Thiourea-Derived Chelating Ligands and Their Organometallic Compounds: Investigations into Their Anticancer Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
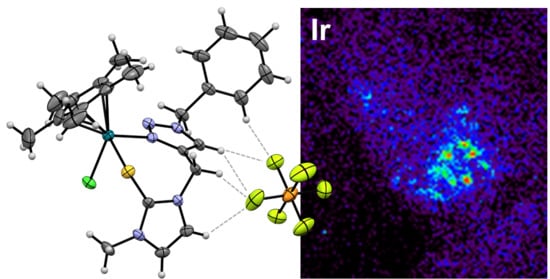
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Physical Measurements
3.2. Syntheses
3.3. Sulforhodamine B Cytotoxicity Assay
3.4. X-ray Fluorescence Microscopy (XFM)
3.4.1. Sample Preparation
3.4.2. Metal Complex Incubation
3.4.3. Advanced Photon Source and Operating Conditions
3.5. DFT Calculations
3.6. Stability Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Storr, T. Ligand Design in Medicinal Inorganic Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2014; p. 449. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, R.; Melchart, M.; Habtemariam, A.; Parsons, S.; Sadler, P.J. Use of Chelating Ligands to Tune the Reactive Site of Half-Sandwich Ruthenium(II)–Arene Anticancer Complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 5173–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, W.H.; Dyson, P.J. Classical and non-classical ruthenium-based anticancer drugs: Towards targeted chemotherapy. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 2006, 4003–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Panichpisal, K.; Kurtzman, N.; Nugent, K. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: A review. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2007, 334, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galluzzi, L.; Senovilla, L.; Vitale, I.; Michels, J.; Martins, I.; Kepp, O.; Castedo, M.; Kroemer, G. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenny, R.G.; Marmion, C.J. Toward Multi-Targeted Platinum and Ruthenium Drugs—A New Paradigm in Cancer Drug Treatment Regimens? Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 1058–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoonjan, M.; Jadhav, V.; Bhatt, P. Arsenic trioxide: Insights into its evolution to an anticancer agent. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 23, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allardyce, C.S.; Dyson, P.J. Ruthenium in Medicine: Current Clinical Uses and Future Prospects. Platinum Met. Rev. 2001, 45, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Rademaker-Lakhai, J.M.; van den Bongard, D.; Pluim, D.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H. A Phase I and pharmacological study with imidazolium-trans-DMSO-imidazole-tetrachlororuthenate, a novel ruthenium anticancer agent. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 3717–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levina, A.; Mitra, A.; Lay, P.A. Recent developments in ruthenium anticancer drugs. Metallomics 2009, 1, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suss-Fink, G. Arene ruthenium complexes as anticancer agents. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 1673–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamo, A.; Sava, G. Ruthenium anticancer compounds: Myths and realities of the emerging metal-based drugs. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 7817–7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Menches, S.M.; Gerner, C.; Berger, W.; Hartinger, C.G.; Keppler, B.K. Structure–activity relationships for ruthenium and osmium anticancer agents–towards clinical development. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 909–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, M.; Hartinger, C.G. Anticancer metallodrugs: Where is the next cisplatin? Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 615–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noffke, A.L.; Habtemariam, A.; Pizarro, A.M.; Sadler, P.J. Designing organometallic compounds for catalysis and therapy. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5219–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, B.S.; Dyson, P.J. Recent progress in the development of organometallics for the treatment of cancer. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2020, 56, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorcier, A.; Ang, W.H.; Bolano, S.; Gonsalvi, L.; Juillerat-Jeannerat, L.; Laurenczy, G.; Peruzzini, M.; Phillips, A.D.; Zanobini, F.; Dyson, P.J. In vitro evaluation of rhodium and osmium RAPTA analogues: The case for organometallic anticancer drugs not based on ruthenium. Organometallics 2006, 25, 4090–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Habtemariam, A.; Pizarro, A.M.; Fletcher, S.A.; Kisova, A.; Vrana, O.; Salassa, L.; Bruijnincx, P.C.; Clarkson, G.J.; Brabec, V.; et al. Organometallic half-sandwich iridium anticancer complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3011–3026. [Google Scholar]
