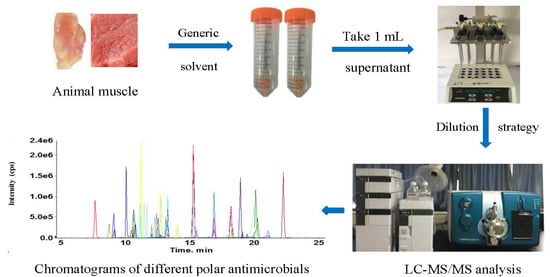
Quick Multi-Class Determination of Residues of Antimicrobial Veterinary Drugs in Animal Muscle by LC-MS/MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of LC-MS/MS Conditions
2.1.1. Optimization of MS/MS Parameters
2.1.2. Optimization of Chromatographic Conditions
2.2. Optimization of Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Screening of the Generic Extraction Solvent
2.2.2. Sample Dilution Strategy
2.3. Method Validation
2.4. Matrix Effects
2.5. Method Application
2.6. Comparison of the Proposed Method and Method from the Literature
3. Materials and Methods
3.1 Reagents and Materials
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.2.1. The Proposed Method
3.2.2. The Method Reported in Literature [32]
3.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis
3.4. Method Validation
3.5. Matrix Effects
3.6. Method Application
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stolker, A.A.; Brinkman, U.A. Analytical strategies for residue analysis of veterinary drugs and growth-promoting agents in food-producing animals—A review. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1067, 15–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulletin 168; Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 2–14.
- Boix, C.; Ibáñez, M.; Sancho, J.V.; León, N.; Yusá, V.; Hernández, F. Qualitative screening of 116 veterinary drugs in feed by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry: Potential application to quantitative analysis. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kemper, N. Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.P.; Reyes, R.C.; Romerogonzález, R.; Frenich, A.G.; Vidal, J.L. Development and validation of a multiclass method for the determination of veterinary drug residues in chicken by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2012, 89, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.L. Environmental pollution by antibiotics and by antibiotic resistance determinants. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2893–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulletin 235; Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 6–25.
- European Commission (EC); Commission Regulation (EU). No. 37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on pharmacologically active substances and their classification regarding maximum residue limits in foodstuffs of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2010, 15, 3–36. [Google Scholar]
- Christodoulou, E.A.; Samanidou, V.F.; Papadoyannis, I.N. Validation of an HPLC-UV method according to the European Union Decision 2002/657/EC for the simultaneous determination of 10 quinolones in chicken muscle and egg yolk. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 859, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassouan, M.K.; Ballesteros, O.; Zafra, A.; Vílchez, J.L.; Navalón, A. Multiresidue method for simultaneous determination of quinolone antibacterials in pig kidney samples by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 859, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, C.; Codony, R.; Compañó, R.; Granados, M.; Prat, M.D. Determination of macrolide antibiotics by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 910, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoev, G.; Michailova, A. Quantitative determination of sulfonamide residues in foods of animal origin by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 871, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, H.; Tie, X.; Ren, Y. Simultaneous determination of 24 sulfonamide residues in meat by ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1200, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado, N.; Morantezarcero, S.; Pérezquintanilla, D.; Sierra, I. Application of a hybrid ordered mesoporous silica as sorbent for solid-phase multi-residue extraction of veterinary drugs in meat by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to ion-trap tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1459, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, A.; Butcher, P.; Maden, K.; Widmer, M. Quantitative multiresidue method for about 100 veterinary drugs in different meat matrices by sub 2-microm particulate high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1194, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Ding, S.; Jiang, H.; Shen, J.; Xia, X. Multiresidue analysis of sulfonamides, quinolones, and tetracyclines in animal tissues by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Wang, S.; Fang, G.