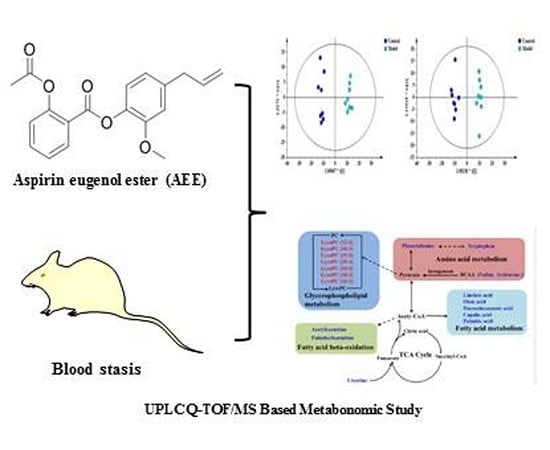
UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-Based Plasma Metabolomics to Evaluate the Effects of Aspirin Eugenol Ester on Blood Stasis in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of AEE on WBV and PV
2.2. Effects of AEE on Coagulation Parameters and Platelet Aggregation
2.3. Effects of AEE on Haematological Analysis and Biochemistry Parameters
2.4. Measurement of Plasma TXB2 and 6-keto-PGF1α
2.5. Effect of AEE on Plasma Metabolomics
2.6. Identification of Potential Biomarkers
2.7. Pathway Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Animals and Grouping
4.3. Rat Acute Blood Stasis Model
4.4. Sample Collection
4.5. Viscosity and Platelet Aggregation Determination
4.6. Plasma Anticoagulation Assay
4.7. Haematological Analysis and Blood Biochemistry
4.8. Sample Preparation for Metabolomics Study
4.9. UPLC-MS Conditions
4.10. Multivariate Analysis and Identification of Potential Metabolites
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mchedlishvili, G. Disturbed blood flow structuring as critical factor of hemorheological disorders in microcirculation. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 1998, 19, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.X.; Han, S.Y.; Wang, X.W.; Ma, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L.; Ma, Z.Z.; Tu, P.F. Effect of the carthamins yellow from Carthamus tinctorius L. on hemorheological disorders of blood stasis in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, X.; Miao, J.J.; Chen, A.Q.; Li, P.; Chen, L.; Liang, J.R.; Xie, R.M.; Zhao, Y. The antithrombotic effect of RSNK in blood-stasis model rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 173, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, Y.; Satoh, K.; Kitadai, M.; Takahashi, T.; Izumi, Y.; Hosomi, N. Effects of pravastatin sodium and simvastatin on plasma fibrinogen level and blood rheology in type II hyperlipoproteinemia. Atherosclerosis. 1996, 122, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.M. Standardization in clinimetrics for syndromatic diagnosis of cerebrovascular diseases in traditional Chinese medicine. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 1988, 8, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toth, K.; Kesmarky, G.; Vekasi, J.; Nemes, J.; Czopf, L.; Kapronczay, P.; Halmosi, R.; Papp, E.; Juricskay, I. Hemorheological and hemodynamic parameters in patients with essential hypertension and their modification by alpha-1 inhibitor drug treatment. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 1999, 21, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.G.; Gao, Z.Y.; Wang, P.L. Study on the diagnostic criteria for coronary heart disease patients of blood stasis syndrome. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012, 32, 1285–1286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liperoti, R.; Vetrano, D.L.; Bernabei, R.; Onder, G. Herbal medications in cardiovascular medicine. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.L.; DeWitt, D.L.; Garavito, R.M. Cyclooxygenases: Structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 145–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Wang, M.H.; Chen, I.J. Antiplatelet and calcium inhibitory properties of eugenol and sodium eugenol acetate. Gen. Pharmacol. 1996, 27, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogalakshmi, B.; Viswanathan, P.; Anuradha, C.V. Investigation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and DNA-protective properties of eugenol in thioacetamide-induced liver injury in rats. Toxicology. 