Physicochemical Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Humic Acids Isolated from Peat of Various Origins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation of the HA Fractions
2.2. Partial Structural Characterization of the HA Fractions
2.3. Content of Carboxylic and Phenolic Groups in the HA Fractions
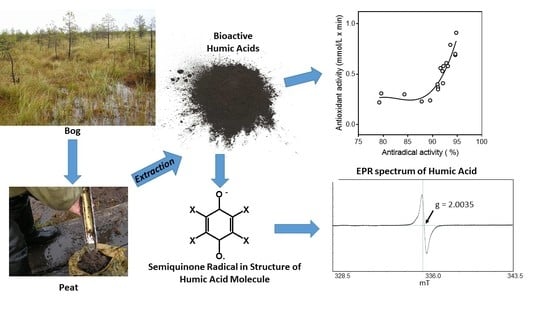
2.4. Antioxidant Activity of the HA Fractions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Isolation of HAs from Peat
3.2. Physical Characterization of HAs
3.3. High Performance Size-Exclusion Chromatography (HP-SEC)
3.4. Chemical Analysis of HAs
3.5. Free Radical Scavenging Activity
3.6. Electrochemical Experiments
3.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orlov, D.S. Humus Acids of Soils; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; p. 378. [Google Scholar]
- Schepetkin, I.; Khlebnikov, A.; Kwon, B.S. Medical drugs from humus matter: Focus on mumie. Drug Dev. Res. 2002, 57, 140–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rensburg, C.E.J. The antiinflammatory properties of humic substances: A mini review. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzeminski, T.F.; Nozynski, J.K.; Grzyb, J.; Porc, M.; Zeglen, S.; Filas, V.; Skopinska-Rozewska, E.; Sommer, E.; Filewska, M. Angiogenesis and cardioprotection after TNF α-inducer-Tolpa peat preparation treatment in rat’s hearts after experimental myocardial infarction in vivo. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2005, 43, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radomska-Lesniewska, D.M.; Skopinska-Rozewska, E.; Jozwiak, J.; Demkow, U.; Balan, B.J. Angiomodulatory properties of some antibiotics and Tolpa peat preparation. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 41, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzozowski, T.; Dembinski, A.; Konturek, S. Influence of Tolpa peat preparation on gastroprotection and on gastric and duodenal ulcers. Acta Pol. Pharm. 1994, 51, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Ah, S.Y.; Woo, S.B.; Jeong, C.S.; Klubachuk, O.N.; Kwon, B.S. Characterization and biological activities of humic substances from mumie. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5245–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Xie, G.; Jutila, M.A.; Quinn, M.T. Complement-fixing activity of fulvic acid from shilajit and other natural sources. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joone, G.K.; Dekker, J.; Elizabeth, C.; van Rensburg, J. Investigation of the immunostimulatory properties of oxihumate. Z. Naturforsch. (C) 2003, 58, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimova, E.S.; Zykova, M.V.; Ligacheva, A.A.; Sherstoboev, E.Y.; Zhdanov, V.V.; Belousov, M.V.; Yusubov, M.S.; Krivoshchekov, S.V.; Danilets, M.G.; Dygai, A.M. Effects of humic acids isolated from peat of various origin on in vitro production of nitric oxide: A screening study. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 161, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trofimova, E.S.; Zykova, M.V.; Ligacheva, A.A.; Sherstoboev, E.Y.; Zhdanov, V.V.; Belousov, M.V.; Yusubov, M.S.; Krivoshchekov, S.V.; Danilets, M.G.; Dygai, A.M. Influence of humic acids extracted from peat by different methods on functional activity of macrophages in vitro. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 162, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belousov, M.V.; Akhmedzhanov, R.R.; Zykova, M.V.; Arbuzov, A.N.; Gur’ev, A.M.; Yusubov, M.S. Antihypoxic activity of native humic acids of Tomsk lowland peat. Pharm. Chem. J. 2014, 48, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousov, M.V.; Akhmedzhanov, R.R.; Zykova, M.V.; Gur’ev, A.M.; Yusubov, M.S. Hepatoprotective properties of native humic acids isolated from lowland peat of Tomsk region. Pharm. Chem. J. 2014, 48, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belousov, M.V.; Akhmedzhanov, R.R.; Zykova, M.V.; Vasil’ev, K.Y.; Yusubov, M.S. Effect of native humic acids from Tomsk region lowland peat on mitochrondrial oxidative phosphorylation under hypoxic conditions. Pharm. Chem. J. 2015, 49, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zykova, M.V.; Belousov, M.V.; Lasukova, T.V.; Gorbunov, A.S.; Logvinova, L.A.; Dygai, A.M. Cardiovascular effects of high-molecular-weight compounds of humic nature. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 163, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pukhova, G.G.; Druzhina, N.A.; Stepchenko, L.M.; Chebotarev, E.E. Effect of sodium humate on animals irradiated with lethal doses. Radiobiologiia 1987, 27, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.J.; Lee, Y.S. Humic-acid: inhibitor of plasmin. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 114, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Y.C.; Wang, S.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Lu, F.J.; Gau, R.J.; Chang, W.C.; Liu, T.Z.; Yang, H.L. Humic acid induces the generation of nitric oxide in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: Stimulation of nitric oxide synthase during cell injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinimehr, S.J. Foundation review: Trends in the development of radioprotective agents. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brezani, V.; Smejkal, K.; Hosek, J.; Tomasova, V. Anti-inflammatory natural prenylated phenolic compounds—Potential lead substances. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altemimi, A.; Lakhssassi, N.; Baharlouei, A.; Watson, D.G.; Lightfoot, D.A. Phytochemicals: Extraction, isolation, and identification of bioactive compounds from plant extracts. Plants 2017, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkan, A.; Sen, H.M.; Sehitoglu, I.; Alacam, H.; Guven, M.; Aras, A.B.; Akman, T.; Silan, C.; Cosar, M.; Karaman, H.I.O. Neuroprotective effect of humic acid on focal cerebral ischemia injury: An experimental study in rats. Inflammation 2015, 38, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbas, A.; Silan, C.; Gulpinar, M.T.; Sancak, E.B.; Ozkanli, S.S.; Cakir, D.U. Renoprotective effect of humic acid on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury: An experimental study in rats. Inflammation 2015, 38, 2042–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagin, Y.F.; Sahin, N.; Polat, A.; Erdogan, M.A.; Atayan, Y.; Eyol, E.; Bilgic, Y.; Seckin, Y.; Colak, C. The acute effect of humic acid on iron accumulation in rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 171, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.X.; Wang, Z.J.; Peng, A.; Hou, J.W.; Xin, W.J. Interaction between fulvic acids of different origins and active oxygen radicals. Sci. China Ser. C 1996, 39, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Avvakumova, N.P.; Gerchikov, A.Y.; Khairullina, V.R.; Zhdanova, A.V. Antioxidant properties of humic substances isolated from peloids. Pharm. Chem. J. 2011, 45, 192–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeschbacher, M.; Graf, C.; Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Sander, M. Antioxidant properties of humic substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4916–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, E.X.; Li, Y.; Niu, J.F.; Zhou, Y.J.; Wang, T.Y.; Crittenden, J.C. Relative importance of humic and fulvic acid on ROS generation, dissolution, and toxicity of sulfide nanoparticles. Water Res. 2017, 124, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adekunle, I.M.; Ajuwon, O.R. Influence of humic acid derived from composted wastes of Nigeria origin on oxidative and antioxidant status of African mud catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Pakistan J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 13, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, S.; D’Addario, C.; Bonechi, C.; Leone, G.; Tognazzi, A.; Consumi, M.; Magnani, A.; Rossi, C. Increasing