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y. Molecularly imprinted polymer online solid-phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-UV for the determination of three sulfonamides in pork and chicken. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2919–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.H.; Lin, S.L.; Fuh, M.R. Determination of sulfonamides in animal tissues by modified QuEChERS and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2016, 164, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.Y.; He, L.M.; Yang, J.W.; Bian, K.; Wang, Z.N.; Yang, H.C.; Liu, Y.H. Determination of 26 veterinary antibiotics residues in water matrices by lyophilization in combination with LC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 949–950, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biselli, S.; Schwalb, U.; Meyer, A.; Hartig, L. A multi-class, multi-analyte method for routine analysis of 84 veterinary drugs in chicken muscle using simple extraction and LC-MS/MS. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 921–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasenaki, M.E.; Bletsou, A.A.; Koulis, G.A.; Thomaidis, N.S. Qualitative Multiresidue Screening Method for 143 Veterinary Drugs and Pharmaceuticals in Milk and Fish Tissue Using Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4493–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, I.; Gérez, N.; Pistón, M.; Heinzen, H.; Cesio, M.V. Determination of pesticide residues in globe artichoke leaves and fruits by GC-MS and LC-MS/MS using the same QuEChERS procedure. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbings, G.; Bigwood, T. The development and validation of a multiclass liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) procedure for the determination of veterinary drug residues in animal tissue using a QuEChERS (QUick, Easy, CHeap, Effective, Rugged and Safe) approach. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 637, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Bao, X.; Zhao, S.; Wu, J.; Han, A.; Ye, Q. Analysis of multi-pesticide residues in the foods of animal origin by GC–MS coupled with accelerated solvent extraction and gel permeation chromatography cleanup. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granelli, K.; Branzell, C. Rapid multi-residue screening of antibiotics in muscle and kidney by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 586, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mol, H.G.; Plazabolaños, P.; Zomer, P.; de Rijk, T.C.; Stolker, A.A.; Mulder, P.P. Toward a generic extraction method for simultaneous determination of pesticides, mycotoxins, plant toxins, and veterinary drugs in feed and food matrixes. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9450–9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Meng, C.; Li, J.; He, L. Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for the determination of ten macrolide drugs residues in animal muscles by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2016, 208, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission (EC). Decision (2002/657/EC) of 12 August 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2002, 221, 3–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Q.; Zeng, Z.L.; Su, Y.J.; Zhang, G.K.; Zhong, X.L.; Liang, Z.P.; He, L.M. Matrix Effects in Analysis of β-Agonists with LC-MS/MS: Influence of Analyte Concentration, Sample Source, and SPE Type. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6359–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Breitbach, Z.S.; Armstrong, D.W. Reduced matrix effects for anionic compounds with paired ion electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 912, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogatsky, E.; Stein, D. Evaluation of matrix effect and chromatography efficiency: New parameters for validation of method development. