HIV-1 Integrase-Targeted Short Peptides Derived from a Viral Protein R Sequence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Development of a Core Vpr-Derived IN Inhibitory Peptide
2.2. Peptide 1a Does Not Interfere with IN–DNA Binding or Induce Aberrant IN Multimerization
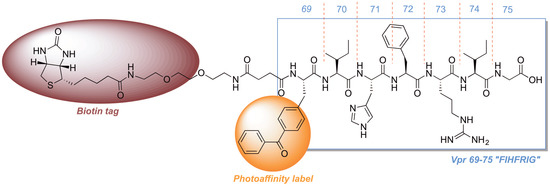
2.3. Development of a Vpr Peptide-Based Photoprobe
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Synthetic
3.2. Peptide Synthesis
3.3. In Vitro Integrase Catalytic Assays
3.4. Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (HTRF)-Based Protein-Protein Interaction Assays
3.5. DNA Binding Experiments
3.6. Crosslinking Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Santo, R. Inhibiting the HIV integration process: Past, present, and the future. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 539–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxtall, J.D.; Scott, L.J. Raltegravir: In treatment-naive patients with HIV-1 infection. Drugs 2010, 70, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills, T.; Vega, V. Elvitegravir: A once-daily inhibitor of HIV-1 integrase. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2012, 21, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, B.M.; Schafer, J.J.; Desimone, J.A., Jr. Dolutegravir: A new integrase strand transfer inhibitor for the treatment of HIV. Pharmacotherapy 2013, 34, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainberg, M.A.; Zaharatos, G.J.; Brenner, B.G. Development of antiretroviral drug resistance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurt, C.B.; Sebastian, J.; Hicks, C.B.; Eron, J.J. Resistance to HIV integrase strand transfer inhibitors among clinical specimens in the united states, 2009–2012. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llano, M.; Vanegas, M.; Fregoso, O.; Saenz, D.; Chung, S.; Peretz, M.; Poeschla, E.M. LEDGF/p75 determines cellular trafficking of diverse lentiviral but not murine oncoretroviral integrase proteins and Is a component of functional lentiviral preintegration complexes. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9524–9537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romani, B.; Engelbrecht, S. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr: Functions and molecular interactions. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mawsawi, L.Q.; Neamati, N. Blocking interactions between HIV-1 integrase and cellular cofactors: An emerging anti-retroviral strategy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, S.N.; Frasson, I.; Palù, G. Strategies for inhibiting function of HIV-1 accessory proteins: A necessary route to AIDS therapy? Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debyser, Z.; Desimmie, B.A.; Taltynov, O.; Demeulemeester, J.; Christ, F. Validation of host factors of HIV integration as novel drug targets for anti-HIV therapy. MedChemComm 2014, 5, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayouka, Z.; Rosenbluh, J.; Levin, A.; Loya, S.; Lebendiker, M.; Veprintsev, D.; Kotler, M.; Hizi, A.; Loyter, A.; Friedler, A. Inhibiting HIV-1 integrase by shifting its oligomerization equilibrium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8316–8321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Connor, R.I.; Chen, B.K.; Choe, S.; Landau, N.R. Vpr is Required for efficient replication of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 in mononuclear phagocytes. Virology 1995, 206, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckstein, D.A.; Sherman, M.P.; Penn, M.L.; Chin, P.S.; De Noronha, C.M.C.; Greene, W.C.; Goldsmith, M.A. HIV-1 Vpr enhances viral burden by facilitating infection of tissue macrophages but not nondividing CD4+ T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogan, M.; Rappaport, J. HIV-1 accessory protein Vpr: Relevance in the pathogenesis of HIV and potential for therapeutic intervention. Retrovirology 2011, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Dang, Y.; Baker, J.J.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, Y.-H. Evidence for Vpr-dependent HIV-1 replication in human CD4+ CEM.NKR T-cells. Retrovirology 2012, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Loyter, A.; Friedler, A. Peptides that inhibit HIV-1 integrase by blocking its protein-protein interactions. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 2795–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, M.E. The HIV-1 Vpr protein: A multifaceted target for therapeutic intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morellet, N.; Bouaziz, S.; Petitjean, P.; Roques, B.P. NMR structure of the HIV-1 regulatory protein VPR. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 327, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischerour, J.; Tauc, P.; Leh, H.; de, R.H.; Roques, B.; Mouscadet, J.-F. The (52–96) C-terminal domain of Vpr stimulates HIV-1 IN-mediated homologous strand transfer of mini-viral DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 2694–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Pointer, D.; Singer, G.; Feng, Y.; Park, K.; Zhao, L.J. Direct binding to nucleic acids by Vpr of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Gene 1998, 212, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleenberg, I.O.; Herschhorn, A.; Hizi, A. Inhibition of the activities of reverse transcriptase and integrase of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 by peptides derived from the homologous viral protein R (Vpr). J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 369, 1230–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Urano, E.; Hashimoto, C.; Tsutsumi, H.; Nakahara, T.; Tanaka, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Maddali, K.; Han, Y.; Hamatake, M.; et al. Peptide HIV-1 integrase inhibitors from HIV-1 gene products. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5356–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, W.; Aikawa, H.; Ohashi, N.; Urano, E.; Metifiot, M.; Fujino, M.; Maddali, K.; Ozaki, T.; Nozue, A.; Narumi, T.; et al. Cell-permeable stapled peptides based on HIV-1 integrase inhibitors derived from HIV-1 gene sroducts. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2235–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.Z.; Metifiot, M.; Maddali, K.; Smith, S.J.; Marchand, C.; Hughes, S.H.; Pommier, Y.; Burke, T.R., Jr. HIV viral protein R (Vpr)-derived peptides designed as HIV-1 integrase photoaffinity ligands. In Proceedings of the 23rd American Peptide Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 22–27 June 2013; Lebl, M., Ed.; American Peptide Society: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 23, pp. 84–85. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachari, N.J.; Walker, L.A.; Tastan, O.; Le, T.; Dempsey, T.M.; Li, Y.; Yanamala, N.; Srinivasan, A.; Klein-Seetharaman, J.; Montelaro, R.C.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr: Oligomerization is an essential feature for its incorporation into virus particles. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessl, J.; Jena, N.; Koh, Y.; Taskent-Sezgin, H.; Slaughter, A.; Feng, L.; de Silva, S.; Wu, L.; Le Grice, S.; Engelman, A. Multimode, cooperative mechanism of action of allosteric HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 16801–16811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiang, M.; Jones, G.S.; Niedziela-Majka, A.; Kan, E.; Lansdon, E.B.; Huang, W.; Hung, M.; Samuel, D.; Novikov, N.; Xu, Y.; et al. New class of HIV-1 integrase (IN) inhibitors with a dual mode of action. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21189–21203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Sharma, A.; Slaughter, A.; Jena, N.; Koh, Y.; Shkriabai, N.; Larue, R.; Patel, P.; Mitsuya, H.; Kessl, J. The A128T resistance mutation reveals aberrant protein multimerization as the primary mechanism of action of allosteric HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 15813–15820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ, F.; Voet, A.; Marchand, A.; Nicolet, S.; Desimmie, B.A.; Marchand, D.; Bardiot, D.; Van der Veken, N.J.; Van, R.B.; Strelkov, S.V.; et al. Rational design of small-molecule inhibitors of the LEDGF/p75-integrase interaction and HIV replication. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fader, L.D.; Malenfant, E.; Parisien, M.; Carson, R.; Bilodeau, F.; Landry, S.; Pesant, M.; Brochu, C.; Morin, S.; Chabot, C.; et al. Discovery of BI 224436, a noncatalytic site integrase inhibitor (NCINI) of HIV-1. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.; Brady, T.; Dyer, B.M.; Malani, N.; Hwang, Y.; Male, F.; Nolte, R.T.; Wang, L.; Velthuisen, E.; Jeffrey, J.; et al. Allosteric inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus integrase: Late block during viral replication and abnormal multimerization involving specific protein domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 20477–20488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Rouzic, E.; Bonnard, D.; Chasset, S.; Bruneau, J.-M.; Chevreuil, F.; Le Strat, F.; Nguyen, J.; Beauvoir, R.; Amadori, C.; Brias, J.; et al. Dual inhibition of HIV-1 replication by integrase-LEDGF allosteric inhibitors is predominant at the post-integration stage. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jurado, K.A.; Wang, H.; Slaughter, A.; Feng, L.; Kessl, J.J.; Koh, Y.; Wang, W.; Ballandras-Colas, A.; Patel, P.A.; Fuchs, J.R.; et al. Allosteric integrase inhibitor potency is determined through the inhibition of HIV-1 particle maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8690–8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Slaughter, A.; Jena, N.; Feng, L.; Kessl, J.J.; Fadel, H.J.; Malani, N.; Male, F.; Wu, L.; Poeschla, E.; et al. A new class of multimerization selective inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiang, M.; Jones, G.S.; Hung, M.; Mukund, S.; Han, B.; Liu, X.; Babaoglu, K.; Lansdon, E.; Chen, X.; Todd, J.; et al. Affinities between the binding partners of the HIV-1 integrase dimer-lens epithelium-derived growth factor (IN dimer-LEDGF) complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 33580–33599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prestwich, G.D.; Dorman, G.; Elliott, J.T.; Marecak, D.M.; Chaudhary, A. Benzophenone photoprobes for phosphoinositides, peptides and drugs. Photochem. Photobiol. 1997, 65, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorman, G.; Prestwich, G.D. Benzophenone photophores in biochemistry. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 5661–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatanaka, Y.; Sadakane, Y. Photoaffinity labeling in drug discovery and developments: Chemical gateway for entering proteomic frontier. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Neamati, N.; Pommier, Y.; Burke, T.R., Jr. Design and synthesis of photoactivable coumarin-containing HIV-1 integrase inhibitors. Heterocycles 1997, 45, 2277–2282. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mawsawi, L.Q.; Fikkert, V.; Dayam, R.; Witvrouw, M.; Burke, T.R., Jr.; Borchers, C.H.; Neamati, N. Discovery of a small-molecule HIV-1 integrase inhibitor-binding site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10080–10085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Marchand, C.; Pommier, Y.; Burke, T.R. Design and synthesis of photoactivatable aryl diketo acid-containing HIV-1 integrase inhibitors as potential affinity probes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 1205–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.Z.; Semenova, E.A.; Liao, C.; Nicklaus, M.; Pommier, Y.; Burke, T.R. Biotinylated biphenyl ketone-containing 2,4-dioxobutanoic acids designed as HIV-1 integrase photoaffinity ligands. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 7816–7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauer, J.C.; Erickson-Viitanen, S.; Wolfe, H.R., Jr.; DeGrado, W.F. p-Benzoyl-l-phenylalanine, a new photoreactive amino acid. Photolabeling of calmodulin with a synthetic calmodulin-binding peptide. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 10695–10700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wahlstrom, J.L.; Randall, M.A.; Lawson, J.D.; Lyons, D.E.; Siems, W.F.; Crouch, G.J.; Barr, R.; Facemyer, K.C.; Cremo, C.R. Structural model of the regulatory domain of smooth muscle heavy meromyosin. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 5123–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongo, N.B.; Tomohiro, T.; Hatanaka, Y. Efficient approach for profiling photoaffinity labeled peptides with a cleavable biotinyl photoprobe. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 1834–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyro, K.; Manandhar, S.P.; Mullen, D.; Schmidt, W.K.; Distefano, M.D. Photoaffinity labeling of Ras converting enzyme using peptide substrates that incorporate benzoylphenylalanine (Bpa) residues: Improved labeling and structural implications. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 7559–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Marik, J.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Lam, K.S. Synthesis of hydrophilic and flexible linkers for peptide derivatization in solid phase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metifiot, M.; Maddali, K.; Naumova, A.; Zhang, X.; Marchand, C.; Pommier, Y. Biochemical and pharmacological analyses of HIV-1 integrase flexible loop mutants resistant to raltegravir. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 3715–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einhauer, A.; Jungbauer, A. The FLAG™ peptide, a versatile fusion tag for the purification of recombinant proteins. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2001, 49, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Barnes, C.O.; DeLucia, M.; Cohen, A.E.; Gronenborn, A.M.; Ahn, J.; Calero, G. The DDB1–DCAF1–Vpr–UNG2 crystal structure reveals how HIV-1 Vpr steers human UNG2 toward destruction. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of select peptides are available from the authors in limited quantities. |






| No. | SEQUENCE i | 3’-P IC50 (µM) | ST IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | FIHFRIG | 17.6 ± 1.2 | 1.3 ± 0.3 |
| 1b | FIHFRIG-amide | 31.5 ± 6 | 7.3 ± 0.8 |
| 1c | Ac-FIHFRIG-amide | 23.5 ± 3 | 4.7 ± 0.3 |
| 2a | FIHFRIA | >111 | 34.7 ± 2.3 |
| 2b | FIHFRIA-amide | >111 | 60.6 ± 8 |
| 2c | Ac-FIHFRIA-amide | 74.5 ± 7 | 30.4 ± 0.7 |
| 3a | FIHFRAG | 66.5 ± 7 | 22.4 ± 1.7 |
| 3b | FIHFRAG-amide | > 111 | >111 |
| 3c | Ac-FIHFRAG-amide | 208 ± 12 | 28 ± 4 |
| 4a | FIHFAIG | >111 | >111 |
| 4b | FIHFAIG-amide | >111 | >111 |
| 4c | Ac-FIHFAIG-amide | >333 | 81 ± 9 |
| 5a | FIHARIG | >111 | 46.6 ± 6.5 |
| 5b | FIHARIG-amide | >111 | >111 |
| 5c | Ac-FIHARIG-amide | >333 | 117 ± 10 |
| 6a | FIAFRIG | 17.4 ± 2.0 | 6.7 ± 1.0 |
| 6b | FIAFRIG-amide | 95.4 ± 5 | 35.0 ± 3.2 |
| 6c | Ac-FIAFRIG-amide | 94 ± 13 | 3.5 ± 0.3 |
| 7a | FAHFRIG | >111 | 73.5 ± 6.0 |
| 7b | FAHFRIG-amide | >111 | >111 |
| 7c | Ac-FAHFRIG-amide | >333 | 127 ± 14 |
| 8a | AIHFRIG | 86.3 ± 5.0 | 22.7 ± 1.4 |
| 8b | AIHFRIG-amide | >111 | >111 |
| 8c | Ac-AIHFRIG-amide | >333 | 46 ± 8 |
| 9a | FIHFRBG | 20 ± 3 | 4.3 ± 1.3 |
| 10a | FIHFBIG | >333 | 48 ± 8 |
| 11a | FIHBRIG | 34 ± 6 | 4.2 ± 0.7 |
| 12a | FIBFRIG | 6.5 ± 0.9 | 2.2 ± 0.6 |
| 13a | FBHFRIG | 37 ± 5 | 20 ± 3 |
| 14a | BIHFRIG | 7.2 ± 1.2 | 2.1 ± 0.3 |
| 15 | Biotin-linker-BIHFRIG | 32 ± 7 | 2.3 ± 0.3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.Z.; Métifiot, M.; Kiselev, E.; Kessl, J.J.; Maddali, K.; Marchand, C.; Kvaratskhelia, M.; Pommier, Y.; Burke, T.R., Jr. HIV-1 Integrase-Targeted Short Peptides Derived from a Viral Protein R Sequence. Molecules 2018, 23, 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081858
Zhao XZ, Métifiot M, Kiselev E, Kessl JJ, Maddali K, Marchand C, Kvaratskhelia M, Pommier Y, Burke TR Jr. HIV-1 Integrase-Targeted Short Peptides Derived from a Viral Protein R Sequence. Molecules. 2018; 23(8):1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081858
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xue Zhi, Mathieu Métifiot, Evgeny Kiselev, Jacques J. Kessl, Kasthuraiah Maddali, Christophe Marchand, Mamuka Kvaratskhelia, Yves Pommier, and Terrence R. Burke, Jr. 2018. "HIV-1 Integrase-Targeted Short Peptides Derived from a Viral Protein R Sequence" Molecules 23, no. 8: 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081858
APA StyleZhao, X. Z., Métifiot, M., Kiselev, E., Kessl, J. J., Maddali, K., Marchand, C., Kvaratskhelia, M., Pommier, Y., & Burke, T. R., Jr. (2018). HIV-1 Integrase-Targeted Short Peptides Derived from a Viral Protein R Sequence. Molecules, 23(8), 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081858