Determination of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Water and Wastewater Samples by Liquid Chromatography-Negative Ion Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
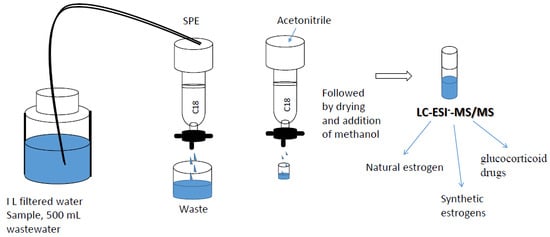
2.1. Optimization of the Solid-Phase Extraction Procedure
2.2. LC-ESI--MS/MS Conditions
2.3. Matrix Effects
2.4. Concentrations of the Target Analytes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Sample Collection and Filtration
3.3. SPE Sorbent Evaluations
3.4. Solid-Phase Extraction
3.5. Apparatus and LC-ESI--MS/MS Conditions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glineur, A.; Barbera, B.; Nott, K.; Carbonnelle, P.; Ronkart, S.; Lognay, G.; Tyteca, E. Trace analysis of estrogenic compounds in surface and groundwater by ultra high performance liquid chromatraography-tandem mass spectrometry as puridine-3-sulfonyl derivatives. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1534, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Chang, C. Improved method for analyzing estrogens in water by liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1070, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glineur, A.; Nott, K.; Philleppe, C.; Ronkart, S.; Purcaro, G. Development and validation of a method for determining estrogenic compounds in surface water at the ultra-trace level required by the EU Water Framework Directive Watch List. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1624, 461242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baronti, C.; Curini, R.; D’Ascenzo, G.; Di Corcia, A.; Gentili, A.; Samperi, R. Monitoring natural and synthetic estrogens at activated sludge sewage treatment plants and in a receiving river water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 5059–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammann, A.; Macikova, P.; Groh, K.; Schirmer, K.; Suter, M. LC-MS/MS determination of potential endocrine disruptors of cortico signalling in rivers and wastewaters. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7653–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, G.; Chen, C.; Wang, G. Comparison of electrospray ionization, atmospheric pressure chemical ionization and atmospheric pressure photoionization for determining estrogenic chemicals in water by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry with chemical derivatizations. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, A.; Moretton, C.; Piram, A.; Faure, R. On-line solid-phase extraction with on-support derivatization for high-sensitivity liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry of estrogens in influent/effluent of wastewater treatment plants. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1145, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission implementing decision (EU) 2018/840 of 5 June 2018 establishing a watch list of substances for union-wide monitoring in the field of water policy pursuant to Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council and repealing Commission Implementing Decision 2015/495. Off. J. Eur. Comm. 2018, L141, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency. Drinking water contaminant candidate list3. Fed. Regist. 2009, 74, 51852. Available online: https://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2009-10-08/pdf/E9-24287.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2020).
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.; Nghiem, L.; Hai, F.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zha, J.; Xu, Y.; Lei, B.; Wang, Z. Occurrences of six steroid estrogens from different effluents in Beijing, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, O.; Smythe, G.; Schäfer, A.; Feitz, A. Fate of steroid estrogens in Australian inland and coastal wastewater treatment Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3351–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iparraguirre, A.; Navarro, P.; Rodil, R.; Prieto, A.; Olivares, M.; Etxebarria, N.; Zuloaga, O. Matrix effect during the membrane-assisted solvent extraction coupled to liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of a variety of endocrine disrupting compounds in wastewater. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1356, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimchirian, R.; Suri, R.; Fu, H. Free synthetic and natural estrogen hormones in influent and effluent of three municipal wastewater treatment plants. Water Environ. Res. 2007, 79, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, S.; Marlatt, V.; Kimpe, L.; Lean, D.; Trudeau, V.; Blais, J. The Occurrence of steroidal estrogens in south-eastern Ontario wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 430, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, S.; Kim, H.; Oh, J.; Park, H. Occurrence and removal of antibiotics, hormones and several other pharmaceuticals in wastewater treatment plants of the largest industrial city of Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4351–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeel, M.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Francis, D.; Yang, Y. Environmental impact of estrogens on human, animal and plant life: A critical review. Environ. Intl. 2017, 99, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothitou, P.; Voutsa, D. Endocrine disrupting compounds in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants in northern Greece. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Morales, T.; Sosa-Ferrera, Z.; Santana-Rodríguez, J. Determination of alkylphenol polyethoxylates, bisphenol-a, 17α-ethynylestradiol and 17β-estradiol and its metabolites in sewage samples by SPE and LC/MS/MS. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 183, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Lam, J.; Kwok, K.; Tsui, M.; Lam, P. Occurrence and fate of endogenous steroid hormones, alkylphenol ethoxylates, bisphenol and phthalates in municipal sewage Treatment Systems. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 61, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R.; Guwy, A. The Removal of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs during wastewater treatment and its impact on the quality of receiving waters. Water Res. 2009, 43, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabe, S.; Pileggi, V.; Nowierski, M.; Kleywegt, S.; Yang, P. Occurrence, removal, and environmental impacts of emerging contaminants detected in water and wastewater in southern Ontario—Part I: Occurrence and removal. Water Pract. Technol. 2016, 11, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzić, S.; Senta, I.; Ahel, M.; Gros, M.; Petrović, M.; Barcelo, D.; Müller, J.; Knepper, T.; Martí, I.; Ventura, F. Occurrence and fate of emerging wastewater contaminants in western Balkan region. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 399, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prieto, A.; Schrader, S.; Moeder, M. Determination of organic priority pollutants and emerging compounds in wastewater and snow samples using multiresidue protocols on the basis of microextraction by packed sorbents coupled to large volume injection gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 6002–6011. [Google Scholar]
- Bono-Blay, F.; Guart, A.; de la Fuente, B.; Pedemonte, M.; Pastor, M.; Borrell, A.; Lacorte, S. Survey of phthalates, alkylphenols, bisphenol a and herbicides in Spanish source waters intended for bottling. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 3339–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.; Cruzeiro, C.; Rocha, E. Development and validation of a GC-MS method for the evaluation of 17 endocrine disruptor compounds, including phytoestrogens and sitosterol, in coastal waters—Their spatial and seasonal levels in Porto Costal Region (Portugal). J. Water Health 2013, 11, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sghaier, R.; Net, S.; Ghorbel-Abid, I.; Bessadok, S.; Le Coz, M.; Hassan-Chehimi, D.; Trabelsi-Ayadi, M.; Tackx, M.; Ouddane, B. Simultaneous detection of 13 endocrine disrupting chemicals in water by a combination of SPE-BSTFA derivatization and GC-MS in transboundary rivers (France-Belgium). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fayad, P.; Prévost, M.; Sauvé, S. On-Line Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled to Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry optimized for the analysis of steroid hormones in urban wastewaters. Talanta 2013, 115, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauković, Z.; Grujić, S.; Matić Bujagić, I.; Laušević, M. Determination of sterols and steroid hormones in surface water and wastewater using liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure chemical ionization-mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2017, 135, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmers, S.; Browne, E.; O’Keefe, P.; Anderton, D.; Kramer, L.; Reckhow, D.; Arcaro, K. Determination of free bisphenol A (BPA) concentrations in breast milk of U.S. women using a sensitive LC/MS/MS method. Chemosphere 2014, 104, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, G. Analysis of steroid estrogens in water using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry with chemical derivatizations. Rapid Comm. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volmer, D.; Hui, J. Rapid Determination of corticosteroids in urine by combined solid phase microextraction/liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1997, 11, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizea Savu, S.; Silvestro, L.; Haag, A.; Sörgel, F. A confirmatory HPLC–MS/MS method for ten synthetic corticosteroids in bovine urines. J. Mass Spectrom. 1996, 31, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluri, K.; Rivier, L.; Dienes-Nagy, A.; You, C.; Maître, A.; Schweizer, C.; Saugy, M.; Mangin, P. Method for confirmation of synthetic corticosteroids in doping urine samples by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 926, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.; Chiu, T.; Boobis, A.; Cartmell, E.; Lester, J.; Scrimshaw, M. Determination of steroid estrogens in wastewater by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1173, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, C.; Ji, S.; Ren, H. Determination of steroid estrogens in wastewater treatment plant of a controceptives producing factory. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 121, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benijts, T.; Lambert, W.; De Leenheer, A. Analysis of multiple endocrine disruptors in environmental waters via wide-spectrum solid-phase extraction and dual-polarity ionization LC-ion trap-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.; Santos, J.