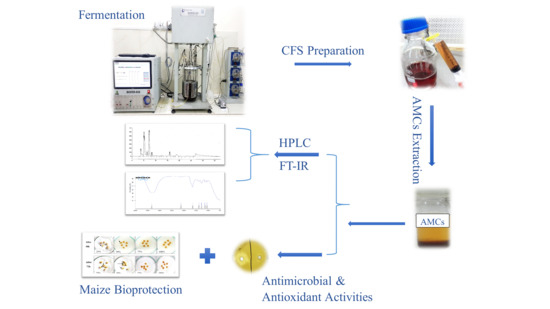
In Vitro Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Lactobacillus coryniformis BCH-4 Bioactive Compounds and Determination of their Bioprotective Effects on Nutritional Components of Maize (Zea mays L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Potential of Antimicrobial Compounds (AMCs)
2.2. Antioxidant Activity (DPPH Scavenging Activity)
2.3. Comparative Antifungal Analysis of AMCs with Commercial Preservatives
2.4. Efficiency of AMCs for Bioprotection of Maize
2.5. Proximate Analysis and β-Carotene Determination of Untreated and Treated Maize Grains
2.6. HPLC Analysis and Antifungal Potential of Low Molecular Weight Organic Acids
2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals, Reagents and Maize Grains
4.2. Microbial Cultures and Growth Media
4.3. Extraction of Antimicrobial Compounds (AMCs)
4.4. Antimicrobial Activity
4.5. Antioxidant Activity
4.6. Comparison of Antifungal Activity of AMCs with Commercial Preservatives
4.7. Bioprotection of Maize Using AMCs
4.8. Proximate Analysis
4.9. Estimation of β-Carotene in Raw and Treated Maize
4.10. Determination of Organic Acids in AMCs Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
4.11. Antifungal Activity of Organic Acids
4.12. Determination of Functional Groups by Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| CFS | Cell free supernatant |
| AMCs | Antimicrobial compounds |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| HPLC | High performance liquid chromatography |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
References
- Rather, I.A.; Seo, B.; Kumar, V.R.; Choi, U.-H.; Choi, K.-H.; Lim, J.; Park, Y.-H. Isolation and characterization of a proteinaceous antifungal compound from Lactobacillus plantarum YML007 and its application as a food preservative. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 57, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, P.M.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K. Cereal fungal infection, mycotoxins, and lactic acid bacteria mediated bioprotection: From crop farming to cereal products. Food Microbiol. 2014, 37, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choquer, M.; Fournier, E.; Kunz, C.; Levis, C.; Pradier, J.-M.; Simon, A.; Viaud, M. Botrytis cinereavirulence factors: New insights into a necrotrophic and polyphageous pathogen. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 277, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonçalves, A.; Gkrillas, A.; Dorne, J.L.; Dall’Asta, C.; Palumbo, R.; Lima, N.; Battilani, P.; Venâncio, A.; Giorni, P. Pre- and Postharvest Strategies to Minimize Mycotoxin Contamination in the Rice Food Chain. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewski, K.; Lahuta, L.B.; Martysiak-Żurowska, D.; Okorski, A.; Nitkiewicz, B.; Zielonka, Ł. Effect of Exogenous Application of Methyl Jasmonate on the Lipid and Carbohydrate Content and Composition of Winter Triticale (Triticosecale Wittm.) Grain and the Severity of Fungal Infections in Triticale Plants and Grain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5932–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Zannini, E.; Lynch, K.M.; Arendt, E. Novel approaches for chemical and microbiological shelf life extension of cereal crops. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 59, 3395–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Befikadu, D. Factors affecting quality of grain stored in Ethiopian traditional storage structures and opportunities for improvement. Int. J. Sci. Basic Appl. Res. 2014, 18, 235–257. [Google Scholar]
- Shiju, M. A review on the effect of fungi on the wheat grain under post harvest storage ecology. Food Environ. Safety J. 2010, 9, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, N.; Nawawi, A.; Othman, I. Fungal spoilage of starch-based foods in relation to its water activity (aw). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2000, 36, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, B.; Prasanna, B.M.; Hellin, J.; Bänziger, M. Crops that feed the world 6. Past successes and future challenges to the role played by maize in global food security. Food Secur. 2011, 3, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akwaji, P.; Umana, E.; Okon, E. Phytochemical and antifungal activity of leaf extracts of Corchorus olitorius and Gongronema latifolium on fungi associated with post-harvest deterioration of maize (Zea mays) seeds in Oban community, Nigeria. World Sci. News 2016, 53, 157–177. [Google Scholar]