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 16, 1757–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiaochan, C.; Koesukwiwat, U.; Yudthavorasit, S.; Leepipatpiboon, N. Efficient hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the multiclass analysis of veterinary drugs in chicken muscle. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 682, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, E.; Su, Y.; Song, X.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, L. Freeze-Thaw Approach: A Practical Sample Preparation Strategy for Residue Analysis of Multi-Class Veterinary Drugs in Chicken Muscle. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 2461–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trufelli, H.; Palma, P.; Famiglini, G.; Cappiello, A. An overview of matrix effects in liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 491–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasenaki, M.E.; Thomaidis, N.S. Multi-residue determination of 115 veterinary drugs and pharmaceutical residues in milk powder, butter, fish tissue and eggs using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 880, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Basha, E.A.; Idkaidek, N.M.; Al-Shunnaq, A.F. Pharmacokinetics of Tilmicosin (Provitil Powder and Pulmotil Liquid AC) Oral Formulations in Chickens. Vet. Res. Commun. 2007, 31, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.W.; Dong, L.L.; Ji, H.; Feng, X.W.; Li, D.; Ding, R.L.; Jiang, S.X. Comparative pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of tylosin tartrate and tylosin phosphate after a single oral and i.v. administration in chickens. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da, S.R.; Reyes, F.G.; Sartori, J.R.; Rath, S. Enrofloxacin assay validation and pharmacokinetics following a single oral dose in chickens. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Therap. 2006, 29, 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- Tansakul, N.; Niedorf, F.; Kietzmann, M. A sulfadimidine model to evaluate pharmacokinetics and residues at various concentrations in laying hen. Food Addit. Contam. 2007, 24, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Analyte | Precursor | Product | DP b (V) | CE c (eV) | Ion Ratio d (RSD e, %) (n = 10) | Relative | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ion | Ion | Pure Solvent | Muscle Matrix | Deviation (%) | |||
| ENR | 360.6 | 316.4 a | 60 | 30 | 52.6 (0.8) | 55.7 (1.2) | 5.9 |
| 245.1 | 60 | 37 | |||||
| CIP | 332.4 | 314.2 a | 60 | 25 | 25.7 (0.8) | 25.0 (0.7) | 2.5 |
| 288.3 | 60 | 25 | |||||
| SAR | 386.4 | 368.2 a | 60 | 28 | 27.8 (1.1) | 21.9 (0.8) | 21.3 |
| 342.3 | 60 | 28 | |||||
| SMM | 281.2 | 156.0 a | 60 | 25 | 24.7 (0.7) | 24.5 (0.5) | 0.9 |
| 215.1 | 60 | 25 | |||||
| SM2 | 279.2 | 186.0 a | 60 | 28 | 66.9 (1.6) | 64.0 (0.9) | 4.3 |
| 156.0 | 60 | 28 | |||||
| SQ | 301.3 | 156.0 a | 62 | 24 | 9.4 (0.3) | 10.3 (2.9) | 9.6 |
| 91.7 | 62 | 44 | |||||
| TIM | 869.6 | 696.4 a | 120 | 63 | 78.1 (6.8) | 76.1 (5.8) | 2.5 |
| 174.4 | 130 | 57 | |||||
| TYL | 916.6 | 174.3 a | 101 | 52 | 50.4 (2.5) | 54.2 (2.4) | 7.4 |
| 772.6 | 101 | 41 | |||||
| KIT | 772.4 | 109.1 a | 90 | 78 | 87.3 (3.2) | 82.0 (2.5) | 6.1 |
| 174.2 | 90 | 50 | |||||
| TAM | 494.5 | 192.2 a | 48 | 29 | 60.8 (3.6) | 50.7 (1.4) | 16.5 |
| 119.2 | 48 | 55 | 52.6 (0.8) | 55.7 (1.2) | 5.9 | ||
| Analyte | Linearity | Spiked Level (μg kg−1) | Intra-Day Recovery (%, n = 6) | Intra-Day RSD a (%, n = 6) | Inter-Day Recovery (%, n = 18) | Inter-Day RSD a (%, n = 18) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (r2) | I | II | III | I | II | III | I | II | III | I | II | III | I | II | III | |||||||||||||
| ENR | 0.9971 | 2 | 50 | 100 | 77.8 | 86.2 | 90.8 | 81.2 | 82.5 | 96.6 | 87.5 | 91.4 | 93.0 | 8.0 | 8.4 | 11 | 4.6 | 7.4 | 2.7 | 3.0 | 6.7 | 5.0 | 84.9 | 86.8 | 90.6 | 7.8 | 9.8 | 3.8 |
| CIP | 0.9994 | 2 | 50 | 100 | 69.0 | 77.2 | 82.5 | 69.8 | 67.6 | 77.4 | 76.6 | 70.8 | 78.2 | 8.7 | 6.7 | 10 | 9.1 | 7.3 | 14 | 6.4 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 76.2 | 71.6 | 75.2 | 13 | 10 | 5.2 |