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Determination of hormones, a plasticizer, preservatives, perfluoroalkylated compounds, and a flame retardant in water samples by ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on the solidification of a floating organic drop. Talanta 2015, 143, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.; Hanke, G.; Umlauf, G.; Eisenreich, S. LC-MS-MS analysis and occurrence of octyl- and nonylphenol, their ethoxylates and their carboxylates in Belgian and Italian textile industry, waste water treatment plant effluents and surface waters. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, A.; Gandrass, J.; Ruck, W. Simultaneous determination of alkylphenol ethoxylates and their biotransformation products by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1035, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyo-Rosales, J.; Rice, C.; Torrents, A. Octyl and nonylphenol ethoxylates and carboxylates in wastewater and sediments by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerrer, I.; Zweigenbaum, J.A.; Thurman, E.M. Analysis of 70 Environmental Protection Agency priority pharmaceuticals in water by EPA Method 1694. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5674–5686. [Google Scholar]
- Lavén, M.; Alsberg, T.; Yu, Y.; Adolfsson-Ericci, M.; Sun, H. Serial mixed-mode cation- and anion-exchange solid-phase extraction for separation of basic, neutral and acidic pharmaceuticals in wastewater and analysis by high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Shi, J.; Wu, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. A new pretreatment and improved method for determination of selected estrogens in high matrix solid sewage samples by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2012, 104, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, D.; Zhang, Z.; Readman, J.; Zhou, J. A comparison of three analytical techniques for the measurement of steroidal estrogens in environmental water samples. Talanta 2009, 78, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitani, K.; Fujioka, M.; Kataoka, H. Fully automated analysis of estrogens in environmental waters by in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr A 2005, 1081, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina-Fulton, R.; Mohamad, A.A. Pressurized solvent extraction with ethyl acetate and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for the analysis of conazole fungicides in matcha. Toxics 2018, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, S.C.; Liu, T.; Luo, S. Prednisolone degradation by UV/chlorine process: Influence factors, transformation products and mechanism. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of 17β-estradiol, estrone, and estriol, 17α-ethinylestradiol, diethylstilbestrol bisphenol A, 4-octylphenol, 4-nonylphenol, prednisolone and prednisone are not available from the authors. |




| Analyte 1 | Retention Time (min) | Quantitative SRM, Confirmation SRMs | Recovery% at 20 ng/L, 100 ng/L and 500 ng/L ±RSD% (n = 4) | SRM1/SRM2 Ratio (±RSD%) SRM1/SRM3 * SRM1/SRM4 ** | LOQs (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DES | 6.57 | 267→252, 267→222, 267→237 | 86.0 ± 5.42, 87.4 ± 3.10, 95.3 ± 7.71 | 1.05 ± 6.52% 1.081 ± 7.29% * | 5.0 |
| E1 | 7.02 | 269→145, 269→143, 269→159, 269→183 | 88.0 ± 12.8, 93.6 ± 4.10, 98.3 ± 5.45 | 9.03 ± 19.9% 5.27 ± 23.1% * 8.30 ± 19.4% ** | 2.0 |
| E2 | 6.95 | 271→145, 271→183, 271→271 | 89.7 ± 6.55, 105 ± 6.48, 105 ± 1.39 | 1.20 ± 8.58% 2.98 ± 10.5% * | 5.0 |
| E3 | 3.98 | 287→145, 187→171 | 82.4 ± 12.4, 102 ± 9.08, 98.3 ± 5.46 | 0.59 ± 21.5% | 3.0 |
| EE | 6.69 | 295→145, 295→195, 295→295 | 99.8 ± 14.4, 112 ± 14.2, 108 ± 2.14 | 1.45 ± 21.3% 0.92 ± 10.6% * | 10 |
| BPA | 5.62 | 227→212, 227→133 | 89.7 ± 4.23, 100 ± 3.84, 112 ± 3.28 | 1.56 ± 17.3% | 1.0 |
| 4OP | 13.13 | 205→106, 205→205 | 85.6 ± 7.98, 109 ± 10.3, 91.2 ± 8.18 | 1.00 ± 1.02% | 1.0 |
| 4NP | 13.80 | 219→106, 219→219 | 80.5 ± 9.49, 105 ± 13.0, 93.3 ± 5.88 | 1.00 ± 1.22% | 2.0 |
| PRDN | 4.34 | 358→327, 327→300, 327→327, | 84.3 ± 5.53, 96.9 ± 8.10, 90.0 ± 4.56 | 4.19 ± 9.27% 13.8 ± 14.5% * | 10 |
| PRNL | 5.02 | 359→329, 359→259, 359→359 | 80.2 ± 6.56, 91.1 ± 8.14, 88.5 ± 15.0 | 3.82 ± 1.97% 10.86 ± 4.45% * | 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aborkhees, G.; Raina-Fulton, R.; Thirunavokkarasu, O. Determination of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Water and Wastewater Samples by Liquid Chromatography-Negative Ion Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 25, 3906. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173906
Aborkhees G, Raina-Fulton R, Thirunavokkarasu O. Determination of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Water and Wastewater Samples by Liquid Chromatography-Negative Ion Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2020; 25(17):3906. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173906
Chicago/Turabian StyleAborkhees, Ghada, Renata Raina-Fulton, and Ondiveerapan Thirunavokkarasu. 2020. "Determination of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Water and Wastewater Samples by Liquid Chromatography-Negative Ion Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 25, no. 17: 3906. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173906
APA StyleAborkhees, G., Raina-Fulton, R., & Thirunavokkarasu, O. (2020). Determination of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Water and Wastewater Samples by Liquid Chromatography-Negative Ion Electrospray Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 25(17), 3906. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173906