Polarizable ab initio QM/MM Study of the Reaction Mechanism of N-tert-Butyloxycarbonylation of Aniline in [EMIm][BF4]
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Parametrization
2.2. Molecular-Dynamics Simulations
2.3. Gas-Phase and Implicit Solvent Calculations
2.4. QM/MM Geometry and Reaction-Path Optimizations
2.5. Combined ELF/NCI Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Parametrization Results
3.2. Optimizations of Critical Points
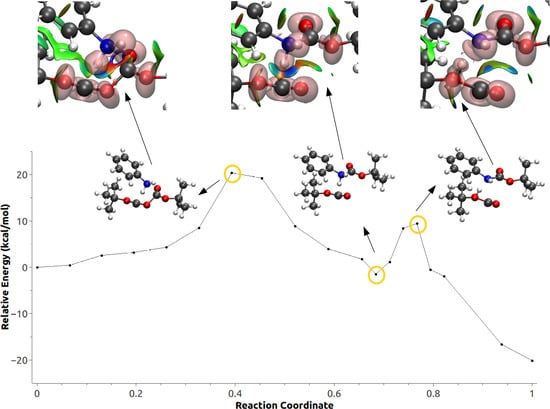
3.3. Minimum Energy Path Optimizations
3.4. Population and Topological Analyses for Critical Structures
3.5. Effect of Polarization on the Reaction Path
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IL | Ionic liquids |
| RTIL | Room temperature ionic liquid |
| EMIm | 1–Ethyl–3–methylimidazolium |
| BF | Tetrafluoroborate |
| QM | Quantum Mechanical |
| MM | Molecular Mechanical |
| MD | Molecular Dynamics |
| NPFF | Non–polarizable force fields |
| PFF | Polarizable force fields |
| GEM | Gaussian Electrostatic Model |
| TS | Transition State |
| RC | Reaction Coordinate |
| GP | Gas–phase |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| ELF | Electron Localization Function |
| NCI | Noncovalent Interaction |
| BFGS | Broyden–Fletcher–Goldfarb–Shanno |
References
- Walden, P. Molecular weights and electrical conductivity of several fused salts. Bull. Acad. Imp. Sci. (St. Petersburg) 1914, 8, 405–422. [Google Scholar]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids. solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids: From knowledge to application. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12518. [Google Scholar]
- Lipsztajn, M.; Osteryoung, R.A. Increased electrochemical window in ambient temperature neutral ionic liquids. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1983, 130, 1968–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Welton, T. (Eds.) Ionic Liquids in Synthesis, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Erbeldinger, M.; Mesiano, A.J.; Russell, A.J. Enzymatic catalysis of formation of z-aspartame in ionic liquid—An alternative to enzymatic catalysis in organic solvents. Biotechnol. Prog. 2000, 16, 1129–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira Lau, R.; Van Rantwijk, F.; Seddon, K.R.; Sheldon, R.A. Lipase-catalyzed reactions in ionic liquids. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 4189–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petkovic, M.; Seddon, K.R.; Rebelo, L.P.; Pereira, C.S. Ionic liquids: A pathway to environmental acceptability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1383–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, C.D.; Illner, P.; van Eldik, R. Understanding chemical reaction mechanisms in ionic liquids: Successes and challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 272–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids: Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. 2. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappe, C.; Malvaldi, M.; Pomelli, C.S. Ionic liquids: Solvation ability and polarity. Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappe, C.; Pieraccini, D. Ionic liquids: Solvent properties and organic reactivity. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2005, 18, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Roy, S.R.; Parikh, N.; Chakraborti, A.K. Nonsolvent application of ionic liquids: Organo-catalysis by 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium cation based room-temperature ionic liquids for chemoselective N-tert-butyloxycarbonylation of amines and the influence of the c-2 hydrogen on catalytic efficiency. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 7132–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chankeshwara, S.V.; Chakraborti, A.K. Catalyst-free chemoselective N-tert-butyloxycarbonylation of amines in water. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 3259–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingale, A.P.; More, V.K.; Gangarde, U.S.; Shinde, S.V. Chemoselective N-tert-butyloxycarbonylation of amines in glycerol. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 10142–10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambasivarao, S.V.; Acevedo, O. Development of OPLS-AA Force Field Parameters for 68 Unique Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2009, 5, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perez-Blanco, M.E.; Maginn, E.J. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Carbon Dioxide and Water at an Ionic Liquid Interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 35, 10488–10499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maginn, E.J. Molecular simulation of ionic liquids: Current status and future opportunities. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 373101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, B.L.; Balasubramanian, S.; Klein, M.L. Modelling room temperature ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2008, 29, 3339–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Pádua, A.A. Using Spectroscopic Data on Imidazolium Cation Conformations to Test a Molecular Force Field for Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7485–7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pópolo, M.G.; Lynden-Bell, R.M.; Kohanoff, J. Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics Simulation of a Room Temperature Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 5895–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, B.L.; Balasubramanian, S. Dynamics in a room–temperature ionic liquid: A computer simulation study of 1,3-dimethylimidazolium chloride. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 123, 144505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borodin, O.; Smith, G.D.; Kim, H. Viscosity of a Room Temperature Ionic Liquid: Predictions from Nonequilibrium and Equilibrium Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 4771–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borodin, O.; Smith, G.D. Development of Many–Body Polarizable Force Fields for Li–Battery Components: 1. Ether, Alkane, and Carbonate–Based Solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 6279–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwörer, M.; Wichmann, C.; Tavan, P. A polarizable QM/MM approach to the molecular dynamics of amide groups solvated in water. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 114504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sneskov, K.; Schwabe, T.; Christiansen, O.; Kongsted, J. Scrutinizing the effects of polarization in QM/MM excited state calculations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 18551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, J.M.; Steinmann, C.; Ruud, K.; Kongsted, J. Polarizable Density Embedding: A New QM/QM/MM-Based Computational Strategy. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 5344–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J. Energy components of aqueous solution: Insight from hybrid QM/MM simulations using a polarizable solvent model. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodin, O. Polarizable Force Field Development and Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 11463–11478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisneros, G.A. Application of gaussian electrostatic model (gem) distributed multipoles in the amoeba force field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 5072–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starovoytov, O.N.; Torabifard, H.; Cisneros, G.A. Development of amoeba force field for 1,3-dimethylimidazolium based ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 7156–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torabifard, H.; Starovoytov, O.N.; Ren, P.; Cisneros, G.A. Development of an amoeba water model using gem distributed multipoles. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2015, 134, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.J.; Allen, M.J.; Cisneros, G.A. Simulations of the water exchange dynamics of lanthanide ions in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ethyl sulfate ([EMIm][EtSO4]) and water. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 30323–30333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.J.; Lin, Z.; Allen, M.J.; Cisneros, G.A. Molecular Dynamics Investigation of Solvent–Exchange Reactions on Lanthanide Ions in Water/1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium Trifuloromethylsulfate ([EMIm][OTf])) and water. J. Phys. Chem. 2018, 148, 024503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torabifard, H.; Reed, L.; Berry, M.T.; Hein, J.E.; Menke, E.; Cisneros, G.A. Computational and Experimental Characterization of a Pyrrolidinium–Based Ionic Liquid for Electrolyte Applications. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 147, 161731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Díaz, E.G.; Vázquez-Montelongo, E.A.; Cisneros, G.A.; Castrejón-González, E.O. Computational investigation of non-covalent interactions in 1-butyl 3-methylimidazolium/bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide [BMIm][Tf2N] in EMD and NEMD. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 054303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponder, J.W.; Wu, C.; Ren, P.; Pande, V.S.; Chodera, J.D.; Schnieders, M.J.; Haque, I.; Mobley, D.L.; Lambrecht, D.S.; DiStasio, R.A., Jr.; et al. Current status of the amoeba polarizable force field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 2549–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, P.; Ponder, J.W. Consistent treatment of inter- and intramolecular polarization in molecular mechanics calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 2002, 23, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, P.; Wu, C.; Ponder, J.W. Polarizable atomic multipole-based molecular mechanics for organic molecules. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 3143–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisneros, G.A.; Piquemal, J.P.; Darden, T.A. Quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics electrostatic embedding with continuous and discrete functions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 13682–13684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, R.E.; Starovoytov, O.N.; Piquemal, J.P.; Cisneros, G.A. Gem*: A molecular electronic density-based force field for molecular dynamics simulations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piquemal, J.P.; Perera, L.; Cisneros, G.A.; Ren, P.; Pedersen, L.G.; Darden, T.A. Towards accurate solvation dynamics of divalent cations in water using the polarizable amoeba force field: From energetics to structure. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 054511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappe, C.; Pomelli, C.S. Computational studies on organic reactivity in ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, O. Simulating Chemical Reactions in Ionic Liquids Using QM/MM Methodology. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 11653–11666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, O.; Jorgensen, W.L. Advances in Quantum and Molecular Mechanical (QM/MM) Simulations for Organic and Enzymatic Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acevedo, O.; Jorgensen, W.L.; Evanseck, J.D. Elucidation of Rate Variations for a Diels–Alder Reaction in Ionic Liquids from QM/MM Simulations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2007, 3, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.; Ghebreab, R.; Doherty, B.; Li, B.; Acevedo, O. Examining Ionic Liquid Effects on Mononuclear Rearrangement of Heterocycles Using QM/MM Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 10786–10796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.; McCann, B.W.; Acevedo, O. Ionic Liquid Effects on Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions from QM/MM Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.; Sambasivarao, S.V.; Acevedo, O. An Ionic Liquid Dependent Mechanism for Base Catalyzed β-Elimination Reactions from QM/MM Simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Maxwell, D.S.; Tirado-Rives, J. Development and testing of the opls all-atom force field on conformational energetics and properties of organic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11225–11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Bruccoleri, R.E.; Olafson, B.D.; States, D.J.; Swaminathan, S.A.; Karplus, M. Charmm: A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 1983, 4, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanommeslaeghe, K.; Hatcher, E.; Acharya, C.; Kundu, S.; Zhong, S.; Shim, J.; Darian, E.; Guvench, O.; Lopes, P.; Vorobyov, I.; et al. Charmm general force field: A force field for drug-like molecules compatible with the charmm all-atom additive biological force fields. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearlman, D.A.; Case, D.A.; Caldwell, J.W.; Ross, W.S.; Cheatham, T.E., III; DeBolt, S.; Ferguson, D.; Seibel, G.; Kollman, P. Amber, a package of computer programs for applying molecular mechanics, normal mode analysis, molecular dynamics and free energy calculations to simulate the structural and energetic properties of molecules. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 91, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Piana, S.; Palmo, K.; Maragakis, P.; Klepeis, J.L.; Dror, R.O.; Shaw, D.E. Improved side-chain torsion potentials for the amber ff99sb protein force field. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2010, 78, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oostenbrink, C.; Villa, A.; Mark, A.E.; Van Gunsteren, W.F. A biomolecular force field based on the free enthalpy of hydration and solvation: The gromos force-field parameter sets 53a5 and 53a6. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1656–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.Y.; Torabifard, H.; Crawford, D.J.; DeNizio, J.E.; Cao, X.J.; Garcia, B.A.; Cisneros, G.A.; Kohli, R.M. Mutations along a TET2 active site scaffold stall oxidation at 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torabifard, H.; Cisneros, G.A. Insight into wild-type and T1372E TET2-mediated 5hmC oxidation using ab initio QM/MM calculations. Chem. Sci. 2018, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Fang, D.; Ito, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Ovchinnikov, V.; Cui, Q. QM/MM free energy simulations: Recent progress and challenges. Mol. Simul. 2016, 42, 1056–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roston, D.; Cui, Q. Chapter nine—QM/MM analysis of transition states and transition state analogues in metalloenzymes. In Methods in Enzymology; Voth, G.A., Ed.; Computational Approaches for Studying Enzyme Mechanism Part A; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 577, pp. 213–250. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilevskaya, T.; Khrenova, M.G.; Nemukhin, A.V.; Thiel, W. Methodological aspects of QM/MM calculations: A case study on matrix metalloproteinase-2. J. Comput. Chem. 2016, 37, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunk, E.; Rothlisberger, U. Mixed Quantum Mechanical/Molecular Mechanical Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Biological Systems in Ground and Electronically Excited States. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 6217–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.; Cisneros, G.A. Alternative pathway for the reaction catalyzed by DNA dealkylase AlkB from Ab initio QM/MM calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 5136–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.; Lord, R.L.; Cisneros, G.A. Ab Initio QM/MM Calculations Show an Intersystem Crossing in the Hydrogen Abstraction Step in Dealkylation Catalyzed by AlkB. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 6410–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, O.; Armacost, K. Claisen Rearrangements: Insight into Solvent Effects and “on Water” Reactivity from QM/MM Simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senn, H.M.; Thiel, W. QM/MM Methods for Biomolecular Systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 1198–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, J.M.; Hu, H.; Rudolph, J.; Yang, W. Mechanism of Cdc25B Phosphatase with the Small Molecule Substrate p-Nitrophenyl Phosphate from QM/MM-MFEP Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 5217–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Lu, Z.; Parks, J.M.; Burger, S.K.; Yang, W. Quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics minimum free-energy path for accurate reaction energetics in solution and enzymes: Sequential sampling and optimization on the potential of mean force surface. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 128, 034105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Lu, Z.; Yang, W. QM/MM Minimum Free-Energy Path: Methodology and Application to Triosephosphate Isomerase. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2007, 3, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tubert-Brohman, I.; Acevedo, O.; Jorgensen, W.L. Elucidation of Hydrolysis Mechanisms for Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase and Its Lys142Ala Variant via QM/MM Simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16904–16913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo, O.; Jorgensen, W.L. Medium Effects on the Decarboxylation of a Biotin Model in Pure and Mixed Solvents from QM/MM Simulations. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 4896–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisneros, G.A.; Liu, H.; Lu, Z.; Yang, W. Reaction path determination for quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical modeling of enzyme reactions by combining first order and second order “chain-of-replicas” methods. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 122, 114502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyden, A.; Lin, H.; Truhlar, D.G. Adaptive partitioning in combined quantum mechanical and molecular mechanical calculations of potential energy functions for multiscale simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 2231–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duster, A.W.; Wang, C.H.; Garza, C.M.; Miller, D.E.; Lin, H. Adaptive quantum/molecular mechanics: What have we learned, where are we, and where do we go from here? Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2017, 7, e1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Alhambra, C. A hybrid semiempirical quantum mechanical and lattice–sum method for electrostatic interactions in fluid simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slipchenko, L.V. Solvation of the excited states of chromophores in polarizable environment: Orbital relaxation versus polarization. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 8824–8830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giese, T.J.; York, D.M. Charge-dependent model for many-body polarization, exchange, and dispersion interactions in hybrid quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 194101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illingworth, C.J.; Parkes, K.E.; Snell, C.R.; Marti, S.; Moliner, V.; Reynolds, C.A. The effect of mm polarization on the qm/mm transition state stabilization: Application to chorismate mutase. Mol. Phys. 2008, 106, 1511–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, E.; Thiel, W. Solvent boundary potentials for hybrid qm/mm computations using classical drude oscillators: A fully polarizable model. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 4527–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, H.; Yamamoto, T. Variational calculation of quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical free energy with electronic polarization of solvent. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 134107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kratz, E.G.; Walker, A.R.; Lagardère, L.; Lipparini, F.; Piquemal, J.P.; Andrés Cisneros, G. Lichem: A qm/mm program for simulations with multipolar and polarizable force fields. J. Comput. Chem. 2016, 37, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, J.S.; Laffan, D.; Thomson, C.; Williams, M.T. Analysis of the reactions used for the preparation of drug candidate molecules. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becke, A.D.; Edgecombe, K.E. A simple measure of electron localization in atomic and molecular systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1990, 92, 5397–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvi, B.; Savin, A. Classification of chemical bonds based on topological analysis of electron localization functions. Nature 1994, 371, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvi, B. How topological partitions of the electron distributions reveal delocalization. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2004, 6, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.R.; Keinan, S.; Mori-Sanchez, P.; Contreras-Garcia, J.; Cohen, A.J.; Yang, W. Revealing Noncovalent Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6498–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Contreras-García, J.; Johnson, E.R.; Keinan, S.; Chaudret, R.; Piquemal, J.P.; Beratan, D.N.; Yang, W. NCIPLOT: A Program for Plotting Noncovalent Interaction Regions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillet, N.; Chaudret, R.; Contreras-García, J.; Yang, W.; Silvi, B.; Piquemal, J.P. Coupling Quantum Interpretative Techniques: Another Look at Chemical Mechanisms in Organic Reactions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 3993–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaudret, R.; Piquemal, J.P.; Cisneros, G.A. Correlation between electron localization and metal ion mutagenicity in DNA synthesis from QM/MM calculations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 11239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.; Chaudret, R.; Piquemal, J.P.; Cisneros, G.A. Toward a Deeper Understanding of Enzyme Reactions Using the Coupled ELF/NCI Analysis: Application to DNA Repair Enzymes. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 2156–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R. Gaussian09 Revision E.01, Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009.