2010, 268, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, S.A.; Simjee, R.U.; Shamim, G.; Gilani, A.H. Eugenol: A dual inhibitor of platelet-activating factor and arachidonic acid metabolism. Phytomedicine 1995, 2, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, X.; Niu, J.; Wei, X.; Liu, X. Synthesis of aspirin eugenol ester and its biological activity. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Zhou, X.; Niu, J.; Wei, X.; Liu, Z. A 15-day oral dose toxicity study of aspirin eugenol ester in Wistar rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1980–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, N.; Li, B. In vivo and in vitro metabolism of aspirin eugenol ester in dog by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kong, X.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. Genotoxic evaluation of aspirin eugenol ester using the Ames test and the mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, N.; Liu, X.W.; Yang, Y.J.; Li, J.Y.; Mohamed, I.; Liu, G.R.; Zhang, J.Y. Preventive effect of aspirin eugenol ester on thrombosis in kappa-carrageenan-induced rat tail thrombosis model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e133125. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Liu, X.W.; Yang, Y.J.; Shen, D.S.; Zhao, X.L.; Mohamed, I.; Kong, X.J.; Li, J.Y. Evaluation on antithrombotic effect of aspirin eugenol ester from the view of platelet aggregation, hemorheology, TXB2/6-keto-PGF1alpha and blood biochemistry in rat model. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Goodacre, R. Metabolomics and systems pharmacology: Why and how to model the human metabolic network for drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today. 2014, 19, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.G.; Frevert, U. Metabolomics in drug discovery and development. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 94, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: Applications to biomarker and metabolic pathway research. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabonomics and its role in drug development and disease diagnosis. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2004, 4, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Hua, Y.; Ji, P.; Yao, W.; Ma, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Wen, Y.; Yang, C.; Wei, Y. Urinary metabolomics study the mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction intervention in acute blood stasis model rats based on liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1074–1075, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Yin, P.; Deng, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, G. Effect of a traditional Chinese medicine preparation Xindi soft capsule on rat model of acute blood stasis: A urinary metabonomics study based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2008, 873, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xiong, X.; Feng, B. Aspirin resistance and promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis: Current situation and prospectives. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014, 2014, 954863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesmarky, G.; Feher, G.; Koltai, K.; Horvath, B.; Toth, K. Viscosity, hemostasis and inflammation in atherosclerotic heart diseases. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2006, 35, 67–73. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Duan, J.A.; Tang, Y.; Guo, J.; Yang, N.; Ma, H.; Shi, X. Taoren-Honghua herb pair and its main components promoting blood circulation through influencing on hemorheology, plasma coagulation and platelet aggregation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, N.; Li, Y.J.; Li, Y.; Dai, R.J.; Meng, W.W.; Chen, Y.; Schlappi, M.; Deng, Y.L. Dragon’s Blood extract has antithrombotic properties, affecting platelet aggregation functions and anticoagulation activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 135, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadley, R.J.; Chi, L.; Rebello, S.S.; Gagnon, A. Contribution of in vivo models of thrombosis to the discovery and development of novel antithrombotic agents. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 43, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shattil, S.J.; Hoxie, J.A.; Cunningham, M.; Brass, L.F. Changes in the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb.IIIa complex during platelet activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 11107–11114. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, K.H.; Han, H.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Jeon, S.D.; Im, G.J.; Lee, B.Y.; Kim, K.; Lim, K.M.; Chung, J.H. Ginkgo biloba extract enhances antiplatelet and antithrombotic effects of cilostazol without prolongation of bleeding time. Thromb Res. 2009, 124, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, C.; Kawasaki, T.; Kato, Y.; Abe, M.; Suzuki, K.; Ohmiya, M.; Funatsu, T.; Morita, Y.; Okada, M. ASP6537, a novel highly selective cyclooxygenase-1 inhibitor, exerts potent antithrombotic effect without “aspirin dilemma”. Thromb Res. 2013, 132, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Leval, X.; Hanson, J.; David, J.L.; Masereel, B.; Pirotte, B.; Dogne, J.M. New developments on thromboxane and prostacyclin modulators part II: Prostacyclin modulators. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogne, J.M.; de Leval, X.; Hanson, J.; Frederich, M.; Lambermont, B.; Ghuysen, A.; Casini, A.; Masereel, B.; Ruan, K.H.; Pirotte, B.; et al. New developments on thromboxane and prostacyclin modulators part I: Thromboxane modulators. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1223–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, A.; Hase, S.; Miyazawa, T.; Ohno, R.; Takeuchi, K. Role of cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2 inhibition in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced intestinal damage in rats: Relation to various pathogenic events. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargaftig, B.B.; Chignard, M.; Benveniste, J. Present concepts on the mechanisms of platelet aggregation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1981, 30, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, N.; Tsujiei, M.; Kimura, H.; Yajima, A.; Nagae, H.; Kimura, C. Maternal and fetal atrial natriuretic peptide levels, maternal plasma renin activity, angiotensin II, prostacyclin and thromboxane A2 levels in normal and preeclamptic pregnancies. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1991, 165, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Chen, W.; Yu, X.; Ding, D.; Zhang, W.; Hua, H.; Xu, M.; Meng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Celastrol aggravates LPS-induced inflammation and injuries of liver and kidney in mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 2078–2086. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Z.J.; Liu, Z.H.; Gong, M.J.; Han, B.; Wang, S.M.; Liang, S.W. Intervention effects of puerarin on blood stasis in rats revealed by a (1)H NMR-based metabonomic approach. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Han, Z.; Chen, A.; Pan, S.; Liang, S.; Wang, S. System responses to chronic cold stress probed via(1)H NMR spectroscopy in plasma and urine matrices. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Tian, N.; Yang, M.; Kong, L. (1)H NMR-based metabolomics approach to evaluate the effect of Xue-Fu-Zhu-Yu decoction on hyperlipidemia rats induced by high-fat diet. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal 2013, 78–79, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Xu, C.; Xue, Y.; Ruan, Q.; Yang, B.; Liu, Z.; Cui, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Jin, J. The therapeutic effect of Ilex pubescens extract on blood stasis model rats according to serum metabolomics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 227, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksem, J.; Jacobson, N.; Neiderhiser, D.H. Lysophosphatidylcholine-induced gastric injury and ulceration in the guinea pig. Am. J. Pathol. 1984, 115, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Loften, J.R.; Linn, J.G.; Drackley, J.K.; Jenkins, T.C.; Soderholm, C.G.; Kertz, A.F. Invited review: Palmitic and stearic acid metabolism in lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 4661–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, K.C. Docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6 omega 3) and linoleic acid are anti-aggregatory, and alter arachidonic acid metabolism in human platelets. Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1985, 17, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellotti, G.M.; Zhang, P.; Nguyen, J.; Abdulla, F.; Chen, C.; Nguyen, P.; Nowotny, C.; Steer, C.J.; Smith, A.; Belcher, J.D. Hepatic overexpression of hemopexin inhibits inflammation and vascular stasis in murine models of sickle cell disease. Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, W.X.; Yuan, Z.K.; Huang, X.P. Detection and analysis on plasma metabolomics in patient with coronary heart disease of Xin-blood stasis syndrome pattern. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2010, 30, 579–584. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, W.; Song, J.; Li, G. Neuroprotective effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on bilirubin encephalopathy in vitro and in vivo. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 2631–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynor, A.; Jantscheff, P.; Ross, T.; Schlesinger, M.; Wilde, M.; Haasis, S.; Dreckmann, T.; Bendas, G.; Massing, U. Saturated and mono-unsaturated lysophosphatidylcholine metabolism in tumour cells: A potential therapeutic target for preventing metastases. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhihetty, P.J.; Beal, M.F. Creatine and its potential therapeutic value for targeting cellular energy impairment in neurodegenerative diseases. Neuromol. Med. 2008, 10, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, R.P.; Stefanello, S.T.; Mauriz, J.L.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J.; Soares, F.A. Creatine and the Liver: Metabolism and Possible Interactions. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachikawa, M.; Hosoya, K.; Ohtsuki, S.; Terasaki, T. A novel relationship between creatine transport at the blood-brain and blood-retinal barriers, creatine biosynthesis, and its use for brain and retinal energy homeostasis. Subcell Biochem. 