectivity. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Kim, D.H.; Ahn, H.N.; Song, Y.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Ryu, J.H. Activation of Estrogen Receptor by Bavachin from Psoralea corylifolia. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistelli, L.; Spera, K.; Flamini, G.; Mele, S.; Morelli, I. Isoflavonoids and chalcones from Anthyllis hermanniae. Phytochemistry 1996, 42, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, H.; Inoue, J.; Tamura, Y.; Mizutani, K. Antioxidative components of Psoralea corylifolia (Leguminosae). Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuete, V.; Sandjo, L.P. Isobavachalcone: An overview. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2012, 18, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, B.K.; Gupta, G.K.; Dhar, K.L.; Atal, C.K. A C-formylated chalcone from Psoralea corylifolia. Phytochemistry 1980, 19, 2034–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoshio, F.; Junko, N.; Taro, N. Five isoprenoid-substituted flavonoids from Glycyrrhiza eurycarpa. Phytochemistry 1993, 35, 515–519. [Google Scholar]
- Beckman, J.S.; Beckman, T.W.; Chen, J.; Marshall, P.A.; Freeman, B.A. Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: Implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1620–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guix, F.X.; Wahle, T.; Vennekens, K.; Snellinx, A.; Chavez-Gutierrez, L.; Ill-Raga, G.; Ramos-Fernandez, E.; Guardia-Laguarta, C.; Lleo, A.; Arimon, M.; Berezovska, O.; et al. Modification of gamma-secretase by nitrosative stress links neuronal ageing to sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Yoon, J.H.; Lim, H.J.; Kim, T.H.; Jin, C.; Kwak, W.J.; Han, C.K.; Ryu, J.H. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase expression in activated microglia and peroxynitrite scavenging activity by Opuntia ficus indica var. saboten. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, K.S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Transcription factor NF-kappaB: A sensor for smoke and stress signals. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1056, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Takeda, K. Role of nuclear IkappaB proteins in the regulation of host immune responses. J. Infect. Chemother. 2008, 14, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, F.; Lenardo, M.J. The nuclear signaling of NF-kappaB: Current knowledge, new insights, and future perspectives. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Fu, W.; Zhang, C.; Xu, D. Isobavachalcone attenuates MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease in mice by inhibition of microglial activation through NF-kB pathway. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Shon, D.H.; Youn, H.S. Isobavachalcone suppresses expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase induced by Toll-like receptor agonists. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 15, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.H.; Li, H.; Han, Y.E.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Ryu, J.-H. Modulation of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in LPS-Stimulated BV-2 Microglia by Prenylated Chalcones from Cullen corylifolium (L.) Medik. through Inhibition of I-κBα Degradation. Molecules 2018, 23, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010109
Kim DH, Li H, Han YE, Jeong JH, Lee HJ, Ryu J-H. Modulation of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in LPS-Stimulated BV-2 Microglia by Prenylated Chalcones from Cullen corylifolium (L.) Medik. through Inhibition of I-κBα Degradation. Molecules. 2018; 23(1):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010109
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Do Hee, Hua Li, Yeong Eun Han, Ji Hye Jeong, Hwa Jin Lee, and Jae-Ha Ryu. 2018. "Modulation of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in LPS-Stimulated BV-2 Microglia by Prenylated Chalcones from Cullen corylifolium (L.) Medik. through Inhibition of I-κBα Degradation" Molecules 23, no. 1: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010109
APA StyleKim, D. H., Li, H., Han, Y. E., Jeong, J. H., Lee, H. J., & Ryu, J. -H. (2018). Modulation of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in LPS-Stimulated BV-2 Microglia by Prenylated Chalcones from Cullen corylifolium (L.) Medik. through Inhibition of I-κBα Degradation. Molecules, 23(1), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010109