Adenosine Receptor Ligands: Coumarin–Chalcone Hybrids as Modulating Agents on the Activity of hARs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Pharmacology
Adenosine Receptor Binding Affinity Assays
2.3. Theoretical Evaluation of ADME Properties
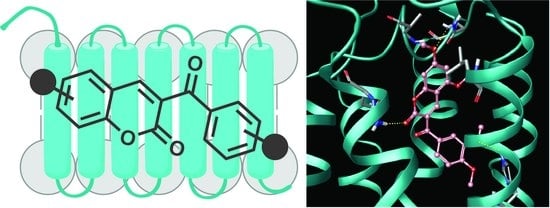
2.4. Molecular Modeling
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Methods
3.1.2. Synthetic Protocol to Obtain the Methoxy-3-benzoylcoumarins 1–4
3.1.3. Synthetic Protocol to Obtain the Hydroxy-3-benzoylcoumarins 5–8
3.2. Biological Assays
3.2.1. Binding Affinity Assays
3.2.2. Statistical Methods
3.3. Theoretical Evaluation of ADME Properties
3.4. Molecular Modeling
3.4.1. Homology Models of hA1 and hA3
3.4.2. Molecular Docking of hA1 and hA3 ARs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fredholm, B.B.; IJzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Linden, J.; Müller, C.E. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. LXXXI. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors-an update. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, S.A.; Quinn, R.J. Adenosine receptors: New opportunities for future drugs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1998, 6, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, B.B.; IJzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Klotz, K.N.; Linden, J. International union of pharmacology. XXV. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 5, 527–552. [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm, B.B.; Arslan, G.; Halldner, L.; Kull, B.; Schulte, G.; Wasserman, W. Structure and function of adenosine receptors and their genes. Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 362, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper-Joyce, C.J.; Khoshouei, M.; Thal, D.M.; Liang, Y.-L.; Nguyen, A.T.N.; Furness, S.G.B.; Venugopal, H.; Baltos, J.-A.; Plitzko, J.M.; Danev, R.; et al. Structure of the adenosine-bound human adenosine A1 receptor-Gi complex. Nature 2018, 558, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Li, C.; Olah, M.E.; Johnson, R.A.; Stiles, G.L.; Civelli, O. Molecular cloning and characterization of an adenosine receptor: The A3 adenosine receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 7432–7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvatore, C.A.; Jacobson, M.A.; Taylor, H.E.; Linden, J.; Johnson, R.G. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human A3 adenosine receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10365–10369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramkumar, V.; Stiles, G.L.; Beaven, M.A.; Ali, H. The A3 adenosine receptor is the unique adenosine receptor which facilitates release of allergic mediators in mast cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 16887–16890. [Google Scholar]
- Linden, J. Cloned adenosine A3 receptors: Pharmacological properties, species differences and receptor functions. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1994, 15, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, J.P.; Pfannkuche, H.J.; Fozard, J.R. A role for mast cells in adenosine A3 receptor-mediated hypotension in the rat. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 115, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Nikodijević, O.; Shi, D.; Gallo-Rodriguez, C.; Olah, M.E.; Stiles, G.L.; Daly, J.W. A role for central A3-adenosine receptors. Mediation of behavioral depressant effects. FEBS Lett. 1993, 336, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vecchio, E.A.; Baltos, J.A.; Nguyen, A.T.N.; Christopoulos, A.; White, P.J.; May, L.T. New paradigms in adenosine receptor pharmacology: Allostery, oligomerization and biased agonism. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175(21), 4036–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; de Castro, S.; Gao, Z.G.; IJzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A. Novel 2- and 4-substituted 1H-imidazo [4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine derivatives as allosteric modulators of the A3 adenosine receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 2098–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopes, L.V.; Sebastião, A.M.; Ribeiro, J.A. Adenosine and related drugs in brain diseases: Present and future in clinical trials. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 1087–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jespers, W.; Schiedel, A.C.; Heitman, L.H.; Cooke, R.M.; Kleene, L.; van Westen, G.J.P.; Gloriam, D.E.; Müller, C.E.; Sotelo, E.; Gutiérrez-de-Terán, H. Structural mapping of adenosine receptor mutations: Ligand binding and signaling mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, R.H.; Frishmanet, W.H. Adenosine1 receptor antagonism: A new therapeutic approach for the treatment of decompensated heart failure. Cardiol. Rev. 2009, 17, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shook, B.; Rassnick, S.; Wallace, N.; Crooke, J.; Ault, M.; Chakravarty, D.; Barbay, J.K.; Wang, A.; Powell, M.T.; Leonard, K.; et al. Design and characterization of optimized adenosine A₂A/A₁ receptor antagonists for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1402–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Hu, Y.M.; Chu, S.F.; Peng, Y.; Chen, N.H. Research progress on adenosine in central nervous system diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.W.; Ceruti, S.; Abbracchio, M.P. Adenosine receptors and neurological disease: Neuroprotection and neurodegeneration. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 193, 535–587. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, C.S.; Welch, W.J.; Schreiner, G.F.; Belardinelli, L. Natriuretic and diuretic actions of a highly selective adenosine receptor antagonist. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 714–720. [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb, S.S.; Skettino, S.L.; Wolff, A.; Beckman, E.; Fisher, M.L.; Freudenberger, R.; Gladwell, T.; Marshall, J.; Cines, M.; Bennett, D.; et al. Effects of BG9719 (CVT-124), an A1 adenosine receptor antagonist, and Furosemide on glomerular filtration rate and natriuresis in patients with congestive heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 35, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Mendonça, A.; Sebastião, A.M.; Ribeiro, J.A. Adenosine: Does it have a neuroprotective role after all? Brain Res. Rev. 2000, 33, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.T.; Ota-Setlik, A.; Xu, H.; D’Agati, V.D.; Jacobson, M.A.; Emala, C.W. A3 adenosine receptor knockout mice are protected against ischemia- and myoglobinuria-induced renal failure. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2003, 284, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolahdouzan, M.; Hamadeh, M.J. The neuroprotective effects of caffeine in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2017, 23, 272–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, A.M.; Coppi, E.; Spalluto, G.; Corradetti, R.; Pedata, F. A3 adenosine receptor antagonists delay irreversible synaptic failure caused by oxygen and glucose deprivation in the rat CA1 hippocampus in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fishman, P.; Bar-Yehuda, S.; Liang, B.T.; Jacobson, K.A. Pharmacological and therapeutic effects of A3 adenosine receptor (A3AR) agonists. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Janes, K.; Chen, C.; Doyle, T.; Tosh, D.K.; Jacobson, K.A.; Salvemini, D. Controlling murine and rat chronic pain through A3 adenosine receptor activation. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baraldi, P.G.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Gessi, S.; Borea, P.A. Adenosine receptor antagonists: Translating medicinal chemistry and pharmacology into clinical utility. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 238–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, S.; Gao, Z.G.; Jacobson, K.A.; Spalluto, G. Progress in the pursuit of therapeutic adenosine receptor antagonists. Med. Res. Rev. 2006, 26, 131–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okajima, F.; Akbar, M.; Abdul Majid, M.; Sho, K.; Tomura, H.; Kondo, Y. Genistein, an inhibitor of protein tyrosine kinase, is also a competitive antagonist for P1-purinergic (adenosine) receptor in FRTL-5 thyroid cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 203, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Moro, S.; Manthey, J.A.; West, P.L.; Ji, X.D. Interactions of flavones and other phytochemicals with adenosine receptors. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2002, 505, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Borges, F.; Roleira, F.; Milhazes, N.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E. Simple coumarins and analogues in medicinal chemistry: Occurrence, synthesis and biological activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 887–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, M.L.; Wu, X.; Liu, X.L. Chalcones: An update on cytotoxic and chemoprotective properties. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowska, Z. A review of anti-infective and anti-inflammatory chalcones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 42, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, C.J.; Andrews, S.P.; Congreve, M.; Errey, J.C.; Hurrell, E.; Marshall, F.H.; Mason, J.S.; Richardson, C.M.; Robertson, N.; Zhukov, A.; et al. Identification of novel adenosine A(2A) receptor antagonists by virtual screening. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1904–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Rodriguez, S.; Matos, M.J.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E.; Borges, F.; Kachler, S.; Klotz, K.N. Chalcone-based derivatives as new scaffolds for hA3 adenosine receptor antagonists. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 607–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, A.; Reis, J.; Matos, M.J.; Uriarte, E.; Borges, F. In search for new chemical entities as adenosine receptor ligands: Development of agents based on benzo-γ-pyrone skeleton. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 54, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.J.; Vilar, S.; Vazquez-Rodriguez, S.; Kachler, S.; Klotz, K.N.; Buccioni, M.; Delogu, G.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E.; Borges, F. Structure-based optimization of coumarin hA3 adenosine receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 2577–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.J.; Vilar, S.; Kachler, S.; Fonseca, A.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E.; Borges, F.; Tatonetti, N.P.; Klotz, K.N. Insight into the interactions between novel coumarin derivatives and human A3 adenosine receptors. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.J.; Vilar, S.; Kachler, S.; Celeiro, M.; Vazquez-Rodriguez, S.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E.; Hripcsak, G.; Borges, F.; Klotz, K.N. Development of novel adenosine receptor ligands based on the 3-amidocoumarin scaffold. Bioorg. Chem. 2015, 61, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.J.; Vilar, S.; Kachler, S.; Vazquez-Rodriguez, S.; Varela, C.; Delogu, G.; Hripcsak, G.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E.; Klotz, K.N.; et al. Progress in the development of small molecules as new human A3 adenosine receptor ligands based on the 3-thiophenylcoumarin core. MedChemComm 2016, 7, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.; Matos, M.J.; Vilar, S.; Kachler, S.; Klotz, K.N.; Uriarte, E.; Borges, F. Coumarins and adenosine receptors: New perceptions in. structure–affinity relationships. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 91, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Rodriguez, S.; Figueroa-Guiñez, R.; Matos, M.J.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E.; Lapier, M.; Maya, J.D.; Olea-Azar, C. Synthesis of coumarin–chalcone hybrids and evaluation of their antioxidant and trypanocidal properties. Med. Chem. Commun. 2013, 4, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, K.N.; Hessling, J.; Hegler, J.; Owman, C.; Kull, B.; Fredholm, B.B.; Lohse, M.J. Comparative pharmacology of human adenosine receptor subtypes-characterization of stably transfected receptors in CHO cells. Arch. Pharmacol. 1997, 357, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, K.N.; Falgner, N.; Kachler, S.; Lambertucci, C.; Vittori, S.; Volpini, R.; Cristalli, G. [3H]HEMADO–a novel tritiated agonist selective for the human adenosine A3 receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 556, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M cheminformatics, Bratislava, Slovak Republic. 2009. Available online: http://www.molinspiration.com/services/properties.html (accessed on 19 September 2020).
- Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. ZINC–a free database of commercially available compounds for virtual screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaakola, V.P.; Griffith, M.T.; Hanson, M.A.; Cherezov, V.; Chien, E.Y.; Lane, J.R.; Ijzerman, A.P.; Stevens, R.C. The 2.6 angstrom crystal structure of a human A2A adenosine receptor bound to an antagonist. Science 2008, 322, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MOE, Version 2011.10; Chemical Computing Group, Inc.: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2011.
- Katritch, V.; Kufareva, I.; Abagyan, R. Structure based prediction of subtype-selectivity for adenosine receptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glide, Version 5.7; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2011.
- Prime, Version 3.0; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2011.
