Innovation in a Continuous System of Distillation by Steam to Obtain Essential Oil from Persian Lime Juice (Citrus latifolia Tanaka)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Industrial Use of Lemons
1.2. Production of Essential Oils
1.3. Types of Essential Oils
1.4. Innovative Technologies
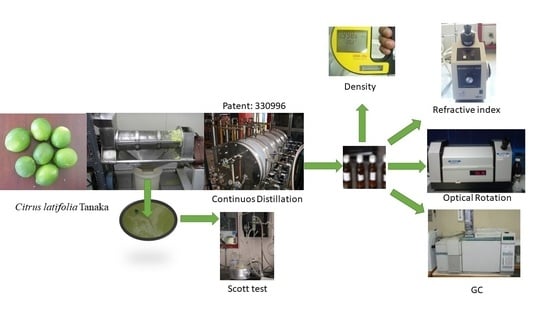
1.5. Continuous Distillation by Steam
1.6. Continuous Distillation Process of Essential Oils
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Content of Essential Oil in Citrus Juice
2.2. Efficiency of the Process and Steam Consumption in Continuous Distillation
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis
2.3.1. Effect of the Fraction Number on the Density and Refractive Index of Essential Oil
2.3.2. Effect of D/F on Density, Optical Rotation, and Density
2.4. Gas Chromatography for Key Compounds
2.4.1. Effect of the Fraction Number on Relative Abundance
2.4.2. Effect of D/F on the Relative Abundance of Compounds
3. Methodology
3.1. Process
3.1.1. Raw Material
3.1.2. Batch Distillation by Steam
3.1.3. Continuous Distillation by Steam
3.1.4. Experimental Design for Continuous Distillation
- The oil recovery efficiency (%);
- The percentage of steam consumption compared to the traditional process (%).
3.2. Physical-Chemical Analysis of the Distilled Essential Oil
3.2.1. Determination of Relative Density
3.2.2. Determination of the Refractive Index
3.2.3. Determination of the Rotatory Power
3.2.4. Determination of the Content of Essential Oil in Lime Juice
3.2.5. Determination of the Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zema, D.A.; Calabrò, P.S.; Folino, A.; Tamburino, V.; Zappia, G.; Zimbone, S.M. Valorisation of citrus processing waste: A review. Waste Manag. 2018, 80, 252–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raddatz-Mota, D.; Franco-Mora, O.; Mendoza-Espinoza, J.A.; Rodríguez-Verástegui, L.L.; Díaz de León-Sánchez, F.; Rivera-Cabrera, F. Effect of different rootstocks on Persian lime (Citrus latifolia T.) postharvest quality. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 257, 108716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma-Escobar, C.A.; Luque de Castro, M.D. Towards a comprehensive exploitation of citrus. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 39, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamma, D.; Christakopoulos, P. Biotransformation of Citrus By-Products into Value Added Products. Waste Biomass Valorization 2014, 5, 529–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, F.R.; Soler-Rivas, C.; Benavente-García, O.; Castillo, J.; Pérez-Alvarez, J.A. By-products from different citrus processes as a source of customized functional fibres. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, J.; van Stempvoort, S.; García-Gallarreta, M.; Houghton, J.A.; Briers, H.K.; Budarin, V.L.; Matharu, A.S.; Clark, J.H. Microwave assisted hydro-distillation of essential oils from wet citrus peel waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.; Costa, P.; Rodrigues, C.E.C.; Rodrigues, A.E. Effect of Citrus sinensis essential oil deterpenation on the aroma profile of the phases obtained by solvent extraction. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2018, 116, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lota, M.-L.; de Rocca Serra, D.; Tomi, F.; Jacquemond, C.; Casanova, J. Volatile Components of Peel and Leaf Oils of Lemon and Lime Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakab, E.; Blazsó, M.; Barta-Rajnai, E.; Babinszki, B.; Sebestyén, Z.; Czégény, Z.; Nicol, J.; Clayton, P.; McAdam, K.; Liu, C. Thermo-oxidative decomposition of lime, bergamot and cardamom essential oils. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 134, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, M.; Goto, M.; Kodama, A.; Hirose, T. Fractional Extraction by Supercritical Carbon Dioxide for the Deterpenation of Bergamot Oil. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 4745–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugo, P.; Mondello, L.; Lamonica, G.; Dugo, G. Characterization of Cold-Pressed Key and Persian Lime Oils by Gas Chromatography, Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectroscopy, High-Performance Liquid Chromatography, and Physicochemical Indices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3608–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzolo, E.; Laudicina, V.A.; Germanà, M.A. Current and potential use of citrus essential oils. Curr. Org. Chem. 2013, 17, 3042–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousbia, N.; Vian, M.A.; Ferhat, M.A.; Meklati, B.Y.; Chemat, F. A new process for extraction of essential oil from Citrus peels: Microwave hydrodiffusion and gravity. J. Food Eng. 2009, 90, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, E. The Essential Oils: Individual Essential Oils of the Plant Families Rutaceae and Labiatae; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Negro, V.; Mancini, G.; Ruggeri, B.; Fino, D. Citrus waste as feedstock for bio-based products recovery: Review on limonene case study and energy valorization. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla, J.D.; Rodríguez, E.; Alba, A.; Vega, H. Sistema multifuncional de destilación, evaporación y extracción de moléculas orgánicas derivadas de productos naturales. Patent 330996. México 2015. Available online: https://siga.impi.gob.mx/newSIGA/content/common/principal.jsf (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Padilla, F.J.; González, O.; Prado, R.; Gutiérrez, H.; Estarrón, M.; Vega, H.A. Nuevo equipo de proceso de destilación fraccionada en continuo por arrastre con vapor de aceites esenciales del jugo de limón mexicano. e-Gnosis 2007, 1. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=73000506 (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Mirna, E.-E.; Mariela, R.-P.; Daniel, P.-d.l.R.J.; Rogelio, P.-R. Innovation in Continuous Rectification for Tequila Production. Processes 2019, 7, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maarse, H. Volatile Compounds in Foods and Beverages; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Simas, D.L.R.; de Amorim, S.H.B.M.; Goulart, F.R.V.; Alviano, C.S.; Alviano, D.S.; da Silva, A.J.R. Citrus species essential oils and their components can inhibit or stimulate fungal growth in fruit. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 98, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AFNOR. Recueil de normes: Les huiles essentielles. In Monographies Relatives aux Huiles Essentielles; AFNOR, Ed.; Paris La Défense: Paris, France, 2000; pp. 661–663. [Google Scholar]
- ISO279:1998. Essential Oils—Determination of Relative Density at 20 Degrees C—Reference Method; ISO, Ed.; Multiple Distributed through American National Standards Institute (ANSI): Gèneve, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]














| Main Effects | Refractive Index | Density (g/mL) | Optical Rotation (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | |
| D/F | 0.0003 | 0.4452 | 0.1354 |
| Fraction number | 0.0000 | 0.0004 | 0.0185 |
| Physicochemical Analysis | Continuous Process Fraction 3, D/F = 0.2 | Batch Process |
|---|---|---|
| Refractive index at 20 °C | 1.469 ± 0.0001 | 1.469 ± 0.00056 |
| Optical rotation (°) | 48.875 ± 6.0 | 45.65 ± 1.6263 |
| Density (g/mL) | 0.857 ± 0.0021 | 0.860 ± 0.00777 |
| Main Effects | d-Limonene | γ-Terpinene | p-Cymene | α-Terpineol | β-Pinene | Neral | Geranial |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | |
| D/F | 0.0000 | 0.7087 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Fraction number | 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 0.0027 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Compound | This Study’s Continuous Processes (% Area) | This Study’s Batch Process (% Area) | Batch Process [8] (% Area) | Microwave-Assisted Hydrodistillation [6] (% Area) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neral | 0.3 | 0.554 ± 0.240 | Neral+ geranial: 0.5 to 2.2 | 0.29 |
| Geranial | 0.6 | 0.438 ± 0.611 | 0.38 |
| Compound | This Study’s Continuous Processes Fraction 1 D/F = 0.4 (% Area) | This Study’s Batch Process (% Area) | Batch Process [8] (% Area) | Microwave-Assisted Hydrodistillation [6] (% Area) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| d-limonene | 60.09 ± 1.21 | 55.26 ± 1.75 | 59.016 | 61.93 |
| γ-terpinene | 14.87 ± 0.58 | 15.14 ± 0.38 | 16.089 | 16.93 |
| α-terpineol | 2.76 ± 0.60 | 2.78 ± 034 | 2.145 | 0.39 |
| β-pinene | 6.57 ± 0.55 | 8.17 ± 0.58 | 6.035 | 11.35 |
| p-cymene | 0.64 ± 0.26 | 0.64 ± 0.07 | 1.507 | 0.21 |
| neral | 0.34 ± 0.007 | 0.55 ± 0.24 | 0.091 | 0.29 |
| geranial | 0.68 ± 0.17 | 0.44 ± 0.61 | 0.121 | 0.38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Padilla-de la Rosa, J.D.; Manzano-Alfaro, M.D.; Gómez-Huerta, J.R.; Arriola-Guevara, E.; Guatemala-Morales, G.; Cardador-Martínez, A.; Estarrón-Espinosa, M. Innovation in a Continuous System of Distillation by Steam to Obtain Essential Oil from Persian Lime Juice (Citrus latifolia Tanaka). Molecules 2021, 26, 4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144172
Padilla-de la Rosa JD, Manzano-Alfaro MD, Gómez-Huerta JR, Arriola-Guevara E, Guatemala-Morales G, Cardador-Martínez A, Estarrón-Espinosa M. Innovation in a Continuous System of Distillation by Steam to Obtain Essential Oil from Persian Lime Juice (Citrus latifolia Tanaka). Molecules. 2021; 26(14):4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144172
Chicago/Turabian StylePadilla-de la Rosa, José Daniel, Magaly Dyanira Manzano-Alfaro, Jaime Rosalío Gómez-Huerta, Enrique Arriola-Guevara, Guadalupe Guatemala-Morales, Anaberta Cardador-Martínez, and Mirna Estarrón-Espinosa. 2021. "Innovation in a Continuous System of Distillation by Steam to Obtain Essential Oil from Persian Lime Juice (Citrus latifolia Tanaka)" Molecules 26, no. 14: 4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144172
APA StylePadilla-de la Rosa, J. D., Manzano-Alfaro, M. D., Gómez-Huerta, J. R., Arriola-Guevara, E., Guatemala-Morales, G., Cardador-Martínez, A., & Estarrón-Espinosa, M. (2021). Innovation in a Continuous System of Distillation by Steam to Obtain Essential Oil from Persian Lime Juice (Citrus latifolia Tanaka). Molecules, 26(14), 4172. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144172