Eleutheroside B Protects against Acute Kidney Injury by Activating IGF Pathway
Abstract
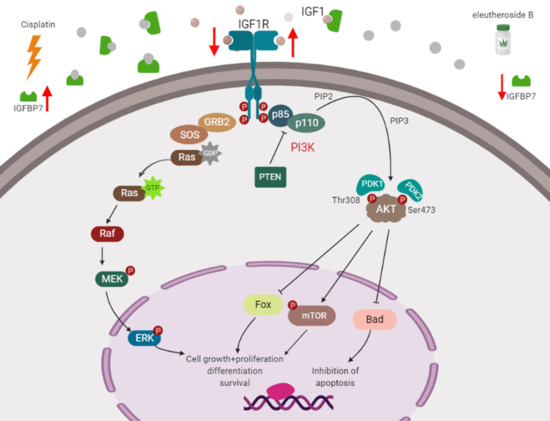
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Eleutheroside B on Cisplatin-Induced Toxicity and Injury in HK-2 Cells
2.2. Effects of Eleutheroside B on Inflammatory Cytokines Induced by Cisplatin in HK-2 Cells
2.3. Effects of Eleutheroside B on Apoptosis and Necroptosis Caused by Cisplatin in HK-2 Cells
2.4. Effect of Eleutheroside B on Cisplatin-Induced Renal Dysfunction and Histopathology
2.5. Effect of Eleutheroside B on Inflammation, Programmed Necrosis, and Apoptosis in Mice with AKI Induced by Cisplatin
2.6. Effect of Eleutheroside B on KIM-1, Inflammation, Necrosis, and Apoptosis in Hypoxia Reoxygenation Injury-Induced (HRI-Induced) HK-2 Cells
2.7. RNA-Seq Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Materials
4.2. Murine Model of Cisplatin-Induced AKI
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. MTT Assay
4.5. Renal RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Immunofluorescence
4.8. Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) Staining
4.9. Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.10. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.11. Gene Transcriptome Analysis Based on RNA-Seq Technology
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doi, K. How to sharpen a novel sword from AKI basic research. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, A. Acute Kidney Injury. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 53, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gameiro, J.; Jorge, S.; Lopes, J.A. Acute Kidney Injury. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 168, 836–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; James, M.T. Acute Kidney Injury. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 167, ITC66–ITC80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.L.; Cerdá, J.; Burdmann, E.A.; Tonelli, M.; García-García, G.; Jha, V.; Susantitaphong, P.; Rocco, M.; Vanholder, R.; Sever, M.S.; et al. International Society of Nephrology’s 0by25 initiative for acute kidney injury (zero preventable deaths by 2025): A human rights case for nephrology. Lancet 2015, 385, 2616–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, R.A. Kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) anemia work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for anemia in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 279–335. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, T.T.; Patel, U.D.; Chang, T.I.; Kennedy, K.F.; Masoudi, F.A.; Matheny, M.E.; Mikhail, K.; Amin, A.P.; Weintraub, W.S.; Curtis, J.P. Validated contemporary risk model of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions: Insights from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry Cath-PCI Registry. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e001380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.W.; Ma, B.; Leung, K.C.; Graham, M.M.; Pannu, N.; Traboulsi, M.; Goodhart, D.; Knudtson, M.L.; James, M.T. Risk Prediction Models for Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Accompanying Cardiac Catheterization: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Can. J. Cardiol. 2017, 33, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeysundera, D.N.; Keyvan, K.; Jean-Yves, D.; Vivek, R.; Chan, C.T.; Granton, J.T.; Scott, B.W. Derivation and validation of a simplified predictive index for renal replacement therapy after cardiac surgery. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2007, 297, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, C.; Weng, Q.; Ye, B. Curcumin protects against acute renal injury by suppressing JAK2/STAT3 pathway in severe acute pancreatitis in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Liu, M.M.; Zang, H.; Ma, Q.Y.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, L.; Ren, G.L.; Li, H.D.; Wu, W.F.; Wang, J. Restoration of E-cadherin by PPBICA protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by attenuating inflammation and programmed cell death. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, X.M.; Li, H.D.; Wu, W.F.; Tang, M.K.; Ren, G.L.; Gao, L.; Li, X.F.; Yang, Y.; Xu, T.; Ma, T.T. Wogonin protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by targeting RIPK1-mediated necroptosis. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havasi, A.; Borkan, S.C. Apoptosis and acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joannes-Boyau, O.; Honore, P.M.; Boer, W.; Rose, T. Septic acute kidney injury and tubular apoptosis: Never a Lone Ranger. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, H.; LeBleu, V.S.; Bosukonda, D.; Keck, P.; Taduri, G.; Bechtel, W.; Okada, H.; Carlson, W.J.; Bey, P.; Rusckowski, M.; et al. Activin-like kinase 3 is important for kidney regeneration and reversal of fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Attawish, A.; Chivapat, S.; Phadungpat, S.; Bansiddhi, J.; Techadamrongsin, Y.; Mitrijit, O.; Chaorai, B.; Chavalittumrong, P. Chronic toxicity of Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Fitoterapia 2004, 75, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, A.; Huang, F.; Yin, Z.; Li, K.; Qin, W.; Chen, M.; et al. Protective effects of gypenosides against fatty liver disease induced by high fat and cholesterol diet and alcohol in rats. Arch. Pharm Res. 2012, 35, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-H.; Chen, S.-H.; Wang, Q.-F.; Chen, J.-C.; Chang, D.-C.; Hsu, S.-L.; Chen, C.-H.; Sheue, C.-R.; Liu, Y.-W. The molecular mechanism of gypenosides-induced G1 growth arrest of rat hepatic stellate cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.W.; Chen, J.C.; Lai, T.Y.; Yang, J.S.; Weng, S.W.; Ma, Y.S.; Lin, H.Y.; Wu, R.S.; Wu, K.C.; Wood, W.G.; et al. Gypenosides suppress growth of human oral cancer SAS cells in vitro and in a murine xenograft model: The role of apoptosis mediated by caspase-dependent and caspase-independent pathways. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-Y.; Yang, J.-S.; Lu, K.-W.; Yu, C.-S.; Chou, S.-T.; Lin, J.-J.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Lin, M.-L.; Chueh, F.-S.; Chen, S.-S.; et al. An Experimental Study on the Antileukemia Effects of Gypenosides In Vitro and In Vivo. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2010, 10, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, A.; Watanabe, H.; Tanaka, R.; Kondo, M.; Chuang, V.T.; Wu, Q.; Endo, M.; Ishima, Y.; Fukagawa, M.; Otagiri, M.; et al. Albumin fusion renders thioredoxin an effective anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory agent for preventing cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraishi, F.; Curtis, L.M.; Truong, L.; Poss, K.; Visner, G.A.; Madsen, K.; Nick, H.S.; Agarwal, A. Heme oxygenase-1 gene ablation or expression modulates cisplatin-induced renal tubular apoptosis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2000, 278, F726–F736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dieterle, F.; Sistare, F.; Goodsaid, F.; Papaluca, M.; Ozer, J.S.; Webb, C.P.; Baer, W.; Senagore, A.; Schipper, M.J. Vonderscher, Renal biomarker qualification submission: A dialog between the FDA-EMEA and Predictive Safety Testing Consortium. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umehara, H.; Goda, S.; Imai, T.; Nagano, Y.; Minami, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Okazaki, T.; Bloom, E.T.; Domae, N. Fractalkine, a CX3C-chemokine, functions predominantly as an adhesion molecule in monocytic cell line THP-1. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2001, 79, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endre, Z.H.; Edelstein, C.L. Animal Models for the Assessment of Acute Renal Dysfunction and Injury. In Clinical Nephrotoxins; De Broe, M.E., Porter, G.A., Bennett, W.M., Deray, G., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Sheng, Y.; Qian, Z. Current Understanding of Inflammatory Responses in Acute Kidney Injury. Curr. Gene Ther. 2017, 17, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.M.; Ren, G.L.; Gao, L.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.D.; Wu, W.F.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Lv, X.W.; Li, J. NADPH oxidase 4 promotes cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via ROS-mediated programmed cell death and inflammation. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Hu, L.; Yang, C. Necroptosis in acute kidney injury: A shedding light. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasparakis, M.; Vandenabeele, P. Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature 2015, 517, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkermann, A. Nonapoptotic cell death in acute kidney injury and transplantation. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linkermann, A.; De Zen, F.; Weinberg, J.; Kunzendorf, U.; Krautwald, S. Programmed necrosis in acute kidney injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ren, G.L.; Wei, B.; Jin, J.; Huang, X.R.; Shao, W.; Li, J.; Meng, X.M.; Lan, H.Y. Conditional knockout of TGF-βRII/Smad2 signals protects against acute renal injury by alleviating cell necroptosis, apoptosis and inflammation. Theranostics 2019, 9, 8277–8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.N.; Liu, M.M.; Wang, F.; Wei, B.; Yang, Q.; Cai, Y.T.