Carotenoid-Related Volatile Compounds of Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) Essential Oils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
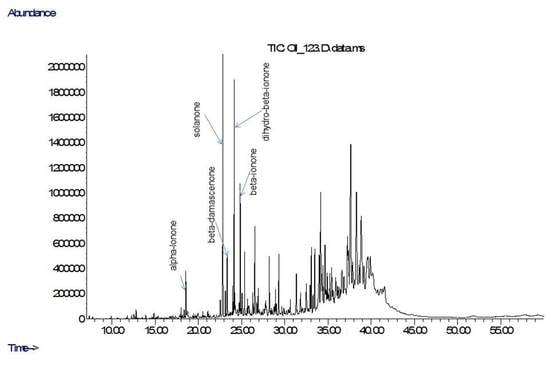
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Beta-Carotene Determination
4.3. Essential Oil (EO) Isolation
4.4. Olfactory Evaluation of The EOs
4.5. Chemical Composition of the EOs
4.6. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mookherjee, B.; Wilson, R. Tobacco constituents—Their importance in flavor and fragrance chemistry. Perfum. Flavor. 1990, 15, 27–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wahlberg, I.; Enzell, C. Tobacco isoprenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1987, 4, 237–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedeltcheva-Antonova, D.; Ivanova, D.; Antonov, L.; Abe, I. Insight into the aroma profile of Bulgarian tobacco absolute oil. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 94, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, K.; Garbe, D.; Surburg, H. Common Fragrance and Flavor Materials. Preparation, Properties and Uses, 4th ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, H.; Harada, M. 4-Hydroxy-beta-damascone and 4-hydroxy-dihydro-beta damascene from cigar tobacco. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1972, 36, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Zlatkis, A.; Park, J.; Lee, U. Isolation of essential oils from tobacco by gas co-distillation/solvent extraction. Chromatographia 1982, 15, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordan, B.; Uhring, M.; Borgerding, M.; Chung, H. Analysis of flue-cured tobacco essential oil by hyphenated analytical techniques. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1988, 26, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.; Mookherjee, B.; Vinals, J. A comparative analysis of the volatile components of Virginia, Burley, Turkish and black tobaccos. In Proceedings of the 184th National ACS Meeting, Kansas City, MO, USA, 14 September 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Bolt, A.J.N.; Purkis, S.W.; Sadd, J.S. A damascone derivative from Nicotiana tabacum. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 613–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterhalter, P.; Rouseff, R. Carotenoid-derived aroma compounds: An introduction. In Carotenoid-derived Aroma Compounds; ACS Symposium Series; Winterhalter, P., Rouseff, R., Eds.; American Chemistry Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; Volume 802, pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori, T.; Kasuga, R.; Matsushita, H.; Kaneko, H.; Noguchi, M. Neutral aroma constituents in Burley tobacco. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1976, 40, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leffingwell, J.C.; Leffingwell, D. Chemical and sensory aspects of tobacco flavor—An overview. Rec. Adv. Tob. Sci. 1988, 14, 169–218. [Google Scholar]
- Leffingwell, J. Basic chemical constituents of tobacco leaf and differences among tobacco types. In Tobacco: Production, Chemistry and Technology; Davis, D., Nielsen, M., Eds.; Blackwell Science: London, UK, 1999; pp. 265–284. [Google Scholar]
- Gloria, M.; Grulke, E.; Gray, J. Effect of type of oxidation on beta-carotene loss and volatile products formation in model systems. Food Chem. 1993, 46, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanasawud, P.; Crouzet, C. Mechanism of formation of volatile compounds by thermal degradation of carotenoids in aqueous medium. 1. Beta-carotene degradation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanasawud, P.; Crouzet, C. Mechanism of formation of volatile compounds by thermal degradation of carotenoids in aqueous medium. 2. Lycopene degradation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demole, E.; Berthet, D. Chemical study of Burley tobacco flavour (Nicotiana tabacum L.). 1. Volatile to medium-volatile constituents (b.p. ≤84%/0.001 Torr). Helv. Chim. Acta 1972, 58, 1866–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-X.; Guo, S.-Y.; Li, L.; Cai, M.-Y.; Wang, B.-X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, C.-Q.; Shi, H.-L. Effects of volatile compounds in tobacco on smoke aroma. J. South. Chin. Univ. Technol. 2005, 33, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori, T.; Kasuga, R.; Kaneko, H.; Noguchi, M. Neutral volatile components of Burley tobacco. Beitr. Tabakforsch. Int. 1978, 9, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Robledo, G.; Rodriquez-Bustamante, E.; Sanchez-Contreras, A.; Rodriquez-Sanoja, R.; Sanchez, S. Production of tobacco aroma from lutein. Specific role of the microorganisms involved in the process. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 62, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, V.; Gochev, V.; Girova, T.; Iliev, I.; Ivanova, T.; Stoyanova, A. Extraction products from tobacco-aroma and bioactive compounds and activities. Cur. Bioact. Compd. 2015, 11, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, V.; Ivanova, T.; Stoyanova, A.; Georgiev, V.; Hristeva, T.; Nikolova, V.; Docheva, M.; Nikolov, N.; Damianova, S. Phytochemicals in leaves and extracts of the variety “Plovdiv 7” of Bulgarian oriental tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Trends Phytoch. Res. 2018, 2, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.