Datura Metel L. Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Dermatitis and Inhibits Inflammatory Cytokines Production through TLR7/8–MyD88–NF-κB–NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Effective Part of Datura metel L. (EPD) Treatment Ameliorated IMQ-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin Lesions
2.2. EPD Inhibited the Aberrant Expression of the Proliferation and Differentiation Markers of Keratinocytes in Mice Dorsal Skin Induced by IMQ
2.3. EPD Inhibited Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in IMQ-Induced Psoriasis-Like Mouse Mode
2.4. EPD Administration Downregulated the Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines
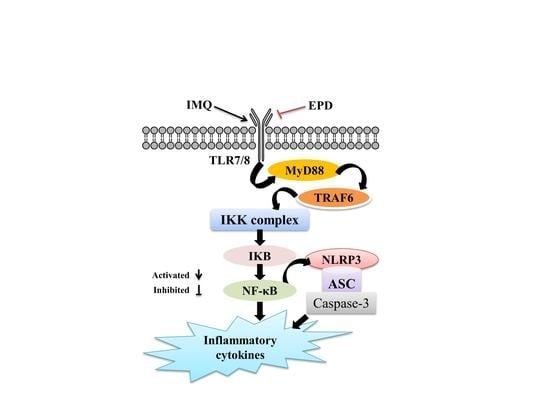
2.5. EPD Suppressed the TLR7/8–MyD88–NF-κB Signaling Pathways and Accordingly Exerted the Therapeutic Effect for Psoriasis
2.6. EPD Inhibited the IMQ-Activated NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Effective Part of Datura metel L. (EPD) Preparation
4.2. Experimental Animal
4.3. Establishment of Psoriasis-Like Dermatitis Mice Model and the Administration with EPD
4.4. Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) Assessment
4.5. Histological Analysis
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Detection of Inflammatory Cytokines in Skin Tissues Lysate
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terhorst, D.; Chelbi, R.; Wohn, C.; Malosse, C.; Tamoutounour, S.; Jorquera, A.; Bajenoff, M.; Dalod, M.; Malissen, B.; Henri, S. Dynamics and Transcriptomics of Skin Dendritic Cells and Macrophages in an Imiquimod-Induced, Biphasic Mouse Model of Psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4953–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, M.; Xie, X.; Di, T.; Zhao, J.; Lin, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, N.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Paeonol ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in BALB/c mice by inhibiting the maturation and activation of dendritic cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, C.; Kirby, B. Psoriasis is a systemic disease with multiple cardiovascular and metabolic comorbidities. Dermatol. Clin. 2015, 33, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutmark-Little, I.; Shah, K.N. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome in pediatric psoriasis. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 33, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chularojanamontri, L.; Wongpraparut, C.; Silpa-Archa, N.; Chaweekulrat, P. Metabolic syndrome and psoriasis severity in South-East Asian patients: An investigation of potential association using current and chronological assessments. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 1424–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.F.; Wang, T.S.; Hung, S.T.; Tsai, P.I.; Schenkel, B.; Zhang, M.; Tang, C.H. Epidemiology and comorbidities of psoriasis patients in a national database in Taiwan. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 63, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidovici, B.B.; Sattar, N.; Prinz, J.; Puig, L.; Emery, P.; Barker, J.N.; van de Kerkhof, P.; Stahle, M.; Nestle, F.O.; Girolomoni, G.; et al. Psoriasis and systemic inflammatory diseases: Potential mechanistic links between skin disease and co-morbid conditions. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 1785–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradors, M.; Blanch, C.; Comellas, M.; Figueras, M.; Lizan, L. Health-related quality of life in patients with psoriasis: A systematic review of the European literature. Qual. Life Res. 2016, 25, 2739–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Korte, J.; Sprangers, M.A.; Mombers, F.M.; Bos, J.D. Quality of life in patients with psoriasis: A systematic literature review. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2004, 9, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, M.M.; Hutchinson, M.; Watkins, L.R.; Yin, H. Toll-like receptor 4 in CNS pathologies. J. Neurochem. 2010, 114, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, F.; Fujimoto, M.; Liu, L.; Nakano, F.; Nakatsuka, Y.; Suzuki, H. Effects of Toll-Like Receptor 4 Antagonists Against Cerebral Vasospasm After Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6624–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avlas, O.; Fallach, R.; Shainberg, A.; Porat, E.; Hochhauser, E. Toll-like receptor 4 stimulation initiates an inflammatory response that decreases cardiomyocyte contractility. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1895–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Grailer, J.J.; Wang, N.; Wang, M.; Yao, J.; Zhong, R.; Gao, G.F.; Ward, P.A.; Tan, D.X.; et al. Melatonin alleviates acute lung injury through inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlström, M.; Ekman, A.K.; Petersson, S.; Söderkvist, P.; Enerbäck, C. Genetic support for the role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in psoriasis susceptibility. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, P.; Hao, S.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y. Association of NLRP1 and NLRP3 Polymorphisms with Psoriasis Vulgaris Risk in the Chinese Han Population. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4714836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Cun, D.; Tong, H.H.Y.; Yan, R.; Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Zheng, Y. Enhanced topical penetration, system exposure and anti-psoriasis activity of two particle-sized, curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles in hydrogel. J. Control. Release. 2017, 254, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okasha, E.F.; Bayomy, N.A.; Abdelaziz, E.Z. Effect of topical application of black seed oil on imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like lesions in the thin skin of adult male albino rats. Anat. Rec. (Hoboken) 2018, 301, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.J.; Sah, S.K.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, J.; Kim, T.Y. Rhododendrin inhibits toll-like receptor-7-mediated psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhao, W.; Xing, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Shi, F.; Bai, Y. Chinese herbal Pulian ointment in treating psoriasis vulgaris of blood-heat syndrome: A multi-center, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, P.; Zheng, Y. Psoriasis therapy by Chinese medicine and modern agents. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.Y.; Xia, Y.G.; Wang, Q.H.; Dou, D.Q.; Kuang, H.X. Baimantuoluosides D-G, four new withanolide glucosides from the flower of Datura metel L. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.Y.; Guo, R.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.F.; Shu, Z.P.; Wang, Z.B.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y.G.; Jiang, H.; et al. Five withanolides from the leaves of Datura metel L. and their inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production. Molecules 2014, 19, 4548–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.H.; Xiao, H.B.; Yang, B.Y.; Yao, F.Y.; Kuang, H.X. Studies on pharmacological actions of the effective parts for psoriasis in Flos Daturae (I)-The Anti-inflammatory, Anti-titillation and Anti-anaphylaxis Actions of Flos daturae. Chin. J. Exp Trad Med. Formulae 2008, 14, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.H.; Xiao, H.B.; Yang, B.Y.; Yao, F.Y.; Kuang, H.X. Studies on Pharmacological actions of the active parts in Flos Daturae for psoriasis (II)-on Immune Funct ion, Epithel ial Cell Mitos is and Skin Keratosis. Chin. J. Exp. Trad. Med. Formulae 2008, 14, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, H.X.; Yang, B.Y.; Xia, Y.G.; Wang, Q.H. Two new withanolide lactones from flos daturae. Molecules 2011, 16, 5833–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.Y.; Xia, Y.G.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.H.; Kuang, H.X. Two novel norwithasteroids with unusual six- and seven-membered ether rings in side chain from flos daturae. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 352019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.R.; Di Chiacchio, N.G.; Alvarenga, M.L.; Mandelbaum, S.H. Involucrin in the differential diagnosis between linear psoriasis and inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus: A report of one case. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2013, 88, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, E.D.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.H.; Bin, B.H.; Bae, I.H.; Lim, K.M.; Yu, S.J.; Cho, E.G.; Lee, T.R. S100A7 (psoriasin) inhibits human epidermal differentiation by enhanced IL-6 secretion through IκB/NF-κB signalling. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Youn, G.S.; An, S.Y.; Kwon, H.Y.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, J. 2,3-Dimethoxy-2’-hydroxychalcone ameliorates TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 expression and subsequent monocyte adhesiveness via NF-kappaB inhibition and HO-1 induction in HaCaT cells. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockenhuber, K.; Hegazy, A.N.; West, N.R.; Ilott, N.E.; Stockenhuber, A.; Bullers, S.J.; Thornton, E.E.; Arnold, I.C.; Tucci, A.; Waldmann, H.; et al. Foxp3+ T reg cells control psoriasiform inflammation by restraining an IFN-I-driven CD8+ T cell response. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Xia, L.; Xia, Y. Fn14 deficiency ameliorates psoriasis-like skin disease in a murine model. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.; Liu, S.; Yi, X.; Zhang, S.; Ding, Y. Serum amyloid A induces interleukin-1β secretion from keratinocytes via the NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 inflammasome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 179, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bech, R.; Jalilian, B.; Agger, R.; Iversen, L.; Erlandsen, M.; Otkjaer, K.; Johansen, C.; Paludan, S.R.; Rosenberg, C.A.; Kragballe, K.; et al. Interleukin 20 regulates dendritic cell migration and expression of co-stimulatory molecules. Mol. Cell. Ther. 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.H.; Wang, C.N.; Cheng, H.H.; Liao, J.W.; Chen, Y.T.; Chao, Y.W.; Jiang, J.L.; Lee, C.C. Baicalin Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Inflammation in Mice. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang-Ngern, M.; Youn, U.J.; Park, E.J.; Kondratyuk, T.P.; Simmons, C.J.; Wall, M.M.; Ruf, M.; Lorch, S.E.; Leong, E.; Pezzuto, J.M.; et al. Withanolides derived from Physalis peruviana (Poha) with potential anti-inflammatory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2755–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Lu, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Yan, Y.; Han, L. Quercetin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice via the NF-kappaB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 48, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Fits, L.; Mourits, S.; Voerman, J.S.; Kant, M.; Boon, L.; Laman, J.D.; Cornelissen, F.; Mus, A.M.; Florencia, E.; Prens, E.P.; et al. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5836–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.K.; Yang, S.H.; Chen, C.C.; Kao, H.C.; Fang, J.Y. Using Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Skin as a Model to Measure the Skin Penetration of Anti-Psoriatic Drugs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swindell, W.R.; Michaels, K.A.; Sutter, A.J.; Diaconu, D.; Fritz, Y.; Xing, X.; Sarkar, M.K.; Liang, Y.; Tsoi, A.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; et al. Imiquimod has strain-dependent effects in mice and does not uniquely model human psoriasis. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, X.; Zhang, L.; Meng, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, M.; Zhai, C.; Liu, Z.; Di, T.; Zhang, L.; et al. Hesperidin inhibits keratinocyte proliferation and imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis via the IRS-1/ERK1/2 pathway. Life Sci. 2019, 219, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Chen, M.; Tong, M.; Zhao, M.; Tang, F.; Xiao, R.; Wen, H. Rutaecarpine inhibited imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis via inhibiting the NF-κB and TLR7 pathways in mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1876–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zong, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Du, W.; Li, L. MiR-744-3p regulates keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation via targeting KLLN in psoriasis. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson-Huang, L.M.; Lowes, M.A.; Krueger, J.G. Putting together the psoriasis puzzle: An update on developing targeted therapies. Dis. Model. Mech. 2012, 5, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alalaiwe, A.; Hung, C.F.; Leu, Y.L.; Tahara, K.; Chen, H.H.; Hu, K.Y.; Fang, J.Y. The active compounds derived from Psoralea corylifolia for photochemotherapy against psoriasis-like lesions: The relationship between structure and percutaneous absorption. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 124, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyerich, K.; Dimartino, V.; Cavani, A. IL-17 and IL-22 in immunity: Driving protection and pathology. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitahata, K.; Matsuo, K.; Hara, Y.; Naganuma, T.; Oiso, N.; Kawada, A.; Nakayama, T. Ascorbic acid derivative DDH-1 ameliorates psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice by suppressing inflammatory cytokine expression. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 138, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.X.; Zhao, J.X.; Meng, Y.J.; Di, T.T.; Xu, X.L.; Xie, X.J.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, N.; Li, P.; et al. Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid inhibits the secretion of cytokines by dendritic cells via the TLR7/8 pathway in an imiquimod-induced psoriasis mouse model and in vitro. Life Sci. 2018, 207, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Duan, X.; Hu, F.; Poorun, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Gan, L.; He, M.; Zhu, K.; et al. Resolvin D1 attenuates imiquimod-induced mice psoriasiform dermatitis through MAPKs and NF-κB pathways. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 89, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, R.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, X.; Xiangfei, D.; Bai, R.; Bi, Z.; Yang, P.; Yang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Su, W.; et al. PAMs ameliorates the imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin disease in mice by inhibition of translocation of NF-κB and production of inflammatory cytokines. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irrera, N.; Vaccaro, M.; Bitto, A.; Pallio, G.; Pizzino, G.; Lentini, M.; Arcoraci, V.; Minutoli, L.; Scuruchi, M.; Cutroneo, G.; et al. BAY 11-7082 inhibits the NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways and protects against IMQ-induced psoriasis. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2017, 131, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Tu, Y.; Huang, L.; Long, Y.; Wang, W.; Yee, H.; Wan, Z.; et al. Huangkui capsule alleviates renal tubular epithelial-mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and TLR4/NF-κB signaling. Phytomedicine 2018, 57, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.R.; Meng, X.; Kuang, H.X. Comparisons of the pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution profiles of withanolide B after intragastric administration of the effective part of Datura metel L. in normal and psoriasis guinea pigs. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1083, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Wand, Q.H.; Yang, B.Y.; Xiao, H.B.; Sun, Y.P.; Kuang, H.X. Protective ef fects of active fraction and const ituents from Flos Daturae on Chinese hamster ovary cells injuried by dimethyl sulfoxide. Chin. Trad. Herbal Drugs 2006, 37, 1826–1831. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.; Yang, B.Y.; Li, T.; Wang, Q.H.; Kuang, H.X. Optimization of Extraction Technology for the Leaves of Datura Metel, L. by Central Composition Design-Response Surface Methodology. Inform. Trad. Chin. Med. 2015, 32, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |








© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, B.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, J.-Y.; Guan, W.; Guo, S.; Kuang, H.-X. Datura Metel L. Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Dermatitis and Inhibits Inflammatory Cytokines Production through TLR7/8–MyD88–NF-κB–NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. Molecules 2019, 24, 2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112157
Yang B-Y, Cheng Y-G, Liu Y, Liu Y, Tan J-Y, Guan W, Guo S, Kuang H-X. Datura Metel L. Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Dermatitis and Inhibits Inflammatory Cytokines Production through TLR7/8–MyD88–NF-κB–NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. Molecules. 2019; 24(11):2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112157
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Bing-You, Yan-Gang Cheng, Yan Liu, Yuan Liu, Jin-Yan Tan, Wei Guan, Shuang Guo, and Hai-Xue Kuang. 2019. "Datura Metel L. Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Dermatitis and Inhibits Inflammatory Cytokines Production through TLR7/8–MyD88–NF-κB–NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway" Molecules 24, no. 11: 2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112157
APA StyleYang, B. -Y., Cheng, Y. -G., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Tan, J. -Y., Guan, W., Guo, S., & Kuang, H. -X. (2019). Datura Metel L. Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Dermatitis and Inhibits Inflammatory Cytokines Production through TLR7/8–MyD88–NF-κB–NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. Molecules, 24(11), 2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112157