2007, 46, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sommer, A.P.; Haddad, M.; Fecht, H.J. Light effect on water viscosity: Implication for ATP biosynthesis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbauer, J.L.; Dorgan, L.J.; Schuster, S.M. Effects of deuterium on the kinetics of beef heart mitochondrial ATPase. Arch. Biochem Biophys. 1984, 231, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Karam, I.; Liu, X.W.; Kong, X.J.; Qin, Z.; Li, S.H.; Jiao, Z.H.; Dong, P.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Li, J.Y. UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-based urine and plasma metabonomics study on the ameliorative effects of aspirin eugenol ester in hyperlipidemia rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 332, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compound is available from the authors. |





| Groups | Plasma Coagulation Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PT (s) | TT (s) | FIB (mg/dL) | |
| Control | 8.11 ± 0.21 | 38.26 ± 1.23 ## | 1.63 ± 0.17 ## |
| Model | 8.65 ± 0.22 | 29.94 ± 2.73 | 3.85 ± 0.12 |
| ASA | 11.56 ± 1.77 ## | 31.93 ± 1.07 # | 3.69 ± 0.13 # |
| AEE | 10.86 ± 0.46 ## | 31.71 ± 0.55 # | 3.21 ± 0.19 #▲ |
| Variable | Unit | Control | Model | ASA | AEE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A: Haematological Analysis | |||||
| WBC | 109/L | 4.19 ± 0.63 ## | 8.11 ± 0.76 | 8.6 ± 2.4 | 10.13 ± 1.28 ## |
| Lymph | 109/L | 2.84 ± 0.55 ## | 1.59 ± 0.34 | 1.64 ± 0.58 | 1.93 ± 0.69 |
| MONON | 109/L | 0.1 ± 0.01 ## | 0.23 ± 0.07 | 0.21 ± 0.10 | 0.28 ± 0.07 |
| Gran | 109/L | 1.25 ± 0.29 ## | 6.3 ± 0.48 | 6.75 ± 1.83 | 7.93 ± 0.94 ## |
| Lymph | % | 65.26 ± 5.54 ## | 19.56 ± 2.8 | 18.7 ± 3.21 | 19.2 ± 3.44 |
| Mon | % | 2.76 ± 0.38 | 2.79 ± 0.49 | 2.63 ± 0.39 | 2.75 ± 0.30 |
| Gran | % | 30.01 ± 5.68 ## | 77.65 ± 3.24 | 78.68 ± 3.25 | 78.05 ± 3.57 |
| RBC | 1012/L | 7.76 ± 0.40 # | 8.46± 1.04 | 7.91 ± 0.17 | 8.42 ± 0.54 |
| HGB | g/L | 145.5 ± 8.44 # | 160.4 ± 23.90 | 147.5 ± 4.47 | 155 ± 5.03 |
| HCT | % | 44.05 ± 2.21 | 47.59 ± 6.340 | 44.16 ± 0.96 | 46.84 ±1.39 |
| MCV | fL | 56.88 ± 0.37 | 56.25 ± 1.08 | 55.89 ± 0.52 | 56.55 ± 0.66 |
| MCH | pg | 18.71 ± 0.25 | 18.85 ± 0.56 | 18.59 ± 0.37 | 18.64 ± 0.28 |
| MCHC | g/L | 329.6 ± 4.57 # | 335.9 ± 5.59 | 333.4 ± 4.57 | 330.5 ± 6.07 # |
| RDW | % | 10.99 ± 0.51 | 10.83 ± 0.46 | 10.83 ± 0.41 | 10.95 ± 0.50 |
| PLT | 109/L | 833.9 ± 68.51 ## | 440.9 ± 140.8 | 600.9 ± 24.2 ## | 678.4 ± 50.0 ## |
| MPV | fL | 5.75 ± 0.26 | 5.7 ± 0.21 | 5.41 ± 0.11 ## | 5.9 ± 0.10 |
| PDW | % | 16.26 ± 0.13 # | 16.46 ± 0.12 | 16.39 ± 0.19 | 16.43 ± 0.14 |
| PCT | % | 0.48 ± 0.03 # | 0.25 ± 0.08 | 0.33 ± 0.01 ## | 0.38 ± 0.03 ##▲ |
| B: Blood Biochemistry | |||||
| T-BIL | μM | 1.66 ± 0.30 | 1.79 ± 0.64 | 0.60 ± 0.11 ## | 0.60 ± 0.14 ## |
| TP | g/L | 64.73 ± 2.29 | 63.03 ± 1.19 | 60.11 ± 2.46 ## | 60.78 ± 1.56 ## |
| ALB | g/L | 29.16 ± 0.68 ## | 27.55 ± 1.08 | 27.35 ± 0.83 | 27.50 ± 1.09 |
| GLB | g/L | 35.56 ± 1.99 | 35.48 ± 1.06 | 32.76 ± 1.95 ## | 33.28 ± 1.08 ## |
| ALB/GLB | 0.84 ± 0.05 # | 0.78 ± 0.05 | 0.84 ± 0.05 # | 0.81 ± 0.04 | |
| ALT | U/L | 55.78 ± 7.71 ## | 203.7 ± 40.22 | 414.3 ± 117.3 ## | 358.0 ± 66.87 ## |
| AST | U/L | 170.13 ± 10.16 ## | 818.5 ± 228.9 | 1155 ± 212 ## | 1223 ± 227 ## |
| AST/ALT | 3.13 ± 0.47 ## | 3.99 ± 0.49 | 2.89 ± 0.45 ## | 3.41 ± 0.37 #▲ | |
| ALP | U/L | 95.75 ± 17.69 # | 84.00 ± 6.65 | 84.25 ± 5.09 | 83.50 ± 3.89 |
| LDH | U/L | 2513 ± 173.9 ## | 2872 ± 250 | 2605.4 ± 143.9 # | 2653 ± 212.1 # |
| CK | U/L | 987.6 ± 89.02 | 1099 ± 450.8 | 1831 ± 480 ## | 2169 ± 522.2 ## |
