Preparation and Evaluation of Oseltamivir Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Silica Gel as Liquid Chromatography Stationary Phase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Derivatization, Polymer Synthesis and Characterization
2.2. Adsorption Experiments
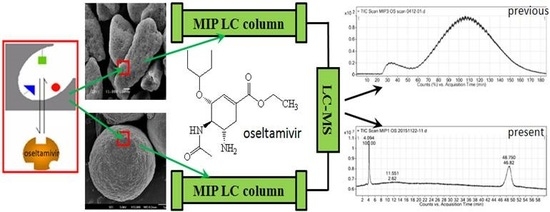
2.3. Specific Affinity of the OSMIP@silica Gel LC Column
3. Experimental
3.1. Reagents and Solvents
3.2. Standard Solutions
3.3. Equipment
3.4. Preparation of MIP
3.4.1. KH570@silica Gel [19]
3.4.2. OSMIP@silica Gel
3.5. Characterization
3.6. Adsorption Experiments
3.7. Specific Affinity of the OSMIP@silica Gel LC Column
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rathbone, D.L. Molecularly imprinted polymers in the drug discovery process. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1854–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nostrum, C.F. Molecular imprinting: A new tool for drug innovation. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2005, 2, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X. New concepts and approaches for drug discovery based on traditional Chinese medicine. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2006, 3, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Haupt, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers as antibody and receptor mimics for assays, sensors and drug discovery. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Pang, W.; Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Hu, J. A target analogue imprinted polymer for the recognition of antiplatelet active ingredients in Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae by LC/MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 58, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, L.; Xu, X. Application of a molecularly imprinted polymer for the effective recognition of different anti-epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6381–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, N.A.; Paisner, D.A.; Huryn, D.; Shea, K.J. Screening of 5-HT(1A) Receptor Antagonists using Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Cai, X. Optimization of polymerization parameters for the sorption of oseltamivir onto molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 3665–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, B. A Non-Biological Method for Screening Active Components against Influenza Virus from Traditional Chinese Medicine by Coupling a LC Column with Oseltamivir Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. PLoS ONE 2013, 12, e84458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoravi, S.; Olsson, G.D.; Karlsson, B.C.G.; Bexborn, F.; Abghoui, Y.; Hussain, J.; Wiklander, J.G.; Nicholls, I.A. In silico screening of molecular imprinting prepolymerization systems: Oseltamivir selective polymers through full-system molecular dynamics-based studies. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 4210–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, P.; Zhao, J.; Peng, Y.; Du, S.; Zhang, Z. Molecularly imprinted layer-coated monodisperse spherical silica microparticles toward affinity-enrichment of isoflavonoid glycosides from Radix puerariae. Analyst 2012, 137, 2891–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Luo, L.; Yao, S. Preparation of l-phenylalanine imprinted polymer based on monodisperse hybrid silica microsphere and its application on chiral separation of phenylalanine racemates as HPLC stationary phase. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 87, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordel, S.; Chapuis-Hugon, F.; Eudes, V.; Pichon, V. Selective extraction of nitroaromatic explosives by using molecularly imprinted silica sorbents. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordel-Madeleine, S.; Eudes, V.; Pichon, V. Identification of the nitroaromatic explosives in post-blast samples by online solid phase extraction using molecularly imprinted silica sorbent coupled with reversed-phase chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5237–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhong, H.; Peng, A.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z. Rapid detection of malachite green in fish based on CdTe quantum dots coated with molecularly imprinted silica. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Peter, A.G.C.; Mosbach, K. Molecular imprinting on microgel spheres. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 435, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, L.H.; Deng, Q.Y. Preparation of Imprinted Polymer with Theophylline on Silica Surface and Its Characteristics. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2005, 44, 49–53. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chrzanowska, A.M.; Poliwoda, A.; Wieczorek, P.P. Surface molecularly imprinted silica for selective solid-phase extraction of biochanin A, daidzein and genistein from urine samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1392, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kang, Y.F.; Wu, W.H.; Duan, W.P.; Kang, J.X.; Xie, J. Preparation of imprinted polymer with Cu2+ ions on silica surface and its characteristics. Chem. Res. Appl. 2012, 24, 873–878. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, M.; Xie, C.; Guan, G.; Wang, D. A surface functional monomer-directing strategy for highly dense imprinting of TNT at surface of silica nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7859–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.R.; Datta, P.K.; Sarkar, M. Sorption recovery of metal ions using silica gel modified with salicylaldoxime. Talanta 1996, 43, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, G.; Chen, Y. Preparation of magnetic indole-3-acetic acid imprinted polymer beads with 4-vinylpyridine and β-cyclodextrin as binary monomer via microwave heating initiated polymerization and their application to trace analysis of auxins in plant tissues. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7337–7344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Yuan, L.; Ding, M.; Wang, S.; Ren, F.; Zhang, J.; Du, S.; Li, F.; Zhou, X. The study of core–shell molecularly imprinted polymers of 17β-estradiol on the surface of silica nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2791–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zander, A.; Findlay, P.; Renner, T.; Sellergren, B.; Swletlow, A. Analysis of nicotine and its oxidation products in nicotine chewing gum by a molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 3304–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.W.; Choi, S.H.; Huh, J.W.; Lim, C.M.; Koh, Y.; Hong, S.B. Peramivir is as effective as oral oseltamivir in the treatment of severe seasonal influenza. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, M.M.; Skoglund, E.W.; Ison, M.G. Peramivir: An intravenous neuraminidase inhibitor. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2015, 16, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Climente, R.; Gomez-Caballero, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Garcia-Mutio, D.; Unceta, N.; Goicolea, M.A.; Barrio, R.J. Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles grafted to porous silica as chiral selectors in liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1508, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Shin, Y.; Barnes, C.; Toth, L. Enhancement of uranyl adsorption capacity and selectivity on silica sol-gel glasses via molecular imprinting. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 2521–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds oseltamivir, peramivir trihydrate and quinocetone are available from the authors. |






| Diameter of Particles (μm) | BET Surface Area (m2·g−1) | Average Pore Diameter (Å) | Pore Volume (cm3·g−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silica gel | 5 | 400 | 70 | 0.70 |
| OSMIP@silica gel | 6~8 | 244.13 ± 47.94 | 47.69 ± 5.57 | 0.29 ± 0.04 |
| NIP@silica gel | 6~8 | 276.29 ± 55.29 | 46.22 ± 4.67 | 0.31 ± 0.03 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.-J.; Liu, X.-W.; Kong, X.-J.; Qin, Z.; Jiao, Z.-H.; Li, S.-H.; Li, J.-Y. Preparation and Evaluation of Oseltamivir Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Silica Gel as Liquid Chromatography Stationary Phase. Molecules 2018, 23, 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081881
Yang Y-J, Liu X-W, Kong X-J, Qin Z, Jiao Z-H, Li S-H, Li J-Y. Preparation and Evaluation of Oseltamivir Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Silica Gel as Liquid Chromatography Stationary Phase. Molecules. 2018; 23(8):1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081881
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ya-Jun, Xi-Wang Liu, Xiao-Jun Kong, Zhe Qin, Zeng-Hua Jiao, Shi-Hong Li, and Jian-Yong Li. 2018. "Preparation and Evaluation of Oseltamivir Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Silica Gel as Liquid Chromatography Stationary Phase" Molecules 23, no. 8: 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081881
APA StyleYang, Y. -J., Liu, X. -W., Kong, X. -J., Qin, Z., Jiao, Z. -H., Li, S. -H., & Li, J. -Y. (2018). Preparation and Evaluation of Oseltamivir Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Silica Gel as Liquid Chromatography Stationary Phase. Molecules, 23(8), 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081881