-P.; Li, T.-S.; Zhang, Y.-G.; Cao, H.-J.; Gong, C.-R.; Zhang, W.-J. The mechanism of carotenoid degradation in flue-cured tobacco and changes in the related enzyme activities at the leaf-drying stage during the bulk curing process. Agric. Sci. Chin. 2010, 9, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leffingwell, J.C.; Alford, E.D. Volatile constituents of Perique tobacco. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 4, 899–915. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev, E.; Stoyanova, A. A Guide for the Specialist in Aromatic Industry, 1st ed.; UFT Academic Publishing House: Plovdiv, Bulgaria, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ohloff, G. The importance of minor components in flavors and fragrances. In Proceedings of the 7th International Congress of Essential Oils, Kyoto, Japan, 7–11 October 1977; pp. 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Alagić, S.; Stančić, I.; Palić, R.; Stojanović, G.; Nikolić, М. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil of the oriental tobacco Yaka. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2002, 14, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; Ye, X. Extraction of essential oil from discarded tobacco leaves by solvent extraction and steam distillation, and identification of its chemical composition. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 39, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulović, N.; Stojanović, G.; Palić, R.; Alagić, S. Chemical composition of the ether and ethyl acetate extracts of Serbian selected tobacco types: Yaka, Prilep and Otlja. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2006, 18, 562–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, G.; Palić, R.; Alagić, S.; Zeković, Z. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil and CO2 extracts of semi-oriental tobacco Otlja. Flavour Fragr. J. 2000, 15, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palić, R.; Stojanović, G.; Alagić, S.; Nikolić, M.; Lepojević, Z. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil and CO2 extracts of the oriental tobacco Prilep. Flavour Fragr. J. 2002, 17, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagić, S.; Stančić, I.; Palić, R.; Stojanović, G.; Lepojević, Z. Chemical composition of the supercritical CO2 extracts of the Yaka, Prilep and Otlija tobaccos. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2006, 18, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, M.; Shimoda, M. Extraction of volatile flavor compounds from tobacco leaf through a low-density polyethylene membrane. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2017, 55, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Sheng, L.; Liu, B.; Tong, H.; Liu, S. Comparison of different extraction methods: Steam distillation, simultaneous distillation and extraction and headspace co-distillation, used for the analysis of the volatile components in aged flue-cured tobacco leaves. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1040, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Shao, X. A comparison of accelerated solvent extraction, Soxhlet extraction, and ultrasonic-assisted extraction for analysis of terpenoids and sterols in tobacco. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, K.; Wei, W.; Guo, F.; Huang, L. Comparison of simultaneous distillation extraction and solid-phase micro-extraction for determination of volatile constituents in tobacco flavor. J. Cent. South. Univ. Technol. 2005, 12, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Lu, X.; Xing, J.; Zhang, S.; Kong, H.; Xu, G.; Wu, C. Comparison of comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for the analysis of tobacco essential oils. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 545, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhu, X.; Gao, Y.; Su, Q. Two-step simultaneous distillation and solvent extraction for isolation both free and bound aroma in tobacco. Ann. Chim. 2006, 96, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Rodriguez, A.; Bronze, M.-R.; da Ponte, M.N. Supercritical fluid extraction of tobacco leaves: A preliminary study on the extraction of solanesol. J. Supercrit. Fluid. 2008, 45, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhu, L.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.; Dai, Y. Analytical method of free and conjugated neutral aroma components in tobacco by solvent extraction coupled with comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr A 2013, 1280, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Cheng, H.; Du, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Chang, S.; Dong, S.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J. Optimization extraction process of aroma components in tobacco. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2013, 51, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Li, Q.; Li, C.; Cao, J.; Lai, Y.; Qiu, K.; Min, S. Determination of aroma components in Chinese southwest tobacco by directly suspended droplet microextraction combined with GC-MS. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2014, 52, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The State Pharmacopoeia of the USSR, 11th ed.; Medicina: Moscow, Russia, 1990.
