Chemo-Preventive Action of Resveratrol: Suppression of p53—A Molecular Targeting Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. How Resveratrol Regulated Cell Signaling Pathways in Cancer
4. Resveratrol and p53 Suppression
5. Resveratrol and Its Bioavailability
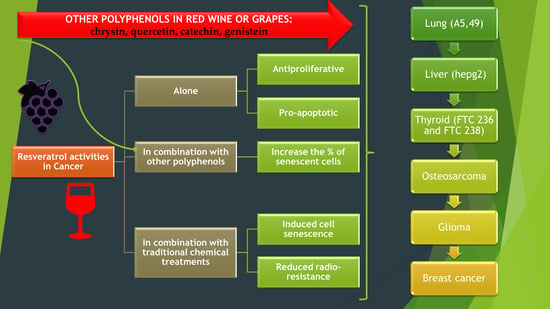
6. Combined Synergistic Effects of Polyphenol Management
7. Resveratrol Clinical Trials and Therapeutic Potential
7.1. Clinical Trial 1
7.2. Clinical Trial 2
7.3. Clinical Trial 3
7.4. Clinical Trial 4
7.5. Clinical Trial 5
7.6. Clinical Trial 6
7.7. Clinical Trial 7
7.8. Clinical Trial 8
7.9. Clinical Trial 9
8. Adverse Effects
9. Recommendations, Challenges, Future Perspectives, and Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, M.O.; Kavan, P.; Miller, W.; Panasci, L.; Assouline, S.; Johnson, N.; Cohen, V.; Patenaude, F.; Pollak, M.; Jagoe, R.T. Systemic cancer therapy: Achievements and challenges that lie ahead. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- West, D.W.; Slattery, M.L.; Robison, L.M.; Schuman, K.L.; Ford, M.H.; Mahoney, A.W.; Lyon, J.L.; Sorensen, A.W. Dietary intake and colon cancer: Sex-and anatomic site-specific associations. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1989, 130, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, D.W.; Slattery, M.L.; Robison, L.M.; French, T.K.; Mahoney, A.W. Adult dietary intake and prostate cancer risk in Utah: A case-control study with special emphasis on aggressive tumors. Cancer Causes Control 1991, 2, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, G.R.; Benito, E.; Castelleto, R.; Cornée, J.; Estève, J.; Gallagher, R.P.; Iscovich, J.M.; Deng-ao, J.; Kaaks, R.; Kune, G.A. Dietary intake of fiber and decreased risk of cancers of the colon and rectum: Evidence from the combined analysis of 13 case-control studies. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1992, 84, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bungau, S.G.; Popa, V.-C. Between Religion and Science Some Aspects Concerning Illness and Healing in Antiquity. Transylv. Rev. 2015, 24, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Langcake, P.; Pryce, R. The production of resveratrol by Vitis vinifera and other members of the Vitaceae as a response to infection or injury. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1976, 9, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Maltese, F.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolic constituents of grapevine and grape-derived products. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrières, J. The French paradox: Lessons for other countries. Heart 2004, 90, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Cai, L.; Udeani, G.O.; Slowing, K.V.; Thomas, C.F.; Beecher, C.W.; Fong, H.H.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Mehta, R.G. Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes. Science 1997, 275, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, L.-M.; Chen, J.-K.; Huang, S.-S.; Lee, R.-S.; Su, M.-J. Cardioprotective effect of resveratrol, a natural antioxidant derived from grapes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 47, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradamante, S.; Barenghi, L.; Villa, A. Cardiovascular protective effects of resveratrol. Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. 2004, 22, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, J.A.; Pearson, K.J.; Price, N.L.; Jamieson, H.A.; Lerin, C.; Kalra, A.; Prabhu, V.V.; Allard, J.S.; Lopez-Lluch, G.; Lewis, K. Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature 2006, 444, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagouge, M.; Argmann, C.; Gerhart-Hines, Z.; Meziane, H.; Lerin, C.; Daussin, F.; Messadeq, N.; Milne, J.; Lambert, P.; Elliott, P. Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1α. Cell 2006, 127, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, V.A.; Patel, K.R.; Viskaduraki, M.; Crowell, J.A.; Perloff, M.; Booth, T.D.; Vasilinin, G.; Sen, A.; Schinas, A.M.; Piccirilli, G. Repeat dose study of the cancer chemopreventive agent resveratrol in healthy volunteers: Safety, pharmacokinetics, and effect on the insulin-like growth factor axis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9003–9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Gong, Q.; Dong, H.; Shi, J. Resveratrol, a neuroprotective supplement for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Akter, R.; Bhattacharya, T.