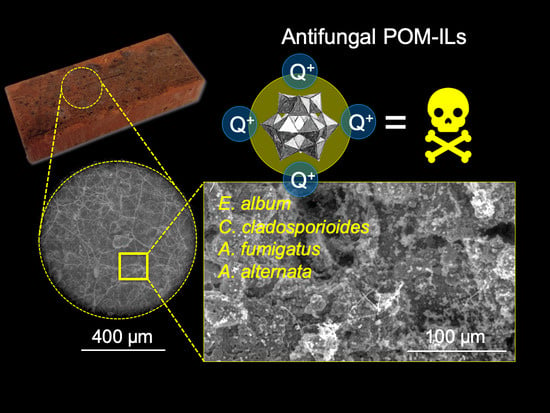
Antifungal Activity of Polyoxometalate-Ionic Liquids on Historical Brick
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis and Characterisation of POM-ILs
3.2. Assessment of Antifungal Activity of POM-ILs by Disc Diffusion Method
3.3. Evaluation of Antifungal Activity on Brick Samples
3.4. Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy (ESEM)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guillitte, O. Bioreceptivity and biodeterioration of brick structures. In Conservation of Historic Brick Structures, 1st ed.; Baer, N.S., Fitz, S., Livingston, R.A., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 69–84. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Cornelio, S.; Mendoza-Vega, J.; Gaylarde, C.C.; Reyes-Estebanez, M.; Morón-Ríos, A.; De la Rosa-García, S.; Ortega-Morales, B.O. Succession of fungi colonizing porous and compact limestone exposed to subtropical environments. Fungal Biol. 2012, 116, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvadori, O.; Municchia, A.C. The Role of fungi and lichens in the biodeterioration of stone monuments. Open Conf. Proc. J. 2016, 7, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwalina, B. Biodeterioration of concrete, brick and other mineral-based building materials. In Understanding Biocorrosion. Fundamentals and Applications, 1st ed.; Liengen, T., Feron, D., Basseguy, R., Beech, I.B., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Sawston, UK, 2014; pp. 281–312. [Google Scholar]
- Sterflinger, K. Fungi as geologic agents. Geomicrobiol. J. 2000, 17, 97–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Ghany, T.M.; Omar, A.M.; Elwkeel, F.M.; Al Abboud, M.A. Fungal deterioration of limestone false-door monument. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lan, W.; Li, H.; Wang, W.D.; Katayama, Y.; Gu, J.D. Microbial community analysis of fresh and old microbial biofilms on Bayon temple sandstone of Angkor Thom, Cambodia. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 60, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.D.; Kigawa, R.; Sato, Y.; Katayama, Y. Addressing the microbiological problems of cultural property and archive documents after earthquake and tsunami. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 85, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrasher, J.D. Fungi, bacteria, nano-particuletes, mycotoxins and human health in water-damaged indoor environments. J. Community Public Health Nurs. 2016, 2, 1000115. [Google Scholar]
- Järvi, K.; Hyvärinen, A.; Täubel, M.; Karvonen, A.M.; Turunen, M.; Jalkanen, K.; Patovirta, R.; Syrjänen, T.; Pirinen, J.; Salonen, H.; et al. Microbial growth in building material samples and occupants’ health in severely moisture-damaged homes. Indoor Air 2018, 28, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxi, S.N.; Portnoy, J.M.; Larenas-Linnemann, D.; Phipatanakul, W.; Barnes, C.; Baxi, S.; Grimes, C.; Horner, W.; Kennedy, K.; Levetin, E.J.; et al. Exposure and health effects of fungi on humans. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2016, 4, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharpe, R.A.; Bearman, N.; Thornton, C.R.; Husk, K.; Osborne, N.J. Indoor fungal diversity and asthma: A meta-analysis and systematic review of risk factors. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevalainen, A.; Täubel, M.; Hyvärinen, A. Indoor fungi: Companions and contaminants. Indoor Air 2015, 25, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.F. Mycotoxin production by indoor mold. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2003, 39, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salin, J.T.; Salkinoja-Salonen, M.; Salin, P.J.; Nelo, K.; Holma, T.; Ohtonen, P.; Syrjälä, H. Building-related symptoms are linked to the in vitro toxicity of indoor dust and airborne microbial propagules in schools: A cross-sectional study. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rylander, R.; Lin, R. (1→3)-β-d-glucan—Relationship to indoor air-related symptoms, allergy and asthma. Toxicology 2000, 152, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumerova, N.I.; Rompel, A. Polyoxometalates in solution: Speciation under spotlight. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streb, C. New trends in polyoxometalate photoredox chemistry: From photosensitisation to water oxidation catalysis. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamase, T. Anti-tumor, -viral, and -bacterial activities of polyoxometalates for realizing an inorganic drug. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 4773–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijelic, A.; Aureliano, M.; Rompel, A. The antibacterial activity of polyoxometalates: Structures, antibiotic effects and future perspectives. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 1153–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murugesan, S.; Quintero, O.A.; Chou, B.P.; Xiao, P.; Park, K.; Hall, J.W.; Jones, R.A.; Henkelman, G.; Goodenough, J.B.; Stevenson, K.J. Wide electrochemical window ionic salt for use in electropositive metal electrodeposition and solid state Li-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2194–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzetta, A.; Perillo, V.; Guazzelli, L.; Chiappe, C. Thermal behavior analysis as a valuable tool for comparing ionic liquids of different classes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 3335–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenbrenner, O.; Supasitmongkol, S.; Taylor, M.; Styring, P. Measurement of vapour pressures of ionic liquids and other low vapour pressure solvents. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S.; De Matteis, L.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Mitchell, S.G.; Streb, C. Removal of multiple contaminants from water by polyoxometalate supported ionic liquid phases (POM-SILPs). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, S.; Kostrzewa, M.; Wierschem, A.; Streb, C. Polyoxometalate ionic liquids as self-repairing acid-resistant corrosion protection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 13596–13599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, A.-L.; Kremer, L.; Herrmann, S.; Mitchell, S.G.; Bondarenko, O.M.; Kahru, A.; Streb, C. Antimicrobial activity of polyoxometalate ionic liquids against clinically relevant pathogens. ChemPlusChem 2017, 82, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, A.; Castillo, I.F.; Müller, D.P.; González, C.; Eyssautier-Chuine, S.; Ziegler, A.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Mitchell, S.G.; Streb, C. Polyoxometalate-ionic liquids (POM-ILs) as anticorrosion and antibacterial coatings for natural stones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 14926–14931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Misra, A.; Zambrzycki, C.; Kloker, G.; Kotyrba, A.; Anjass, M.H.; Franco Castillo, I.; Mitchell, S.G.; Güttel, R.; Streb, C. water purification and microplastics removal using magnetic polyoxometalate-supported ionic liquid phases (magPOM-SILPs). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 1601–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajkowska, K.; Otlewska, A.; Koziróg, A.; Piotrowska, M.; Nowicka-Krawczyk, P.; Hachułka, M.; Wolski, G.J.; Kunicka-Styczyńska, A.; Gutarowska, B.; Żydzik-Białek, A. Assessment of biological colonization of historic buildings in the former Auschwitz II-Birkenau concentration camp. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kemme, M.; Heinzel-Wieland, R. Quantitative assessment of antimicrobial activity of PLGA films loaded with 4-hexylresorcinol. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hage-Hülsmann, J.; Grünberger, A.; Thies, S.; Santiago-Schübel, B.; Klein, A.S.; Pietruszka, J.; Binder, D.; Hilgers, F.; Domröse, A.; Drepper, T.; et al. Natural biocide cocktails: Combinatorial antibiotic effects of prodigiosin and biosurfactants. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, M.; Otlewska, A.; Rajkowska, K.; Koziróg, A.; Hachułka, M.; Nowicka-Krawczyk, P.; Wolski, G.J.; Gutarowska, B.; Kunicka-Styczyńska, A.; Zydzik-Białek, A. Abiotic determinants of the historical buildings biodeterioration in the former Auschwitz II-Birkenau concentration and extermination camp. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutarowska, B.; Żakowska, Z. Elaboration and application of mathematical model for estimation of mould contamination of some building materials based on ergosterol content determination. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2002, 49, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminskyj, S.G.; Dahms, T.E. High spatial resolution surface imaging and analysis of fungal cells using SEM and AFM. Micron 2008, 39, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petkovic, M.; Hartmann, D.O.; Adamova, G.; Seddon, K.R.; Rebeloa, L.P.N.; Pereira, C.S. Unravelling the mechanism of toxicity of alkyltributylphosphonium chlorides in Aspergillus nidulans conidia. New J. Chem. 2012, 36, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.; Shah, J.K.; Zhua, Y.; Maginn, E.J. Amphiphilic interactions of ionic liquids with lipid biomembranes: A molecular simulation study. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 8641–8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Ananikov, V.P. Biological activity of ionic liquids and their application in pharmaceutics and medicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7132–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziróg, A.; Otlewska, A.; Gapińska, M.; Michlewska, S. Influence of gemini surfactants on biochemical profile and ultrastructure of Aspergillus brasiliensis. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, M.; Suzuki, T.; Fujita, Y.; Oda, M.; Matsumoto, N.; Yamase, T. Enhancement of antibacterial activity of beta-lactam antibiotics by [P2W18O62]6−, [SiMo12O40]4−, and [PTi2W10O40]7− against methicillin-resistant and vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkowska, K.; Koziróg, A.; Otlewska, A.; Piotrowska, M.; Nowicka-Krawczyk, P.; Brycki, B.; Kunicka-Styczyńska, A.; Gutarowska, B. Quaternary ammonium biocides as antimicrobial agents protecting historical wood and brick. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2016, 63, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| POM-IL | POM-IL Short Name |
|---|---|
| [PW12O40][(C6H13)4N]3 | [PW12O40][THexA]3 |
| [PW12O40][(C7H15)4N]3 | [PW12O40][THepA]3 |
| [PW12O40][(C8H17)4N]3 | [PW12O40][TOctA]3 |
| [SiW11O39][(C6H13)3(C14H29)N]8 | [SiW11O39][THTDA]8 |
| [SiW12O40][(C6H13)3(C14H29)N]4 | [SiW12O40][THTDA]4 |
| [SiW11O39][(C8H17)4N]8 | [SiW11O39][TOctA]8 |
| [SiW11O39][(CH3)3(C8H17)N]8 | [SiW11O39][TMOA]8 |
| [SiW12O40][(CH3)3(C8H17)N]4 | [SiW12O40][TMOA]4 |
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajkowska, K.; Koziróg, A.; Otlewska, A.; Piotrowska, M.; Atrián-Blasco, E.; Franco-Castillo, I.; Mitchell, S.G. Antifungal Activity of Polyoxometalate-Ionic Liquids on Historical Brick. Molecules 2020, 25, 5663. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235663
Rajkowska K, Koziróg A, Otlewska A, Piotrowska M, Atrián-Blasco E, Franco-Castillo I, Mitchell SG. Antifungal Activity of Polyoxometalate-Ionic Liquids on Historical Brick. Molecules. 2020; 25(23):5663. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235663
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajkowska, Katarzyna, Anna Koziróg, Anna Otlewska, Małgorzata Piotrowska, Elena Atrián-Blasco, Isabel Franco-Castillo, and Scott G. Mitchell. 2020. "Antifungal Activity of Polyoxometalate-Ionic Liquids on Historical Brick" Molecules 25, no. 23: 5663. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235663
APA StyleRajkowska, K., Koziróg, A., Otlewska, A., Piotrowska, M., Atrián-Blasco, E., Franco-Castillo, I., & Mitchell, S. G. (2020). Antifungal Activity of Polyoxometalate-Ionic Liquids on Historical Brick. Molecules, 25(23), 5663. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235663