- Parrish, R.M.; Burns, L.A.; Smith, D.G.; Simmonett, A.C.; DePrince, A.E., III; Hohenstein, E.G.; Bozkaya, U.; Sokolov, A.Y.; Di Remigio, R.; Richard, R.M.; et al. Psi4 1.1: An open-source electronic structure program emphasizing automation, advanced libraries, and interoperability. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2017, 13, 3185–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harger, M.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Dalby, K.; Lagardère, L.; Piquemal, J.P.; Ponder, J.; Ren, P. Tinker-openmm: Absolute and relative alchemical free energies using amoeba on gpus. J. Comput. Chem. 2017, 38, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.D.; Head-Gordon, M. Long-range corrected hybrid density functionals with damped atom–atom dispersion corrections. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 6615–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditchfield, R.H.; Hehre, W.J.; Pople, J.A. Self-Consistent Molecular-Orbital Methods. IX. An Extended Gaussian-Type Basis for Molecular-Orbital Studies of Organic Molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1971, 54, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Bernhard Schlegel, H. Combining synchronous transit and quasi-newton methods to find transition states. Isr. J. Chem. 2000, 33, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Duke, R.E.; Cisneros, G.A. A new smoothing function to introduce long-range electrostatic effects in QM/MM calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143, 044103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kratz, E.G.; Duke, R.E.; Cisneros, G.A. Long-range electrostatic corrections in multipolar/polarizable qm/mm simulations. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2016, 135, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkelman, G.; Uberuaga, B.P.; Jónsson, H. A climbing image nudged elastic band method for finding saddle points and minimum energy paths. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 9901–9904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, S.K.; Yang, W. Quadratic string method for determining the minimum-energy path based on multiobjective optimization. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 054109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisneros, G.A.; Yang, W. Comparison of reaction barriers in energy and free energy for enzyme catalysis. In Multi-Scale Quantum Models for Biocatalysis: Modern Techniques and Applications; York, D.M., Lee, T.-S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 57–78. [Google Scholar]
- Gokcan, H.; Vazquez-Montelongo, E.A.; Cisneros, G.A. LICHEM 1.1: Recent Improvements and New Capabilities. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2018. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Noury, S.; Krokidis, X.; Fuster, F.; Silvi, B. Computational tools for the electron localization function topological analysis. Comput. Chem. 1999, 23, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilmé, J.; Piquemal, J.P. Advancing beyond charge analysis using the electronic localization function: Chemically intuitive distribution of electrostatic moments. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, A.J. Distributed multipole analysis, or how to describe a molecular charge distribution. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1981, 83, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabifard, H.; Cisneros, G.A. Computational investigation of O2 diffusion through an intra-molecular tunnel in AlkB; influence of polarization on O2 transport. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6230–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Mechanism | Configuration C1 | Configuration C2 |
