Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Some New Substituted Quinoxalines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
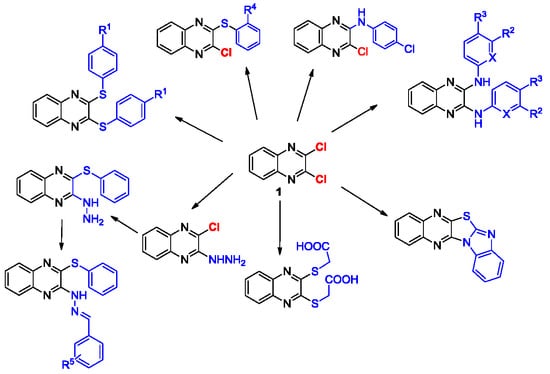
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Evaluation
3. Experimental
3.1. Instruments and Apparatus
3.2. Agar Disk-Diffusion Method
3.3. Determination of MIC
3.4. Synthesis of Quinoxaline-2,3-dione
3.5. Synthesis of 2,3-DCQ (1)
3.6. Synthesis of 2,3-bis(arylthio)quinoxaline (2a–e)
3.6.1. 2,3-Dithiophenylquinoxaline (2a)
3.6.2. 2,3-Di(thio-4-fluorophenyl)quinoxaline (2b)
3.6.3. 2,3-Di(thio-4-bromophenyl)quinoxaline (2c)
3.6.4. 2,3-Di(thio-4-chlorophenyl)quinoxaline (2d)
3.6.5. 2,3-Di(thio-4-methylphenyl)quinoxaline (2e)
3.7. Synthesis of N2,N3-Diarylquinoxaline-2,3-diamine (3a–g)
3.7.1. N2,N3-Di(pyridin-2-yl)quinoxaline-2,3-diamine (3a)
3.7.2. N2,N3-Diphenylquinoxaline-2,3-diamine (3b)
3.7.3. N2,N3-Bis(3-chlorophenyl)quinoxaline-2,3-diamine (3c)
3.7.4. N2,N3-Dip-tolylquinoxaline-2,3-diamine (3d)
3.7.5. N2,N3-Bis(3,4-dimethylphenyl)quinoxaline-2,3-diamine (3e)
3.7.6. N2,N3-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)quinoxaline-2,3-diamine (3f)
3.7.7. N2,N3-Bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)quinoxaline-2,3-diamine (3g)
3.8. Synthesis and Characterization of 2,2’-(Quinoxaline-2,3-diylbis(sulfanediyl))diacetic acid (4)
3.9. Synthesis and Characterization of 3-Chloro-N-(4-chlorophenyl)quinoxalin-2-amine (5)
3.10. Synthesis of 2-Chloro-3-(arylthio)quinoxaline (6a–b)
3.10.1. 2-Chloro-3-(phenylthio)quinoxaline (6a)
3.10.2. 2-(3-Chloroquinoxalin-2-ylthio)benzoic Acid (6b)
3.11. Synthesis of 2-Chloro-3-hydrazinylquinoxaline (7)
3.12. Synthesis of 2-Hydrazinyl-3-(phenylthio)quinoxaline (8)
3.13. Synthesis of (2-(2-Arylidenehydrazinyl)-3-(phenylthio)quinoxaline (9a–f)
3.13.1. 2-(2-Benzylidenehydrazinyl)-3-(phenylthio)quinoxaline (9a)
3.13.2. 2-(2-(4-Nitrobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)-3-(phenylthio)quinoxaline (9b)
3.13.3. 2-(2-(3-Nitrobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)-3-(phenylthio)quinoxaline (9c)
3.13.4. 2-(2-(4-Methoxybenzylidene)hydrazinyl)-3-(phenylthio)quinoxaline (9d)
3.13.5. 2-(2-(4-Chlorobenzylidene)hydrazinyl)-3-(phenylthio)quinoxaline (9e)
3.13.6. 4-((2-(3-(Phenylthio)quinoxalin-2-yl)hydrazono)methyl)phenol (9f)
3.14. Synthesis of Benzimidazo[2′,1′:2,3]thiazolo[4,5-b]quinoxaline (10)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Synthesis and biological activity of new quinoxaline antibiotics of echinomycin analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2004, 14, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, G.; Makino, K.; Kurasawa, Y. Recent progress in the quinoxaline chemistry. Synthesis and biological activity. Heterocycles 1988, 27, 2481–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsami, A.; Bünnagel, T.W.; Farrell, T.; Scharber, M.; Choulis, S.A.; Brabec, C.J.; Scherf, U. Alternating quinoxaline/oligothiophene copolymers—synthesis and unexpected absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1353–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaung, J.-Y. Synthesis and halochromism of new quinoxaline fluorescent dyes. Dyes Pigments 2006, 71, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justin Thomas, K.; Velusamy, M.; Lin, J.T.; Chuen, C.-H.; Tao, Y.-T. Chromophore-labeled quinoxaline derivatives as efficient electroluminescent materials. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 1860–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dailey, S.; Feast, W.J.; Peace, R.J.; Sage, I.C.; Till, S.; Wood, E.L. Synthesis and device characterisation of side-chain polymer electron transport materials for organic semiconductor applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 2238–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.P.; Zhu, Y.; Jenekhe, S.A. Quinoxaline-containing polyfluorenes: Synthesis, photophysics, and stable blue electroluminescence. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, A.; Loriga, M.; Piras, S.; Paglietti, G.; Colla, P.L.; Busonera, B.; Collu, G.; Loddo, R. Synthesis of variously substituted 3-phenoxymethyl quinoxalin-2-ones and quinoxalines capable to potentiate in vitro the antiproliferative activity of anticancer drugs in multi-drug resistant cell lines. Med. Chem. 2006, 2, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.A.; Mullick, P.; Pandit, S.; Kaushik, D. Synthesis of hydrazones derivatives of quinoxalinone-prospective antimicrobial and antiinflammatory agents. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2009, 66, 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Piras, S.; Loriga, M.; Paglietti, G. Quinoxaline chemistry. Part XVII. Methyl [4-(substituted 2-quinoxalinyloxy) phenyl] acetates and ethyl N-{[4-(substituted 2-quinoxalinyloxy) phenyl] acetyl} glutamates analogs of methotrexate: Synthesis and evaluation of in vitro anticancer activity. Farmaco 2004, 59, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sabbagh, O.I.; El-Sadek, M.E.; Lashine, S.M.; Yassin, S.H.; El-Nabtity, S.M. Synthesis of new 2 (1H)-quinoxalinone derivatives for antimicrobial and antiinflammatory evaluation. Med. Chem. Res. 2009, 18, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, T.; Gigante, B.; Marques, M.M.; Gilchrist, T.L.; De Clercq, E. Synthesis and antiviral evaluation of benzimidazoles, quinoxalines and indoles from dehydroabietic acid. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2004, 12, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Al-Masoudi, I.; Hassan, H.G.; Al-Masoudi, N. Synthesis and anti-HIV activity of new homo acyclic nucleosides, 1-(pent-4-enyl) quinoxalin-2-ones and 2-(pent-4-enyloxy) quinoxalines. Chem Hetrocycl Com 2007, 43, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Ghosh, N.N.; Chandra, R. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of substituted 5-[4-[2-(6, 7-dimethyl-1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydro-2-oxo-4-quinoxalinyl) ethoxy] phenyl] methylene] thiazolidine-2, 4-dione derivatives as potent euglycemic and hypolipidemic agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, B.; Ma, M.; Chen, X.; Qin, X.; He, M.; Hussain, S.; Jing, C.; Ma, B. An efficient synthesis of quinoxalinone derivatives as potent inhibitors of aldose reductase. Chemmedchem 2012, 7, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarges, R.; Howard, H.R.; Browne, R.G.; Lebel, L.A.; Seymour, P.A.; Koe, B.K. 4-Amino [1, 2, 4] triazolo [4, 3-a] quinoxalines. A novel class of potent adenosine receptor antagonists and potential rapid-onset antidepressants. J. Med. Chem. 1990, 33, 2240–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancizu, S.; Moreno, E.; Solano, B.; Villar, R.; Burguete, A.; Torres, E.; Pérez-Silanes, S.; Aldana, I.; Monge, A. New 3-methylquinoxaline-2-carboxamide 1, 4-di-N-oxide derivatives as anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis agents. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 2713–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, K.; Ganesh, A.; Ashok, D. Microwave assisted synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of quinoxaline derivatives. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2013, 5, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, H.-A.S.; Al-Marhabi, A.R.; Ammar, Y.A. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 2, 3-disubstituted and fused quinoxalines as potential anticancer and antimicrobial agents. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2017, 74, 445–458. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, X.; Desrivot, J.; Bories, C.; Loiseau, P.M.; Franck, X.; Hocquemiller, R.; Figadere, B. Synthesis and antiprotozoal activity of some new synthetic substituted quinoxalines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, J.; Moreau, S.; Mouray, E.; Sinou, V.; Forfar, I.; Fabre, S.B.; Desplat, V.; Millet, P.; Parzy, D.; Jarry, C. New ferrocenic pyrrolo [1,2-a] quinoxaline derivatives: Synthesis, and in vitro antimalarial activity. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 9133–9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Yamasaki, E.F.; Chan, K.K.; Shen, L.L.; Snapka, R.M. Chloroquinoxaline sulfonamide (NSC 339004) is a topoisomerase IIα/β poison. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 5937–5940. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Huang, K.-C.; Yamasaki, E.F.; Chan, K.K.; Chohan, L.; Snapka, R.M. XK469, a selective topoisomerase IIβ poison. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12168–12173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H. Characterization of cell lines resistant to topoisomerase targeting drugs and mechanistic studies of Quinoxaline solid tumor drugs-a new chemical class of topoisomerase II poisons. Ph.D. Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kakodkar, N.C.; Peddinti, R.; Kletzel, M.; Tian, Y.; Guerrero, L.J.; Undevia, S.D.; Geary, D.; Chlenski, A.; Yang, Q.; Salwen, H.R. The quinoxaline anti-tumor agent R-(+)-XK469 inhibits neuroblastoma tumor growth. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2011, 56, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagdic, O.; Tornuk, F. Antimicrobial properties of organosulfur compounds. In Dietary phytochemicals and microbes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 127–156. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, E.A.; Demmig-Adams, B. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties of garlic and onions. Nutr. Food Sci. 2007, 37, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-L.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Li, H.-M.; Tang, Y.-L.; Liang, X.-H.; Chen, T.; Tang, Y.-J. Comparison of carbon-sulfur and carbon-amine bond in therapeutic drug: 4β-S-aromatic heterocyclic podophyllum derivatives display antitumor activity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14814–14830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Kumar, M.; Mishra, A.; Kumar, A.; Kant, R.; RS, T. Synthesis and antibacterial studies of some new amides of 5-sulphosalicylic acid. Neoplasma 1990, 41, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, C.S.; Ren, W.X. A recyclable copper catalysis in quinoxaline synthesis from α-hydroxyketones and o-phenylenediamines. J. Organomet. Chem. 2009, 694, 3215–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaksar, S.; Rostamnezhad, F. A novel one-pot synthesis of quinoxaline derivatives in fluorinated alcohols. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 2581–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymani, R.; Niakan, N.; Tayeb, S.; Hakimi, S. Synthesis of novel aryl quinoxaline derivatives by new catalytic methods. Orient. J. Chem. 2012, 28, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Qian, C. Ytterbium triflate-catalyzed heterocyclization of 1,2-phenylenediamines and alkyl oxalates under solvent-free conditions via Phillips reaction: A facile synthesis of quinoxaline-2,3-diones derivatives. Synth. Commun. 2004, 34, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogo, J.; Kaplum, V.; Sangi, D.P.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Corrêa, A.G.; Nakamura, C.V. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 2, 3-disubstituted quinoxaline derivatives as antileishmanial and antitrypanosomal agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akar, D.; Incesu, Z.; Gündogdu-Karaburun, N.; Benkli, K.; Isikdag, I. Synthesis and antitumor activity of some 6-chloro- and 6,7-dichloro-2,3-disubstitutedquinoxaline derivatives. Turkish J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 1, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlicz, A.; Kraska, J.; Wojciechowski, L. Quinoxaline derivatives. PL 83335A5, 31 December 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.A.; Mullick, P.; Manchanda, H. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of 2,3-disubstituted quinoxalines. Indian J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2008, 18, 197–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ajani, O.O.; Obafemi, C.A.; Nwinyi, O.C.; Akinpelu, D.A. Microwave assisted synthesis and antimicrobial activity of 2-quinoxalinone-3-hydrazone derivatives. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickevičienė, K.; Baranauskaitė, R.; Kantminienė, K.; Stasevych, M.; Komarovska-Porokhnyavets, O.; Novikov, V. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of N-substituted-β-amino acid derivatives containing 2-hydroxyphenyl, benzo [b] phenoxazine and quinoxaline moieties. Molecules 2015, 20, 3170–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Narasimhan, B. Hydrazides/hydrazones as antimicrobial and anticancer agents in the new millennium. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Bodeis, S.; Walker, R.D.; White, D.G.; Zhao, S.; McDermott, P.F.; Meng, J. Comparison of the Etest and agar dilution for in vitro antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Campylobacter. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawar, P.Y.; Bhise, S.B. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of some new quinoxalinedione derivatives. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2007, 5, 700–710. [Google Scholar]