| SAR | 0.9986 | 2 | 10 | 20 | 77.3 | 77.2 | 89.2 | 79.5 | 77.3 | 99.7 | 76.9 | 81.2 | 91.9 | 6.3 | 11 | 10 | 5.1 | 2.6 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 9.0 | 11 | 81.2 | 85.5 | 83.3 | 20 | 13 | 11 |
| SMM | 0.9986 | 2 | 50 | 100 | 67.5 | 78.1 | 79.0 | 75.4 | 75.6 | 79.4 | 74.7 | 79.6 | 81.8 | 5.3 | 3.8 | 5.3 | 2.4 | 5.5 | 4.6 | 5.1 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 74.9 | 76.8 | 78.7 | 8.9 | 2.9 | 4.6 |
| SM2 | 0.9996 | 2 | 50 | 100 | 85.9 | 85.5 | 93.7 | 83.2 | 82.6 | 94.7 | 75.7 | 80.6 | 81.0 | 4.6 | 5.2 | 5.6 | 6.8 | 4.2 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 6.9 | 5.6 | 88.4 | 86.8 | 79.1 | 2.4 | 6.3 | 9.0 |
| SQ | 0.9994 | 2 | 50 | 100 | 68.8 | 67.9 | 77.4 | 69.7 | 69.2 | 68.4 | 70.2 | 69.1 | 70.7 | 4.3 | 1.1 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 2.5 | 6.3 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 0.8 | 71.4 | 69.1 | 70.0 | 7.7 | 6.3 | 6.4 |
| TIM | 0.9984 | 5 | 50 | 100 | 81.5 | 82.1 | 102.4 | 75.0 | 72.2 | 80.9 | 75.6 | 71.1 | 80.7 | 3.3 | 7.9 | 4.4 | 4.3 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 14 | 13 | 6.9 | 88.7 | 76.0 | 75.8 | 12 | 7.9 | 12 |
| TYL | 0.9992 | 5 | 50 | 100 | 80.2 | 67.3 | 80.4 | 80.3 | 67.2 | 75.8 | 79.3 | 68.8 | 67.9 | 7.6 | 6.5 | 4.3 | 3.3 | 4.3 | 5.5 | 5.6 | 5.2 | 7.2 | 76.0 | 74.4 | 72.0 | 12 | 15 | 12 |
| KIT | 0.9997 | 5 | 50 | 100 | 69.2 | 73.7 | 76.8 | 67.1 | 69.5 | 70.5 | 68.2 | 72.9 | 71.0 | 8.7 | 7.9 | 1.4 | 3.5 | 14 | 6.0 | 5.4 | 8.4 | 6.9 | 73.2 | 69.0 | 70.7 | 6.6 | 8.7 | 9.3 |
| TAM | 0.9998 | 2 | 50 | 100 | 74.4 | 69.1 | 80.4 | 73.9 | 72.7 | 73.3 | 80.4 | 75.2 | 74.7 | 5.7 | 16 | 1.3 | 8.3 | 12 | 7.9 | 5.8 | 8.4 | 4.8 | 74.6 | 73.3 | 76.8 | 10 | 8.4 | 6.5 |
| Analyte | LOD a | LOQ b | MRLs c (μg kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (μg kg−1) | (μg kg−1) | China | European Union | |
| ENR | 0.5 | 2.0 | 100 d | 100 d |
| CIP | 0.5 | 2.0 | 100 d | 100 d |
| SAR | 0.5 | 2.0 | 10 | NS f |
| SMM | 0.5 | 2.0 | 100 e | 100 e |
| SM2 | 0.5 | 2.0 | 100 | 100 e |
| SQ | 0.5 | 2.0 | 100 e | 100 e |
| TIM | 2.0 | 5.0 | 75 | 75 |
| TYL | 2.0 | 5.0 | 200 | 100 |
| KIT | 2.0 | 5.0 | 100 | NS f |
| TAM | 0.3 | 2.0 | 100 | 100 |
| Category | I | II |
|---|---|---|
| Compound (X) | FQs (3), SAs (3), | FAs (4), SAs (4), MCs (4), LINCs (2), |
| MCs (3), and TAM | AGs (3),β-LACTs (3), TCs (3) and AMPR | |
| Mobile phase | 0.05% formic acid in ACN (A) and 0.05% formic acid in water (B) | 50 mm ammonium formate in water at pH 2.5 (A) and ACN (B) |
| Extraction solvent | 1% acetic acid in ACN | 2% TCA aqueous solution: ACN (1:1, v/v) |
| Dilution times | 10 | 10 |
| LOD (μg kg−1) | 0.3 (TAM)–2.0 (MCs) | 0.1 (SAs)–20 (DSTR) |
| LOQ (μg kg−1) | 2.0 (TAM–5.0 (MCs) | 0.3 (SAs)–60 (DSTR) |
| Recovery (%) | 67.1 (KIT)–96.6 (ENR) | 53 (ENR)–99 (OXO) |
| Matrix effects (%) | −28.4 (SQ)–21.3 (ENR) | −99 (AMPR)–53 (DSTR) |
| Days | I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII | VIII |
| Drugs | A | A + B | A + B + C | B + C | C | - | No. 2 | No. 3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Li, E.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, J.; He, L. Quick Multi-Class Determination of Residues of Antimicrobial Veterinary Drugs in Animal Muscle by LC-MS/MS. Molecules 2018, 23, 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071736
Zhang M, Li E, Su Y, Zhang Y, Xie J, He L. Quick Multi-Class Determination of Residues of Antimicrobial Veterinary Drugs in Animal Muscle by LC-MS/MS. Molecules. 2018; 23(7):1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071736
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Meiyu, Erfen Li, Yijuan Su, Yingxia Zhang, Jingmeng Xie, and Limin He. 2018. "Quick Multi-Class Determination of Residues of Antimicrobial Veterinary Drugs in Animal Muscle by LC-MS/MS" Molecules 23, no. 7: 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071736
APA StyleZhang, M., Li, E., Su, Y., Zhang, Y., Xie, J., & He, L. (2018). Quick Multi-Class Determination of Residues of Antimicrobial Veterinary Drugs in Animal Muscle by LC-MS/MS. Molecules, 23(7), 1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071736