An Application of Fit Quality to Screen MDM2/p53 Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
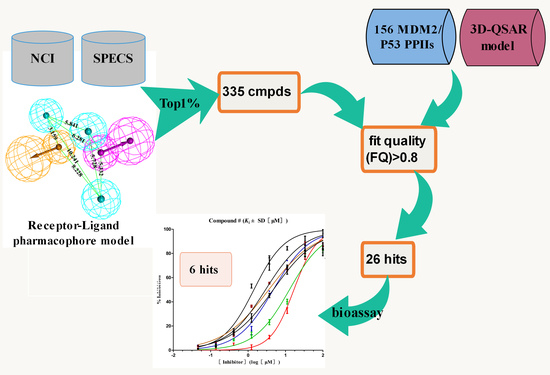
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Pharmacophore Model Generation
2.1.1. The Receptor-Ligand Pharmacophore Model Generation
2.1.2. The Generation and Validation of 3D-QSAR Pharmacophore Model
2.2. Development and Validation of Ligand Efficiency Based Virtual Screening Strategy
2.3. Hit Identification
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Pharmacophore Generation
4.1.1. The Generation and Validation of Receptor-Ligand Pharmacophore Model
4.1.2. The Generation 3D-QSAR Pharmacophore Model
4.2. Virtual Screening
4.2.1. Pharmacophore Screening
4.2.2. FQ-based Screening
4.3. Bioassay
4.3.1. In Vitro Antitumor Activity
4.3.2. Fluorescence Polarization Binding Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, J.G.; Bourbeau, M.P.; Wohlhieter, G.E.; Bartberger, M.D.; Michelsen, K.; Hungate, R.; Gadwood, R.C.; Gaston, R.D.; Evans, B.; Mann, L.W.; et al. Discovery and optimization of chromenotriazolopyrimidines as potent inhibitors of the mouse double minute 2-tumor protein 53 protein-protein interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7044–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, H.R.; Li, Z.; Yip, M.L.; Sung, S.S.; Lawrence, N.J.; McLaughlin, M.L.; McManus, G.J.; Zaworotko, M.J.; Sebti, S.M.; Chen, J.; et al. Identification of a disruptor of the MDM2-p53 protein-protein interaction facilitated by high-throughput in silico docking. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 3756–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, A.L.; Nikolovska-Coleska, Z.; Zhong, H.; Wang, S.; Carlson, H.A. Small molecule inhibitors of the MDM2-p53 interaction discovered by ensemble-based receptor models. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12809–12814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Discovery of a Nanomolar Inhibitor of the Human Murine Double Minute 2 (MDM2)-p53 Interaction through an Integrated, Virtual Database Screening Strategy. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3759–3762. [Google Scholar]
- Dezi, C.; Carotti, A.; Magnani, M.; Baroni, M.; Padova, A.; Cruciani, G.; Macchiarulo, A.; Pellicciari, R. Molecular Interaction Fields and 3D-QSAR Studies of p53−MDM2. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 1451–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Chi, S.-W.; Kim, D.-H.; Han, K.-H.; Irwin, D.K.; Guy, R.K. Proteomimetic Libraries-Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of p53-MDM2 Interaction Inhibitors. J. Comb. Chem. 2006, 8, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, J.M.; Wigle, T.J.; Norris, J.L.; Lam, R.; Korboukh, V.K.; Gao, C.; Ingerman, L.A.; Kireev, D.B.; Senisterra, G.; Vedadi, M.; et al. Small-molecule ligands of methyl-lysine binding proteins. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 2504–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manepalli, S.; Geffert, L.M.; Surratt, C.K.; Madura, J.D. Discovery of Novel Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors through Development of a Protein-Based Pharmacophore. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vu, B.; Wovkulich, P.; Pizzolato, G.; Lovey, A.; Ding, Q.; Jiang, N.; Liu, J.J.; Zhao, C.; Glenn, K.; Wen, Y.; et al. Discovery of RG7112: A Small-Molecule MDM2 Inhibitor in Clinical Development. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernard, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S. AM-8553: A novel MDM2 inhibitor with a promising outlook for potential clinical development. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 4934–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.J.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, J.; Ross, T.M.; Chu, X.J.; Bartkovitz, D.; Podlaski, F.; Janson, C.; et al. Discovery of RG7388, a potent and selective p53-MDM2 inhibitor in clinical development. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5979–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Li, Z.; Rew, Y.; Gribble, M.; Bartberger, M.D.; Beck, H.P.; Canon, J.; Chen, A.; Chen, X.; Chow, D.; et al. Discovery of AMG 232, a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable MDM2-p53 inhibitor in clinical development. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 1454–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P.; Masuya, K.; Furet, P.; Kallen, J.; Valat-Stachyra, T.; Ferretti, S.; Berghausen, J.; Bouisset-Leonard, M.; Buschmann, N.; Pissot-Soldermann, C.; et al. Discovery of a Dihydroisoquinolinone Derivative (NVP-CGM097): A Highly Potent and Selective MDM2 Inhibitor Undergoing Phase 1 Clinical Trials in p53wt Tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 6348–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, A.; Lu, J.; Liu, L.; Du, D.; Bernard, D.; McEachern, D.; Przybranowski, S.; Li, X.; Luo, R.; Wen, B.; et al. Discovery of 4-((3′R,4′S,5′R)-6′-Chloro-4′-(3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)-1′-ethyl-2′′-oxodispiro[ cyclohexane-1,2′-pyrrolidine-3′,3′′-indoline]-5′-carboxamido)bicyclo[2.2. 2]octane-1-carboxylic Acid (AA-115/APG-115): A Potent and Orally Active Murine Double Minute 2 (MDM2) Inhibitor in Clinical Development. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2819–2839. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Jonge, M.; de Weger, V.A.; Dickson, M.A.; Langenberg, M.; Le Cesne, A.; Wagner, A.J.; Hsu, K.; Zheng, W.; Mace, S.; Tuffal, G.; et al. A phase I study of SAR405838, a novel human double minute 2 (HDM2) antagonist, in patients with solid tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 76, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perola, E. An analysis of the binding efficiencies of drugs and their leads in successful drug discovery programs. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2986–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hann, M.M.; Keseru, G.M. Finding the sweet spot: The role of nature and nurture in medicinal chemistry. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L.; Groom, C.R.; Alex, A. Ligand efficiency: A useful metric for lead selection. Drug Discov. Today 2004, 9, 430–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L.; Keseru, G.M.; Leeson, P.D.; Rees, D.C.; Reynolds, C.H. The role of ligand efficiency metrics in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortes-Ciriano, I. Benchmarking the Predictive Power of Ligand Efficiency Indices in QSAR. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 1576–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugaya, N. Training based on ligand efficiency improves prediction of bioactivities of ligands and drug target proteins in a machine learning approach. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 2525–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, R.P. Debunking the Idea that Ligand Efficiency Indices Are Superior to pIC50 as QSAR Activities. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripphausen, P.; Nisius, B.; Peltason, L.; Bajorath, J. Quo vadis, virtual screening? A comprehensive survey of prospective applications. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8461–8467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gade, D.R.; Makkapati, A.; Yarlagadda, R.B.; Peters, G.J.; Sastry, B.S.; Rajendra Prasad, V.V.S. Elucidation of chemosensitization effect of acridones in cancer cell lines: Combined pharmacophore modeling, 3D QSAR, and molecular dynamics studies. Comput. Biol. Chem 2018, 74, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Cao, S.; Su, P.C.; Patel, R.; Shah, D.; Chokshi, H.B.; Szukala, R.; Johnson, M.E.; Hevener, K.E. Hit identification and optimization in virtual screening: Practical recommendations based on a critical literature analysis. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 6560–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colmenarejo, G. Compound Prioritization in Single-Concentration Screening Data Using Ligand Efficiency Indexes. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, C.H.; Tounge, B.A.; Bembenek, S.D. Ligand binding efficiency: Trends, physical basis, and implications. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 2432–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Wei, J.L.; Xu, L.L.; Xi, M.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Liu, F.; Guo, X.K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, M.Y.; et al. Effective screening strategy using ensembled pharmacophore models combined with cascade docking: Application to p53-MDM2 interaction inhibitors. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 2715–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolber, G.; Langer, T. LigandScout: 3-D pharmacophores derived from protein-bound ligands and their use as virtual screening filters. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anighoro, A.; Rastelli, G. Enrichment factor analyses on G-protein coupled receptors with known crystal structure. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolovska-Coleska, Z.; Wang, R.; Fang, X.; Pan, H.; Tomita, Y.; Li, P.; Roller, P.P.; Krajewski, K.; Saito, N.G.; Stuckey, J.A.; et al. Development and optimization of a binding assay for the XIAP BIR3 domain using fluorescence polarization. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 332, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–6 are available from the authors. |









 | ||||||
| Kia (μM) | MTT b IC50 c (μM) | Selectivity d | FQ e | FQ-Test f | ||
| HepG2 (wt-p53) | Hep3B (p53 null) | |||||
| 1 | 3.90 | 8.63 | 77.51 | 8.98 | 1.00 | 0.75 |
| 2 | 2.21 | 5.38 | 33.51 | 6.23 | 0.85 | 0.78 |
| 3 | 0.62 | 4.40 | 47.29 | 10.75 | 1.16 | 0.86 |
| 4 | 0.82 | 5.35 | 34.81 | 6.51 | 0.98 | 0.83 |
| 5 | 0.94 | 4.77 | 23.21 | 4.87 | 0.96 | 0.80 |
| 6 | 0.59 | 5.54 | 20.53 | 3.71 | 0.98 | 0.83 |
| Nutlin-3a | 0.25 | 2.31 | 25.35 | 10.97 | 1.01 | 0.84 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, X.; Bao, G.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Zhao, N.-Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.-L. An Application of Fit Quality to Screen MDM2/p53 Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123174
Xue X, Bao G, Zhang H-Q, Zhao N-Y, Sun Y, Zhang Y, Wang X-L. An Application of Fit Quality to Screen MDM2/p53 Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitors. Molecules. 2018; 23(12):3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123174
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Xin, Gang Bao, Hai-Qing Zhang, Ning-Yi Zhao, Yuan Sun, Yue Zhang, and Xiao-Long Wang. 2018. "An Application of Fit Quality to Screen MDM2/p53 Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitors" Molecules 23, no. 12: 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123174
APA StyleXue, X., Bao, G., Zhang, H. -Q., Zhao, N. -Y., Sun, Y., Zhang, Y., & Wang, X. -L. (2018). An Application of Fit Quality to Screen MDM2/p53 Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitors. Molecules, 23(12), 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123174