Removal of V(V) From Solution Using a Silica-Supported Primary Amine Resin: Batch Studies, Experimental Analysis, and Mathematical Modeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization
2.2. Batch Studies
2.2.1. Effect of Initial pH
2.2.2. Sorption Kinetics
2.2.3. Sorption Isotherm
2.2.4. Effect of Coexisting Ions
2.2.5. Sorption Thermodynamics
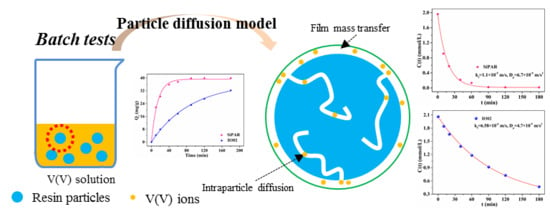
2.3. Mathematical Modeling
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of SiPAR
3.2.1. Preparation of Silica-Supported Polystyrene (SiPS)
3.2.2. Preparation of Silica-Supported Chloromethylated Polystyrene (SiPS-CH2Cl)
3.2.3. Preparation of Silica-Supported Primary Amine Resin (SiPAR)
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Batch Experiments
3.5. Mathematical Models
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, S.; Shen, C. Separation and recovery of vanadium from a sulfuric-acid leaching solution of stone coal by solvent extraction using trialkylamine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 164, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiviskä, T.; Khalid, M.K.; Sarpola, A.; Tanskanen, J. Removal of vanadium from industrial wastewater using iron sorbents in batch and continuous flow pilot systems. J. Environ. Manage. 2017, 190, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, B.; Ma, W. The influence of vanadate in calcined Mg/Al hydrotalcite synthesis on adsorption of vanadium (V) from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 181–182, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Zhang, X.; Dong, M.; Xue, X. A novel method to remove chromium, vanadium and ammonium from vanadium industrial wastewater using a byproduct of magnesium-based wet flue gas desulfurization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 336, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imtiaz, M.; Rizwan, M.S.; Xiong, S.; Li, H.; Ashraf, M.; Shahzad, S.M.; Shazad, M.; Rizwan, M.; Tu, S. Vanadium, recent advancements and research prospects: A review. Environ. Int. 2015, 80, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Hao, L.; Tian, C.; Yuan, S.; Feng, C.; Li, J.; Borthwick, A.G.L. Microbial reduction and precipitation of vanadium (V) in groundwater by immobilized mixed anaerobic culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mthombeni, N.H.; Mbakop, S.; Ochieng, A.; Onyango, M.S. Vanadium (V) adsorption isotherms and kinetics using polypyrrole coated magnetized natural zeolite. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 66, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, B.; Zheng, S.; Wang, S.; Du, H.; Dreisinger, D.B.; Zhang, Y. A cleaner vanadium extraction method featuring non-salt roasting and ammonium bicarbonate leaching. J. Cleaner Prod. 2017, 149, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostampour, L.; Taher, M.A. Determination of trace amounts of vanadium by UV–vis spectrophotometric after separation and preconcentration with modified natural clinoptilolite as a new sorbent. Talanta 2008, 75, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, A.; Shahwan, T.; Çağır, A.; Eroğlu, A.E. Synthesis of aminopropyl triethoxysilane-functionalized silica and its application in speciation studies of vanadium(IV) and vanadium(V). Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, T.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y. Comparison of ion exchange and solvent extraction in recovering vanadium from sulfuric acid leach solutions of stone coal. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 131–132, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, B.-Y.; Lee, C.-S.; Hwang, T.-S. A new hybrid ion exchanger: effect of system parameters on the adsorption of vanadium (V). J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, H.I.; Jones, A.; Rogerson, M.; Greenway, G.M.; Lisbona, D.F.; Burke, I.T.; Mayes, W.M. Removal and recovery of vanadium from alkaline steel slag leachates with anion exchange resins. J. Environ. Manage. 2016, 1–9. (In Press) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ning, P.; Lin, X.; Wang, X.; Cao, H. High-efficient extraction of vanadium and its application in the utilization of the chromium-bearing vanadium slag. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 301, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, H. Efficient separation of vanadium from chromium by a novel ionic liquid-based synergistic extraction strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.C.; Sarangi, K. Separation of vanadium using both hollow fiber membrane and solvent extraction technique–A comparative study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wei, W.; Xie, B. A novel anion exchange method based on in situ selectively reductive desorption of Cr(VI) for its separation from V(V): Toward the comprehensive use of hazardous wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Paudyal, H.; Zhao, J.; Huo, F.; Inoue, K.; Liu, H. Adsorptive recovery of vanadium(V) from chromium(VI)-containing effluent by Zr(IV)-loaded orange juice residue. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 248, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Fakhri, A.; Bharti, A.K.; Agarwal, S.; Naji, M. Optimization by response surface methodology for vanadium (V) removal from aqueous solutions using PdO-MWCNTs nanocomposites. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 234, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Xiao, L.; Song, S.; Zhang, B. Removal of vanadium from molybdate solution by ion exchange. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 95, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Westerhoff, P.; Mustafa, S. Vanadium removal by metal (hydr)oxide adsorbents. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, S.; Mandegarzad, S.; Anbia, M. Preparation and characterization of metal organic framework-derived nanoporous carbons for highly efficient removal of vanadium from aqueous solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 812, 152051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, M.V.; Dragan, E.S.; Trochimczuk, A.W. Sorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Zn(II) by iminodiacetate chelating resins in non-competitive and competitive conditions. Desalin 2009, 249, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, M. Separation and recovery of chromium and vanadium from vanadium-containing chromate solution by ion exchange. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 136, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Jalajamony, S.; Divya, L. Efficiency of Amine-Modified Poly(glycidyl methacrylate)-Grafted Cellulose in the Removal and Recovery of Vanadium(V) from Aqueous Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 2118–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Radhakrishnan, P.G. Adsorptive performance of an amine-functionalized poly(hydroxyethylmethacrylate)-grafted tamarind fruit shell for vanadium(V) removal from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Yin, X.; Chen, L.; He, X.; Lin, Z.; Liu, C.; Ning, S.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y. An integrated process for removal and recovery of Cr(VI) from electroplating wastewater by ion exchange and reduction–precipitation based on a silica-supported pyridine resin. J. Cleaner Prod. 2019, 236, 117631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ye, Z.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, C.; Ning, S.; Khayambashi, A.; Wei, Y. Microporous silica-supported cation exchanger with superior dimensional stability and outstanding exchange kinetics, and its application in element removal and enrichment. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 142, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yin, X.; Yu, Q.; Lu, S.; Meng, F.; Ning, S.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y. Rapid and selective capture of perrhenate anion from simulated groundwater by a mesoporous silica-supported anion exchanger. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 274, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Xia, W.; Zhang, W. Preparation and characterization of chitosan-zirconium(IV) composite for adsorption of vanadium(V). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013. (In Press) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Rodríguez, A.; Hernández-Viezcas, J.A.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; Perales-Pérez, O.; Román-Velázquez, F.R. Synthesis of protonated chitosan flakes for the removal of vanadium(III, IV and V) oxyanions from aqueous solutions. Microchem. J. 2015, 118, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Liu, C.; Fu, C.; Wu, P.; Liu, C.; Jiang, W. Selective separation of Cr(VI) and V(V) from solution by simple pH controlled two-step adsorption/desorption process with ZrO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Minocha, A.K.; Pudasainee, D.; Chungb, H.