- Suleiman, R.; Rosentrater, K.; Bern, C. Effects of deterioration parameters on storage of maize: A review. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 147–165. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, S.; Sati, N. Artificial preservatives and their harmful effects: Looking toward nature for safer alternatives. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2013, 4, 2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschetto, F.A.; Lopes, M.F.; Silva, B.P.; Neto, M.C.L. Sodium benzoate inhibits germination, establishment and development of rice plants. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 2019, 31, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregirchak, N.; Stabnikova, O.; Stabnikov, V. Application of Lactic Acid Bacteria for Coating of Wheat Bread to Protect it from Microbial Spoilage. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2020, 75, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, N.; Otani, T.; Inai, T. Nisin, a food preservative produced by Lactococcus lactis, affects the localization pattern of intermediate filament protein in HaCaT cells. Anat. Sci. Int. 2018, 94, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnürer, J.; Magnusson, J. Antifungal lactic acid bacteria as biopreservatives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.A.; Salman, M.; Numan, M.; Javed, M.R.; Zubair, M.; Mustafa, G. Characterization of antifungal metabolites produced by Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus coryniformis isolated from rice rinsed water. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatti-Kaul, R.; Chen, L.; Dishisha, T.; El Enshasy, H.A. Lactic acid bacteria: From starter cultures to producers of chemicals. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azat, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Kayir, A.; Lin, D.-B.; Zhou, W.-W.; Zheng, X. Probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditionally fermented Xinjiang cheese. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2016, 17, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crowley, S.; Mahony, J.; Van Sinderen, D. Current perspectives on antifungal lactic acid bacteria as natural bio-preservatives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedler, S.; Balti, R.; Neves, A.R. Bioprotective mechanisms of lactic acid bacteria against fungal spoilage of food. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 56, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozogul, F.; Hamed, I. The importance of lactic acid bacteria for the prevention of bacterial growth and their biogenic amines formation: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 58, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.; Olivares, M.; Marin, M.; Xaus, J.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, J.M. Characterization of a reuterin-producing Lactobacillus coryniformis strain isolated from a goat’s milk cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 104, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusson, J.; Schnürer, J. Lactobacillus coryniformis subsp. coryniformis Strain Si3 Produces a Broad-Spectrum Proteinaceous Antifungal Compound. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piper, J.D.; Piper, P.W. Benzoate and Sorbate Salts: A Systematic Review of the Potential Hazards of These Invaluable Preservatives and the Expanding Spectrum of Clinical Uses for Sodium Benzoate. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.P. Recent approaches in food bio-preservation—A review. Open Veter. J. 2018, 8, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.N.; Mohandas, C.; Nambisan, B. Purification of an antifungal compound, cyclo(l-Pro-d-Leu) for cereals produced by Bacillus cereus subsp. thuringiensis associated with entomopathogenic nematode. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavermicocca, P.; Valerio, F.; Evidente, A.; Lazzaroni, S.; Corsetti, A.; Gobbetti, M. Purification and Characterization of Novel Antifungal Compounds from the Sourdough Lactobacillus plantarum Strain 21B. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4084–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tebyanian, H.; Bakhtiari, A.; Karami, A.; Kariminik, A. Antimicrobial Activity of some Lactobacillus Species against Intestinal Pathogenic Bacteria. Int. Lett. Nat. Sci. 2017, 65, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, A.; Venâncio, A.; Abrunhosa, L. Antifungal effect of organic acids from lactic acid bacteria on Penicillium nordicum. Food Addit. Contam. 2018, 35, 1803–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, P.; Lou, L.; Zhan, J.; Fan, M.; Li, D.; Liao, Q. Antioxidant Activities of Lactic Acid Bacteria for Quality Improvement of Fermented Sausage. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2960–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Li, D.; Niu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Q. Antioxidant activity of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from traditional Chinese fermented foods. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koleva, I.I.; Van Beek, T.A.; Linssen, J.P.H.; De Groot, A.; Evstatieva, L.N. Screening of Plant Extracts for Antioxidant Activity: A Comparative Study on Three Testing Methods. Phytochem. Anal. 2002, 13, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedare, S.B.; Singh, R.P. Genesis and development of DPPH method of antioxidant assay. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, P.; Modi, H.A. Comparative study of DPPH, ABTS and FRAP assays for determination of antioxidant activity. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 3, 636–641. [Google Scholar]
- Lara-Villoslada, F.; Sierra, S.; Martin, R.; Delgado, S.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Olivares, M.; Xaus, J. Safety assessment of two probiotic strains, Lactobacillus coryniformis CECT5711 and Lactobacillus gasseri CECT5714. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, E.H.; Yang, E.J.; Woo, E.R.; Chang, H.C. Purification and characterization of antifungal compounds from Lactobacillus plantarum HD1 isolated from kimchi. Food Microbiol. 2014, 41, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Chang, H.C. Purification of a new antifungal compound produced by Lactobacillus plantarum AF1 isolated from kimchi. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessione, E.; Cirrincione, S. Bioactive Molecules Released in Food by Lactic Acid Bacteria: Encrypted Peptides and Biogenic Amines. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swain, M.R.; Ray, R.C. Nutritional values and bioactive compounds in lactic acid fermented vegetables and fruits. In Lactic Acid Fermentation of Fruits and Vegetables; Paramithiotis, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Shehu, K.; Aliero, A. Effects of purple blotch infection on the proximate and mineral contents of onion leaf. Int. J. Pharma Sci. Res. 2010, 1, 131–133. [Google Scholar]
- Sawant, S.G.; Gawai, D.U. Effect of fungal infections on nutritional value of papaya fruits. Curr. Bot. 2011, 2, 43–44. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, R.A. Effect of Carotenoids on Aflatoxin B1 Synthesis by Aspergillus flavus. Phytopathology 1997, 87, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Umana, E.J.; Ishoro, A.P.; Okey, E.N.; Akpan, J.B. Mycoflora associated with cocoa (Theobroma cacao) pods obtained in the field and their effects on seed nutritional contents. J. Agric. Crop Res. 2014, 2, 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Khanafari, A.; Soudi, H.; Miraboulfathi, M. Biocontrol of Aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin B1 production in corn. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2007, 4, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Muhialdin, B.J.; Algboory, H.L.; Kadum, H.; Mohammed, N.K.; Saari, N.; Hassan, Z.; Hussin, A.S.M. Antifungal activity determination for the peptides generated by Lactobacillus plantarum TE10 against Aspergillus flavus in maize seeds. Food Control. 2020, 109, 106898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyasi, T.A.; Jideani, A.I.O.; Mchau, G.R. Effect of organic acid pretreatment on some physical, functional and antioxidant properties of flour obtained from three unripe banana cultivars. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quitmann, H.; Fan, R.; Czermak, P. Acidic organic compounds in beverage, food, and feed production. In Biotechnology of Food and Feed Additives; Zorn, H., Czermak, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 143, pp. 91–141. [Google Scholar]
- Ashokkumar, R.; Ramaswamy, M. Phytochemical screening by FTIR spectroscopic analysis of leaf extracts of selected Indian medicinal plants. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 395–406. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmalakshmi, S.; Priyanga, S.; Devaki, K. Fourier Transform Infra-Red spectroscopy analysis of Erythrina variegata L. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 9, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar]
