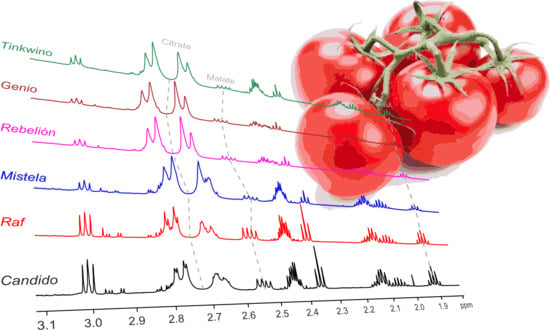
NMR Metabolomics Applied on the Discrimination of Variables Influencing Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Metabolomics Platform in Plant Sciences
2.1. NMR Suitability in Plant and Fruit Metabolomics
2.2. Design an NMR-Based Metabolomics Study in Plant Science
2.2.1. Sample Provision and Preparation
2.2.2. Data Acquisition
2.2.3. Data Analysis
2.2.4. Data Interpretation
3. Applications of NMR-Based Metabolomics in Tomato
3.1. Assessing Fruit Development, Fruit Phenotypes, and Genetic Diversity
3.2. Characterization of Tomato Quality, Origin, and Authenticity
3.3. Compositional and Quality Changes According to Agronomic Practices
3.4. Characterization and Detection of Unintended Effects in Genetically Modified Crops
3.5. Study Post-Harvest Processes in Tomato Fruits
3.6. Impact of Abiotic and Biotic Stress
3.7. Metabolomics in Tomato-Derived Products
4. Final Remarks
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Desai, N.; Alexander, D. Chapter 4. Metabolite profiling for plant research. In From Plant Genomics to Plant Biotechnology, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Centre, New Delhi, India, 2013; pp. 49–65. [Google Scholar]
- Nadella, K.D.; Marla, S.S.; Kumar, P.A. Metabolomics in Agriculture. OMICS 2012, 16, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, R.A.; Gang, D.R.; Charlton, A.J.; Fiehn, O.; Kuiper, H.A.; Reynolds, T.L.; Tjeerdema, R.S.; Jeffery, E.H.; German, J.B.; Ridley, W.P.; et al. Applications of Metabolomics in Agriculture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8984–8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Lin, T.; Qin, M.; Peng, M.; Yang, C.; et al. Rewiring of the Fruit Metabolome in Tomato Breeding. Cell 2018, 172, 249–261.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.-J.; Shaykhutdinov, R.; Weljie, A.M.; Vogel, H.J.; Facchini, P.J.; Park, S.-U.; Kim, Y.-K.; Yang, T.-J. Quality Assessment of Ginseng by 1H NMR Metabolite Fingerprinting and Profiling Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7513–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, J.G.M.; Brasil, A.J.M.; Cruz, G.C.F.; de Souza, R.N.; Tasic, L. NMR-based metabolomics strategies: Plants, animals and humans. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1078–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudeau, P. NMR-based metabolomics and fluxomics: Developments and future prospects. Analyst 2020, 145, 2457–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deborde, C.; Fontaine, J.-X.; Jacob, D.; Botana, A.; Nicaise, V.; Richard-Forget, F.; Lecomte, S.; Decourtil, C.; Hamade, K.; Mesnard, F.; et al. Optimizing 1D 1H-NMR profiling of plant samples for high throughput analysis: Extract preparation, standardization, automation and spectra processing. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.-X.; Pan, Y.-G.; He, F.-P.; Yuan, M.-Q.; Li, S.-B. Pathway Analysis and Metabolites Identification by Metabolomics of Etiolation Substrate from Fresh-Cut Chinese Water Chestnut (Eleocharis tuberosa). Molecules 2016, 21, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, R.; Cagliani, L.R. The potentiality of NMR-based metabolomics in food science and food authentication assessment. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2019, 57, 558–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, O.; Urrutia, M.; Bernillon, S.; Giauffret, C.; Tardieu, F.; Le Gouis, J.; Langlade, N.; Charcosset, A.; Moing, A.; Gibon, Y. Fortune telling: Metabolic markers of plant performance. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beauvoit, B.; Belouah, I.; Bertin, N.; Cakpo, C.B.; Colombié, S.; Dai, Z.; Gautier, H.; Génard, M.; Moing, A.; Roch, L.; et al. Putting primary metabolism into perspective to obtain better fruits. Ann. Bot. 2018, 122, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Vos, R.C.; Hall, R.D.; Moing, A. Metabolomics of A Model Fruit: Tomato. In Annual Plant Reviews Online; Roberts, J.A., Ed.; Wiley & Sons: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2018; Vol. 43, pp. 109–155. [Google Scholar]
- Nicola, S.; Tibaldi, G.; Fontana, E.; Crops, A.-V.; Plants, A. Tomato Production Systems and Their Application to the Tropics. Acta Hortic. 2009, 821, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fentik, D. Review on Genetics and Breeding of Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill). Adv. Crop. Sci. Tech. 2017, 5, 306. [Google Scholar]