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.Q.; Jiang, L.; Li, C.; et al. RIPK1 inhibitor Cpd-71 attenuates renal dysfunction in cisplatin-treated mice via attenuating necroptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 2019, 133, 1609–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.L.; Baxter, R.C. Signalling pathways of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF binding protein-3. Growth Factors 2011, 29, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firth, S.M.; Baxter, R.C. Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr. Rev. 2002, 23, 824–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwa, V.O.Y.; Rosenfeld, R.G. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins: A proposed superfamily. Acta Paediatr. Suppl. 1999, 88, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samani, A.A.; Yakar, S.; LeRoith, D.; Brodt, P. The role of the IGF system in cancer growth and metastasis: Overview and recent insights. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 20–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollak, M.N.; Schernhammer, E.S.; Hankinson, S.E. Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Nagalla, S.R.; Yamanaka, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Wilson, E.; Rosenfeld, R.G. Synthesis and characterization of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP)-7. Recombinant human mac25 protein specifically binds IGF-I and -II. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 30322–30325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evdokimova, V.; Tognon, C.E.; Benatar, T.; Yang, W.; Krutikov, K.; Pollak, M.; Sorensen, P.H.; Seth, A. IGFBP7 binds to the IGF-1 receptor and blocks its activation by insulin-like growth factors. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulyana, Y.; Ho, I.A.; Sia, K.C.; Newman, J.P.; Toh, X.Y.; Endaya, B.B.; Chan, J.K.; Gnecchi, M.; Huynh, H.; Chung, A.Y.; et al. Paracrine factors of human fetal MSCs inhibit liver cancer growth through reduced activation of IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt signaling. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hematulin, A.; Sagan, D.; Eckardt-Schupp, F.; Moertl, S. NBS1 is required for IGF-1 induced cellular proliferation through the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK cascade. Cell. Signal. 2008, 20, 2276–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedegund, M. The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways present molecular targets for the effective treatment of advanced melanoma. Front. Biosci. 2005, 10, 2986–3001. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hilger, R.A.; Scheulen, M.E.; Strumberg, D. The Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK Pathway in the Treatment of Cancer. Onkologie 2002, 25, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smalley, K.S.M. A pivotal role for ERK in the oncogenic behaviour of malignant melanoma? Int. J. Cancer 2003, 104, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, T.; Wan, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Bian, J.; Bao, R.; Deng, X.; Yang, T. IGFBP7 regulates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury through ERK1/2 signaling. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 120, 7602–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds eleutheroside B are available from the authors. |







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zang, H.; Yang, Q.; Li, J. Eleutheroside B Protects against Acute Kidney Injury by Activating IGF Pathway. Molecules 2019, 24, 3876. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213876
Zang H, Yang Q, Li J. Eleutheroside B Protects against Acute Kidney Injury by Activating IGF Pathway. Molecules. 2019; 24(21):3876. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213876
Chicago/Turabian StyleZang, Hongmei, Qin Yang, and Jun Li. 2019. "Eleutheroside B Protects against Acute Kidney Injury by Activating IGF Pathway" Molecules 24, no. 21: 3876. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213876
APA StyleZang, H., Yang, Q., & Li, J. (2019). Eleutheroside B Protects against Acute Kidney Injury by Activating IGF Pathway. Molecules, 24(21), 3876. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213876