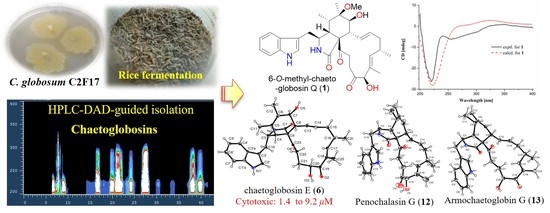
HPLC-DAD-Guided Isolation of Diversified Chaetoglobosins from the Coral-Associated Fungus Chaetomium globosum C2F17
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Elucidation
2.2. Biological Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Strain and Fermentation
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Computational Methods
3.5. X-Ray Crystallography
3.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.7. Anti-Tuberculosis Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, X.M.; Xu, R.F.; Gu, Y.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L. Biological and chemical diversity of coral-derived microorganisms. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 3707–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, V.T.; Dat, T.T.H.; Vinh, L.B.; Cuong, L.C.V.; Oanh, P.T.T.; Ha, H.; Kim, Y.H.; Anh, H.L.T.; Yang, S.Y. Coral and coral-associated microorganisms: A prolific source of potential bioactive natural products. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H.Q.; Zong, S.C.; Gao, J.M.; Zhang, A.L. Chemical and bioactive diversities of the genus Chaetomium secondary metabolites. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherlach, K.; Boettger, D.; Remme, N.; Hertweck, C. The chemistry and biology of cytochalasans. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 869–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.C.; Chen, C.M.; Tong, Q.Y.; Yang, J.; Wei, G.Z.; Xue, Y.B.; Wang, J.P.; Luo, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.H. Asperflavipine A: A cytochalasan heterotetramer uniquely defined by a highly complex tetradecacyclic ring system from Aspergillus flavipes QCS12. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2017, 56, 5242–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H.; Gu, M.L.; Han, C.; Guo, X.J.; Yin, G.P.; Kong, L.Y. Aureochaeglobosins A-C, three [4+2] adducts of chaetoglobosin and aureonitol derivatives from Chaetomium globosum. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 3345–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Wang, J.P.; Liu, J.J.; Zhu, H.C.; Sun, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.W.; Luo, Z.W.; Yao, G.M.; Xue, Y.B.; et al. Armochaetoglobins A-J: Cytochalasan alkaloids from Chaetomium globosum TW1-1, a fungus derived from the terrestrial arthropod Armadillidium vulgare. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.X.; He, Y.; Li, F.L.; Chai, C.W.; Zhang, J.W.; Guo, J.R.; Chen, C.M.; Wang, J.P.; Zhu, H.C.; Hu, Z.X.; et al. Antibacterial activity against drug-resistant microbial pathogens of cytochalasan alkaloids from the arthropod-associated fungus Chaetomium globosum TW1-1. Bioorganic Chem. 2018, 83, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, X.W.; Ding, Y.M.; Deng, J. Total synthesis of asperchalasines A, D, E, and H. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2018, 57, 14221–14224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.Y.; Tian, C.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, Z.G.; Dong, Z.; Li, Y.H.; Gao, M.H.; Zhang, H.L.; Liu, G.; Tang, Y.F. Total syntheses of asperchalasines A-E. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2018, 57, 14216–14220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Lei, X.Q.; Wang, Y.H.; Dong, Z.; Liu, G.; Tang, Y.F. Total syntheses of periconiasins A-E. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2016, 55, 6992–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skellam, E. The biosynthesis of cytochalasans. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.W.; Chen, C.M.; Tao, H.M.; Lin, X.P.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.F.; Liu, Y.H. Structurally diverse diketopiperazine alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor SCSIO 41016. Org. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.W.; Lin, X.P.; Tao, H.M.; Wang, J.F.; Li, J.Y.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.F.; Liu, Y.H. Isochromophilones A–F, cytotoxic chloroazaphilones from the marine mangrove endophytic fungus Diaporthe sp. SCSIO 41011. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, W.X.; Feng, Y.J.; Blunt, J.W.; Cole, A.L.J.; Munro, M.H.G. Chaetoglobosins Q, R, and T, three further new metabolites from Chaetomium globosum. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1722–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xiao, J.; Gao, Y.Q.; Tang, J.J.; Zhang, A.L.; Gao, J.M. Chaetoglobosins from Chaetomium globosum, an endophytic fungus in Ginkgo biloba, and their phytotoxic and cytotoxic Activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3734–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thohinung, S.; Kanokmedhakul, S.; Kanokmedhakul, K.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Tusskorn, O.; Soytong, K. Cytotoxic 10-(Indol-3-yl)-13 cytochalasans from the fungus Chaetomium elatum ChE01. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.C.; Kong, M.Z.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, G.D.; Tian, H.Y.; Li, X.X.; Guo, L.D.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Gao, H. Chaetoglobosin Y, a new cytochalasan from Chaetomium globosum. Fitoterapia 2014, 93, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, C.; Yamada, T.; Ito, Y.; Minoura, K.; Numata, A. Cytotoxic cytochalasans from a Penicillium species separated from a marine alga. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 2997–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Gong, J.J.; Liu, X.R.; Dai, C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, X.N.; Wang, J.P.; Luo, Z.W.; Zhou, Y.; Xue, Y.B.; et al. Cytochalasans produced by the coculture of Aspergillus flavipes and Chaetomium globosum. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Tong, Q.Y.; Zhu, H.C.; Tan, D.D.; Zhang, J.W.; Xue, Y.B.; Yao, G.M.; Luo, Z.W.; Wang, J.P.; Wang, Y.Y.; et al. Nine new cytochalasan alkaloids from Chaetomium globosum TW1-1 (Ascomycota, Sordariales). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hua, C.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Sun, L.; Dou, H.; Tan, R.X.; Hou, Y.Y. Chaetoglobosin F, a small molecule compound, possesses immunomodulatory properties on bone marrow-derived dendritic cells via TLR9 signaling pathway. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.W.; Zhou, X.F.; Lin, X.P.; Qin, X.C.; Zhang, T.Y.; Wang, J.F.; Tu, Z.C.; Yang, B.; Liao, S.R.; Tian, Y.Q.; et al. Antituberculosis compounds from a deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO Ind09F01. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 1958–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1−16 are available from the authors. |



| No. | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 173.6, C | ||
| 2-NH | 8.13, s | 1, 3, 4, 9 | |
| 3 | 54.2, CH | 3.44, m | 1, 4, 5, 9, 3′ |
| 4 | 40.5, CH | 2.91, dd (7.0, 2.1) | 1, 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11, 23 |
| 5 | 37.4, CH | 1.98, m | 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 11, 12 |
| 6 | 76.9, C | ||
| 7 | 71.9, CH | 3.24, d (4.9) | 6, 8, 9, 12, 13, |
| 8 | 47.6, CH | 2.27, t (10.5) | 1, 7, 9,13, 23 |
| 9 | 61.9, C | ||
| 10 | 31.0, CH2 | 2.61, dd (14.7, 6.3) 2.51, overlapped | 3, 4, 2′, 3′, 3a′ |
| 11 | 12.7, CH3 | 0.85, d (6.3) | 4, 5, 6 |
| 12 | 19.5, CH3 | 1.13, s | 5, 6, 7 |
| 13 | 129.5, CH | 6.02, dd (14.0, 10.5) | 8, 15 |
| 14 | 131.7, CH | 4.93, m | 8, 15, 16 |
| 15 | 41.8, CH2 | 2.24, m | 13, 16, 17, 24, |
| 16 | 31.6, CH | 2.53, overlapped | |
| 17 | 139.0, CH | 5.45, d (9.1) | 15, 16, 19, 24, 25 |
| 18 | 132.5, C | ||
| 19 | 81.8, CH | 4.95, d (4.9) | 17, 20, 21, 25 |
| 20 | 200.7, C | ||
| 21 | 132.5, CH | 6.42, d (16.8) | 19, 22, 23 |
| 22 | 136.0, CH | 7.70, d (16.8) | 20 |
| 23 | 199.3, C | ||
| 24 (16-Me) | 20.9, CH3 | 0.95, d (6.3) | 15, 16, 17 |
| 25 (18-Me) | 10.8, CH3 | 1.31, s | 17, 18, 19 |
| 26 (6-OMe) | 49.2, CH3 | 3.04, s | 6 |
| 1′-NH | 10.86, s | 2′, 3′, 1′a, 3′a | |
| 1′a | 136.1, C | ||
| 2′ | 123.4, CH | 7.08, d (2.1) | 3′, 1′a, 3′a |
| 3′ | 109.9, C | ||
| 3′a | 127.3, C | ||
| 4′ | 118.1, CH | 7.46, d (8.4) | 3′, 6′, 1′a |
| 5′ | 118.3, CH | 6.95, t (7.7) | 7′, 3′a |
| 6′ | 120.9, CH | 7.04, t (7.7) | 4′, 1′a |
| 7′ | 111.4, CH | 7.31, d (8.4) | 5′, 3′a |
| 7-OH | 4.13, d (8.4) | 6, 7, 8 | |
| 19-OH | 5.22, d (4.9) | 19, 18, 20 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.-W.; Gao, C.-H.; Lu, H.-M.; Wang, J.-M.; Su, Z.-Q.; Tao, H.-M.; Zhou, X.-F.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.-H. HPLC-DAD-Guided Isolation of Diversified Chaetoglobosins from the Coral-Associated Fungus Chaetomium globosum C2F17. Molecules 2020, 25, 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051237
Luo X-W, Gao C-H, Lu H-M, Wang J-M, Su Z-Q, Tao H-M, Zhou X-F, Yang B, Liu Y-H. HPLC-DAD-Guided Isolation of Diversified Chaetoglobosins from the Coral-Associated Fungus Chaetomium globosum C2F17. Molecules. 2020; 25(5):1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051237
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xiao-Wei, Cheng-Hai Gao, Hu-Mu Lu, Jia-Min Wang, Zi-Qi Su, Hua-Ming Tao, Xue-Feng Zhou, Bin Yang, and Yong-Hong Liu. 2020. "HPLC-DAD-Guided Isolation of Diversified Chaetoglobosins from the Coral-Associated Fungus Chaetomium globosum C2F17" Molecules 25, no. 5: 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051237
APA StyleLuo, X.-W., Gao, C.-H., Lu, H.-M., Wang, J.-M., Su, Z.-Q., Tao, H.-M., Zhou, X.-F., Yang, B., & Liu, Y.-H. (2020). HPLC-DAD-Guided Isolation of Diversified Chaetoglobosins from the Coral-Associated Fungus Chaetomium globosum C2F17. Molecules, 25(5), 1237. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051237