photostability and water-solubility of carotenoids: Synthesis and characterization of beta-carotene-humic acid complexes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2010, 101, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, M.A.; Ahmad, N.; Agarwal, S.P.; Mahmood, D.; Khalid Anwer, M.; Iqbal, Z. Comparative evaluation of humic substances in oral drug delivery. Results Pharma Sci. 2011, 1, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karadirek, S.; Kanmaz, N.; Balta, Z.; Demircivi, P.; Uzer, A.; Hizal, J.; Apak, R. Determination of total antioxidant capacity of humic acids using CUPRAC, Folin-Ciocalteu, noble metal nanoparticle- and solid-liquid extraction-based methods. Talanta 2016, 153, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, O.V.; Efimova, I.V.; Khil’ko, S.L. Antioxidant and pro-oxidant activity of ascorbic and humic acids in radical-chain oxidation processes. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 85, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimova, I.V.; Khil’ko, S.L.; Smirnova, O.V. Antioxidant activity of humic acids in radical-chain oxidation processes. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 85, 1351–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Zykova, M.V.; Belousov, M.V.; Gur’ev, A.M.; Akhmedzhanov, R.R.; Yusubov, M.S. Standardization of humic acids of lowland wood-grass peat from tomsk region. Pharm. Chem. J. 2014, 47, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetvicka, V.; Vashishta, A.; Fuentes, M.; Baigorri, R.; Garcia-Mina, J.M.; Yvin, J.-C. The relative abundance of oxygen alkyl-related groups in aliphatic domains is involved in the main pharmacological-pleiotropic effects of humic acids. J. Med. Food 2013, 16, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Esteves, V.I.; Duarte, A.C. Differences between humic substances from riverine, estuarine, and marine environments observed by fluorescence spectroscopy. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2001, 28, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudina, N.V.; Pisareva, S.I.; Saratikov, A.S. Antiulcerogenic activity of phenol compounds of peat. Chem. Plant. Mater. 1998, 289, G1024–G1029. [Google Scholar]
- Gostishcheva, M.V.; Belousov, M.V.; Yusubov, M.S.; Ismatova, R.R.; Dmitruk, S.E. Comparative IR spectral characteristics of humic acids from peats of different origin in the Tomsk area. Pharm. Chem. J. 2009, 43, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perminova, I.V.; Frimmel, F.H.; Kudryavtsev, A.V.; Kulikova, N.A.; Abbt-Braun, G.; Hesse, S.; Petrosyan, V.S. Molecular weight characteristics of humic substances from different environments as determined by size exclusion chromatography and their statistical evaluation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 2477–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boguta, P.; Sokolowska, Z. Interactions of Zn(II) ions with humic acids isolated from various type of soils. Effect of pH, Zn concentrations and humic acids chemical properties. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vialykh, E.A.; Ilarionov, S.A.; Abdelrahman, H.M.; Vialykh, I.A. Changes in amino acids content of humic acids sequentially extracted from peat and sod-podzolic soil. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 94, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccone, C.; Miano, T.M.; Shotyk, W. Qualitative comparison between raw peat and related humic acids in an ombrotrophic bog profile. Org. Geochem. 2007, 38, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, A.; Ripmeester, J.A. Isolation and characterization of humic acids from Alberta oil sands and related materials. Fuel 1990, 69, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, B.P.; Dittmar, T. From mass to structure: An aromaticity index for high-resolution mass data of natural organic matter. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Huang, W.L.; Peng, P.; Sheng, G.Y.; Fu, J.M. Chemical and molecular heterogeneity of humic acids repetitively extracted from a peat. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, B.E.; Chen, H.M.; Hatcher, P.G. A non-thermogenic source of black carbon in peat and coal. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 144, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gu, B.H.; LeBoeuf, E.J.; Pan, H.J.; Dai, S. Spectroscopic characterization of the structural and functional properties of natural organic matter fractions. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, T.M.; Senesi, N. Synchronous excitation fluorescence spectroscopy applied to soil humic substances chemistry. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 118, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsolnay, A.; Baigar, E.; Jimenez, M.; Steinweg, B.; Saccomandi, F. Differentiating with fluorescence spectroscopy the sources of dissolved organic matter in soils subjected to drying. Chemosphere 1999, 38, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T. Fluorescence inner-filtering correction for determining the humification index of dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.; Nada, A.; Kamal, D.E. Density functional theory and FTIR spectroscopic study of carboxyl group. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2005, 43, 911–917. [Google Scholar]
- Korotkova, E.I.; Karbainov, Y.A.; Avramchik, O.A. Investigation of antioxidant and catalytic properties of some biologically active substances by voltammetry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 375, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mal’tseva, E.V.; Yudina, N.V.; Lomovskii, O.I. Electrochemical reduction of oxygen in the presence of humic acids. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 2011, 85, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffaldi, R.; Schnitzer, M. Electron-spin resonance spectrometry of humic substances. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 1972, 36, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwicki, M.; Jaszewski, A.R.; Jezierska, J.; Jerzykiewicz, M.; Jezierski, A. The pH-induced shift in the g-tensor components of semiquinone-type radicals in humic acids-DFT and EPR studies. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2008, 462, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.M.; Valentao, P.; Pereira, J.A.; Andradeet, P.B. Phenolics: From chemistry to biology. Molecules 2009, 14, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebnikov, A.I.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Domina, N.G.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Quinn, M.T. Improved quantitative structure-activity relationship models to predict antioxidant activity of flavonoids in chemical, enzymatic, and cellular systems. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 1749–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurmi, J.T.; Tratnyek, P.G. Electrochemical properties of natural organic matter (NOM), fractions of nom, and model biogeochemical electron shuttles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitzer, M.; Levesque, M. Electron-spin resonance as a guide to the degree of humification of peats. Soil Sci. 1979, 127, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.H.; Simoes, M.L.; de Oliveira, L.C.; Rocha, J.C.; Neto, L.M.; Milori, D.M.B.P. Multimethod study of the degree of humification of humic substances extracted from different tropical soil profiles in Brazil’s Amazonian region. Geoderma 2005, 127, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segnini, A.; Posadas, A.; Quiroz, R.; Milori, D.M.B.P.; Saab, S.C.; Neto, L.M.; Vaz, C.M.P. Spectroscopic assessment of soil organic matter in wetlands from the high Andes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandiran, P.; Santhoshkumar, P.; Vasanthkumar, S. Synthesis of chemical and electrochemical ‘off-on-off’ fluorescent switches of new 5H-benzo[b]carbazole-6,11-dione derivatives. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretennikova, E.E. Lead in the natural peat cores of ridge-hollow complex in the taiga zone of West Siberia. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 80, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, M.M.D.; Arend, K.; Fernandes, A.N.; Giovanela, M.; Szpoganicz, B. Application of potentiometry to characterize acid and basic sites in humic substances - testing the BEST7 program with a weak-acid mixture. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 445, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandwilliams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free-radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Sahgal, G.; Ramanathan, S.; Sasidharan, S.; Mordi, M.N.; Ismail, S.; Mansor, S.M. In vitro antioxidant and xanthine oxidase inhibitory activities of methanolic Swietenia mahagoni seed extracts. Molecules 2009, 14, 4476–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avramchik, O.A.; Korotkova, E.I.; Plotnikov, E.; Lukina, A.; Karbainov, Y.A. Antioxidant and electrochemical properties of calcium and lithium ascorbates. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 37, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of peat and humic acids are available from the authors. |







| Peat Type, Sample Name, Sampling Depth (cm), and Degree of Decay (%) | Fraction | Yield (%) | E4:E6 | HIX | Mr (kDa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raised bog sphagnum Peat 1, 20–70 cm, 5–10% | HAb-1 | 6.5 ± 0.1 | 2.85 ± 0.05 | 0.99 | 34.6 |
| HAp-1 | 3.1 ± 0.1 a | 1.50 ± 0.02 b | 0.83 | 39.7 | |
| Raised bog pine-cotton-grass, Peat 2, 10–50 cm, 30–35% | HAb-2 | 31.4 ± 0.2 | 2.91 ± 0.02 | 0.69 | 19.0 |
| HAp-2 | 13.2 ± 0.1 a | 2.04 ± 0.02 b | 0.66 | 22.8 | |
| Raised bog magellanicum, Peat 3, 20–70 cm, 10–15% | HAb-3 | 16.9 ± 0.1 | 3.17 ± 0.01 | 0.75 | 27.8 |
| HAp-3 | 4.2 ± 0.1 a | 2.15 ± 0.01 b | 0.76 | 18.8 | |
| Raised bog fuscum, Peat 4, 20–70 cm, 5–10% | HAb-4 | 13.3 ± 0.1 | 2.91 ± 0.02 | 0.73 | 31.4 |
| HAp-4 | 3.9 ± 0.1 a | 1.53 ± 0.02 b | 0.49 | 25.8 | |
| Low-mire woody, Peat 5, 10–50 cm, 25–30% | HAb-5 | 38.2 ± 0.4 | 2.91 ± 0.03 | 0.81 | 24.4 |
| HAp-5 | 26.0 ± 0.3 a | 1.68 ± 0.04 b | 0.80 | 21.2 | |
| Low-mire grass-moss, Peat 6, 200–250 cm, 35–50% | HAb-6 | 21.5 ± 0.2 | 3.41 ± 0.02 | 0.98 | 22.1 |
| HAp-6 | 6.8 ± 0.1 a | 1.34 ± 0.01 b | 0.85 | 20.9 | |
| Low-mire grass, Peat 7, 230–270 cm, 40–45% | HAb-7 | 37.3 ± 0.4 | 3.25 ± 0.06 | 1.21 | 20.8 |
| HAp-7 | 17.4 ± 0.6 a | 1.48 ± 0.01 b | 1.14 | 16.7 | |
| Low-mire woody peat, Peat 8, 50–100 cm, 30–35% | HAb-8 | 38.6 ± 0.1 | 3.18 ± 0.07 | 1.01 | 17.6 |
| HAp-8 | 17.9 ± 0.1 a | 1.68 ± 0.01 b | 1.07 | 17.2 | |
| Mesotrophic carex peat, Peat 9, 150–200 cm, 40–45% | HAb-9 | 27.3 ± 0.1 | 3.13 ± 0.05 | 0.78 | 20.0 |
| HAp-9 | 8.0 ± 0.1 a | 1.38 ± 0.01 b | 0.88 | 17.5 |
| Fraction | С | Н | N | О |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAb-1 | 53.3 ± 0.61 | 6.0 ± 0.06 | 3.9 ± 0.04 | 28.6 ± 0.39 |
| HAp-1 | 42.5 ± 0.61 a | 4.6 ± 0.05 a | 3.9 ± 0.04 | 28.5 ± 0.38 |
| HAb-2 | 52.2 ± 0.64 | 5.6 ± 0.05 | 2.8 ± 0.03 | 31.5 ± 0.36 |
| HAp-2 | 52.2 ± 0.65 | 4.8 ± 0.05 a | 2.2 ± 0.03 a | 31.6 ± 0.39 |
| HAb-3 | 54.2 ± 0.68 | 6.0 ± 0.06 | 3.9 ± 0.05 | 30.9 ± 0.45 |
| HAp-3 | 51.5 ± 0.64 a | 4.8 ± 0.05 a | 3.4 ± 0.04 a | 30.1 ± 0.40 |
| HAb-4 | 53.9 ± 0.69 | 6.0 ± 0.05 | 3.5 ± 0.04 | 30.0 ± 0.45 |
| HAp-4 | 49.3 ± 0.62 a | 4.7 ± 0.05 a | 3.2 ± 0.04 | 33.6 ± 0.44 a |
| HAb-5 | 51.8 ± 0.74 | 5.4 ± 0.05 | 3.5 ± 0.03 | 31.5 ± 0.38 |
| HAp-5 | 52.5 ± 0.65 | 4.6 ± 0.05 a | 3.1 ± 0.04 a | 27.8 ± 0.36 a |
| HAb-6 | 52.3 ± 0.65 | 5.1 ± 0.05 | 3.4 ± 0.05 | 32.8 ± 0.38 |
| HAp-6 | 46.4 ± 0.61 a | 4.2 ± 0.04 a | 3.2 ± 0.03 | 29.3 ± 0.38 a |
| HAb-7 | 49.2 ± 0.62 | 4.8 ± 0.05 | 3.6 ± 0.04 | 29.0 ± 0.46 |