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Alkahtani, S.; Arafah, M.W.; Al-Johani, N.S.; Alhoshani, N.M.; Alkeraishan, N.; Alhenaky, A.J.F.I.P. Resveratrol and Neuroprotection: Impact and its Therapeutic Potential in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 134, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Moher, D. Updating guidance for reporting systematic reviews: Development of the PRISMA 2020 statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 134, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varoni, E.M.; Lo Faro, A.F.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Iriti, M. Anticancer molecular mechanisms of resveratrol. Front. Nutr. 2016, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shukla, Y.; Singh, R. Resveratrol and cellular mechanisms of cancer prevention. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, M.; Kumar, R.; Ahmad, N. Resveratrol in cancer management: Where are we and where we go from here? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, H.S.; Garland, L.L.; Hsu, C.-H.; Vining, D.R.; Chew, W.M.; Miller, J.A.; Perloff, M.; Crowell, J.A.; Alberts, D.S. Resveratrol modulates drug-and carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes in a healthy volunteer study. Cancer Prev. Res. 2010, 3, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zhu, H. Upregulation of endogenous antioxidants and phase 2 enzymes by the red wine polyphenol, resveratrol in cultured aortic smooth muscle cells leads to cytoprotection against oxidative and electrophilic stress. Pharmacol. Res. 2006, 53, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciolino, H.P.; Yeh, G.C. Inhibition of aryl hydrocarbon-induced cytochrome P-450 1A1 enzyme activity and CYP1A1 expression by resveratrol. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 56, 760–767. [Google Scholar]
- Ciolino, H.P.; Daschner, P.J.; Yeh, G.C. Resveratrol inhibits transcription of CYP1A1 in vitro by preventing activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 5707–5712. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lançon, A.; Hanet, N.; Jannin, B.; Delmas, D.; Heydel, J.-M.; Lizard, G.; Chagnon, M.-C.; Artur, Y.; Latruffe, N. Resveratrol in human hepatoma HepG2 cells: Metabolism and inducibility of detoxifying enzymes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delmas, D.; Lançon, A.; Colin, D.; Jannin, B.; Latruffe, N. Resveratrol as a chemopreventive agent: A promising molecule for fighting cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 423–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frombaum, M.; Le Clanche, S.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Borderie, D. Antioxidant effects of resveratrol and other stilbene derivatives on oxidative stress and NO bioavailability: Potential benefits to cardiovascular diseases. Biochimie 2012, 94, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, D.; Tinhofer, I.; Tonko, M.; Hübl, H.; Ausserlechner, M.; Greil, R.; Kofler, R.; Csordas, A. Resveratrol causes arrest in the S-phase prior to Fas-independent apoptosis in CEM-C7H2 acute leukemia cells. Cell Death Differ. 2000, 7, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chin, Y.-T.; Hsieh, M.-T.; Yang, S.-H.; Tsai, P.-W.; Wang, S.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Lee, Y.-S.; Cheng, G.-Y.; HuangFu, W.-C.; London, D. Anti-proliferative and gene expression actions of resveratrol in breast cancer cells in vitro. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 12891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Costa, D.C.F.; Casanova, F.A.; Quarti, J.; Malheiros, M.S.; Sanches, D.; dos Santos, P.S.; Fialho, E.; Silva, J.L. Transient transfection of a wild-type p53 gene triggers resveratrol-induced apoptosis in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48746. [Google Scholar]
- Dörrie, J.; Gerauer, H.; Wachter, Y.; Zunino, S.J. Resveratrol induces extensive apoptosis by depolarizing mitochondrial membranes and activating caspase-9 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4731–4739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bishayee, A. Cancer prevention and treatment with resveratrol: From rodent studies to clinical trials. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delmas, D.; Solary, E.; Latruffe, N. Resveratrol, a phytochemical inducer of multiple cell death pathways: Apoptosis, autophagy and mitotic catastrophe. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 1100–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, F.; Quarti, J.; da Costa, D.C.F.; Ramos, C.A.; da Silva, J.L.; Fialho, E. Resveratrol chemosensitizes breast cancer cells to melphalan by cell cycle arrest. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 2586–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmas, D.; Aires, V.; Limagne, E.; Dutartre, P.; Mazué, F.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Latruffe, N. Transport, stability, and biological activity of resveratrol. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehm, B.D.; Levenson, A.S.; Liu, H.; Lee, E.-J.; Amundsen, B.M.; Cushman, M.; Jordan, V.C.; Jameson, J.L. Estrogenic effects of resveratrol in breast cancer cells expressing mutant and wild-type estrogen receptors: Role of AF-1 and AF-2. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 88, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Lastra, C.A.; Villegas, I. Resveratrol as an antioxidant and pro-oxidant agent: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Portland Press Ltd.: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hadi, S.; Ullah, M.; Azmi, A.; Ahmad, A.; Shamim, U.; Zubair, H.; Khan, H. Resveratrol mobilizes endogenous copper in human peripheral lymphocytes leading to oxidative DNA breakage: A putative mechanism for chemoprevention of cancer. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, V.; Brassart, B.; Carlier, A.; Scagliarini, A.; Mandard, S.; Limagne, E.; Solary, E.; Martiny, L.; Tarpin, M.; Delmas, D. A role for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in resveratrol-induced colon cancer cell apoptosis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, X.; Jin, Y.; Hofseth, A.B.; Pena, E.; Habiger, J.; Chumanevich, A.; Poudyal, D.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Singh, U.P. Resveratrol suppresses colitis and colon cancer associated with colitis. Cancer Prev. Res. 2010, 3, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Corre, L.; Chalabi, N.; Delort, L.; Bignon, Y.J.; Bernard-Gallon, D. Resveratrol and breast cancer chemoprevention: Molecular mechanisms. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, F.; Pasche, C.; Lucchini, F.; Ghidoni, R.; Ferraroni, M.; La Vecchia, C. Resveratrol and breast cancer risk. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2005, 14, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, G.; Øvrebø, S.; Eilertsen, E.; Haugen, A.; Mollerup, S. Analysis of resveratrol as a lung cancer chemopreventive agent in A/J mice exposed to benzo [a] pyrene. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 91, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whyte, L.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Torres, K.; Mehta, R.G. Molecular mechanisms of resveratrol action in lung cancer cells using dual protein and microarray analyses. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 12007–12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niu, X.-F.; Liu, B.-Q.; Du, Z.-X.; Gao, Y.-Y.; Li, C.; Li, N.; Guan, Y.; Wang, H.-Q. Resveratrol protects leukemic cells against cytotoxicity induced by proteasome inhibitors via induction of FOXO1 and p27 Kip1. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeong, S.H.; Jo, W.S.; Song, S.; Suh, H.; Seol, S.-Y.; Leem, S.-H.; Kwon, T.K.; Yoo, Y.H. A novel resveratrol derivative, HS1793, overcomes the resistance conferred by Bcl-2 in human leukemic U937 cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, J.K.; Surh, Y.-J. Cancer chemopreventive and therapeutic potential of resveratrol: Mechanistic perspectives. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athar, M.; Back, J.H.; Kopelovich, L.; Bickers, D.R.; Kim, A.L. Multiple molecular targets of resveratrol: Anti-carcinogenic mechanisms. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 486, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rayalam, S.; Yang, J.Y.; Ambati, S.; Della-Fera, M.A.; Baile, C.A. Resveratrol induces apoptosis and inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Phytother. Res. Int. J. Devoted Pharmacol. Toxicol. Eval. Nat. Prod. Deriv. 2008, 22, 1367–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenealey, J.D.; Subramanian, L.; Van Ginkel, P.R.; Darjatmoko, S.; Lindstrom, M.J.; Somoza, V.; Ghosh, S.K.; Song, Z.; Hsung, R.P.; Kwon, G.S. Resveratrol metabolites do not elicit early pro-apoptotic mechanisms in neuroblastoma cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4979–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cody, V.; Davis, P.J.; Davis, F.B. Molecular modeling of the thyroid hormone interactions with αvβ3 integrin. Steroids 2007, 72, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Kannappan, R.; Reuter, S.; Kim, J.H.; Aggarwal, B.B. Chemosensitization of tumors by resveratrol. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartolacci, C.; Andreani, C.; Amici, A.; Marchini, C. Walking a tightrope: A perspective of resveratrol effects on breast cancer. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 19, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreani, C.; Bartolacci, C.; Wijnant, K.; Crinelli, R.; Bianchi, M.; Magnani, M.; Hysi, A.; Iezzi, M.; Amici, A.; Marchini, C. Resveratrol fuels HER2 and ERα-positive breast cancer behaving as proteasome inhibitor. Aging 2017, 9, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogelstein, B.; Lane, D.; Levine, A.J. Surfing the p53 network. Nature 2000, 408, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousden, K.H.; Lane, D.P. p53 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichler, M.; Algül, H.; Behne, D.; Hölzlwimmer, G.; Michalke, B.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Schmidt, J.; Schmid, R.M.; Brielmeier, M. Selenium status alters tumour differentiation but not incidence or latency of pancreatic adenocarcinomas in Ela-TGF-α p53+/− mice. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 2002–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuckerman, V.; Wolyniec, K.; Sionov, R.V.; Haupt, S.; Haupt, Y. Tumour suppression by p53: The importance of apoptosis and cellular senescence. J. Pathol. A J. Pathol. Soc. Great Br. Irel. 2009, 219, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuster, J.J.; Sanz-González, S.M.; Moll, U.M.; Andrés, V. Classic and novel roles of p53: Prospects for anticancer therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meek, D.W. Tumour suppression by p53: A role for the DNA damage response? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koncz, C.; deJong, F.; Villacorta, N.; Szakonyi, D.; Koncz, Z. The spliceosome-activating complex: Molecular mechanisms underlying the function of a pleiotropic regulator. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bunz, F.; Dutriaux, A.; Lengauer, C.; Waldman, T.; Zhou, S.; Brown, J.; Sedivy, J.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage. Science 1998, 282, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.H.T.; Verchere, C.B.; Warnock, G.L. Adult stem or progenitor cells in treatment for type 1 diabetes: Current progress. Can. J. Surg. 2007, 50, 137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- She, Q.-B.; Bode, A.M.; Ma, W.-Y.; Chen, N.-Y.; Dong, Z. Resveratrol-induced activation of p53 and apoptosis is mediated by extracellular-signal-regulated protein kinases and p38 kinase. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1604–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z. Molecular mechanism of the chemopreventive effect of resveratrol. Mutat. Res./Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagenesis 2003, 523, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C. Phase I clinical trial of curcumin, a chemopreventive agent, in patients with high-risk or pre-malignant lesions. Anticancer Res 2001, 21, e2900. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, P.-C.; Ng, L.-T.; Lin, L.-T.; Richardson, C.D.; Wang, G.-H.; Lin, C.-C. Resveratrol arrests cell cycle and induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma Huh-7 cells. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Post-translational modification of p53 in tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etienne-Selloum, N.; Dandache, I.; Sharif, T.; Auger, C.; Schini-Kerth, V.B. Polyphenolic compounds targeting p53-family tumor suppressors: Current progress and challenges. Futur. Asp. Tumor Suppressor Gene 2013, 129–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Ma, W.-Y.; Goranson, A.; Dong, Z. Resveratrol suppresses cell transformation and induces apoptosis through a p53-dependent pathway. Carcinogenesis 1999, 20, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alkhalaf, M.; Jaffal, S. Potent antiproliferative effects of resveratrol on human osteosarcoma SJSA1 cells: Novel cellular mechanisms involving the ERKs/p53 cascade. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.-L.; Chiang, L.-C.; Lin, C.-C. Resveratrol-induced apoptosis is mediated by p53-dependent pathway in Hep G2 cells. Life Sci. 2002, 72, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, A.; Davis, F.B.; Lin, H.