Protective Effects of Sal B on Oxidative Stress-Induced Aging by Regulating the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Zebrafish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
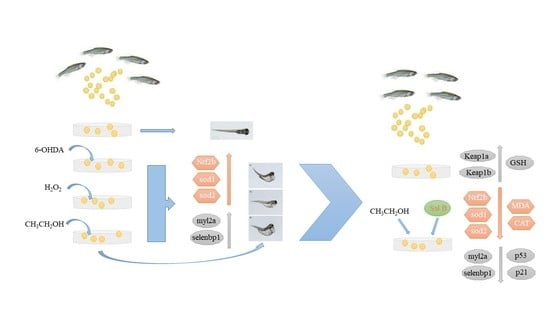
2. Results
2.1. Ethanol Aging Model Establishment
2.2. H2O2 Aging Model Establishment
2.3. 6-OHDA Aging Model Establishment
2.4. Expression of Aging-Related Genes Up-Regulated after Aging Induction
2.5. Expression of Nrf2 and Sod Genes Were Also Up-Regulated after Aging Induction
2.6. Ethanol-Induced Damage and Aging Recovered after Salvanic Acid B Treatment
2.6.1. Embryo Mortality Reduced after Sal B Treatment
2.6.2. Oxidative Stress Decreased after Sal B Treatment
2.6.3. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity Changed after Sal B Treatment
2.6.4. Antioxidant-Related Gene Expression Changed after Sal B Treatment
2.6.5. Aging-Related Genes myl2a, selenbp1, p53 and p21 Expression Decreased after Salvanic Acid B Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Zebrafish Culture
4.2. Establishment of Aging Models
4.3. Morphological Observation
4.4. Significant Concentration of Aging Agent Treatment
4.5. Sal-B Treatment
4.6. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity Detection
4.7. Total RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
4.8. Data Analysis
4.9. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.10. Ethics Statements
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Li, S.M.; Lu, S.M.; Kang, F.; An, L.G.; Zhang, H.F. Research progress and application of aging animal model. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2011, 31, 3869–3872. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.Q. Neuroprotective Effects and its Mechanism of Phenylethanoid Glycosides via Nrf2-ARE Signaling Pathway. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kuilman, T.; Michaloglou, C.; Mooi, W.J.; Peeper, D.S. The essence of senescenc. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2463–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, S.B.; Tucci, V.; Uchiyama, J.; Fabian, N.J.; Lin, M.C.; Bayliss, P.E.; Neuberg, D.S.; Zhdanova, I.V.; Kishi, S. Differential effects of genotoxic stress on both concurrent body growth and gradual senescence in the adult zebrafish. Aging Cell 2007, 6, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, S.J.; Bayliss, P.E.; Uchiyama, J.Z.; Koshimizu, E.; Qi, J.; Nanjappa, P.; Imamura, S.; Islam, A.; Neuberg, D.; Amsterdam, A.; et al. The identification of zebrafish mutants showing alterations in senescence-associated biomarkers. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, E.T.; Murtha, J.M. The use of mature zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a model for human aging and disease. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. C 2004, 138, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, M.J.H.; Zerulla, T.C.; Tierney, K.B. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a model for the study of aging and exercise: Physical ability and trainability decrease with age. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 50, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J. The Role of STAT3 in the Aging of Neurons Induced by 27-Hydroxycholesterol and the Neurobehavioral Injury of Zebrafish. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.S.; Yang, Q.Y.; Wang, D.J.; Li, H.Y. Indentification and expression of carbonic anhydrase 2, myosin regulatory light chain 2 and selenium-binding protein 1 in zebrafish Danio rerio: Implication for age-related biomarkers. Gene Expr. Patterns 2018, 29, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, C.Y.; Kim, K.; Choi, J.Y.; Bahn, Y.J.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, C.; Kwon, K.S. Quantitative proteome analysis of age-related changes in mouse gastrocnemius muscle using mTRAQ. Proteomics 2014, 14, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueugneau, M.; Coudy-Gandilhon, C.; Gourbeyre, O.; Chambon, C.; Combaret, L.; Polge, C.; Taillandier, D.; Attaix, D.; Friguet, B.; Maier, A.B.; et al. Proteomics of muscle chronological ageing in post-menopausal women. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Georgalis, T.; Perry, S.F.; Gilmour, K.M. The role of branchial carbonic anhydrase in acid-base regulation in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Exp. Biol 2006, 209, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kida, E.; Palminiello, S.; Golabek, A.A.; Walu, M.; Wierzba-Bobrowicz, T.; Rabe, A.; Albertini, G.; Wisniewski, K.E. Carbonic anhydrase II in the developing and adult human brain. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 65, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sender, S.; Böttcher, K.; Cetin, Y.; Gros, G. Carbonic anhydrase in the gills of seawater- and freshwater-acclimated flounders Platichthys flesus: Purification, characterization, and immunohistochemical localization. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1999, 47, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, K.A.; McElhinny, A.S.; Beckerle, M.C.; Gregorio, C.C. Striated muscle cytoarchitecture: An intricate web of form and function. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 18, 637–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gannon, J.; Staunton, L.; O’connell, K.; Doran, P.; Ohlendieck, K. Phosphoproteomic analysis of aged skeletal muscle. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 22, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lowey, S.; Waller, G.S.; Trybus, K.M. Skeletal muscle myosin light chains are essential for physiological speeds of shortening. Nature 1993, 365, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porat, A.; Sagiv, Y.; Elazar, Z. A 56-kDa selenium-binding protein participates in intra-Golgi protein transport. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 14457–14465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeong, J.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Sytkowski, A.J. Human selenium binding protein-1 (hSP56) interacts with VDU1 in a selenium-dependent manner. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 379, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Fang, W.F.; Huang, Y.; Hu, F.; Ying, Q.; Yang, W.C.; Xiong, B. Reduction of selenium-binding protein 1 sensitizes cancer cells to selenite via elevating extracellular glutathione: A novel mechanism of cancer-specific cytotoxicity of selenite. Free Radic. Bio. Med. 2015, 79, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Liu, Y. Progress in Hallmarkers and Cellular Models of Senescence. Life Sci. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.L.; Gong, Y.Z. Research Advances on the Relationship between Cell Senescence and Oxidative Stress. p16, p53/p21. Med. Recapitul. 2011, 17, 682–685. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.Z.; Zhu, H.G. Establishment of aging animal model induced by D-galactose and its detection method. J. Fudan Univ. 2007, 4, 617–619. [Google Scholar]
- Marazita, M.C.; Dugour, A.; Ramella, M.D.M.; Figueroa, J.M.; Suburo, A.M. Oxidative stress-induced premature senescence dysregulates VEGF and CFH expression in retinal pigment epithelial cells: Implications for Age-related Macular Degeneration. Redox Biol. 2016, 7, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, X.X.; Hong, B.Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.K.; Chen, W.D.; Yu, N.J.; Peng, D.Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.Y. Review of chemical composition, pharmacological effects and clinical applications of Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma and predictive analysis of its Q-markers. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2021, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liu, W.; Mu, Y.P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.N.; Zhao, C.Q.; Chen, J.M.; Liu, P. Pharmacological Effects of Salvianolic Acid B Against Oxidative Damage. Front. Pharmacol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Guo, X.W.; Zheng, H.Z.; Li, D.P.; Jia, G.B.; Wang, J. Current progress of research on pharmacologic actions of salvianolic acid B. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2012, 18, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.B.; Li, Y.; Xue, L.M.; Richele, P.S.; Gao, S.H.; Niu, J.Z.; Qin, L.P.; Zhang, D.W.; Dieter, B. Salvia miltiorrhiza: An ancient Chinese herbal medicine as a source for anti-osteoporotic drugs. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1401–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Ma, R.F.; Yu, N.; Liu, H.X.; Zhu, R.Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, S.J.; Gao, Y.S.; Ge, D.Y.; Niu, J.Z.; et al. Salvianolic acid B prevents mandibular osteoporosis through anti-oxidation in high fat diet exposed mice. Chin. J. Osteoporos. 2017, 23, 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Diao, Y.; Kuang, W.; Li, Q.; Tian, Y.; Gao, J.; Dai, L.F.; Cao, L.L.; Wang, W.B.; Wei, L.J. Salvianolic Acid B Alleviate the Osteoblast Activity Decreasing under Simulated Microgravity by Keap1/Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 46, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.T.; Liu, A.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Guan, D.H.; Chen, T.X. Salvianolic acid B (Sal B) alleviates the decreased activity induced by prednisolone acetate on osteoblasts by up-regulate bone formation and differentiation genes. Food Funct. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, I.S.; Hsieh, C.C.; Chiu, J.H.; Shiao, M.S.; Lui, W.Y.; Wu, C.W. Salvianolic acid B enhances in vitro angiogenesis and improves skin flap survival in Sprague-Dawley rats. J. Surg. Res. 2003, 115, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.W.; Wang, Y.F.; Yu, H.Q.; Li, W.; Wu, J.F.; Cai, C.F.; He, Y.Z. Salvianolic acid B inhibits ototoxic drug–induced ototoxicity by suppression of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 6883–6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.H.P.; Ting, A.C.; Leow, B.G.; Najimudin, N.; Watanabe, N.; Azzam, G. Alleviatory effects of Danshen, Salvianolic acid A and Salvianolic acid B on PC12 neuronal cells and Drosophila melanogaster model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, J.S. Zebrafish make a big splash. Cell 1996, 87, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Streisinger, G.; Walker, C.; Dower, N.; Knauber, D.; Singer, F. Production of clones of homozygous diploid zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio). Nature 1981, 291, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, S.; Uchiyama, J.; Baughman, A.M.; Goto, T.; Lin, M.C.; Tsai, S.B. The zebrafish as a vertebrate model of functional aging and very gradual senescence. Exp. Gerontol. 2003, 38, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, P.H.; Xu, B.L.; Huang, L.F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Tian, X.Y.; et al. Salvianolic Acid B Prevents Bone Loss in Prednisone-Treated Rats through Stimulation of Osteogenesis and Bone Marrow Angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Akinyi, M.; Li, Y.; Duan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, G. Danshensu protects isolated heart against ischemia reperfusion injury through activation of Akt/ERK1/2/Nrf2 signaling. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 14793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.L., Jr.; Tchekalarova, J.D.; Atanasova, M.; da Conceição Machado, K.; de Sousa Rios, M.A.; Găman, A.M.; Yele, S.; Shill, M.C.; Khan, I.N.; Islam, M.A.; et al. Anticonvulsant effect of anacardic acid in murine models: Putative role of GABAergic and antioxidant mechanisms. Anticonvulsant effect of anacardic acid in murine models: Putative role of GABAergic and antioxidant mechanisms. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Gene Name | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| Elfa | F: 5’-GGCCCCTGCCAATGTA-3’ R: 5’-GGGCTTGCCAGGGAC-3’ |
| Nrf2a | F: 5’-GAGCGGGAGAAATCACACAGAATG-3’ R: 5’-CAGGAGCTGCATGCACTCATCG-3’ |
| Nrf2b | F: 5’-GCCACGTTATGCTGGGTTTC-3’ R: 5’-CTGCGGACAACGATAGCAGA-3’ |
| sod1 | F: 5’-CTAGCCCGCTGACATTACATC-3’ R: 5’-TTGCCCACATAGAAATGCAC-3’ |
| sod2 | F: 5’-CGCATGTTCCCAGACATCTA-3’ R: 5’-GAGCGGAAGATTGAGGATTG-3’ |
| myl2a | F: 5’-AAAAGGCCGTCCATCCCATT-3’ R: 5’-TTTTTAGGAGCCATGCCGGA-3’ |
| ca2 | F: 5’-CAGACGACAAGGGCTCCGAAC-3’ R: 5’-AAAACCCCAACCACAGCAAGA-3’ |
| selenbp1 | F: 5’-CGAGGTGGTAATCGACATTTG-3’ R: 5’-AATAACGCGGCGAAGAAGATG-3’ |
| keap1a | F: 5’-GTGTGGAGTGCTACTGTCCC-3’ R: 5’-TCCTCCTCTGGCAGGATACC--3’ |
| keap1b | F: 5’-ATCGAGGGGATACACCCCAA-3’ R: 5’-AGCTGCTCCACCAGGAAATC-3’ |
| p21 | F: 5’-CACGCCCACAGCACACCATATC-3’ R: 5’-CGGTCATCTTTCCCTTGCCCTTC-3’ |
| p53 | F: 5’-GATGTGGTGCCTGCCTCAGATG-3’ R: 5’-GAGTCGCTTCTTCCTTCGTCCTTC-3’ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, E.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, L.; Wei, L. Protective Effects of Sal B on Oxidative Stress-Induced Aging by Regulating the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Zebrafish. Molecules 2021, 26, 5239. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175239
Li E, Wang Y, Li Q, Li L, Wei L. Protective Effects of Sal B on Oxidative Stress-Induced Aging by Regulating the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Zebrafish. Molecules. 2021; 26(17):5239. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175239
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Erzhuo, Yunhao Wang, Qiao Li, Li Li, and Lijun Wei. 2021. "Protective Effects of Sal B on Oxidative Stress-Induced Aging by Regulating the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Zebrafish" Molecules 26, no. 17: 5239. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175239
APA StyleLi, E., Wang, Y., Li, Q., Li, L., & Wei, L. (2021). Protective Effects of Sal B on Oxidative Stress-Induced Aging by Regulating the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Zebrafish. Molecules, 26(17), 5239. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175239