- Hari, N.; Nair, V.P. FTIR spectroscopic analysis of leaf extract in hexane in Jasminum azoricum L. IJSRST 2018, 4, 170–172. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, J.L.; Santos, L. Analysis of organic acids in wines by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, J.A.; Campos, F.M.; Figueiredo, A.R.; Hogg, T.A. Ability of lactic acid bacteria to produce volatile phenols. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2006, 57, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Brosnan, B.; Furey, A.; Arendt, E.; Murphy, P.; Coffey, A. Antifungal activity of Lactobacillus against Microsporum canis, Microsporum gypseum and Epidermophyton floccosum. Bioengineered 2012, 3, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Yan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Qi, W. Production and Characterization of Antifungal Compounds Produced by Lactobacillus plantarum IMAU10014. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cizeikiene, D.; Juodeikiene, G.; Paškevičius, A.; Bartkiene, E. Antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria against pathogenic and spoilage microorganism isolated from food and their control in wheat bread. Food Control. 2013, 31, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zola, F.G.; Rodrigues, A.C.; Oliveira, B.D.; Sacramento, N.T.B.; Taylor, J.G.; Pinto, U.M.; Bertoldi, M.C. Mineral and centesimal contents, antioxidant activity and antimicrobial action of phenolic compounds from Eugenia Brasiliensis Lam. Pulp. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 39, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gangwar, M.; Gautam, M.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Tripathi, Y.B.; Goel, R.K.; Nath, G. Antioxidant Capacity and Radical Scavenging Effect of Polyphenol Rich Mallotus philippenensis Fruit Extract on Human Erythrocytes: An In Vitro Study. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Association of Officiating Analytical Chemists. Official Method of Analysis, 18th ed.; Association of Officiating Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Junpatiw, A.; Lertrat, K.; Lomthaisong, K.; Tangwongchai, R. Effects of steaming, boiling and frozen storage on carotenoid contents of various sweet corn cultivars. Int. Food. Res. J. 2013, 20, 2219. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the Lactobacillus coryniformis BCH-4 AMCs are available from the authors. Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |






| Parameters (%) | Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 (Raw Grains) | A2 (A. flavus Inoculated Grains) | A3 (A. flavus + AMCs Inoculated Grains) | |
| Moisture | 23.90 ± 0.36 a | 26.26 ± 0.39 b | 24.00 ± 0.35 a |
| Protein | 8.63 ± 0.43 b | 6.30 ± 0.41 a | 10.73 ± 0.39 c |
| Fat | 3.26 ± 0.12 b | 1.96 ± 0.08 a | 3.90 ± 0.05 c |
| Fiber | 19.50 ± 0.30 b | 17.03 ± 0.32 a | 21.33 ± 0.12 c |
| Ash | 8.50 ± 0.40 b | 6.86 ± 0.31 a | 10.00 ± 0.11 c |
| β-Carotene (μg/100 g) | 241.33 ± 0.33 b | 235.66 ± 0.33 a | 242.00 ± 0.57 b |
| Sr. No. | Identified Organic Acid | Molecular Weight (g/mole) | Retention Time (min) | Concentration (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2-Oxopropanoic acid | 88.06 | 3.72 | 0.51 |
| 2 | 2-Hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid | 192.12 | 5.05 | 11.87 |
| 3 | 2-Hydroxybutanedioic acid | 134.08 | 6.41 | 0.79 |
| 4 | 2-Hydroxypropanoic acid | 90.08 | 7.22 | 11.85 |
| 5 | Propanedioic acid | 104.06 | 8.38 | 0.003 |
| 6 | Butanedioic acid | 118.09 | 15.94 | 2.84 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salman, M.; Tariq, A.; Ijaz, A.; Naheed, S.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Soliman, M.H.; Javed, M.R. In Vitro Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Lactobacillus coryniformis BCH-4 Bioactive Compounds and Determination of their Bioprotective Effects on Nutritional Components of Maize (Zea mays L.). Molecules 2020, 25, 4685. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204685
Salman M, Tariq A, Ijaz A, Naheed S, Hashem A, Abd_Allah EF, Soliman MH, Javed MR. In Vitro Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Lactobacillus coryniformis BCH-4 Bioactive Compounds and Determination of their Bioprotective Effects on Nutritional Components of Maize (Zea mays L.). Molecules. 2020; 25(20):4685. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204685
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalman, Mahwish, Anam Tariq, Anam Ijaz, Shazia Naheed, Abeer Hashem, Elsayed Fathi Abd_Allah, Mona H. Soliman, and Muhammad Rizwan Javed. 2020. "In Vitro Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Lactobacillus coryniformis BCH-4 Bioactive Compounds and Determination of their Bioprotective Effects on Nutritional Components of Maize (Zea mays L.)" Molecules 25, no. 20: 4685. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204685
APA StyleSalman, M., Tariq, A., Ijaz, A., Naheed, S., Hashem, A., Abd_Allah, E. F., Soliman, M. H., & Javed, M. R. (2020). In Vitro Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Lactobacillus coryniformis BCH-4 Bioactive Compounds and Determination of their Bioprotective Effects on Nutritional Components of Maize (Zea mays L.). Molecules, 25(20), 4685. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204685