Improving Interlaminar Fracture Toughness and Impact Performance of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Laminated Composite by Using Thermoplastic Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of the Laminated Composites
2.1.1. Effect of Toughener Type on the Interlaminar Toughening of the CF/EP Laminated Composites
2.1.2. Areal Density Effect of PI on the Interlaminar Toughening of the CF/EP Laminated Composites
2.2. Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of the Laminated Composites
2.3. Impact Testing of the Laminated Composites
2.4. Damage Analysis
3. Experiments
3.1. Materials
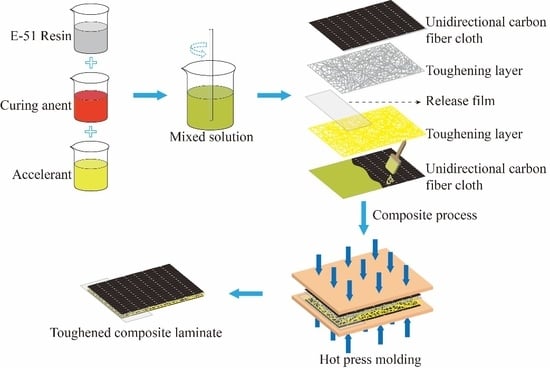
3.2. Composite Preparation
3.3. Mode I Interlaminar Test
3.4. Mode II Test
3.5. Impact Test
3.6. Morphology
4. Conclusions
- Comparing the effects of two types of tougheners, the addition of PI fiber significantly increased the interlaminar toughness, while the addition of PP fiber reduced the interlaminar toughness. Interlaminar cracking was hindered by the debonding between PI fibers and matrix, the deformation and fracture of PI fibers, which greatly improves the interlaminar toughness. By contrast, PP fibers were molten into a continuous phase without the formation of fiber bridge and the interface between melted PP fibers and resin matrix was poor bonding, which reduces the interlaminar toughness.
- In modes I and II of interlaminar fracture toughness testing, GIC and GIIC first increased and then decreased with the increase of the areal density of the PI-toughened layer. GIC and GIIC of composite laminates reached their maximum values at 30 PI, which increased by 98.49% and 84.07%, respectively, compared with those of the non-toughened composite laminates. However, when areal density reached 40 g/m2, GIC and GIIC presented a downward trend due to the entanglement of fibers and the insufficient diffusion of epoxy resin in the toughened layer.
- In low-velocity impact testing, when the toughened layer is 30 PI, Fmax and Ee increase by 92.38% and 299.08%, respectively, compared with the non-toughened composite laminates. Moreover, the damage morphology after low-velocity impact testing showed that severe delamination areas and fiber breakage did not occur in the 30 PI-toughened composite, and only a few signs of carbon fiber damage were observed, indicating that the 30 PI toughened layer had the best toughening effect.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marsh, G. Airbus A350 XWB update. Reinf. Plast. 2010, 54, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.C.; Zhang, Y. Perspectives of carbon nanotubes/polymer nanocomposites for wind blade materials. Renew Sust. Energ. Rev. 2014, 30, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Qu, P.; Liu, G.; Yi, X.; Su, H.; Jia, Y. Analysis on low velocity impact damage of laminated composites toughened by structural toughening layer. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 1280–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoluzzi, D.B.; Gomes, G.F.; Hirayama, D.; Ancelotti, A.C. Development of a 3D reinforcement by tufting in carbon fiber/epoxy composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2019, 100, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, K.V.; Basavarajappa, S.; Sherigara, B.S. Damage characterisation of glass/textile fabric polymer hybrid composites in sea water environment. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Sun, X.; Guan, X.; Mu, Y.; Jia, Y. Effect of interlaminar toughness on the low-velocity impact damage in composite laminates. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.R.; Long, S.C.; Zhang, X.Q.; Yao, X.H. Study on the delamination behavior of thick composite laminates under low-energy impact. Compos. Struct. 2018, 184, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.Z.H.; Karuppanan, S.; Megat-Yusoff, P.S.M.; Sajid, Z. Impact resistance and damage tolerance of fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Struct. 2019, 217, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.W. Impact Response of Carbon Fibre Fabric/Thermoset-Thermoplastic Combined Polymer Composites. Adv. Compos. Lett. 2017, 26, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.B.; Zhang, H.Y.; Ma, C.; Xu, X.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.C.; Wei, R.B.