| BUN | mM | 7.39 ± 0.34 ## | 8.68 ± 0.79 | 8.76 ± 1.12 | 10.27 ± 0.71 ## |
| CR | μM | 40.11 ± 1.25 ## | 51.36 ± 8.32 | 40.01 ± 4.06 ## | 46.11 ± 3.58 #▲ |
| UA | μM | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 002 | 0.17 ± 0.12## | 0.08 ± 0.02▲ |
| GLU | mM | 5.98 ± 0.66 ## | 3.88 ± 0.62 | 3.96 ± 0.72 | 3.68 ± 0.35 |
| TG | mM | 0.76 ± 0.16 | 0.83 ± 0.10 | 1.15 ± 0.19 ## | 1.17 ± 0.06 ## |
| No. | SM | Formula | m/z | RT | Metabolite | Fold Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M/C | ASA/M | AEE/M | ||||||
| 1 | ESI+ | C30H50NO7P | 568.3406 | 17.68 | LysoPC (22:6) | 0.47 ** | 0.84 | 1.10 |
| 2 | ESI+ | C26H48NO7P | 518.3243 | 16.91 | LysoPC (18:3) | 0.29 ** | 1.71 ** | 2.43 ** |
| 3 | ESI+ | C4H9N3O2 | 132.0769 | 1.36 | Creatine | 2.40 ** | 0.70 * | 0.92 |
| 4 | ESI+ | C23H48NO7P | 482.3261 | 17.91 | LysoPC (15:0) | 0.53 ** | 0.68 ** | 1.38 ** |
| 5 | ESI+ | C9H17NO4 | 204.1225 | 2.03 | Acetylcarnitine | 1.75 ** | 0.62 ** | 0.61 * |
| 6 | ESI+ | C28H50NO7P | 544.3412 | 17.85 | LysoPC (20:4) | 0.47 ** | 0.80 * | 1.20 * |
| 7 | ESI+ | C23H45NO4 | 400.3426 | 22.44 | Palmitoylcarnitine | 2.36 ** | 1.08 | 0.60 ** |
| 8 | ESI+ | C24H50NO7P | 496.3411 | 19.78 | LysoPC (16:0) | 0.63 ** | 0.88 * | 1.54 ** |
| 9 | ESI+ | C26H50NO7P | 520.3410 | 18.06 | LysoPC (18:2) | 0.54 ** | 0.89 | 1.61 ** |
| 10 | ESI+ | C9H11NO2 | 166.0858 | 3.65 | Phenylalanine | 1.24 ** | 1.05 | 0.77 ** |
| 11 | ESI+ | C24H48NO7P | 494.3246 | 17.29 | LysoPC (16:1) | 0.56 ** | 1.16 | 1.48 ** |
| 12 | ESI+ | C6H13NO2 | 132.1020 | 2.16 | Isoleucine | 1.36 ** | 0.65 ** | 0.33 ** |
| 13 | ESI+ | C5H11NO2 | 118.0862 | 1.95 | Valine | 1.21 | 0.66 ** | 0.60 ** |
| 14 | ESI- | C18H32O2 | 279.2328 | 22.01 | Linoleic acid | 2.19 * | 0.62 | 0.40 * |
| 15 | ESI- | C18H34O2 | 281.2483 | 23.43 | Oleic acid | 2.39 * | 0.69 | 0.43 * |
| 16 | ESI- | C22H32O2 | 327.2328 | 21.38 | Docosahexaenoic acid | 1.50 ** | 0.59 ** | 0.42 ** |
| 17 | ESI- | C11H12N2O2 | 203.0817 | 5.99 | Tryptophan | 1.09 | 0.56 ** | 0.49 ** |
| 18 | ESI- | C20H32O2 | 303.2327 | 21.69 | Copalic acid | 1.29 | 0.59 ** | 0.52 ** |
| 19 | ESI- | C16H32O2 | 255.2326 | 23.21 | Palmitic acid | 2.1 5 ** | 0.59 | 0.34 ** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, D.; Ma, N.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qin, Z.; Li, S.; Jiao, Z.; Kong, X.; Li, J. UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-Based Plasma Metabolomics to Evaluate the Effects of Aspirin Eugenol Ester on Blood Stasis in Rats. Molecules 2019, 24, 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132380
Shen D, Ma N, Yang Y, Liu X, Qin Z, Li S, Jiao Z, Kong X, Li J. UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-Based Plasma Metabolomics to Evaluate the Effects of Aspirin Eugenol Ester on Blood Stasis in Rats. Molecules. 2019; 24(13):2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132380
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Dongshuai, Ning Ma, Yajun Yang, Xiwang Liu, Zhe Qin, Shihong Li, Zenghua Jiao, Xiaojun Kong, and Jianyong Li. 2019. "UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-Based Plasma Metabolomics to Evaluate the Effects of Aspirin Eugenol Ester on Blood Stasis in Rats" Molecules 24, no. 13: 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132380
APA StyleShen, D., Ma, N., Yang, Y., Liu, X., Qin, Z., Li, S., Jiao, Z., Kong, X., & Li, J. (2019). UPLC-Q-TOF/MS-Based Plasma Metabolomics to Evaluate the Effects of Aspirin Eugenol Ester on Blood Stasis in Rats. Molecules, 24(13), 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132380