- Tohge, T.; Fernie, A.R. Metabolomics-Inspired Insight into Developmental, Environmental and Genetic Aspects of Tomato Fruit Chemical Composition and Quality. Plant. Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 1681–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mannina, L.; Sobolev, A.P.; Viel, S. Liquid state 1H high field NMR in food analysis. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2012, 66, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, A.P.; Mannina, L.; Proietti, N.; Carradori, S.; Daglia, M.; Giusti, A.M.; Antiochia, R.; Capitani, D. Untargeted NMR-based methodology in the study of fruit metabolites. Molecules 2015, 20, 4088–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albert, K. Liquid chromatography–nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 856, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, K.; Dachtler, M.; Glaser, T.; Händel, H.; Lacker, T.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Strohschein, S.; Tseng, L.-H.; Braumann, U. On-Line Coupling of Separation Techniques to NMR. J. High. Resolut. Chromatogr. 1999, 22, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.L.; Baker, J.M.; Beale, M.H. Recent applications of NMR spectroscopy in plant metabolomics. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jézéquel, T.; Deborde, C.; Maucourt, M.; Zhendre, V.; Moing, A.; Giraudeau, P. Absolute quantification of metabolites in tomato fruit extracts by fast 2D NMR. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingol, K.; Zhang, F.; Bruschweiler-Li, L.; Brüschweiler, R. Quantitative Analysis of Metabolic Mixtures by Two-Dimensional 13C Constant-Time TOCSY NMR Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6414–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guennec, A.L.; Giraudeau, P.; Caldarelli, S. Evaluation of Fast 2D NMR for Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5946–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. NMR-based plant metabolomics: Where do we stand, where do we go? Trends Biotechnol 2011, 29, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biais, B.; Bernillon, S.; Deborde, C.; Cabasson, C.; Rolin, D.; Tadmor, Y.; Burger, J.; Schaffer, A.A.; Moing, A. Precautions for harvest, sampling, storage, and transport of crop plant metabolomics samples. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 860, 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; Ribeiro-Barros, A.I.; António, C. Experimental Design and Sample Preparation in Forest Tree Metabolomics. Metabolites 2019, 9, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnes, S.; Benton, H.P.; Casazza, K.; Cooper, S.J.; Cui, X.; Du, X.; Engler, J.; Kabarowski, J.H.; Li, S.; Pathmasiri, W.; et al. Training in metabolomics research. I. Designing the experiment, collecting and extracting samples and generating metabolomics data. J. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 51, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salem, M.A.; Perez de Souza, L.; Serag, A.; Fernie, A.R.; Farag, M.A.; Ezzat, S.M.; Alseekh, S. Metabolomics in the Context of Plant Natural Products Research: From Sample Preparation to Metabolite Analysis. Metabolites 2020, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, M.C.M.; Caldana, C.; Wolf, L.D.; de Abreu, L.G.F. The Importance of Experimental Design, Quality Assurance, and Control in Plant Metabolomics Experiments. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1778, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Fernie, A.R.; Aharoni, A.; Willmitzer, L.; Stitt, M.; Tohge, T.; Kopka, J.; Carroll, A.J.; Saito, K.; Fraser, P.D.; DeLuca, V. Recommendations for Reporting Metabolite Data. Plant. Cell 2011, 23, 2477–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.K.; Verpoorte, R. Sample preparation for plant metabolomics. Phytochem. Anal. 2010, 21, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiziani, S.; Schwartz, S.J.; Vodovotz, Y. Profiling of carotenoids in tomato juice by one- and two-dimensional NMR. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6094–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allwood, J.W.; De Vos, R.C.H.; Moing, A.; Deborde, C.; Erban, A.; Kopka, J.; Goodacre, R.; Hall, R.D. Plant Metabolomics and Its Potential for Systems Biology Research. Methods Enzymol. 2011, 500, 299–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sauerschnig, C.; Doppler, M.; Bueschl, C.; Schuhmacher, R. Methanol Generates Numerous Artifacts during Sample Extraction and Storage of Extracts in Metabolomics Research. Metabolites 2017, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abreu, A.C.; Marín, P.; Aguilera-Sáez, L.M.; Tristán, A.I.; Peña, A.; Oliveira, I.; Simões, M.; Valera, D.; Fernández, I. Effect of a Shading Mesh on the Metabolic, Nutritional, and Defense Profiles of Harvested Greenhouse-Grown Organic Tomato Fruits and Leaves Revealed by NMR Metabolomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12972–12985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dona, A.C.; Kyriakides, M.; Scott, F.; Shephard, E.A.; Varshavi, D.; Veselkov, K.; Everett, J.R. A guide to the identification of metabolites in NMR-based metabonomics/metabolomics experiments. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emwas, A.H.; Roy, R.; McKay, R.T.; Tenori, L.; Saccenti, E.; Gowda, G.A.N.; Raftery, D.; Alahmari, F.; Jaremko, L.; Jaremko, M.; et al. NMR Spectroscopy for Metabolomics Research. Metabolites 2019, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ross, A.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Dieterle, F.; Senn, H. Chapter 3. NMR Spectroscopy Techniques for Application to Metabonomics. In The Handbook of Metabonomics and Metabolomics; Lindon, J.C., Nicholson, J.K., Holmes, E., Eds.; Elsevier, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 55–112. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/book/9780444528414/the-handbook-of-metabonomics-and-metabolomics (accessed on 11 December 2007).
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalystR 3.0: Toward an Optimized Workflow for Global Metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, J.; Krumsiek, J.; Theis, F.J. Statistical methods for the analysis of high-throughput metabolomics data. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 4, e201301009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, S.; Cin, V.D.; Fei, Z.; Li, H.; Bliss, P.; Taylor, M.G.; Klee, H.J.; Tieman, D.M. Flavour compounds in tomato fruits: Identification of loci and potential pathways affecting volatile composition. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Huang, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Zeng, J. Metabolomics Analysis of the Peels of Different Colored Citrus Fruits (Citrus reticulata cv. ‘Shatangju’) During the Maturation Period Based on UHPLC-QQQ-MS. Molecules 2020, 25, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krauss, S.; Schnitzler, W.H.; Grassmann, J.; Woitke, M. The influence of different electrical conductivity values in a simplified recirculating soilless system on inner and outer fruit quality characteristics of tomato. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorais, M.; Ehret, D.; Papadopoulos, A. Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) health components: From the seed to the consumer. Phytochem. Rev. 2008, 7, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilahun, S.; Park, D.; Seo, M.; Jeong, C. Review on factors affecting the quality and antioxidant properties of tomatoes. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 1678–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, E.M.S.; Iglesias, M.J.; Ortiz, F.L.; Pérez, I.S.; Galera, M.M. Study of the suitability of HRMAS NMR for metabolic profiling of tomatoes: Application to tissue differentiation and fruit ripening. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano Garcia, P.; Neves Dos Santos, F.; Zanotta, S.; Eberlin, M.N.; Carazzone, C. Metabolomics of Solanum lycopersicum Infected with Phytophthora infestans Leads to Early Detection of Late Blight in Asymptomatic Plants. Molecules 2018, 23, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tikunov, Y.; Lommen, A.; de Vos, C.H.R.; Verhoeven, H.A.; Bino, R.J.; Hall, R.D.; Bovy, A.G. A novel approach for nontargeted data analysis for metabolomics. Large-scale profiling of tomato fruit volatiles. Plant. Physiol. 2005, 139, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, M.C.; Kim, Y.X.; Lee, S.; Jung, E.S.; Singh, D.; Sung, J.; Lee, C.H. Comparative Metabolomics Unravel the Effect of Magnesium Oversupply on Tomato Fruit Quality and Associated Plant Metabolism. Metabolites 2019, 9, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moco, S.; Forshed, J.; De Vos, R.C.H.; Bino, R.J.; Vervoort, J. Intra- and inter-metabolite correlation spectroscopy of tomato metabolomics data obtained by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance. Metabolomics 2008, 4, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemaire-Chamley, M.; Mounet, F.; Deborde, C.; Maucourt, M.; Jacob, D.; Moing, A. NMR-Based Tissular and Developmental Metabolomics of Tomato Fruit. Metabolites 2019, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mounet, F.; Lemaire-Chamley, M.; Maucourt, M.; Cabasson, C.; Giraudel, J.-L.; Deborde, C.; Lessire, R.; Gallusci, P.; Bertrand, A.; Gaudillère, M.; et al. Quantitative metabolic profiles of tomato flesh and seeds during fruit development: Complementary analysis with ANN and PCA. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moço, S. Metabolomics Technologies applied to the Identification of Compounds in Plants. PhD Thesis, Wageningen Universiteit, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sorrequieta, A.; Abriata, L.A.; Boggio, S.B.; Valle, E.M. Off-the-Vine Ripening of Tomato Fruit Causes Alteration in the Primary Metabolite Composition. Metabolites 2013, 3, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saltveit, M.E. Determining tomato fruit maturity with nondestructive in vivo nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 1991, 1, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musse, M.; Quellec, S.; Cambert, M.; Devaux, M.-F.; Lahaye, M.; Mariette, F. Monitoring the postharvest ripening of tomato fruit using quantitative MRI and NMR relaxometry. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2009, 53, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-C.; Wang, T.-T.; Chen, J.-H.; Lin, T.-T. Spatial–temporal analyses of lycopene and sugar contents in tomatoes during ripening using chemical shift imaging. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2011, 62, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; McCarthy, K.L.; McCarthy, M.J. Study of tomato maturity using nuclear magnetic resonance relaxometry and imaging. Acta Hortic. 2016, 1119, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounet, F.; Moing, A.; Garcia, V.; Petit, J.; Maucourt, M.; Deborde, C.; Bernillon, S.; Le Gall, G.; Colquhoun, I.; Defernez, M.; et al. Gene and Metabolite Regulatory Network Analysis of Early Developing Fruit Tissues Highlights New Candidate Genes for the Control of Tomato Fruit Composition and Development. Plant. Physiol. 2009, 149, 1505–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malmendal, A.; Amoresano, C.; Trotta, R.; Lauri, I.; De Tito, S.; Novellino, E.; Randazzo, A. NMR Spectrometers as “Magnetic Tongues”: Prediction of Sensory Descriptors in Canned Tomatoes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 10831–10838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thissen, U.; Coulier, L.; Overkamp, K.M.; Jetten, J.; van der Werff, B.J.C.; van de Ven, T.; van der Werf, M.J. A proper metabolomics strategy supports efficient food quality improvement: A case study on tomato sensory properties. Food Qual. Prefer. 2011, 22, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.G.; Zanor, M.I.; Pratta, G.R.; Stegmayer, G.; Boggio, S.B.; Conte, M.; Bermúdez, L.; Coluccio Leskow, C.; Rodríguez, G.R.; Picardi, L.A.; et al. Metabolic analyses of interspecific tomato recombinant inbred lines for fruit quality improvement. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1416–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Pérez, E.M.; García López, J.; Iglesias, M.J.; López Ortiz, F.; Toresano, F.; Camacho, F. HRMAS-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy characterization of tomato “flavor varieties” from Almería (Spain). Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 3212–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallamace, D.; Corsaro, C.; Salvo, A.; Cicero, N.; Macaluso, A.; Giangrosso, G.; Ferrantelli, V.; Dugo, G. A multivariate statistical analysis coming from the NMR metabolic profile of cherry tomatoes (The Sicilian Pachino case). Physica A 2014, 401, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deborde, C.; Maucourt, M.; Baldet, P.; Bernillon, S.; Biais, B.; Talon, G.; Ferrand, C.; Jacob, D.; Ferry-Dumazet, H.; de Daruvar, A.; et al. Proton NMR quantitative profiling for quality assessment of greenhouse-grown tomato fruit. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, M.J.; Lopez, J.G.; Lujan, J.F.C.; Ortiz, F.L.; Pereznieto, H.B.; Toresano, F.; Camacho, F. Effect of genetic and phenotypic factors on the composition of commercial marmande type tomatoes studied through HRMAS NMR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2014, 142, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, M.J.; García-López, J.; Collados-Luján, J.F.; López-Ortiz, F.; Díaz, M.; Toresano, F.; Camacho, F. Differential response to environmental and nutritional factors of high-quality tomato varieties. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, M.; Christoph, N.; Wachter, H.; Holzgrabe, U. 1H NMR profiling as an approach to differentiate conventionally and organically grown tomatoes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8530–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, M.; Monakhova, Y.; Erich, S.; Christoph, N.; Wachter, H.; Holzgrabe, U. Differentiation of Organically and Conventionally Grown Tomatoes by Chemometric Analysis of Combined Data from Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Mid-infrared Spectroscopy and Stable Isotope Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9666–9675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masetti, O.; Ciampa, A.; Nisini, L.; Valentini, M.; Sequi, P.; Dell’Abate, M.T. Cherry tomatoes metabolic profile determined by H-1-High Resolution-NMR spectroscopy as influenced by growing season. Food Chem. 2014, 162, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bénard, C.; Bernillon, S.; Biais, B.; Osorio, S.; Maucourt, M.; Ballias, P.; Deborde, C.; Colombié, S.; Cabasson, C.; Jacob, D.; et al. Metabolomic profiling in tomato reveals diel compositional changes in fruit affected by source-sink relationships. