Evaluating the Removal of the Antibiotic Cephalexin from Aqueous Solutions Using an Adsorbent Obtained from Palm Oil Fiber
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. CPX Removal Performance of Each Adsorbent
2.2. Effect of pH on CPX Adsorption
2.3. Effect of Chemical Structure on CPX Adsorption
2.4. Effect of Adsorbent Dose
2.5. Adsorption Kinetics
2.6. Isotherm Studies
2.7. Thermodynamic Behavior
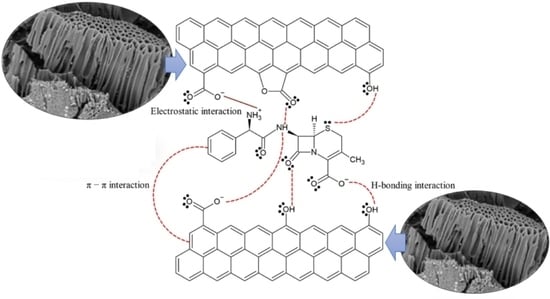
2.8. Adsorption Process
2.9. Effect of Complex Matrices on CFX Adsorption
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Biochar Preparation
3.3. Biochar Characterization
3.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Reza, R.A.; Ahmaruzzaman, M.; Sil, A.K.; Gupta, V.K. Comparative adsorption behavior of ibuprofen and clofibric acid onto microwave assisted activated bamboo waste. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 9331–9339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.S.; Liu, Q.; Shu, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.Z.; Kong, Q. Removal of cephalexin from effluent by activated carbon prepared from alligator weed: Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic analyses. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 104, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, A.J.; Murby, E.J.; Kolpin, D.W.; Costanzo, S.D. The occurrence of antibiotics in an urban watershed: From wastewater to drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2711–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, L.A.; Palma-Goyes, R.E.; Vazquez-Arenas, J.; Romero-Ibarra, I.; Ostos, C.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Efficient cephalexin degradation using active chlorine produced on ruthenium and iridium oxide anodes: Role of bath composition, analysis of degradation pathways and degradation extent. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.W.; Tan, X.F.; Liu, Y.G.; Tian, S.R.; Zeng, G.M.; Jiang, L.H.; Liu, S.B.; Li, J.; Liu, N.; Yin, Z.H. Comprehensive adsorption studies of doxycycline and ciprofloxacin antibiotics by biochars prepared at different temperatures. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mondal, S.; Patel, S. Naproxen Removal Capacity Enhancement by Transforming the Activated Carbon into a Blended Composite Material. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, G.; Abolghasemi, H.; Esmaieli, M.; Sadeghi Pouya, E. Aqueous phase adsorption of cephalexin by walnut shell-based activated carbon: A fixed-bed column study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 375, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundogdu, A.; Duran, C.; Senturk, H.B.; Soylak, M.; Ozdes, D.; Serencam, H.; Imamoglu, M. Adsorption of phenol from aqueous solution on a low-cost activated carbon produced from tea industry waste: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic study. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2012, 57, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.J.; Theydan, S.K. Adsorption of cephalexin onto activated carbons from Albizia lebbeck seed pods by microwave-induced KOH and K2CO3 activations. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211–212, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.A.; Kareem, S.L. Adsorption of tetracycline fom wastewater by using Pistachio shell coated with ZnO nanoparticles: Equilibrium, kinetic and isotherm studies. Alex. Eng. J. 2019, 58, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Kan, E. Engineered biochar from agricultural waste for removal of tetracycline in water. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 284, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes-Laverde, M.; Silva-Agredo, J.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Removal of norfloxacin in deionized, municipal water and urine using rice (Oryza sativa) and coffee (Coffea arabica) husk wastes as natural adsorbents. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-Laverde, M.; Salamanca, M.; Silva-Agredo, J.; Manrique-Losada, L.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Selective removal of acetaminophen in urine with activated carbons from rice (Oryza sativa) and coffee (Coffea arabica) husk: Effect of activating agent, activation temperature and analysis of physical-chemical interactions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Nunez, J.A.; Ramirez-Contreras, N.E.; Rodriguez, D.T.; Silva-Lora, E.; Frear, C.S.; Stockle, C.; Garcia-Perez, M. Evolution of palm oil mills into bio-refineries: Literature review on current and potential uses of residual biomass and effluents. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 110, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, S.; Robles, I.; Ramirez, A.; Flórez, E.; Acelas, N. Mercury removal from wastewater using agroindustrial waste adsorbents. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guechi, E.K.; Hamdaoui, O. Evaluation of potato peel as a novel adsorbent for the removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 10677–10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoriyekomwan, J.E.; Tahmasebi, A.