Novel Cationic Prodrug of Ubiquinol-10 Enhances Intestinal Absorption via Efficient Formation of Nanosized Mixed-Micelles with Bile Acid Anions
Abstract
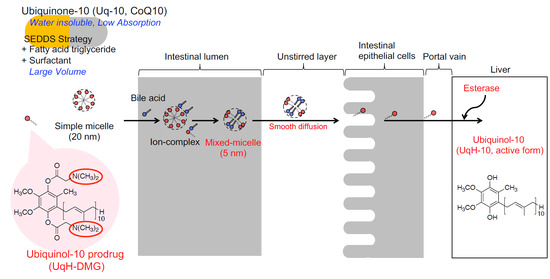
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Properties of UqH-10 Derivatives
2.2. Micelle Formation of UqH-DMG in Water
2.3. Mixed-Micelle Formation of UqH-DMG with Taurocholic Acid
2.4. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of UqH-10 Derivatives
2.5. Plasma Concentrations of UqH-10 after Single Oral Administration of UqH-Derivatives in Fasted and Postprandial Rats
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Animals
3.3. Instrumental Analyses
3.4. Synthesis of Ubiquinol-10 N,N-Dimethylglycinate Derivatives
3.5. Water Solubility
3.6. Micellization of UqH-DMG in Water
3.7. Mixed-Micellization of UqH-DMG with Taurocholic Acid
3.7.1. Preparation of Aqueous Solutions of UqH-DMG with Taurocholic Acid
3.7.2. Determination of Particle Sizes
3.8. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of UqH-Derivatives
3.9. HPLC Analysis
3.9.1. HPLC System and Conditions for Water Solubility and Hydrolysis Study
3.9.2. HPLC System and Conditions for Pharmacokinetic Study
3.10. Dosing Protocol
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ernster, L.; Dallner, G. Biochemical, physiological and medical aspects of ubiquinone function. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta - Mol. Basis Dis. 1995, 1271, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhagavan, H.N.; Chopra, R.K. Coenzyme Q10: Absorption, tissue uptake, metabolism and pharmacokinetics. Free Radic. Res. 2006, 40, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Camacho, J.D.; Bernier, M.; López-Lluch, G.; Navas, P. Coenzyme Q. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beal, M.F.; Oakes, D.; Shoulson, I.; Henchcliffe, C.; Galpern, W.R.; Haas, R.; Juncos, J.L.; Nutt, J.G.; Voss, T.S.; Ravina, B.; et al. A Randomized Clinical Trial of High-Dosage Coenzyme Q10 in Early Parkinson Disease No Evidence of Benefit. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.K.; Wang, L.P.; Chen, L.; Yao, X.P.; Yang, K.Q.; Gao, L.G.; Zhou, X.L. Coenzyme Q10 treatment of cardiovascular disorders of ageing including heart failure, hypertension and endothelial dysfunction. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 450, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoe, K.; Kitano, M.; Kishida, H.; Kubo, H.; Fujii, K.; Kitahara, M. Study on safety and bioavailability of ubiquinol (Kaneka QH (TM)) after single and 4-week multiple oral administration to healthy volunteers. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 47, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, C.J.H.; Trevaskis, N.L.; Charman, W.N. Lipids and lipid-based formulations: optimizing the oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kommuru, T.R.; Gurley, B.; Khan, M.A.; Reddy, I.K. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) of coenzyme Q10: formulation development and bioavailability assessment. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 212, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoue, S.; Uchida, A.; Kuriyama, K.; Nakamura, T.; Seto, Y.; Kato, M.; Hatanaka, J.; Tanaka, T.; Miyoshi, H.; Yamada, S. Novel solid self-emulsifying drug delivery system of coenzyme Q10 with improved photochemical and pharmacokinetic behaviors. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 46, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheuk, S.Y.; Shih, F.F.; Champagne, E.T.; Daigle, K.W.; Patindo, J.A.; Mattison, C.P.; Boue, S.M. Nano-encapsulation of coenzyme Q(10) using octenyl succinic anhydride modified starch. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikorska, M.; Lanthier, P.; Miller, H.; Beyers, M.; Sodja, C.; Zurakowski, B.; Gangaraju, S.; Pandey, S.; Sandhu, J.K. Nanomicellar formulation of coenzyme Q10 (Ubisol-Q10) effectively blocks ongoing neurodegeneration in the mouse 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine model: Potential use as an adjuvant treatment in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 2329–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Yamaki, Y.; Nishimura, Y.; Miyashita, M.; Maruyama, S.; Takekuma, Y.; Sugawara, M. Enhancement of intestinal absorption of coenzyme Q10 using emulsions containing oleyl polyethylene acetic acids. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 142, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, J.; Karube, Y.; Hanada, M.; Matsunaga, K.; Matsushima, Y.; Sendo, T.; Aoyama, T. Vitamin-k prodrugs 1. Synthesis of amino-acid esters of menahydroquinone-4 and enzymatic reconversion to an active form. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, J.; Karube, Y.; Hanada, M.; Matsunaga, K.; Matsushima, Y.; Sendo, T.; Oishi, R. Vitamin K prodrugs. 2. Water-soluble prodrugs of menahydroquinone-4 for systemic site-specific delivery. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 1973–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, S.; Yamamoto, Y. Simultaneous detection of ubiquinol and ubiquinone in human plasma as a marker of oxidative stress. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 250, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compound, UqH-DMG is available from the authors. |




| Parameters | UqH-DMG a | UqH-1-DMG | UqH-4-DMG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rat | Human | |||
| Km (×10−3 M) | 3.89 a | 4.63 | 0.0751 | 0.0722 |
| Vmax (×10−6 M·min−1) | 0.603 a | 0.821 | 0.119 | 0.123 |
| Vmax/Km (×10−3 min−1) | 0.155 a | 0.177 | 1.58 | 1.70 |
| Parameters | Uq-10 | UqH-4-DMG | UqH-DMG | Uq-10 | UqH-4-DMG | UqH-DMG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasted | Postprandial | |||||
| n | 4 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Dose (μmol·kg−1) | 40.5 | |||||
| Cmax (μmol·L−1) | 0.143 ± 0.0826 | 0.763 ± 0.209 | 0.800 ± 0.157 | 1.99 ± 0.472 | 3.01 ± 0.423 | 2.24 ± 0.110 |
| Tmax (h) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| AUC0-24h (μmol·L−1·h) | 2.16 ± 0.878 | 7.13 ± 1.71 | 5.10 ± 1.57 | 35.0 ± 1.78 | 39.3 ± 6.78 | 34.4 ± 6.51 |
| MRT (h) | 8.56 ± 1.96 | 8.96 ± 0.710 | 8.43 ± 0.956 | 12.2 ± 0.971 | 9.12 ± 0.565 | 11.5 ± 0.525 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Setoguchi, S.; Hidaka, R.; Nagata-Akaho, N.; Watase, D.; Koga, M.; Matsunaga, K.; Karube, Y.; Takata, J. Novel Cationic Prodrug of Ubiquinol-10 Enhances Intestinal Absorption via Efficient Formation of Nanosized Mixed-Micelles with Bile Acid Anions. Molecules 2020, 25, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030546
Setoguchi S, Hidaka R, Nagata-Akaho N, Watase D, Koga M, Matsunaga K, Karube Y, Takata J. Novel Cationic Prodrug of Ubiquinol-10 Enhances Intestinal Absorption via Efficient Formation of Nanosized Mixed-Micelles with Bile Acid Anions. Molecules. 2020; 25(3):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030546
Chicago/Turabian StyleSetoguchi, Shuichi, Ryoji Hidaka, Nami Nagata-Akaho, Daisuke Watase, Mitsuhisa Koga, Kazuhisa Matsunaga, Yoshiharu Karube, and Jiro Takata. 2020. "Novel Cationic Prodrug of Ubiquinol-10 Enhances Intestinal Absorption via Efficient Formation of Nanosized Mixed-Micelles with Bile Acid Anions" Molecules 25, no. 3: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030546
APA StyleSetoguchi, S., Hidaka, R., Nagata-Akaho, N., Watase, D., Koga, M., Matsunaga, K., Karube, Y., & Takata, J. (2020). Novel Cationic Prodrug of Ubiquinol-10 Enhances Intestinal Absorption via Efficient Formation of Nanosized Mixed-Micelles with Bile Acid Anions. Molecules, 25(3), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030546