|---|---|---|
| a | 114.46 | 27.42 |
| b | 174.51 | – |
| c | −27.93 | −20.88 |
| d | −21.86 | −20.14 |
| Atom | Reactant | Transition State | Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| C(1) | 0.90(0.89) | 0.92(1.02) | 0.93(0.93) |
| O(13) | −0.45(−0.45) | −0.66(−0.66) | −0.60(−0.60) |
| N(43) | −0.95(−0.94) | −0.76(−0.76) | −0.79(−0.78) |
| H(44) | 0.39(0.39) | 0.42(0.43) | 0.40(00.39) |
| H(45) | 0.38(0.38) | 0.41(0.41) | 0.43(00.44) |
| Basin | GP Pop. | DCM Pop. | C1 TS1 Pop. | C2 TS1 Pop. | C2 TS2 Pop. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(H44,N43) | 2.26 | 2.24 | 2.16 | 2.21 | 2.17 |
| V(H45,N43) | 2.34 | 2.33 | 2.48 | 2.24 | – |
| V(C1,O15) | 1.79 | 1.73 | 1.69 | 1.61 | 1.87 |
| V(C1,O14) | 2.50 | 2.30 | 2.21 | 2.00 | 2.37 |
| V(C1,O13) | – | – | 1.23 | 1.20 | – |
| V(C6,O13) | 2.14 | 2.13 | 1.89 | 1.84 | 2.17 |
| V(C6,O12) | 2.68 | 2.65 | 2.57 | 2.64 | 2.44 |
| V(C1,N43) | 2.06 | 2.07 | 2.54 | 2.81 | 2.06 |
| V(H45) | – | – | – | – | 0.51 |
| Basin | 1st TS | MI | 2nd TS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pop. | (au) | Pop. | (au) | Pop. | (au) | |
| V(H44,N43) | 2.24 | 1.869 | 2.18 | 1.765 | 2.16 | 1.64 |
| V(H45,N43) | 2.31 | 1.817 | 2.18 | 1.756 | – | – |
| V(H45,O11) | – | – | – | – | 1.64 | 1.35 |
| V(C1,O15) | 1.86 | 0.08 | 1.93 | 0.073 | 1.84 | 0.041 |
| V(C1,O14) | 2.46 | 0.726 | 2.4 | 0.55 | 2.27 | 0.237 |
| V(C1,O13) | 1.23 | 0.319 | – | – | – | – |
| V(C1,N43) | – | – | 2.00 | 0.148 | 2.6 | 1.085 |
| V(C6,O13) | 1.67 | 0.069 | 2.09 | 0.242 | 2.39 | 0.577 |
| V(C6,O12) | 2.39 | 0.645 | 2.13 | 0.239 | 2.24 | 0.393 |
| V(C6,O11) | 1.81 | 0.019 | 1.58 | 0.061 | 1.18 | 0.294 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vázquez-Montelongo, E.A.; Vázquez-Cervantes, J.E.; Cisneros, G.A. Polarizable ab initio QM/MM Study of the Reaction Mechanism of N-tert-Butyloxycarbonylation of Aniline in [EMIm][BF4]. Molecules 2018, 23, 2830. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112830
Vázquez-Montelongo EA, Vázquez-Cervantes JE, Cisneros GA. Polarizable ab initio QM/MM Study of the Reaction Mechanism of N-tert-Butyloxycarbonylation of Aniline in [EMIm][BF4]. Molecules. 2018; 23(11):2830. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112830
Chicago/Turabian StyleVázquez-Montelongo, Erik Antonio, José Enrique Vázquez-Cervantes, and G. Andrés Cisneros. 2018. "Polarizable ab initio QM/MM Study of the Reaction Mechanism of N-tert-Butyloxycarbonylation of Aniline in [EMIm][BF4]" Molecules 23, no. 11: 2830. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112830
APA StyleVázquez-Montelongo, E. A., Vázquez-Cervantes, J. E., & Cisneros, G. A. (2018). Polarizable ab initio QM/MM Study of the Reaction Mechanism of N-tert-Butyloxycarbonylation of Aniline in [EMIm][BF4]. Molecules, 23(11), 2830. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112830