- Podsiadly, R. Synthesis and photochemical reaction of novel, visible-wavelength oxidizable polymerization sensitizer based on the 12H-quinoxalino[2,3-b][1,4]benzothiazine skeleton. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2009, 202, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, D.; Turner, E.E. Aryloxy derivatives of pyrimidines, quinoxalines and quinolines. J. Chem. Soc. 1937, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, S.D.; Cheeseman, G.W.H. Quinoxalines and related compounds. X. The formation of indolo[2,3-b]quinoxalines and 2-p-aminophenyl-3-anilinoquinoxalines from 2-anilinoquinoxalines. Tetrahedron 1978, 34, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, O.; Rode, C.; Walther, D.; Beckert, R.; Gorls, H. New derivatives of quinoxaline - syntheses, complex formation and their application as controlling ligands for zinc catalyzed epoxide-CO2-copolymerization. Z. Naturforsch. B Chem. Sci. 2002, 57, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, P.; Ganapaty, S.; Babu, R.C.H. In vitro antimicrobial and antitubercular activity of some new hydrazides, hydrazones and sulfonamides of quinoxalines. J. Pharm. Chem. 2008, 2, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 2–10 are available from the authors. |




| Antibacterial Activity Zone of Inhibition (mm) | Antifungal Activity Zone of Inhibition (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G+ bacteria | G− bacteria | |||||
| Compounds | S. aureus | B. subtilis | E. coli | P. vulgaris | C. albicans | A. flavus |
| 2a | 26 | 30 | 18 | 15 | 17 | 14 |
| 2b | 22 | 19 | 25 | 39 | 16 | 12 |
| 2c | 25 | 20 | 27 | 31 | 13 | 15 |
| 2d | 28 | 44 | 34 | 11 | 11 | 5 |
| 3a | 13 | 12 | 14 | 24 | 19 | 14 |
| 3b | 19 | 28 | 39 | 23 | 18 | 9 |
| 3c | 35 | 41 | 37 | 15 | 18 | 16 |
| 3d | 16 | 30 | 32 | 27 | 11 | 19 |
| 3e | 26 | 24 | 27 | 16 | 18 | 11 |
| 3f | 30 | 29 | 30 | 28 | 17 | 14 |
| 3g | 37 | 29 | 28 | 16 | 17 | 15 |
| 4 | 27 | 38 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 15 |
| 5 | 22 | 37 | 37 | 24 | 18 | 12 |
| 6a | 22 | 35 | 24 | 19 | 25 | 17 |
| 6b | 29 | 31 | 35 | 23 | 22 | 11 |
| 8 | 15 | 9 | 9 | 11 | 7 | 9 |
| 9a | 22 | 18 | 25 | 23 | 10 | 9 |
| 9b | 17 | 13 | 18 | 20 | 11 | 11 |
| 9c | 14 | 12 | 22 | 21 | 10 | 15 |
| 9d | 20 | 11 | 14 | 12 | 11 | 7 |
| 9e | 19 | 10 | 19 | 18 | 19 | 5 |
| 9f | 13 | 15 | 17 | 11 | 11 | 8 |
| 10 | 13 | 26 | 24 | 15 | 34 | 27 |
| Ketoconazole | - | - | - | - | 20 | 16 |
| Gentamycin | 24 | 26 | 30 | 25 | - | - |
| DMSO | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Compounds | S. aureus | B. subtilis | E. coli | P. vulgaris | C. albicans | A. flavus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2a | 32 | 32 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 64 |
| 2b | 64 | 128 | 64 | 8 | 64 | 256 |
| 2c | 32 | 64 | 64 | 16 | 128 | 64 |
| 2d | 32 | 16 | 8 | 128 | 256 | >256 |
| 3a | >256 | >256 | >256 | 256 | 128 | 128 |
| 3b | 256 | 64 | 16 | 32 | 64 | >256 |
| 3c | 32 | 16 | 8 | 64 | 64 | 64 |
| 3d | 256 | 32 | 16 | 16 | >256 | 64 |
| 3e | 64 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 64 | 128 |
| 3f | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 128 | 256 |
| 3g | 32 | 32 | 16 | 64 | 128 | 128 |
| 4 | 32 | 16 | >256 | >256 | 64 | 64 |
| 5 | 256 | 32 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 256 |
| 6a | 64 | 16 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 32 |
| 6b | 32 | 32 | 16 | 32 | 32 | >256 |
| 10 | 256 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 16 | 16 |
| Ketoconazole | - | - | - | - | 32 | 32 |
| Gentamycin | 32 | 32 | 16 | 16 | - | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Atawy, M.A.; Hamed, E.A.; Alhadi, M.; Omar, A.Z. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Some New Substituted Quinoxalines. Molecules 2019, 24, 4198. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224198
El-Atawy MA, Hamed EA, Alhadi M, Omar AZ. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Some New Substituted Quinoxalines. Molecules. 2019; 24(22):4198. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224198
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Atawy, Mohamed A., Ezzat A. Hamed, Mahjoba Alhadi, and Alaa Z. Omar. 2019. "Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Some New Substituted Quinoxalines" Molecules 24, no. 22: 4198. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224198
APA StyleEl-Atawy, M. A., Hamed, E. A., Alhadi, M., & Omar, A. Z. (2019). Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Some New Substituted Quinoxalines. Molecules, 24(22), 4198. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224198