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J. Formation of hollow carbon nanofibers on bio-char during microwave pyrolysis of palm kernel shell. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 148, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Microwave assisted preparation of activated carbon from pomelo skin for the removal of anionic and cationic dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, S.; Ramirez, A.P.; Flórez, E.; Acelas, N.Y. Adsorbent materials obtained from palm waste and its potential use for contaminants removal from aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Moreno, L.; Bazhari, S.; Gasco, G.; Méndez, A.; El Azzouzi, M.; Romero, E. New insights into the efficient removal of emerging contaminants by biochars and hydrochars derived from olive oil wastes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.A.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Kareem, S.L.; Zarrabi, M.; Al-Ma’abreh, A.M. Simultaneous adsorption of tetracycline, amoxicillin, and ciprofloxacin by pistachio shell powder coated with zinc oxide nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 13, 4629–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasucka, P.; Pan, B.; Sik Ok, Y.; Mohan, D.; Sarkar, B.; Oleszczuk, P. Engineered biochar—A sustainable solution for the removal of antibiotics from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisales-Cifuentes, C.M.; Serna Galvis, E.A.; Porras, J.; Flórez, E.; Torres-Palma, R.A.; Acelas, N. Kinetics, isotherms, effect of structure, and computational analysis during the removal of three representative pharmaceuticals from water by adsorption using a biochar obtained from oil palm fiber. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 326, 124753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, C.H.; Cheah, W.K.; Sim, Y.L.; Pung, S.Y.; Yeoh, F.Y. Conversion and characterization of activated carbon fiber derived from palm empty fruit bunch waste and its kinetic study on urea adsorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanday, W.A.; Ahmed, M.J.; Okoye, P.U.; Hummadi, E.H.; Hameed, B.H. Single-step pyrolysis of phosphoric acid-activated chitin for efficient adsorption of cephalexin antibiotic. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 280, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari, G.; Abolghasemi, H.; Esmaieli, M. Batch adsorption of cephalexin antibiotic from aqueous solution by walnut shell-based activated carbon. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 58, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Han, L. Characteristics of tetracycline adsorption by cow manure biochar prepared at different pyrolysis temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 285, 121348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, J.; Shafique, U.; Salman, M.; Dar, A.; Anwar, S. Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from water by adsorption on peels of banana. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1752–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghipour, D.; Amouei, A.; Estaji, M.; Taghavi, K.; Allahabadi, A. Cephalexin adsorption from aqueous solutions by biochar prepared from plantain wood: Equilibrium and kinetics studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 143, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster Stoffe. Stockholm Kongl. svenska vetenskaps-akad. Handlinger 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by wood. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 1998, 76, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of Adsorption on Carbon from Solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshin, S.; Rashtbari, Y.; Ramavandi, B.; Fazlzadeh, M.; Vosoughi, M.; Mokhtari, S.A.; Shirmardi, M.; Rehman, R. Magnetic nanocomposite of filamentous algae activated carbon for efficient elimination of cephalexin from aqueous media. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarghandi, M.R.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Mohseni-Bandpi, A.; Zarrabi, M. Adsorption of cephalexin from aqueous solution using natural zeolite and zeolite coated with manganese oxide nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 211, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, M.H.; Austin, J.B. The Adsorption of Gases on Plane Surfaces of Mica. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–471. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez, A.; Ocampo, R.; Giraldo, S.; Padilla, E.; Flórez, E.; Acelas, N. Removal of Cr (VI) from an aqueous solution using an activated carbon obtained from teakwood sawdust: Kinetics, equilibrium, and density functional theory calculations. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashtbari, Y.; Hazrati, S.; Azari, A.; Afshin, S.; Fazlzadeh, M.; Vosoughi, M. A novel, eco-friendly and green synthesis of PPAC-ZnO and PPAC-nZVI nanocomposite using pomegranate peel: Cephalexin adsorption experiments, mechanisms, isotherms and kinetics. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Adhikari, B.; Majumder, S.B. Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies of azo dye adsorption from aqueous solution by chemically modified lignocellulosic jute fiber. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 6502–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajab, M.S.; Chia, C.H.; Zakaria, S.; Jani, S.M.; Ayob, M.K.; Chee, K.L.; Khiew, P.S.; Chiu, W.S. Citric acid modified kenaf core fibres for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7237–7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentouami, A.; Ouali, M.S. Cadmium removal from aqueous solutions by hydroxy-8 quinoleine intercalated bentonite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 293, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, C.H.; Duong, T.D.; Nguyen, K.L.; Zakaria, S. Thermodynamic aspects of sorption of Fe2+ onto unbleached kraft fibres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 307, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Qian, F.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. Preparation of magnetic porous carbon from waste hydrochar by simultaneous activation and magnetization for tetracycline removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 154, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, A.P.; Giraldo, S.; Flórez, E.; Acelas, N. Preparación de carbón activado a partir de residuos de palma de aceite y su aplicación para la remoción de colorantes Preparation of activated carbon from palm oil wastes and their application for methylene blue removal Abstract Preparação de carvão ativa. Afinidad 2012, 559, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Adsorbent Material | Surface Area (m2/g) | pHPZC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| F_Zn | 835.3 | 4.0 | |
| S_Zn | 575.1 | 2.3 | |
| F_HA | 14.8 | 4.8 | |
| Acid groups F_Zn | Carboxylic | Phenolic | Lactones |
| Value (mmol g−1) | 1.65 | 0.20 | 0.15 |
| Initial Concentration | |||||||
| 10 mg L−1 | 15 mg L−1 | 20 mg L−1 | 25 mg L−1 | 35 mg L−1 | 50 mg L−1 | 70 mg L−1 | |
| Experimental qe (mg g−1) | 5.64 | 8.51 | 11.86 | 14.76 | 18.36 | 26.50 | 37.68 |
| Pseudo-First Order | |||||||
| qe (mg g−1) | ------ | 0.59 | 1.12 | 1.68 | 4.68 | 6.18 | 3.39 |
| k1 (min−1) | ------ | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.04 |
| Δqe (%) | ------ | 93 | 91 | 89 | 74 | 77 | 91 |
| R2 | ------ | 0.969 | 0.999 | 0.990 | 0.989 | 0.928 | 0.889 |
| Pseudo-Second Order | |||||||
| qe (mg g−1) | 5.68 | 8.56 | 12.0 | 14.8 | 18.9 | 27.3 | 38.17 |
| k2 (min−1) | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.28 |
| Δqe (%) | 0.59 | 0.54 | 1.56 | 0.24 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 1.28 |
| R2 | 0.999 | 1 | 1 | 0.999 | 1 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| Intraparticle Diffusion Model | |||||||
| kd1 | 0.146 | 0.146 | 0.164 | 0.224 | 1.073 | 1.351 | 0.7947 |
| C1 | 4.756 | 7.537 | 10.68 | 12.94 | 12.56 | 18.52 | 32.45 |
| R2 | 0.981 | 0.979 | 0.999 | 0.942 | 0.988 | 0.931 | 0.9751 |
| kd2 | 0.022 | 0.033 | −0.008 | 0.055 | 0.297 | 0.428 | 0.455 |
| C2 | 5.39 | 8.160 | 11.945 | 14.163 | 16.077 | 23.234 | 34.18 |
| R2 | 0.831 | 0.980 | 0.7913 | 0.999 | 0.9812 | 0.9583 | 0.993 |
| Biochar | Qm (mg g−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Palm | 57.47 | This study |
| Alligator weed | 45.00 | [2] |
| pomegranate peel | 87.18 | [38] |
| Albizia lebbeck seed pods | 118.08 | [9] |
| Temperature (°C) | Activation Energy, Ea (kJ/mol) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (J/mol) | ΔG° (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 91.6 | 62.2 | 228.5 | −3.65 |
| 25 | −5.93 | |||
| 30 | −7.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acelas, N.; Lopera, S.M.; Porras, J.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Evaluating the Removal of the Antibiotic Cephalexin from Aqueous Solutions Using an Adsorbent Obtained from Palm Oil Fiber. Molecules 2021, 26, 3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113340
Acelas N, Lopera SM, Porras J, Torres-Palma RA. Evaluating the Removal of the Antibiotic Cephalexin from Aqueous Solutions Using an Adsorbent Obtained from Palm Oil Fiber. Molecules. 2021; 26(11):3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113340
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcelas, Nancy, Sandra M. Lopera, Jazmín Porras, and Ricardo A. Torres-Palma. 2021. "Evaluating the Removal of the Antibiotic Cephalexin from Aqueous Solutions Using an Adsorbent Obtained from Palm Oil Fiber" Molecules 26, no. 11: 3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113340
APA StyleAcelas, N., Lopera, S. M., Porras, J., & Torres-Palma, R. A. (2021). Evaluating the Removal of the Antibiotic Cephalexin from Aqueous Solutions Using an Adsorbent Obtained from Palm Oil Fiber. Molecules, 26(11), 3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113340