- Congreve, M.; Andrews, S.P.; Doré, A.S.; Hollenstein, K.; Hurrell, E.; Langmead, C.J.; Mason, J.S.; Ng, I.W.; Tehan, B.; Zhukov, A.; et al. Discovery of 1,2,4-triazine derivatives as adenosine A(2A) antagonists using structure based drug design. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, O.; Colotta, V.; Catarzi, D.; Varano, F.; Poli, D.; Filacchioni, G.; Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F.; Borea, P.A.; Paoletta, S.; et al. 2-Phenylpyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one as a new scaffold to obtain potent and selective human A3 adenosine receptor antagonists: New insights into the receptor-antagonist recognition. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7640–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, A.; Reis, J.; Kachler, S.; Paoletta, S.; Uriarte, E.; Klotz, K.N.; Moro, S.; Borges, F. Discovery of novel A3 adenosine receptor ligands based on chromone scaffold. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (IC50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ertl, P.; Rohde, B.; Selzer, P. Fast calculation of molecular polar surface area as a sum of fragment-based contributions and its application to the prediction of drug transport properties. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3714–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, W.; Day, T.; Jacobson, M.P.; Friesner, R.A.; Farid, R. Novel procedure for modeling ligand/receptor induced fit effects. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 534–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |





| Compound | hA1 (Ki µM) a | hA3 (Ki µM) a |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | >100 | >100 |
| 2 | >100 | >100 |
| 3 | >30 b | 9.03 (6.28–13.0) |
| 4 | >100 | 2.49 (2.33–2.66) |
| 5 | 39.5 (25.3–61.5) | 34.5 (29.7–40.1) |
| 6 | 54.0 (49.8–58.5) | >60 b |
| 7 | 17.7 (16.0–19.5) | >30 b |
| 8 | 29.1 (20.4–41.5) | >60 b |
| Theophylline | 6.77 (4.07–11.3) | 86.4 (73.6−101) |
| Compound | clogP | TPSA (Å2) | n-OH Acceptors | n-OHNH Donors | Volume (Å3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.04 | 65.75 | 5 | 0 | 270.07 |
| 2 | 3.08 | 74.98 | 6 | 0 | 295.62 |
| 3 | 3.06 | 84.22 | 7 | 0 | 321.16 |
| 4 | 3.47 | 74.98 | 6 | 0 | 295.16 |
| 5 | 2.43 | 87.74 | 5 | 2 | 235.01 |
| 6 | 1.93 | 107.97 | 6 | 3 | 243.03 |
| 7 | 1.63 | 128.20 | 7 | 4 | 251.05 |
| 8 | 2.12 | 107.97 | 6 | 3 | 243.03 |
| AUROC | hA1 | hA3 |
|---|---|---|
| test 1 a | 0.91 | 0.95 |
| test 2 b | 0.86 | 0.82 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vazquez-Rodriguez, S.; Vilar, S.; Kachler, S.; Klotz, K.-N.; Uriarte, E.; Borges, F.; Matos, M.J. Adenosine Receptor Ligands: Coumarin–Chalcone Hybrids as Modulating Agents on the Activity of hARs. Molecules 2020, 25, 4306. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184306
Vazquez-Rodriguez S, Vilar S, Kachler S, Klotz K-N, Uriarte E, Borges F, Matos MJ. Adenosine Receptor Ligands: Coumarin–Chalcone Hybrids as Modulating Agents on the Activity of hARs. Molecules. 2020; 25(18):4306. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184306
Chicago/Turabian StyleVazquez-Rodriguez, Saleta, Santiago Vilar, Sonja Kachler, Karl-Norbert Klotz, Eugenio Uriarte, Fernanda Borges, and Maria João Matos. 2020. "Adenosine Receptor Ligands: Coumarin–Chalcone Hybrids as Modulating Agents on the Activity of hARs" Molecules 25, no. 18: 4306. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184306
APA StyleVazquez-Rodriguez, S., Vilar, S., Kachler, S., Klotz, K. -N., Uriarte, E., Borges, F., & Matos, M. J. (2020). Adenosine Receptor Ligands: Coumarin–Chalcone Hybrids as Modulating Agents on the Activity of hARs. Molecules, 25(18), 4306. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184306