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.T.; Shao, Q.; et al. Trace electrosprayed nanopolystyrene facilitated dispersion of multiwalled carbon nanotubes: Simultaneously strengthening and toughening epoxy. Carbon 2019, 142, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, N.H.; Young, T.M.; McGrail, P.T.; Stanley, W.F. Inclusion of a thermoplastic phase to improve impact and post-impact performances of carbon fibre reinforced thermosetting composites—A review. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 582–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daelemans, L.; van der Heijden, S.; De Baere, I.; Rahier, H.; Van Paepegem, W.; De Clerck, K. Nanofibre bridging as a toughening mechanism in carbon/epoxy composite laminates interleaved with electrospun polyamide nanofibrous veils. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heijden, S.; Daelemans, L.; De Schoenmaker, B.; De Baere, I.; Rahier, H.; Van Paepegem, W.; De Clerck, K. Interlaminar toughening of resin transfer moulded glass fibre epoxy laminates by polycaprolactone electrospun nanofibres. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 104, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsotsis, T.K. Interlayer toughening of composite materials. Polym. Compos. 2009, 30, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Yi, X.; Liu, G.; Liu, L. Simultaneously increasing the electrical conductivity and fracture toughness of carbon–fiber composites by using silver nanowires-loaded interleaves. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 97, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, W.W.; Shi, Y.Y. Low-velocity impact damage research on CFRPs with Kevlar-fiber toughening. Compos. Struct. 2019, 216, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasaee, M.; Bond, I.P.; Trask, R.S.; Greenhalgh, E.S. Mode I interfacial toughening through discontinuous interleaves for damage suppression and control. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Hu, X.; Chen, H. Effects of aramid-fibre toughening on interfacial fracture toughness of epoxy adhesive joint between carbon-fibre face sheet and aluminium substrate. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2014, 48, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Bai, Y.; Hu, X.; Lu, P. Enhanced epoxy adhesion between steel plates by surface treatment and CNT/short-fibre reinforcement. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 127, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.N.; Kumar, V.; Verma, S.K. Fracture toughness behaviour of carbon fibre epoxy composite with Kevlar reinforced interleave. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2006, 132, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Saz-Orozco, B.; Ray, D.; Stanley, W.F. Effect of thermoplastic veils on interlaminar fracture toughness of a glass fiber/vinyl ester composite. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 2501–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, V.A.; Hogg, P.J.; Sampson, W.W. The influence of the nonwoven veil architectures on interlaminar fracture toughness of interleaved composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 110, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasaee, M.; Bond, I.P.; Trask, R.S.; Greenhalgh, E.S. Mode II interfacial toughening through discontinuous interleaves for damage suppression and control. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Noguchi, H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cheong, S.K. Effect of Interleaved NonWoven Carbon Tissue on Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Laminated Composites: Part I – Mode II. J. Compos. Mater. 2002, 36, 2153–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Cheong, S.-K.; Noguchi, H. A toughening and strengthening technique of hybrid composites with non-woven tissue. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 207, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Noro, Y.; Sugimoto, K.-I.; Endo, M. Mode I and mode II interlaminar fracture toughness of CFRP laminates toughened by carbon nanofiber interlayer. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.R.; Jiang, Z.H.; Fei, B.H.; Hse, C.Y.; Sun, Z.J. Tensile behaviour and fracture mechanism of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens). Holzforschung 2015, 69, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalfon-Cohen, E.; Kopp, R.; Furtado, C.; Ni, X.C.; Arteiro, A.; Borstnar, G.; Mavrogordato, M.N.; Sinclair, I.; Spearing, S.M.; Camanho, P.P.; et al. Synergetic effects of thin plies and aligned carbon nanotube interlaminar reinforcement in composite laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 166, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denneulin, S.; Viot, P.; Leonardi, F.; Lataillade, J.-L. The influence of acrylate triblock copolymer embedded in matrix on composite structures’ responses to low-velocity impacts. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matadi Boumbimba, R.; Coulibaly, M.; Khabouchi, A.; Kinvi-Dossou, G.; Bonfoh, N.; Gerard, P. Glass fibres reinforced acrylic thermoplastic resin-based tri-block copolymers composites: Low velocity impact response at various temperatures. Compos. Struct. 2017, 160, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, A.; Arikan, V. Low-velocity impact response of E-glass reinforced thermoset and thermoplastic based sandwich composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 127, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daelemans, L.; van der Heijden, S.; De Baere, I.; Rahier, H.; Van Paepegem, W.; De Clerck, K. Damage-Resistant Composites Using Electrospun Nanofibers: A Multiscale Analysis of the Toughening Mechanisms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11806–11818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Guo, Z.Z. A simple method for determining the mode I interlaminar fracture toughness of composite without measuring the growing crack length. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2018, 191, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M. Measuring the rate-dependent mode I fracture toughness of composites—A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 81, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzon, B.G.; Hawkins, S.C.; Huynh, C.P.; Radjef, R.; Brown, C. An investigation of Mode I and Mode II fracture toughness enhancement using aligned carbon nanotubes forests at the crack interface. Compos. Struct. 2013, 106, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daelemans, L.; Cohades, A.; Meireman, T.; Beckx, J.; Spronk, S.; Kersemans, M.; De Baere, I.; Rahier, H.; Michaud, V.; Van Paepegem, W.; et al. Electrospun nanofibrous interleaves for improved low velocity impact resistance of glass fibre reinforced composite laminates. Mater. Des. 2018, 141, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the CF/EP toughened by PP and PI are available from the authors. |













| Sample | Fmax (KN) | Dmax (mm) | Ea (J) | Ee (J) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-toughened | 3.15 | 7.90 | 15.34 | 2.18 |
| 10PI-toughened | 2.88 | 9.38 | 7.96 | 8.35 |
| 20PI-toughened | 4.34 | 5.60 | 9.15 | 8.03 |
| 30PI-toughened | 6.06 | 5.77 | 8.78 | 8.70 |
| 40PI-toughened | 5.80 | 6.49 | 11.30 | 6.45 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Wu, L.-W.; Jiang, Q.; Tian, D.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, H.-J. Improving Interlaminar Fracture Toughness and Impact Performance of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Laminated Composite by Using Thermoplastic Fibers. Molecules 2019, 24, 3367. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183367
Chen L, Wu L-W, Jiang Q, Tian D, Zhong Z, Wang Y, Fu H-J. Improving Interlaminar Fracture Toughness and Impact Performance of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Laminated Composite by Using Thermoplastic Fibers. Molecules. 2019; 24(18):3367. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183367
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ling, Li-Wei Wu, Qian Jiang, Da Tian, Zhili Zhong, Yan Wang, and Hong-Jun Fu. 2019. "Improving Interlaminar Fracture Toughness and Impact Performance of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Laminated Composite by Using Thermoplastic Fibers" Molecules 24, no. 18: 3367. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183367
APA StyleChen, L., Wu, L. -W., Jiang, Q., Tian, D., Zhong, Z., Wang, Y., & Fu, H. -J. (2019). Improving Interlaminar Fracture Toughness and Impact Performance of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Laminated Composite by Using Thermoplastic Fibers. Molecules, 24(18), 3367. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183367