An Injectable, Dual Responsive, and Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Oxidized Sodium Alginate and Hydrazide-Modified Poly(ethyleneglycol)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
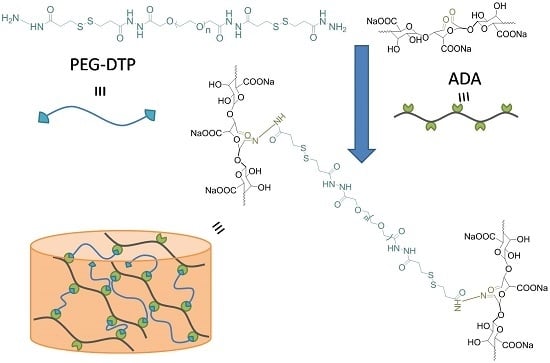
2.1. Preparation and Rheological Characterization of PEG-DTP/ADA Hydrogel
2.2. Mechanical Properties of ADA/PEG-DTP Hydrogels
2.3. Self-Healing and Injectability of PEG-DTP/ADA Hydrogels
2.4. Dual Responsive Properties of PEG-DTP/ADA Hydrogels
2.5. Degradation and Drug Release Ability of PEG-DTP/ADA Hydrogels
2.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Sodium Alginate Dialdehyde (ADA)
3.3. Synthesis of Hydrazide-Terminated Poly(ethyleneglycol) (PEG-DTP)
3.4. Preparation of PEG-DTP/ADA Hydrogel
3.5. Characterizations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, X.; Hilborn, J.; Heerschap, A.; Ossipov, D.A. Injectable in situ forming hybrid iron oxide-hyaluronic acid hydrogel for magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahanta, A.K.; Senapati, S.; Maiti, P. A polyurethane–chitosan brush as an injectable hydrogel for controlled drug delivery and tissue engineering. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 6233–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Pan, C.; Xu, T.; Zhang, L. Zwitterionic hydrogels promote skin wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 5105–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. 3D graphene oxide-polymer hydrogel: Near-infrared light-triggered active scaffold for reversible cell capture and on-demand release. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6737–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Tao, L. Synthesis of an injectable, self-healable and dual responsive hydrogel for drug delivery and 3D cell cultivation. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, R.; Griffith, M.; Phopase, J. Applications of self-assembling peptide scaffolds in regenerative medicine: The way to the clinic. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 8466–8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.J.; Urban, R.M.; Pourzal, R.; Turner, T.M.; Skipor, A.K.; Jacobs, J.J. Nanoscale surface modification by anodic oxidation increased bone ingrowth and reduced fibrous tissue in the porous coating of titanium-alloy femoral hip arthroplasty implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoque, J.; Bhattacharjee, B.; Prakash, R.G.; Paramanandham, K.; Haldar, J. Dual function injectable hydrogel for controlled release of antibiotic and local antibacterial therapy. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, Y. A thermo-degradable hydrogel with light-tunable degradation and drug release. Biomaterials 2017, 112, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Jia, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Liu, P. Facile preparation of pH/reduction dual-responsive prodrug nanohydrogels for tumor-specific intracellular triggered release with enhanced anticancer efficiency. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2840–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyarmati, B.; Vajna, B.; Nemethy, A.; Laszlo, K.; Szilagyi, A. Redox- and pH-responsive cysteamine-modified poly(aspartic acid) showing a reversible sol-gel transition. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.; An, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, R.; Qin, J.; Tian, Y.; Deng, K. Self-healable polymer gels with multi-responsiveness of gel–sol–gel transition and degradability. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Li, N.; Hua, Y.; Shi, Y.; Bao, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, L. Physiological pH-dependent gelation for 3D printing based on the phase separation of gelatin and oxidized dextran. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 13023–13026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.K.; Lee, D.S. In situ gelling pH- and temperature-sensitive biodegradable block copolymer hydrogels for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 193, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ma, X.; Dong, Q.; Song, D.; Hargrove, D.; Vora, S.R.; Ma, A.W.K.; Lu, X.; Lei, Y. Self-healing of thermally-induced, biocompatible and biodegradable protein hydrogel. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56183–56192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlato, M.; Reichert, S.; Barney, N.; Murphy, W.L. Poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels with adaptable mechanical and degradation properties for use in biomedical applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Su, Q.; Zhang, J.; Dong, A.; Lin, C.; Zhang, J. Facile access to multisensitive and self-healing hydrogels with reversible and dynamic boronic ester and disulfide linkages. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; An, H.; Qin, J. Self-activated healable hydrogels with reversible temperature responsiveness. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 25544–25551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Qian, W.; Chen, R.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Shi, D.; Dong, W.; Chen, M.; Zhao, Y. One-pot preparation of autonomously self-healable elastomeric hydrogel from boric acid and random copolymer bearing hydroxyl groups. ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, W.; Ngai, T.; Le, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, N.; Huang, Y.; Wen, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T. Mussel-inspired multifunctional supramolecular hydrogels with self-healing, shape memory and adhesive properties. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 5343–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wu, X.; Liu, F.; Dou, Y.; Hu, Z.; Hao, W. A fluorescent, self-healing and pH sensitive hydrogel rapidly fabricated from hpamam and oxidized alginate with injectability. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 34254–34260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; He, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X. Synergistic therapeutic effects of schiff’s base cross-linked injectable hydrogels for local co-delivery of metformin and 5-fluorouracil in a mouse colon carcinoma model. Biomaterials 2016, 75, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Liu, G.; Peng, L.; Guo, J.; Tao, L.; Yuan, J.; Chang, C.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L. Highly efficient self-healable and dual responsive cellulose-based hydrogels for controlled release and 3D cell culture. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1703174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halacheva, S.S.; Adlam, D.J.; Hendow, E.K.; Freemont, T.J.; Hoyland, J.; Saunders, B.R. Injectable biocompatible and biodegradable pH-responsive hollow particle gels containing poly(acrylic acid): The effect of copolymer composition on gel properties. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1814–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Wang, T.; Feng, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, K.; Chen, X.; Cui, L.; Yin, J. Injectable in situ self-cross-linking hydrogels based on poly(l-glutamic acid) and alginate for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 4495–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.; Kiser, P. In situcrosslinked hydrogels formed using Cu(I)-free huisgen cycloaddition reaction. Polym. Int. 2009, 58, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Du, F.; Song, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Cao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, G.; Yang, H.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of reactive poloxamer 407s for biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2009, 138, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Q.S.; El-Hamshary, H.; El-Newehy, M.; Mo, X. Injectable photo crosslinked enhanced double-network hydrogels from modified sodium alginate and gelatin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibizadeh, M.; Rostamizadeh, K.; Dalali, N.; Ramazani, A. Preparation and characterization of pegylated multiwall carbon nanotubes as covalently conjugated and non-covalent drug carrier: A comparative study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 74, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |









© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Q.; Xu, C.; Tang, Q.; Yang, H. An Injectable, Dual Responsive, and Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Oxidized Sodium Alginate and Hydrazide-Modified Poly(ethyleneglycol). Molecules 2018, 23, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030546
Wang L, Zhou W, Wang Q, Xu C, Tang Q, Yang H. An Injectable, Dual Responsive, and Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Oxidized Sodium Alginate and Hydrazide-Modified Poly(ethyleneglycol). Molecules. 2018; 23(3):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030546
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lei, Wanfu Zhou, Qingguo Wang, Chao Xu, Quan Tang, and Haiyang Yang. 2018. "An Injectable, Dual Responsive, and Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Oxidized Sodium Alginate and Hydrazide-Modified Poly(ethyleneglycol)" Molecules 23, no. 3: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030546
APA StyleWang, L., Zhou, W., Wang, Q., Xu, C., Tang, Q., & Yang, H. (2018). An Injectable, Dual Responsive, and Self-Healing Hydrogel Based on Oxidized Sodium Alginate and Hydrazide-Modified Poly(ethyleneglycol). Molecules, 23(3), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030546