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 3391–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazzei, P.; Vinale, F.; Woo, S.L.; Pascale, A.; Lorito, M.; Piccolo, A. Metabolomics by Proton High -Resolution Magic-Angle-Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance of Tomato Plants Treated with Two Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Trichoderma. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3538–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lun, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Genomic analyses provide insights into the history of tomato breeding. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldina, S.; Picarella, M.E.; Troise, A.D.; Pucci, A.; Ruggieri, V.; Ferracane, R.; Barone, A.; Fogliano, V.; Mazzucato, A. Metabolite Profiling of Italian Tomato Landraces with Different Fruit Types. Front. Plant. Sci. 2016, 7, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perez-Fons, L.; Wells, T.; Corol, D.I.; Ward, J.L.; Gerrish, C.; Beale, M.H.; Seymour, G.B.; Bramley, P.M.; Fraser, P.D. A genome-wide metabolomic resource for tomato fruit from Solanum pennellii. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noteborn, H.P.; Lommen, A.; van der Jagt, R.C.; Weseman, J.M. Chemical fingerprinting for the evaluation of unintended secondary metabolic changes in transgenic food crops. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 77, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, G.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Davis, A.L.; Collins, G.J.; Verhoeyen, M.E. Metabolite Profiling of Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) Using 1H NMR Spectroscopy as a Tool To Detect Potential Unintended Effects Following a Genetic Modification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2447–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moing, A.; Maucourt, M.; Renaud, C.; Ere, M.; Brouquisse, R.; Lebouteiller, B.; Gousset-Dupont, A.; Vidal, J.; Granot, D.; Denoyes-Rothan, B.; et al. Quantitative metabolic profiling by 1-dimensional 1H-NMR analyses: Application to plant genetics and functional genomics. Funct. Plant. Biol. 2004, 31, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattoo, A.K.; Sobolev, A.P.; Neelam, A.; Goyal, R.K.; Handa, A.K.; Segre, A.L. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy-based metabolite profiling of transgenic tomato fruit engineered to accumulate spermidine and spermine reveals enhanced anabolic and nitrogen-carbon interactions. Plant. Physiol. 2006, 142, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neily, M.H.; Matsukura, C.; Maucourt, M.; Bernillon, S.; Deborde, C.; Moing, A.; Yin, Y.G.; Saito, T.; Mori, K.; Asamizu, E.; et al. Enhanced polyamine accumulation alters carotenoid metabolism at the transcriptional level in tomato fruit over-expressing spermidine synthase. J. Plant. Physiol. 2011, 168, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobolev, A.P.; Neelam, A.; Fatima, T.; Shukla, V.; Handa, A.K.; Mattoo, A.K. Genetic introgression of ethylene-suppressed transgenic tomatoes with higher-polyamines trait overcomes many unintended effects due to reduced ethylene on the primary metabolome. Front. Plant. Sci. 2014, 5, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kausch, K.D.; Sobolev, A.P.; Goyal, R.K.; Fatima, T.; Laila-Beevi, R.; Saftner, R.A.; Handa, A.K.; Mattoo, A.K. Methyl jasmonate deficiency alters cellular metabolome, including the aminome of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) fruit. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelam, A.; Cassol, T.; Mehta, R.A.; Abdul-Baki, A.A.; Sobolev, A.P.; Goyal, R.K.; Abbott, J.; Segre, A.L.; Handa, A.K.; Mattoo, A.K. A field-grown transgenic tomato line expressing higher levels of polyamines reveals legume cover crop mulch-specific perturbations in fruit phenotype at the levels of metabolite profiles, gene expression, and agronomic characteristics. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 2337–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fatima, T.; Sobolev, A.P.; Teasdale, J.R.; Kramer, M.; Bunce, J.; Handa, A.K.; Mattoo, A.K. Fruit metabolite networks in engineered and non-engineered tomato genotypes reveal fluidity in a hormone and agroecosystem specific manner. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bisht, H.; Bhagat, D.; Bhatnagar, M.K. Metabolic Profiling of Tomatoes with Pest Infestation Using GC-MS and NMR Spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2014, 6, 550–556. [Google Scholar]