| HAp-7 | 49.5 ± 0.62 | 4.1 ± 0,04 a | 3.3 ± 0.03 | 28.5 ± 0.35 |
| HAb-8 | 51.7 ± 0.57 | 5.4 ± 0.05 | 3.8 ± 0.03 | 32.1 ± 0.39 |
| HAp-8 | 52.1 ± 0.65 | 4.5 ± 0.04 a | 3.1 ± 0.03 a | 31.0 ± 0.42 |
| HAb-9 | 52.7 ± 0.56 | 5.3 ± 0.06 | 3.0 ± 0.03 | 32.0 ± 0.38 |
| HAp-9 | 51.9 ± 0.63 | 4.7 ± 0,05 a | 3.1 ± 0,03 | 30.6 ± 0.43 |
| Fraction | Acid Groups (mmol/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| СООН | ОНphenolic | Total Acidity | |
| HAb-1 | 2.5 ± 0.01 | 2.7 ± 0.03 | 5.2 ± 0.06 |
| HAp-1 | 2.4 ± 0.01 | 3.4 ± 0.02 a | 5.7 ± 0.03 a |
| HAb-2 | 2.8 ± 0.01 | 2.9 ± 0.01 | 5.8 ± 0.02 |
| HAp-2 | 2.7 ± 0.01 | 4.1 ± 0.02 a | 6.8 ± 0.04 a |
| HAb-3 | 2.4 ± 0.01 | 2.2 ± 0.03 | 5.7 ± 0.06 |
| HAp-3 | 2.8 ± 0.01 a | 3.3 ± 0.02 a | 6.1 ± 0.03 a |
| HAb-4 | 2.6 ± 0.01 | 3.5 ± 0.03 | 6.1 ± 0.06 |
| HAp-4 | 2.5 ± 0.01 | 3.6 ± 0.02 | 6.1 ± 0.03 |
| HAb-5 | 2.8 ± 0.01 | 3.1 ± 0.02 | 5.9 ± 0.03 |
| HAp-5 | 2.8 ± 0.01 | 3.2 ± 0.03 | 6.0 ± 0.05 |
| HAb-6 | 2.8 ± 0.01 | 3.1 ± 0.01 | 5.9 ± 0.01 |
| HAp-6 | 2.6 ± 0.01 a | 3.5 ± 0.02 a | 6.2 ± 0.03 a |
| HAb-7 | 2.6 ± 0.01 | 4.1 ± 0.03 | 6.7 ± 0.06 |
| HAp-7 | 2.7 ± 0.01 | 4.8 ± 0.03 a | 7.5 ± 0.06 a |
| HAb-8 | 2.6 ± 0.01 | 3.1 ± 0.02 | 5.7 ± 0.03 |
| HAp-8 | 3.0 ± 0,01 a | 3.5 ± 0.02 a | 6.5 ± 0.04 a |
| HAb-9 | 2.6 ± 0,01 | 3.1 ± 0.01 | 5.7 ± 0.01 |
| HAp-9 | 3.1 ± 0.01 a | 3.1 ± 0.01 | 6.2 ± 0.02 a |
| Fraction | Voltammetry (µmol/L × min−1) | DPPH (% Inhibition) | PMC (spin/g × 10−16) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HAb-1 | 0.24 ± 0.05 | 89.5 ± 0.02 | 5.47 |
| HAp-1 | 0.23 ± 0.03 | 87.8 ± 0.14 a | 5.05 |
| HAb-2 | 0.37 ± 0.05 | 91.1 ± 0.20 | 6.60 |
| HAp-2 | 0.58 ± 0.06 a | 92.2 ± 0.12 | 7.06 |
| HAb-3 | 0.56 ± 0.03 | 91.6 ± 0.22 | 7.57 |
| HAp-3 | 0.35 ± 0.04 a | 91.1 ± 0.20 | 5.55 |
| HAb-4 | 0.61 ± 0.05 | 92.8 ± 0.26 | 7.8 |
| HAp-4 | 0.79 ± 0.06 a | 93.6 ± 0.15 | 8.69 |
| HAb-5 | 0.40 ± 0.05 | 91.0 ± 0.20 | 5.91 |
| HAp-5 | 0.53 ± 0.02 a | 92.0 ± 0.23 | 6.78 |
| HAb-6 | 0.58 ± 0.06 | 93.1 ± 0.27 | 7.93 |
| HAp-6 | 0.69 ± 0.07 a | 94.6 ± 0.18 | 14.4 |
| HAb-7 | 0.70 ± 0.02 | 94.6 ± 0.25 | 9.6 |
| HAp-7 | 0.91 ± 0.05 a | 94.8 ± 0.18 | 16.3 |
| HAb-8 | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 84.3 ± 0.01 | 5.42 |
| HAp-8 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 79.6 ± 0.12 a | 5.74 |
| HAb-9 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 79.2 ± 0.11 | 4.49 |
| HAp-9 | 0.41 ± 0.05 a | 92.1 ± 0.14 a | 6.9 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zykova, M.V.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Belousov, M.V.; Krivoshchekov, S.V.; Logvinova, L.A.; Bratishko, K.A.; Yusubov, M.S.; Romanenko, S.V.; Quinn, M.T. Physicochemical Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Humic Acids Isolated from Peat of Various Origins. Molecules 2018, 23, 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040753
Zykova MV, Schepetkin IA, Belousov MV, Krivoshchekov SV, Logvinova LA, Bratishko KA, Yusubov MS, Romanenko SV, Quinn MT. Physicochemical Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Humic Acids Isolated from Peat of Various Origins. Molecules. 2018; 23(4):753. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040753
Chicago/Turabian StyleZykova, Maria V., Igor A. Schepetkin, Mikhail V. Belousov, Sergey V. Krivoshchekov, Lyudmila A. Logvinova, Kristina A. Bratishko, Mekhman S. Yusubov, Sergey V. Romanenko, and Mark T. Quinn. 2018. "Physicochemical Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Humic Acids Isolated from Peat of Various Origins" Molecules 23, no. 4: 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040753
APA StyleZykova, M. V., Schepetkin, I. A., Belousov, M. V., Krivoshchekov, S. V., Logvinova, L. A., Bratishko, K. A., Yusubov, M. S., Romanenko, S. V., & Quinn, M. T. (2018). Physicochemical Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Humic Acids Isolated from Peat of Various Origins. Molecules, 23(4), 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040753