-K.; Kimb, S.-H.; Kimc, H.-S.; Leed, G.; Mine, B.; Jeon, B.-H. Vanadium removal from water by waste metal sludge and cement immobilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 144, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujeeb, V.M.A.; Alikutty, P.; Muraleedharan, K. Synthesis, characterization and vanadium (V) sorption studies on some chitosan derivatives. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 4, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Leiviskä, T. Surface modification of pine bark with quaternary ammonium groups and its use for vanadium removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Sun, H.; Lessl, J.; Wang, N. Removal of V (V) and Pb (II) by nanosized TiO2 and ZnO from aqueous solution. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2018, 164, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.-L.; Sun, S.-Y.; Song, X.; Li, P.; Yu, J.-G. Lithium ion recovery from brine using granulated polyacrylamide–MnO2 ion-sieve. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmatzadeh, A.A.; Karimi-Jashni, A.; Talebbeydokhti, N.; Kløve, B. Adsorption kinetics of nitrate ions on ion exchange resin. Desalin 2013, 326, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds SiPAR are available from the authors. |




| Sample | Surface Area (m2/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | Pore Volume (mL/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 80.4 | 50.3 | 1.02 |
| SiPAR | 68.31 | 41.22 | 0.60 |
| D302 | 30.36 | 33.43 | 0.25 |
| Resin | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe(mg/g) | k1(min−1) | R2 | Qe (mg/g) | k2(g/mg min) | R2 | |
| SiPAR | 39.26 | 0.0704 | 0.9926 | 40.25 | 0.02 | 0.9990 |
| D302 | 36.84 | 0.0112 | 0.9986 | 52.49 | 0.00017 | 0.9989 |
| Langmuir | Redlich–Peterson | Freundlich | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm | KL | R2 | KR | aR | n | R2 | KF | n | R2 |
| mg/g | L/mg | mg/g | Ln/mg(n−1) | ||||||
| 64.17 | 0.836 | 0.93 | 214.17 | 5.19 | 0.899 | 0.995 | 33.51 | 6.98 | 0.979 |
| Adsorbent | C0 (mg/L) | Adsorption Capacity | Equilibrium Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MZ-PPY | 25–250 | 65 mg/g | About 90 min a | [7] |
| Zr(IV)-SOW | - | 51.1 mg/g | 20 h | [18] |
| Cell-AE | 25–600 | 197.75 mg/g | 1 h | [25] |
| PGTFS–NH3+Cl− | 10–300 | 45.86 mg/g | 4 h | [26] |
| ZrO2 | - | 54.3 mg/g | 24 h | [32] |
| Waste metal sludge | 7.6–48.4 | 24.8 mg/g | 7 h | [33] |
| CCSB | 20–150 | 148.15 mg/g | 9 h | [34] |
| GTMAC | 10-591 | 34.3 mg/g | 24 h | [35] |
| TiO2 nanoparticles | 3-800 | 50 mg/g | 30 min | [36] |
| D302 | 700 | 4 mg/g | >3 h | This work |
| SiPAR | 50–400 | 70.57 mg/g | 90 min | This work |
| Resins | SiPAR | D302 |
|---|---|---|
| Matrix | St-DVB | St-DVB |
| Physical form | Spherical bead | Spherical bead |
| Average particle diameter | 100 µm | 590 µm |
| Functional groups | R–NH2 | R–NH2 |
| Resin particle porosity, εp | 72.7% | 8.6% |
| Resin particle apparent density, ρp | 1.6426 × 103 kg/m3 | 1.0421 × 103 kg/m3 |
| Total exchange capacity | 0.66 meq/g | 3 meq/g |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Ye, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y. Removal of V(V) From Solution Using a Silica-Supported Primary Amine Resin: Batch Studies, Experimental Analysis, and Mathematical Modeling. Molecules 2020, 25, 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061448
Huang X, Ye Z, Chen L, Chen X, Liu C, Yin Y, Wang X, Wei Y. Removal of V(V) From Solution Using a Silica-Supported Primary Amine Resin: Batch Studies, Experimental Analysis, and Mathematical Modeling. Molecules. 2020; 25(6):1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061448
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xi, Zhenxiong Ye, Lifeng Chen, Xujie Chen, Caocong Liu, Yuan Yin, Xinpeng Wang, and Yuezhou Wei. 2020. "Removal of V(V) From Solution Using a Silica-Supported Primary Amine Resin: Batch Studies, Experimental Analysis, and Mathematical Modeling" Molecules 25, no. 6: 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061448
APA StyleHuang, X., Ye, Z., Chen, L., Chen, X., Liu, C., Yin, Y., Wang, X., & Wei, Y. (2020). Removal of V(V) From Solution Using a Silica-Supported Primary Amine Resin: Batch Studies, Experimental Analysis, and Mathematical Modeling. Molecules, 25(6), 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061448