Anti-Hypochlorite and Catalytic Activity of Commercially Available Moringa oleifera Diet Supplement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Total Phenolic Content Determination
2.2. Antioxidative Assay
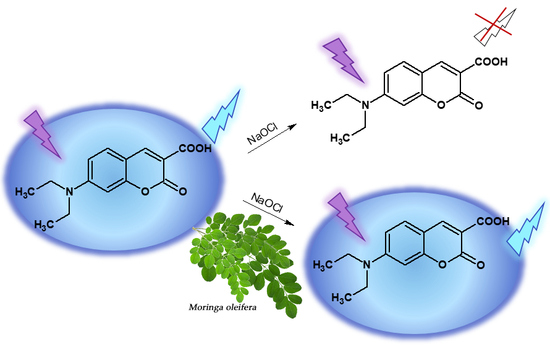
2.3. Determination of Anti-Hypochlorite Potential
2.3.1. Synthesis of Coumarin-Derived Hypochlorite-Sensitive Fluorescent Probe 7-DCCA
2.3.2. Anti-Hypochlorite Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Methods
3.3.1. Extract Preparation
3.3.2. Total Phenolic Content Determination
3.3.3. Antioxidant Assay
3.3.4. Synthesis of 7-Diethylamino-Coumarin-3-Carboxylic Acid
3.3.5. Anti-Hypochlorite Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 7-DCCA | 7-diethylamino-coumarin-3-carboxylic acid |
| AA | ascorbic acid |
| DW | dry weight |
| FCR | Folin–Ciocalteu reagent |
| GAE | gallic acid equivalents |
| OCl− | hypochlorite ion |
| RCS | reactive chlorine species |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| TPC | total phenolic content |
| TROL | TROLOX |
References
- Gopalakrishnan, L.; Doriya, K.; Kumar, D.S. Moringa oleifera: A review on nutritive importance and its medicinal application. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2016, 5, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.; Spada, A.; Battezzati, A.; Schiraldi, A.; Aristil, J.; Bertoli, S. Cultivation, Genetic, Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Moringa oleifera Leaves: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12791–12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popoola, J.O.; Obembe, O.O. Local knowledge, use pattern and geographical distribution of Moringa oleifera Lam. (Moringaceae) in Nigeria. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, F.; Lafit, S.; Ashraf, M.; Gilani, A.H. Moringa oleifera: A Food Plant with Multiple Medicinal Uses. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagul, S.D.; Rajput, J.D.; Bendre, R.S. Synthesis of 3-carboxycoumarins at room temperature in water extract of banana peels. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Bhanger, M.I. Effect of season and production location on antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera leaves grown in Pakistan. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakade, V.; Cukrowska, E.; Chimuka, L. Comparison of antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera and selected vegetables in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2013, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddhuraju, P.; Becker, K. Antioxidant Properties of Various Solvent Extracts of Total Phenolic Constituents from Three Different Agroclimatic Origins of Drumstick Tree (Moringa oleifera Lam.) Leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergera-Jimenez, M.; Almatrafi, M.M.; Fernandez, M.L. Bioactive Components in Moringa Oleifera Leaves Protect against Chronic Disease. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślik, E.; Gręda, W.; Adamus, W. Contents of polyphenols in fruit and vegetables. Food Chem. 2006, 94, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Neveu, V.; Vos, F.; Scalbert, A. Identification of the 100 richest dietary sources of polyphenols: An application of the Phenol-Explorer database. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klebanoff, S.J. Myeloperoxidase: Friend and foe. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 77, 598–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettle, A.J.; Albrett, A.M.; Chapman, A.L.; Dickerhof, N.; Forbes, L.V.; Khalilova, I.; Turnet, R. Measuring chlorine bleach in biology and medicine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pękal, A.; Pyrzynska, K. Effect of pH and metal ions on DPPH radical scavenging activity of tea. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 66, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawidowicz, A.L.; Olszowy, M. Mechanism change in estimating of antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds. Talanta 2012, 97, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michiels, J.A.; Kevers, C.; Pincemail, J.; Defraigne, J.O.; Dommes, J. Extraction conditions can greatly influence antioxidant capacity assays in plant food matrices. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.J.; Lee, K.S.; Hyacinth, H.I.; Hibbert, J.M.; Reid, M.E.; Wheatley, A.O.; Asemota, H.N. An Investigation of the Antioxidant Capacity in Extracts from Moringa oleifera Plants Grown in Jamaica. Plants 2017, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreelatha, S.; Padma, P.R. Antioxidant Activity and Total Phenolic Content of Moringa oleifera Leaves in Two Stages of Maturity. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2009, 64, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Wang, X.; Lam, K.S. A convenient synthesis of coumarin-3-carboxylic acids via Knoevenagel condensation of Meldrum’s acid with ortho-hydroxyaryl aldehydes or ketones. Tetrahedron. Lett. 2003, 44, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalehshahi, H.G.; Balalaie, S.; Aliahmadi, A. Peptides N-Connected to Hydroxycoumarin and cinnamic acid derivatives: Synthesis and Fluorescence Spectroscopic, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 8831–8842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmachari, G. Room Temperature One-Pot Green Synthesis of Coumarin-3-carboxylic Acids in Water: A Practical Method for the Large-Scale Synthesis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2350–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorito, S.; Taddeo, V.A.; Genovese, S.; Epifano, F. A green chemical synthesis of coumarin-3-carboxylic and cinnamic acids using crop-derived products and waste waters as solvents. Tetrahedron. Lett. 2016, 57, 4795–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Song, B.; Youan, J. Bioanalytical methods for hypochlorous acid detection: Recent advances and challenges. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 99, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, M.B.; Kettle, A.J.; Winterbourn, C.C. Inside the Neutrophil Phagosome: Oxidants, Myeloperoxidase, and Bacterial Killing. Blood 1998, 92, 3007–3017. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Albrich, J.M.; McCarthy, C.A.; Hurst, J.K. Biological reactivity of hypochlorous acid: Implications for microbicidal mechanisms of leukocyte myeloperoxidase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, W.H.; Olivieri, V.O., Jr.; Krusé, C.W. The reaction of nucleotides with aqueous hypochlorous acid. Water Res. 1979, 13, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.C.M.; Winterbourn, C.C. Oxidative damage to fibronectin: I. The effects of the neutrophil myeloperoxidase system and HOCl. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1991, 285, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.C.; Vissers, M.C.M.; Domigan, N.M.; Winterbourn, C.C. Modification of red cell membrane lipids by hypochlorous acid and haemolysis by preformed lipid chlorohydrins. Redox Rep. 1997, 3, 236–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.; Zhi, W.; Ye, D.; Zhang, W.; Ni, L. Rapid detection of hypochlorite by a coumarin-based hydrazide in aqueous solution and its application in live-cell imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Gong, A.; Hu, F.; Zhang, C. A Fluorescent Probe for Hypochlorite Based on Modulating the Unique Rotation of N-N Single Bond in Acetohydrazide. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10435–10438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.C.; Venkatesan, P.; Wei, L.F.; Wu, S.P. A coumarin-based fluorescent probe for thiols and its application in cell imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 232, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Y.; Hsu, C.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Wei, L.F.; Wu, S.P. A hypochlorous acid turn-on fluorescent probe based on HOCl-promoted oxime oxidation and its application in cell imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 196, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Seth, D. Photophysical Properties of 7-(diethylamino)Coumarin-3-carboxylic Acid in the Nanocage of Cyclodextrins and in Different Solvents and Solvent Mixtures. Photochem. Photobiol. 2013, 89, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starzak, K.; Matwijczuk, A.; Creaven, B.; Matwijczuk, A.; Wybraniec, S.; Karcz, D. Fluorescence Quenching-Based Mechanism for Determination of Hypochlorite by Coumarin-Derived Sensors. Int. Mol. J. Sci. 2019, 20, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, W.D.; Haken, H.; Wolf, H.C. Molecular Physics and Elements of Quantum Chemistry: Introduction to Experiments and Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Cao, H.; Xiao, J. 2-Polyphenols: Absorption, bioavailability, and metabolomics. In Polyphenols: Properties, Recovery, and Applications; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 45–67. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |




| IC50 [mM] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| pH 3 | pH 5 | pH 7.4 | |
| Moringa (aq) | 0.41 ± 0.02 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
| 7-DCCA 1 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.00 |
| ascorbic acid 2 | 1.81 ± 0.09 | 1.11 ± 0.07 | 1.22 ± 0.13 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Starzak, K.; Creaven, B.; Matwijczuk, A.; Matwijczuk, A.; Karcz, D. Anti-Hypochlorite and Catalytic Activity of Commercially Available Moringa oleifera Diet Supplement. Molecules 2019, 24, 3330. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183330
Starzak K, Creaven B, Matwijczuk A, Matwijczuk A, Karcz D. Anti-Hypochlorite and Catalytic Activity of Commercially Available Moringa oleifera Diet Supplement. Molecules. 2019; 24(18):3330. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183330
Chicago/Turabian StyleStarzak, Karolina, Bernadette Creaven, Arkadiusz Matwijczuk, Alicja Matwijczuk, and Dariusz Karcz. 2019. "Anti-Hypochlorite and Catalytic Activity of Commercially Available Moringa oleifera Diet Supplement" Molecules 24, no. 18: 3330. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183330
APA StyleStarzak, K., Creaven, B., Matwijczuk, A., Matwijczuk, A., & Karcz, D. (2019). Anti-Hypochlorite and Catalytic Activity of Commercially Available Moringa oleifera Diet Supplement. Molecules, 24(18), 3330. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183330