- Hanif, M.; Babak, M.V.; Hartinger, C.G. Development of anticancer agents: Wizardry with osmium. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almodares, Z.; Lucas, S.J.; Crossley, B.D.; Basri, A.M.; Pask, C.M.; Hebden, A.J.; Phillips, R.M.; McGowan, P.C. Rhodium, iridium, and ruthenium half-sandwich picolinamide complexes as anticancer agents. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Romero-Canelon, I.; Qamar, B.; Hearn, J.M.; Habtemariam, A.; Barry, N.P.; Pizarro, A.M.; Clarkson, G.J.; Sadler, P.J. The potent oxidant anticancer activity of organoiridium catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 3941–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Sadler, P.J. Organoiridium complexes: Anticancer agents and catalysts. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, X.-M.; Damu, G.L.V.; Geng, R.-X.; Zhou, C.-H. Comprehensive Review in Current Developments of Imidazole-Based Medicinal Chemistry. Med. Res. Rev. 2014, 34, 340–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, A.; Siddiqui, W.A.; Akbar, J.; Mustafa, G.; Krautscheid, H.; Ullah, N.; Mirza, B.; Sher, F.; Hanif, M.; Hartinger, C.G. Metal complexes of benzimidazole derived sulfonamide: Synthesis, molecular structures and antimicrobial activity. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2016, 443, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gust, R. Update on metal N-heterocyclic carbene complexes as potential anti-tumor metallodrugs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 329, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Joshi, H.; Sharma, K.N.; Gupta, P.L.; Singh, A.K. 2-Propanol vs. glycerol as hydrogen source in catalytic activation of transfer hydrogenation with (η6-Benzene)ruthenium(II) complexes of unsymmetrical bidentate chalcogen ligands. Organometallics 2014, 33, 3629–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.G.; Huang, Y.B.; Lin, Y.J.; Jin, G.X. Syntheses and structures of half-sandwich iridium(III) and rhodium(III) complexes with organochalcogen (S, Se) ligands bearing N-methylimidazole and their use as catalysts for norbornene polymerization. Dalton Trans. 2008, 5612–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, G.E.; Tokmic, K.; Oian, C.S.; Rabinovich, D.; Valle, H.U.; Hollis, T.K.; Kelly, J.T.; Cuellar, K.A.; McNamara, L.E.; Hammer, N.I.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, photophysical properties, and catalytic activity of an SCS bis(N-heterocyclic thione) (SCS-NHT) Pd pincer complex. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 14475–14482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Joshi, H.; Bhaskar, R.; Singh, A.K. Complexes of (η5-Cp*)Ir(III) with 1-benzyl-3-phenylthio/selenomethyl-1, 3-dihydrobenzoimidazole-2-thione/selenone: Catalyst for oxidation and 1, 2-substituted benzimidazole synthesis. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 2228–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-M.; Li, H.-Y.; Li, H.-X.; Young, D.J.; Wang, Y.; Lang, J.-P. Palladium(II) Chloride Complexes of N,N′-Disubstituted Imidazole-2-thiones: Syntheses, Structures, and Catalytic Performances in Suzuki–Miyaura and Sonogashira Coupling Reactions. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 11230–11243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.G.; Gao, L.L.; Wang, Z.B.; Sun, L.Y.; Han, Y.F. Synthesis, Characterization, and Catalytic Activities of Palladium Complexes with Phenylene-Bridged Bis(thione) Ligands. Organometallics 2019, 38, 1946–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragoni, M.C.; Arca, M.; Demartin, F.; Devillanova, F.A.; Garau, A.; Isaia, F.; Lippolis, V.; Verani, G. Anti-thyroid drug methimazole: X-ray characterization of two novel ionic disulfides obtained from its chemical oxidation by I2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4538–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, G.; Jayaram, P.N.; Mugesh, G. Inhibition of lactoperoxidase-catalyzed oxidation by imidazole-based thiones and selones: A mechanistic study. Chem. Asian J. 2013, 8, 1910–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, D.; Roy, G.; Mugesh, G. Antithyroid Drugs and Their Analogues: Synthesis, Structure, and Mechanism of Action. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2706–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.M.; Naz, F.; Taha, M.; Khan, A.; Perveen, S.; Choudhary, M.I.; Voelter, W. Synthesis and in vitro urease inhibitory activity of N,N’-disubstituted thioureas. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 74, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandioller, W.; Kurzwernhart, A.; Hanif, M.; Meier, S.M.; Henke, H.; Keppler, B.K.; Hartinger, C.G. Pyrone derivatives and metals: From natural products to metal-based drugs. J. Organomet. Chem. 2011, 696, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudej, R.; Kljun, J.; Kandioller, W.; Repnik, U.; Turk, B.; Hartinger, C.G.; Keppler, B.K.; Miklavčič, D.; Turel, I. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of the Thionated Antibacterial Agent Nalidixic Acid and Its Organoruthenium(II) Complex. Organometallics 2012, 31, 5867–5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.; Nawaz, M.A.H.; Babak, M.V.; Iqbal, J.; Roller, A.; Keppler, B.K.; Hartinger, C.G. RutheniumII (η6-arene) complexes of thiourea derivatives: Synthesis, characterization and urease inhibition. Molecules 2014, 19, 8080–8092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, A.; Machado, R.C.; Grazul, R.M.; Lopes, M.T.P.; Correa, C.C.; Dos Santos, H.F.; Vieira de Almeida, M.; Silva, H. Novel antitumor adamantane-azole gold(I) complexes as potential inhibitors of thioredoxin reductase. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 21, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Y.; Chiu, C.K.C.; Huang, H.Y.; Lam, Y.P.Y.; Habtemariam, A.; Malcomson, T.; Paterson, M.J.; Clarkson, G.J.; O’Connor, P.B.; Chao, H.; et al. Organoiridium Photosensitizers Induce Specific Oxidative Attack on Proteins within Cancer Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 14898–14902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harringer, S.; Happl, B.; Ozenil, M.; Kast, C.; Hejl, M.; Wernitznig, D.; Legin, A.A.; Schweikert, A.; Gajic, N.; Roller, A.; et al. Synthesis, Modification, and Biological Evaluation of a Library of Novel Water-Soluble Thiopyridone-Based Organometallic Complexes and Their Unexpected (Biological) Behavior. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 5419–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legina, M.S.; Nogueira, J.J.; Kandioller, W.; Jakupec, M.A.; Gonzalez, L.; Keppler, B.K. Biological evaluation of novel thiomaltol-based organometallic complexes as topoisomerase IIα inhibitors. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 25, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tremlett, W.D.J.; Tong, K.K.H.; Steel, T.R.; Movassaghi, S.; Hanif, M.; Jamieson, S.M.F.; Söhnel, T.; Hartinger, C.G. Hydroxyquinoline-derived anticancer organometallics: Introduction of amphiphilic PTA as an ancillary ligand increases their aqueous solubility. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 199, 110768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunxiang, Q.; Tiansong, D.; Li, H.; Theyssen, N.; Zhenshan, H. Hydrogen-bonding interaction in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquids. China Sci. Tech. Pap. 2012, 7, 707–711. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Habtemariam, A.; Basri, A.M.; Braddick, D.; Clarkson, G.J.; Sadler, P.J. Structure–activity relationships for organometallic osmium arene phenylazopyridine complexes with potent anticancer activity. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 10553–10562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Canelón, I.; Salassa, L.; Sadler, P.J. The contrasting activity of iodido versus chlorido ruthenium and osmium arene azo-and imino-pyridine anticancer complexes: Control of cell selectivity, cross-resistance, p53 dependence, and apoptosis pathway. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, M.A.; Smith, A.K. Arene Ruthenium(II) Complexes Formed by Dehydrogenation of Cyclohexadienes with Ruthenium(III) Trichloride. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1974, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, R.; Graham, W.; Heinekey, D.; Hoyano, J.; McMaster, A.; Mattson, B.; Michel, S. Synthesis and structure of dicarbonylbis(η-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)diiridium. Inorg. Chem. 1990, 29, 2023–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseley, K.; Kang, J.; Maitlis, P. Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl-rhodium and-iridium halides. Part II. Reactions with mono-, di-, and tri-olefins. J. Chem. Soc. A 1970, 2875–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, K.Q.; Timerbulatova, M.G.; Peterson, M.B.; Bhadbhade, M.; Messerle, B.A. Cationic Rh and Ir complexes containing bidentate imidazolylidene–1,2,3-triazole donor ligands: Synthesis and preliminary catalytic studies. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 14298–14308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourhis, L.J.; Dolomanov, O.V.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.; Puschmann, H. The anatomy of a comprehensive constrained, restrained refinement program for the modern computing environment–Olex2 dissected. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Adv. 2015, 71, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macrae, C.F.; Sovago, I.; Cottrell, S.J.; Galek, P.T.A.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Platings, M.; Shields, G.P.; Stevens, J.S.; Towler, M.; et al. Mercury 4.0: From visualization to analysis, design and prediction. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2020, 53, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morrison, D.E.; Aitken, J.B.; de Jonge, M.D.; Ioppolo, J.A.; Harris, H.H.; Rendina, L.M. High mitochondrial accumulation of new gadolinium(III) agents within tumour cells. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 2252–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Busse, M.; Windsor, M.S.A.; Tefay, A.J.; Kardashinsky, M.; Fenton, J.M.; Morrison, D.E.; Harris, H.H.; Rendina, L.M. Tumor cell uptake and selectivity of gadolinium(III)-phosphonium complexes: The role of delocalisation at the phosphonium centre. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 177, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weekley, C.M.; Kenkel, I.; Lippert, R.; Wei, S.; Lieb, D.; Cranwell, T.; Wedding, J.L.; Zillmann, A.S.; Rohr, R.; Filipovic, M.R.; et al. Cellular Fates of Manganese(II) Pentaazamacrocyclic Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Mimetics: Fluorescently Labeled MnSOD Mimetics, X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy, and X-ray Fluorescence Microscopy Studies. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 6076–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, E.A.; Rayner, B.S.; McLeod, A.I.; Wu, L.E.; Marshall, C.P.; Levina, A.; Aitken, J.B.; Witting, P.K.; Lai, B.; Cai, Z.; et al. Silicon nitride as a versatile growth substrate for microspectroscopic imaging and mapping of individual cells. Mol. Biosyst. 2010, 6, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaussian 09, Revision A.1; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016.
- Scalmani, G.; Frisch, M.J. Continuous surface charge polarizable continuum models of solvation. I. General formalism. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 114110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruud, K.; Helgaker, T.; Bak, K.L.; Jørgensen, P.; Jensen, H.J.A. Hartree–Fock limit magnetizabilities from London orbitals. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 99, 3847–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helgaker, T.; Watson, M.; Handy, N.C. Analytical calculation of nuclear magnetic resonance indirect spin–spin coupling constants at the generalized gradient approximation and hybrid levels of density-functional theory. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 9402–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sychrovský, V.; Gräfenstein, J.; Cremer, D. Nuclear magnetic resonance spin–spin coupling constants from coupled perturbed density functional theory. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 3530–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barone, V.; Peralta, J.E.; Contreras, R.H.; Snyder, J.P. DFT Calculation of NMR J FF Spin− Spin Coupling Constants in Fluorinated Pyridines. J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 5607–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, J.E.; Scuseria, G.E.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Frisch, M.J. Basis set dependence of NMR spin–spin couplings in density functional theory calculations: First row and hydrogen atoms. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 375, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Frisch, M.J. Calculation of Nuclear Spin-Spin Coupling Constants of Molecules with First and Second Row Atoms in Study of Basis Set Dependence. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2006, 2, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |







| Complex | 2aCl | 3b | 3bCl | 4a | 4bCl | 1bNH3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bond length/Å | ||||||
| M–X a | 2.4110(5) | 2.424(1) | 2.4137(8) | 2.4122(8) | 2.409(1) | 2.152(2) |
| M–S | 2.4147(6) | 2.426(1) | 2.4276(8) | 2.4091(8) | 2.396(1) | 2.3895(4) |
| M–Ntri | 2.127(2) | 2.139(5) | 2.112(3) | 2.089(3) | 2.090(4) | 2.110(2) |
| C=S | 1.698(3) | 1.713(6) | 1.699(3) | 1.706(3) | 1.716(5) | 1.717(2) |
| M–Cp*centroid | 1.666 | 1.791 | 1.786 | 1.790 | 1.785 | 1.679 |
| Bond angle/° | ||||||
| S–M–Ntri | 96.90(6) | 96.4(1) | 97.14(7) | 97.60(8) | 96.7(1) | 95.14(4) |
| S–M–X a | 86.75(2) | 88.79(5) | 92.22(3) | 88.49(3) | 89.90(4) | 86.66(5) |
| Ntri–M–X a | 83.77(5) | 85.6(1) | 87.33(7) | 86.28(8) | 86.0(1) | 81.69(6) |
| M–S=C | 113.00(9) | 107.3(2) | 111.6(1) | 115.1(1) | 112.6(2) | 114.12(6) |
| Complex | Proton | δexp/ppm | δsim/ppm | Δ(δexp − δsim)/ppm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3b | H-3 | 7.22 | 7.05 | 0.17 |
| H-4b | 5.38 | 5.04 | 0.34 | |
| H-6 | 8.30 | 8.01 | 0.29 | |
| 3bBF4 | H-3 | 7.47 | 6.95 | 0.52 |
| H-4b | 5.58 | 5.26 | 0.32 | |
| H-6 | 8.58 | 9.02 | 0.44 | |
| 3bCl | H-3 | 7.85 | 7.92 | 0.07 |
| H-4b | 6.08 | 6.14 | 0.06 | |
| H-6 | 9.20 | 9.06 | 0.14 |
| Compound | IC50 Values (μM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCT116 | NCI-H460 | SiHa | SW480 | |
| 1a | 61 ± 27 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 2a | 42 ± 6 | 45 ± 6 | >100 | >100 |
| 3a | 76 ± 39 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 4a | 20 ± 3 | 25 ± 1 | 71 ± 4 | 83 ± 24 |
| 1b | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 2b | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 3b | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 4b | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, K.K.H.; Hanif, M.; Lovett, J.H.; Hummitzsch, K.; Harris, H.H.; Söhnel, T.; Jamieson, S.M.F.; Hartinger, C.G. Thiourea-Derived Chelating Ligands and Their Organometallic Compounds: Investigations into Their Anticancer Activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163661
Tong KKH, Hanif M, Lovett JH, Hummitzsch K, Harris HH, Söhnel T, Jamieson SMF, Hartinger CG. Thiourea-Derived Chelating Ligands and Their Organometallic Compounds: Investigations into Their Anticancer Activity. Molecules. 2020; 25(16):3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163661
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Kelvin K. H., Muhammad Hanif, James H. Lovett, Katja Hummitzsch, Hugh H. Harris, Tilo Söhnel, Stephen M. F. Jamieson, and Christian G. Hartinger. 2020. "Thiourea-Derived Chelating Ligands and Their Organometallic Compounds: Investigations into Their Anticancer Activity" Molecules 25, no. 16: 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163661
APA StyleTong, K. K. H., Hanif, M., Lovett, J. H., Hummitzsch, K., Harris, H. H., Söhnel, T., Jamieson, S. M. F., & Hartinger, C. G. (2020). Thiourea-Derived Chelating Ligands and Their Organometallic Compounds: Investigations into Their Anticancer Activity. Molecules, 25(16), 3661. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163661