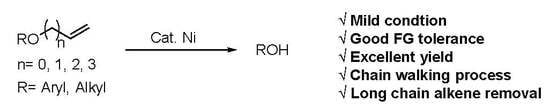
Nickel-Catalyzed Removal of Alkene Protecting Group of Phenols, Alcohols via Chain Walking Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Representative General Procedure for Nickel-Catalyzed Deprotecting Reaction
4.2. Characterization Data for Products 2a–2s, 5 and 7 (Tables 2, 3 and Scheme 2)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Wuts, P.G.M.; Green, T.W. Protection for Phenols and Catechols; John Wiley Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 367–430. [Google Scholar]
- Wuts, P.G.M.; Green, T.W. Greene’s Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, 4th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto, H.; Kondo, Y. Facile removal strategy for allyl and allyloxycarbonyl protecting groups using solid-supported barbituric acid under palladium catalysis. Synlett 2003, 2003, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, W.F.; England, M.D.; Mealy, M.J.; Thongsornkleeb, C.; Teng, L. Facile O-Deallylation of Allyl Ethers via SN2‘ Reaction with tert-Butyllithium. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beugelmans, R.; Bourdet, S.; Bigot, A.; Zhu, J. Reductive deprotection of aryl allyl ethers with Pd(Ph3)4/NaBH4. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 4349–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitov, P.I.; Bundle, D.R. Mild oxidative one-pot allyl group cleavage. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 2835–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vutukuri, D.R.; Bharathi, P.; Yu, Z.; Rajasekaran, K.; Tran, M.-H.; Thayumanavan, S. A Mild Deprotection Strategy for Allyl-Protecting Groups and Its Implications in Sequence Specific Dendrimer Synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W. Pd-Catalyzed Debenzylation and Deallylation of Ethers and Esters with Sodium Hydride. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 3016–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemming, D.S.; Talbot, E.P.; Steel, P.G. A mild copper catalyzed method for the selective deprotection of aryl allyl ethers. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Calvo, M.; Couceiro, J.R.; Destito, P.; Rodriguez, J.; Mosquera, J.; Mascareñas, J.L. Intracellular deprotection reactions mediated by palladium complexes equipped with designed phosphine ligands. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 6055–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gärtner, D.; Konnerth, H.; von Wangelin, A.J. Highly practical iron-catalyzed C–O cleavage reactions. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 2541–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleta, Z.; Makowski, B.T.; Soo’s, T.; Dembinski, R. Thionation using fluorous Lawesson’s reagent. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 1625–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, S.W.; Pastine, S.J.; Sames, D. Ru (III)-catalyzed cyclization of arene-alkene substrates via intramolecular electrophilic hydroarylation. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.-Z.; Chen, C.-F. A highly efficient approach to [4] pseudocatenanes by threefold metathesis reactions of a triptycene-based tris [2] pseudorotaxane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 13158–13159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Cho, S.Y.; Hughes, R.; Winssinger, N.; Smethurst, C.; Labischinski, H.; Endermann, R. Solid-and Solution-Phase Synthesis of Vancomycin and Vancomycin Analogues with Activity against Vancomycin-Resistant Bacteria. Chem. Eur. J. 2001, 7, 3798–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wipf, P.; Aslan, D.C. Synthesis of bicyclic ortho esters by epoxy ester rearrangements and study of their ring-opening reactions. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, E.J.; Guzman-Perez, A.; Noe, M.C. Highly enantioselective and regioselective catalytic dihydroxylation of homoallylic alcohol derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 3481–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Asao, N. Selective reactions using allylic metals. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 2207–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, A.G.M.; Lebold, S.A.; Zhang, X. 3-Butenyl esters as convenient protecting groups for carboxylic acids. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 7317–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadot, C.; Dalko, P.I.; Cossy, J. Olefin isomerization by a ruthenium carbenoid complex. Cleavage of allyl and homoallyl groups. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 1839–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipshutz, B.H.; Ghorai, S.; Leong, W.W.Y. Deprotection of Homoallyl (hAllyl) Derivatives of Phenols, Alcohols, Acids, and Amines. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 2854–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, H.; Juliá-Hernández, F.; Martin, R.; Marek, I. Walking Metals for Remote Functionalization Sommer. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, E.W.; Mei, T.-S.; Burckle, A.J.; Sigman, M.S. Enantioselective Heck Arylations of Acyclic Alkenyl Alcohols Using a Redox-Relay Strategy. Science 2012, 338, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seayad, A.; Ahmed, M.; Klein, H.; Jackstell, R.; Gross, T.; Beller, M. Internal Olefins to Linear Amines. Science 2002, 297, 1676–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, T.-S.; Patel, H.H.; Sigman, M.S. Enantioselective construction of remote quaternary stereocentres. Nature 2014, 508, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buslov, I.; Becouse, J.; Mazza, S.; Montandon-Clerc, M.; Hu, X. Chemoselective Alkene Hydrosilylation Catalyzed by Nickel Pincer Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14523–14526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buslov, I.; Song, F.; Hu, X. An Easily Accessed Nickel Nanoparticle Catalyst for Alkene Hydrosilylation with Tertiary Silanes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12295–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juliá-Hernández, F.; Moragas, T.; Cornella, J.; Martin, R. Remote carboxylation of halogenated aliphatic hydrocarbons with carbon dioxide. Nature 2017, 545, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Z.; Romano, C.; Martin, R. Site-selective catalytic deaminative alkylation of unactivated olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 16197–16201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Z.; Borjesson, M.; Martin-Montero, R.; Martin, R. Site-Selective Ni-Catalyzed Reductive Coupling of alpha-Haloboranes with Unactivated Olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12765–12769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhu, S. Mild and Regioselective Benzylic C−H Functionalization: Ni-Catalyzed Reductive Arylation of Remote and Proximal Olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.-M.; Zhu, S. Remote Migratory Cross-Electrophile Coupling and Olefin Hydroarylation Reactions Enabled by in Situ Generation of NiH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13929–13935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Song, P.; Xu, X.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Y. Migratory Reductive Acylation between Alkyl Halides or Alkenes and Alkyl Carboxylic Acids by Nickel Catalysis. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 3253–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhu, S. Nickel-Catalysed Selective Migratory Hydrothiolation of Alkenes and Alkynes with Thiols. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, J.; He, Y.; Ye, F.; Zhu, S. Remote sp3 C–H Amination of Alkenes with Nitroarenes. Chem 2018, 4, 1645–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhu, S. NiH-Catalyzed Remote Asymmetric Hydroalkylation of Alkenes with Racemic α-Bromo Amides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1754–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, J.S.; Schramm, Y.; Sergeev, A.G.; Clot, E.; Eisenstein, O.; Hartwig, J.F. Linear-Selective Hydroarylation of Unactivated Terminal and Internal Olefins with Trifluoromethyl-Substituted Arenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13098–13101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matt, C.; Kölblin, F.; Streuff, J. Reductive C–O, C–N, and C–S Cleavage by a Zirconium Catalyzed Hydrometalation/β-Elimination Approach. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 6983–6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yi, J.; Xu, H.; Li, S.; Yuan, R. An Efficient, One-Pot Transamidation of 8-Aminoquinoline Amides Activated by Tertiary-Butyloxycarbonyl. Molecules 2019, 24, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, J.; Badir, S.O.; Kammer, L.M.; Ribagorda, M.; Molander, G.A. Deaminative Reductive Arylation Enabled by Nickel/Photoredox Dual Catalysis. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 3346–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Liu, J.-H.; Liang, J.; Dai, J.-J.; Yang, C.-T.; Fu, Y.; Liu, L. Alkylboronic Esters from Palladium- and Nickel-Catalyzed Borylation of Primary and Secondary Alkyl Bromides. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2012, 354, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudnik, A.S.; Fu, G.C. Nickel-Catalyzed Coupling Reactions of Alkyl Electrophiles, Including Unactivated Tertiary Halides, To Generate Carbon–Boron Bonds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10693–10697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Bachman, S.; Dudnik, A.S.; Fu, G.C. Nickel-Catalyzed Enantioconvergent Borylation of Racemic Secondary Benzylic Electrophiles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 14529–14532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didiuk, M.T.; Morken, J.P.; Hoveyda, A.H. Directed Regio- and Stereoselective Nickel-Catalyzed Addition of Alkyl Grignard Reagents to Allylic Ethers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 7273–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, N.A.; Zhang, W. Transition metal-catalyzed allylic substitution reactions with unactivated allylic substrates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7929–7967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Romero, E.; Matsui, J.K.; Molander, G.A. Regioselective Single-Electron Tsuji–Trost Reaction of Allylic Alcohols: A Photoredox/Nickel Dual Catalytic Approach. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 6543–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, C.; Qian, Q.; Deng, W.; Gong, H. Nickel-catalyzed cross-coupling of unactivated alkyl halides using bis(pinacolato)diboron as reductant. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 4022–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Chen, H.; Sessler, J.L.; Gong, H. Zn-Mediated Fragmentation of Tertiary Alkyl Oxalates Enabling Formation of Alkylated and Arylated Quaternary Carbon Centers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Gong, H. Preparation of Vinyl Arenes by Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Coupling of Aryl Halides with Vinyl Bromides. Angew. Chem. Chem. Int. 2016, 55, 15544–15548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Xue, W.; Gong, H. Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Coupling of Aryl Halides with Unactivated tert-Alkyl Halides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11562–11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everson, D.A.; Jones, B.A.; Weix, D.J. Replacing Conventional Carbon Nucleophiles with Electrophiles: Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Alkylation of Aryl Bromides and Chlorides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6146–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Weix, D.J. Mechanism and Selectivity in Nickel-Catalyzed Cross-Electrophile Coupling of Aryl Halides with Alkyl Halides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16192–16197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 2a–2p are available from the authors. |





| entry | Deviation from standard conditions | Yield of 2 (%) a |
| 1 | None | 96(92) b |
| 2 | Ni(COD)2 | 84 |
| 3 | NiCl2 instead of NiCl2(DME) | 53 |
| 4 | L2 instead of L1 | 37 |
| 5 | L3 | 9 |
| 6 | L4 | 42 |
| 7 | L5 | 45 |
| 8 | B2pin2 w/o additives | 61 |
| 9 | Zn instead of B2pin2 | 5< |
| 10 | Mn instead of B2pin2 | 5< |
| 11 | No CH3OH | 73 |
| 12 | No H2O | 78 |
| 13 | LiOH instead of LiOtBu | 71 |
| 14 | KOH instead of LiOtBu | 68 |
| 15 | THF instead of DMA | 56 |
| 16 | No Ni | 0 |
| 17 | No B2pin2 | 0 |
| 18 | 20 mmol scale | 86 |
| 19 | 1% loading of nickel, 2% L1 | 52(42) c |

| Substrate | Product | Substrate | Product |
 | 2a: 92%, 88% a |  | 2s: 96% |
 | 2c: 87%, 90% a; 2f: 92%,84% a |  | 2c: 93% |
 | 2g: X = I, 63%; 2h: X = Br, 65% |  | 2a: 81% |
 | 2i: 95% |  | 2d: 74% |
 | 2o: 83% |  | 2e: 72% |
 | 2r: 53% |  | 2p: 63% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, C.; Niu, H.; Ning, J.; Wu, W.; Yi, J. Nickel-Catalyzed Removal of Alkene Protecting Group of Phenols, Alcohols via Chain Walking Process. Molecules 2020, 25, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030602
Meng C, Niu H, Ning J, Wu W, Yi J. Nickel-Catalyzed Removal of Alkene Protecting Group of Phenols, Alcohols via Chain Walking Process. Molecules. 2020; 25(3):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030602
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Chenkai, Haolin Niu, Juehan Ning, Wengang Wu, and Jun Yi. 2020. "Nickel-Catalyzed Removal of Alkene Protecting Group of Phenols, Alcohols via Chain Walking Process" Molecules 25, no. 3: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030602
APA StyleMeng, C., Niu, H., Ning, J., Wu, W., & Yi, J. (2020). Nickel-Catalyzed Removal of Alkene Protecting Group of Phenols, Alcohols via Chain Walking Process. Molecules, 25(3), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030602