- Zoghlami, L.B.; Djebali, W.; Abbes, Z.; Hediji, H.; Maucourt, M.; Moing, A.; Brouquisse, R.; Chaibi, W. Metabolite modifications in Solanum lycopersicum roots and leaves under cadmium stress. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 567–579. [Google Scholar]
- Hédiji, H.; Djebali, W.; Cabasson, C.; Maucourt, M.; Baldet, P.; Bertrand, A.; Boulila Zoghlami, L.; Deborde, C.; Moing, A.; Brouquisse, R.; et al. Effects of long-term cadmium exposure on growth and metabolomic profile of tomato plants. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2010, 73, 1965–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifah, E.N.; Murti, R.H.; Nuringtyas, T.R. Metabolomics Approach for The Analysis of Resistance of Four Tomato Genotypes (Solanum lycopersicum L.) to Root-Knot Nematodes (Meloidogyne incognita). Open Life Sci. 2019, 14, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gresa, M.P.; Lisón, P.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R.; Rodrigo, I.; Conejero, V.; Bellés, J.M. Metabolic fingerprinting of Tomato Mosaic Virus infected Solanum lycopersicum. J. Plant. Physiol. 2012, 169, 1586–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirnezhad, M.; Romero-González, R.R.; Leiss, K.A.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R.; Klinkhamer, P.G.L. Metabolomic analysis of host plant resistance to thrips in wild and cultivated tomatoes. Phytochem. Anal. 2010, 21, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Falco, B.; Manzo, D.; Incerti, G.; Garonna, A.P.; Ercolano, M.; Lanzotti, V. Metabolomics approach based on NMR spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis to explore the interaction between the leafminer Tuta absoluta and tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Phytochem. Anal. 2019, 30, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Gresa, M.P.; Paya, C.; Rodrigo, I.; Belles, J.M.; Barcelo, S.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R.; Lison, P. Effect of Benzothiadiazole on the Metabolome of Tomato Plants Infected by Citrus exocortis Viroid. Viruses-Basel 2019, 11, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Consonni, R.; Cagliani, L.; Stocchero, M.; Porretta, S. Evaluation of the Production Year in Italian and Chinese Tomato Paste for Geographical Determination Using O2PLS Models. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7520–7525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolev, A.P.; Segre, A.; Lamanna, R. Proton high-field NMR study of tomato juice. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2003, 41, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, M.D.; Harter, T.; McCarthy, M.J.; Augustine, M.P. Towards using NMR to screen for spoiled tomatoes stored in 1000 L, aseptically sealed, metal-lined totes. Sensors (Basel) 2014, 14, 4167–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bondia-Pons, I.; Cañellas, N.; Abete, I.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Perez-Cornago, A.; Navas-Carretero, S.; Ángeles Zulet, M.; Correig, X.; Martínez, J.A. Nutri-Metabolomics: Subtle Serum Metabolic Differences in Healthy Subjects by NMR-Based Metabolomics after a Short-Term Nutritional Intervention with Two Tomato Sauces. OMICS J. Int. Biol. 2013, 17, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohge, T.; Alseekh, S.; Fernie, A.R. On the regulation and function of secondary metabolism during fruit development and ripening. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 65, 4599–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abreu, A.C.; Fernández, I. NMR Metabolomics Applied on the Discrimination of Variables Influencing Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Molecules 2020, 25, 3738. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163738
Abreu AC, Fernández I. NMR Metabolomics Applied on the Discrimination of Variables Influencing Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Molecules. 2020; 25(16):3738. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163738
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbreu, Ana Cristina, and Ignacio Fernández. 2020. "NMR Metabolomics Applied on the Discrimination of Variables Influencing Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum)" Molecules 25, no. 16: 3738. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163738
APA StyleAbreu, A. C., & Fernández, I. (2020). NMR Metabolomics Applied on the Discrimination of Variables Influencing Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Molecules, 25(16), 3738. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163738