- Manuelyan, H. Express methods for assessing the carotenoid composition of tomato fruits. In Genetic Improvement of Tomato; Kalloo, G., Ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 193–195. [Google Scholar]
- Balinova, A.; Diakov, G. On improved apparatus for microdistillation of rose flowers. Plant. Sci. 1974, 11, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Tsonev, I.K.; Chenikov, V.V. Investigation of the aromatic substances of tobacco. Tabak 1962, 23, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |


| Tobacco | Carotenoids, mg/100 g DW | β-Carotene, mg/100 g DW | Essential Oil, mg/g DW |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCV 1 | 5.93 ± 0.05 5,a | 3.73 ± 0.03 a | 2.32 ± 0.11 a |
| BU 2 | 22.23 ± 0.20 b | 20.34 ± 0.18 b | 2.63 ± 0.12 a |
| OR(Kr) 3 | 6.27 ± 0.06 a | 5.45 ± 0.05 c | 4.44 ± 0.14 b |
| OR(Pd7) 4 | 13.60 ± 0.11 c | 12.09 ± 0.10 d | 3.01 ± 0.11 c [22] |
| Tobacco | Component | Ref. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Ionone | β-Ionone | Dihydro-β-Ionone | β-Damascenone | ||||||
| % of TIC 8 | mg/100 g DW | % of TIC | mg/100 g DW | % of TIC | mg/100 g DW | % of TIC | mg/100 g DW | ||
| FCV 1 | 1.37 ± 0.01 5,a | 0.61 ± 0.01 5,a | nd 6 | nd | 2.17 ± 0.02 a | 0.96 ± 0.02 a | 2.92 ± 0.02 a | 1.26 ± 0.02 a | [21] |
| BU 2 | 1.86 ± 0.01 b | 0.73 ± 0.01 b | nd | nd | 3.10 ± 0.02 7, b | 1.19 ± 0.02 7,b | 3.53 ± 0.02 b | 1.35 ± 0.02 b | [21] |
| OR(Kr) 3 | 0.91 ± 0.01 c | 0.20 ± 0.00 c | 2.76 ± 0.02 | 1.08 ± 0.02 | 5.92 ± 0.03 c | 1.34 ± 0.03 c | 1.59 ± 0.01 c | 0.36 ± 0.01 c | [21] |
| OR(Pd7) 4 | 4.32 ± 0.02 d | 1.43 ± 0.02 d | nd | nd | 5.19 ± 0.03 c | 1.73 ± 0.03 d | 3.71 ± 0.02 b | 1.23 ± 0.02 a | [22] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popova, V.; Ivanova, T.; Prokopov, T.; Nikolova, M.; Stoyanova, A.; Zheljazkov, V.D. Carotenoid-Related Volatile Compounds of Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) Essential Oils. Molecules 2019, 24, 3446. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193446
Popova V, Ivanova T, Prokopov T, Nikolova M, Stoyanova A, Zheljazkov VD. Carotenoid-Related Volatile Compounds of Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) Essential Oils. Molecules. 2019; 24(19):3446. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193446
Chicago/Turabian StylePopova, Venelina, Tanya Ivanova, Tsvetko Prokopov, Milena Nikolova, Albena Stoyanova, and Valtcho D. Zheljazkov. 2019. "Carotenoid-Related Volatile Compounds of Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) Essential Oils" Molecules 24, no. 19: 3446. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193446
APA StylePopova, V., Ivanova, T., Prokopov, T., Nikolova, M., Stoyanova, A., & Zheljazkov, V. D. (2019). Carotenoid-Related Volatile Compounds of Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) Essential Oils. Molecules, 24(19), 3446. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193446