-Y.; Davis, P.J. Resveratrol induces apoptosis in thyroid cancer cell lines via a MAPK-and p53-dependent mechanism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.; Chen, Q.; Siddiqui, I.; Sarva, K.; Srivastava, R.K. Sensitization of TRAIL-resistant LNCaP cells by resveratrol (3, 4’, 5 tri-hydroxystilbene): Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. J. Mol. Signal. 2007, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; DeMarco, V.G.; Nicholl, M.B. Resveratrol enhances radiation sensitivity in prostate cancer by inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting cell senescence and apoptosis. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.C.; Wong, C.; John Bennett, D.; Wu, J.M. Regulation of p53 and cell proliferation by resveratrol and its derivatives in breast cancer cells: An in silico and biochemical approach targeting integrin αvβ3. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2732–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, A.; Liu, C.; Sanli, T.; Tsiani, E.; Singh, G.; Bristow, R.G.; Dayes, I.; Lukka, H.; Wright, J.; Tsakiridis, T. Resveratrol enhances prostate cancer cell response to ionizing radiation. Modulation of the AMPK, Akt and mTOR pathways. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bom, A.P.A.; Rangel, L.P.; Costa, D.C.; de Oliveira, G.A.; Sanches, D.; Braga, C.A.; Gava, L.M.; Ramos, C.H.; Cepeda, A.O.; Stumbo, A.C. Mutant p53 aggregates into prion-like amyloid oligomers and fibrils implications for cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 28152–28162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cino, E.A.; Soares, I.N.; Pedrote, M.M.; De Oliveira, G.A.; Silva, J.L. Aggregation tendencies in the p53 family are modulated by backbone hydrogen bonds. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Fersht, A.R. Multisite aggregation of p53 and implications for drug rescue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2634–E2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lasagna-Reeves, C.A.; Clos, A.L.; Castillo-Carranza, D.; Sengupta, U.; Guerrero-Muñoz, M.; Kelly, B.; Wagner, R.; Kayed, R. Dual role of p53 amyloid formation in cancer; loss of function and gain of toxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soragni, A.; Janzen, D.M.; Johnson, L.M.; Lindgren, A.G.; Nguyen, A.T.-Q.; Tiourin, E.; Soriaga, A.B.; Lu, J.; Jiang, L.; Faull, K.F. A designed inhibitor of p53 aggregation rescues p53 tumor suppression in ovarian carcinomas. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, J.L.; Gallo, C.V.D.M.; Costa, D.C.; Rangel, L.P. Prion-like aggregation of mutant p53 in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bom, A.P.D.A.; Freitas, M.S.; Moreira, F.S.; Ferraz, D.; Sanches, D.; Gomes, A.M.; Valente, A.P.; Cordeiro, Y.; Silva, J.L. The p53 core domain is a molten globule at low pH functional implications of a partially unfolded structure. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 2857–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishimaru, D.; Maia, L.F.; Maiolino, L.M.; Quesado, P.A.; Lopez, P.C.; Almeida, F.C.; Valente, A.P.; Silva, J.L. Conversion of wild-type p53 core domain into a conformation that mimics a hot-spot mutant. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 333, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klabunde, T.; Petrassi, H.M.; Oza, V.B.; Raman, P.; Kelly, J.W.; Sacchettini, J.C. Rational design of potent human transthyretin amyloid disease inhibitors. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 312–321. [Google Scholar]
- Bourgault, S.; Choi, S.; Buxbaum, J.N.; Kelly, J.W.; Price, J.L.; Reixach, N. Mechanisms of transthyretin cardiomyocyte toxicity inhibition by resveratrol analogs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 410, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Florio, P.; Folli, C.; Cianci, M.; Del Rio, D.; Zanotti, G.; Berni, R. Transthyretin binding heterogeneity and anti-amyloidogenic activity of natural polyphenols and their metabolites. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 29769–29780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evers, F.; Jeworrek, C.; Tiemeyer, S.; Weise, K.; Sellin, D.; Paulus, M.; Struth, B.; Tolan, M.; Winter, R. Elucidating the mechanism of lipid membrane-induced IAPP fibrillogenesis and its inhibition by the red wine compound resveratrol: A synchrotron X-ray reflectivity study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9516–9521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Karmakar, S.; Batra, R.; Sharma, P.; Pradhan, P.; Singh, J.; Kundu, B.; Chowdhury, P.K. Polyphenols in combination with β-cyclodextrin can inhibit and disaggregate α-synuclein amyloids under cell mimicking conditions: A promising therapeutic alternative. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2017, 1865, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, X.-P.; Yang, S.-G.; Wang, Y.-J.; Zhang, X.; Du, X.-T.; Sun, X.-X.; Zhao, M.; Huang, L.; Liu, R.-T. Resveratrol inhibits beta-amyloid oligomeric cytotoxicity but does not prevent oligomer formation. Neurotoxicology 2009, 30, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz da Costa, D.C.; Fialho, E.; Silva, J.L. Cancer chemoprevention by resveratrol: The p53 tumor suppressor protein as a promising molecular target. Molecules 2017, 22, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Consortium, D.S.D.; Consortium, D.M.D.; Mahajan, A.; Go, M.J.; Zhang, W.; Below, J.E.; Gaulton, K.J.; Ferreira, T.; Horikoshi, M.; Johnson, A.D. Genome-wide trans-ancestry meta-analysis provides insight into the genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 234. [Google Scholar]
- Walle, T.; Hsieh, F.; DeLegge, M.H.; Oatis, J.E.; Walle, U.K. High absorption but very low bioavailability of oral resveratrol in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gambini, J.; Inglés, M.; Olaso, G.; Lopez-Grueso, R.; Bonet-Costa, V.; Gimeno-Mallench, L.; Mas-Bargues, C.; Abdelaziz, K.; Gomez-Cabrera, M.; Vina, J. Properties of resveratrol: In vitro and in vivo studies about metabolism, bioavailability, and biological effects in animal models and humans. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 837042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vang, O. Resveratrol: Challenges in analyzing its biological effects. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1348, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatelli, P.; Ghiselli, A.; Buchetti, B.; Carnevale, R.; Natella, F.; Germano, G.; Fimognari, F.; Di Santo, S.; Lenti, L.; Violi, F. Polyphenols synergistically inhibit oxidative stress in subjects given red and white wine. Atherosclerosis 2006, 188, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stervbo, U.; Vang, O.; Bonnesen, C. A review of the content of the putative chemopreventive phytoalexin resveratrol in red wine. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotches-Ribalta, M.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Estruch, R.; Escribano, E.; Urpi-Sarda, M. Pharmacokinetics of resveratrol metabolic profile in healthy humans after moderate consumption of red wine and grape extract tablets. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 66, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.; Vaz-da-Silva, M.; Falcão, A.; Soares, E.; Costa, R.; Loureiro, A.I.; Fernandes-Lopes, C.; Rocha, J.F.; Nunes, T.; Wright, L. Pharmacokinetic and safety profile of trans-resveratrol in a rising multiple-dose study in healthy volunteers. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, S7–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boocock, D.J.; Patel, K.R.; Faust, G.E.; Normolle, D.P.; Marczylo, T.H.; Crowell, J.A.; Brenner, D.E.; Booth, T.D.; Gescher, A.; Steward, W.P. Quantitation of trans-resveratrol and detection of its metabolites in human plasma and urine by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 848, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bode, L.M.; Bunzel, D.; Huch, M.; Cho, G.-S.; Ruhland, D.; Bunzel, M.; Bub, A.; Franz, C.M.; Kulling, S.E. In vivo and in vitro metabolism of trans-resveratrol by human gut microbiota. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aires, V.; Limagne, E.; Cotte, A.K.; Latruffe, N.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Delmas, D. Resveratrol metabolites inhibit human metastatic colon cancer cells progression and synergize with chemotherapeutic drugs to induce cell death. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maria, S.; Scognamiglio, I.; Lombardi, A.; Amodio, N.; Caraglia, M.; Cartenì, M.; Ravagnan, G.; Stiuso, P. Polydatin, a natural precursor of resveratrol, induces cell cycle arrest and differentiation of human colorectal Caco-2 cell. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mikstacka, R.; Rimando, A.M.; Ignatowicz, E. Antioxidant effect of trans-resveratrol, pterostilbene, quercetin and their combinations in human erythrocytes in vitro. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2010, 65, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Hu, B.; An, H.-M.; Shen, K.-P.; Xu, L.; Deng, S.; Wei, M.-M. Synergistic anticancer effects of curcumin and resveratrol in Hepa1-6 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erdogan, C.S.; Vang, O. Challenges in analyzing the biological effects of resveratrol. Nutrients 2016, 8, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazué, F.; Delmas, D.; Murillo, G.; Saleiro, D.; Limagne, E.; Latruffe, N. Differential protective effects of red wine polyphenol extracts (RWEs) on colon carcinogenesis. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebeler, S.E.; Brenneman, C.A.; Kim, G.-S.; Jewell, W.T.; Webb, M.R.; Chacon-Rodriguez, L.; MacDonald, E.A.; Cramer, A.C.; Levi, A.; Ebeler, J.D. Dietary catechin delays tumor onset in a transgenic mouse model. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angel-Morales, G.; Noratto, G.; Mertens-Talcott, S. Red wine polyphenolics reduce the expression of inflammation markers in human colon-derived CCD-18Co myofibroblast cells: Potential role of microRNA-126. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, M.; di Modugno, F.; Floroian, L.; Tit, D.M.; Restani, P.; Bungau, S.; Iovan, C.; Badea, G.E.; Aleya, L. Electrochemical strategies for gallic acid detection: Potential for application in clinical, food or environmental analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, D.; Gimazane, A.; Lizard, G.; Izard, J.C.; Solary, E.; Latruffe, N.; Delmas, D. Effects of resveratrol analogs on cell cycle progression, cell cycle associated proteins and 5fluoro-uracil sensitivity in human derived colon cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2780–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nessa, A.; Hossain, M.R.; Rahman, M.H.; Rahman, S.M.; Al Mamun, A.; Khan, J.M. Evaluation of 105 Cases of Dyspepsia by Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy and Ultrasonography of Hepatobiliary System in a Rural Setting. J. Armed Forces Med. Coll. Bangladesh 2015, 11, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.Q.; Bai, Y.; Lin, Y.W.; Zheng, X.Y.; Qin, J.; Yang, K.; Xie, L.P. Resveratrol confers resistance against taxol via induction of cell cycle arrest in human cancer cell lines. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Chávez, J.; Fonseca-Sánchez, M.A.; Arechaga-Ocampo, E.; Flores-Pérez, A.; Palacios-Rodríguez, Y.; Domínguez-Gómez, G.; Marchat, L.A.; Fuentes-Mera, L.; Mendoza-Hernández, G.; Gariglio, P. Proteomic profiling reveals that resveratrol inhibits HSP27 expression and sensitizes breast cancer cells to doxorubicin therapy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heiduschka, G.; Lill, C.; Seemann, R.; Brunner, M.; Schmid, R.; Houben, R.; Bigenzahn, J.; Thurnher, D. The effect of resveratrol in combination with irradiation and chemotherapy. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2014, 190, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podhorecka, M.; Halicka, D.; Klimek, P.; Kowal, M.; Chocholska, S.; Dmoszynska, A. Resveratrol increases rate of apoptosis caused by purine analogues in malignant lymphocytes of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 2011, 90, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Limbert, C.; Päth, G.; Ebert, R.; Rothhammer, V.; Kassem, M.; Jakob, F.; Seufert, J. PDX1-and NGN3-mediated in vitro reprogramming of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells into pancreatic endocrine lineages. Cytotherapy 2011, 13, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazué, F.; Colin, D.; Gobbo, J.; Wegner, M.; Rescifina, A.; Spatafora, C.; Fasseur, D.; Delmas, D.; Meunier, P.; Tringali, C. Structural determinants of resveratrol for cell proliferation inhibition potency: Experimental and docking studies of new analogs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 2972–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalal, M.; Delmas, D.; Meunier, P.; Latruffe, N.; Vervandier-Fasseur, D. Inhibition of cancer derived cell lines proliferation by synthesized hydroxylated stilbenes and new ferrocenyl-stilbene analogs. Comparison with resveratrol. Molecules 2014, 19, 7850–7868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, H.J.; Yang, J.-Y.; Ambati, S.; Della-Fera, M.A.; Hausman, D.B.; Rayalam, S.; Baile, C.A. Combined effects of genistein, quercetin, and resveratrol in human and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamin, L.L.; Filippi-Chiela, E.C.; Dillenburg-Pilla, P.; Horn, F.; Salbego, C.; Lenz, G. Resveratrol and quercetin cooperate to induce senescence-like growth arrest in C6 rat glioma cells. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, R.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Rahman, M.H.J.C.P.D. Flavonoids and Polyphenolic Compounds as Potential Talented Agents for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease and their Antioxidant Activities. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santi, C.; Pietrabissa, A.; Spisni, R.; Mosca, F.; Pacifici, G. Sulphation of resveratrol, a natural product present in grapes and wine, in the human liver and duodenum. Xenobiotica 2000, 30, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedzwiecki, A.; Roomi, M.W.; Kalinovsky, T.; Rath, M. Anticancer efficacy of polyphenols and their combinations. Nutrients 2016, 8, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, G.J.; Yi, S.S.; Heo, S.-H.; Park, C.-R.; Nam, H.-S.; Cho, M.-K.; Lee, S.-H. Cisplatin and resveratrol induce apoptosis and autophagy following oxidative stress in malignant mesothelioma cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 97, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, I.A.; Sanna, V.; Ahmad, N.; Sechi, M.; Mukhtar, H. Resveratrol nanoformulation for cancer prevention and therapy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 2015, 1348, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.S. Dendrimer nanotechnology for enhanced formulation and controlled delivery of resveratrol. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1348, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, O.L.; Friesenhahn, G.; Javors, M.A.; Smoliga, J.M. Development of a lozenge for oral transmucosal delivery of trans-resveratrol in humans: Proof of concept. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi-Chiela, E.C.; Thomé, M.P.; e Silva, M.M.B.; Pelegrini, A.L.; Ledur, P.F.; Garicochea, B.; Zamin, L.L.; Lenz, G. Resveratrol abrogates the temozolomide-induced G2 arrest leading to mitotic catastrophe and reinforces the temozolomide-induced senescence in glioma cells. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sprouse, A.A.; Herbert, B.-S. Resveratrol augments paclitaxel treatment in MDA-MB-231 and paclitaxel-resistant MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 5363–5374. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Wang, L.; Schulte, B.A.; Yang, A.; Tang, S.; Wang, G.Y. Resveratrol enhances ionizing radiation-induced premature senescence in lung cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Liu, D.; Niu, H.; Zhu, G.; Xu, Y.; Ye, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Resveratrol reverses Doxorubicin resistance by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through modulating PTEN/Akt signaling pathway in gastric cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esposito, T.; Schettino, C.; Polverino, P.; Allocca, S.; Adelfi, L.; D’Amico, A.; Capaldo, G.; Varriale, B.; Di Salle, A.; Peluso, G. Synergistic interplay between curcumin and polyphenol-rich foods in the mediterranean diet: Therapeutic prospects for neurofibromatosis 1 patients. Nutrients 2017, 9, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boocock, D.J.; Faust, G.E.; Patel, K.R.; Schinas, A.M.; Brown, V.A.; Ducharme, M.P.; Booth, T.D.; Crowell, J.A.; Perloff, M.; Gescher, A.J. Phase I dose escalation pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers of resveratrol, a potential cancer chemopreventive agent. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2007, 16, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vang, O. What is new for resveratrol? Is a new set of recommendations necessary. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 2013, 1290, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vang, O.; Ahmad, N.; Baile, C.A.; Baur, J.A.; Brown, K.; Csiszar, A.; Das, D.K.; Delmas, D.; Gottfried, C.; Lin, H.-Y. What is new for an old molecule? Systematic review and recommendations on the use of resveratrol. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Wightman, E.L.; Reay, J.L.; Lietz, G.; Okello, E.J.; Wilde, A.; Haskell, C.F. Effects of resveratrol on cerebral blood flow variables and cognitive performance in humans: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover investigation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1590–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chachay, V.S.; Macdonald, G.A.; Martin, J.H.; Whitehead, J.P.; O’Moore–Sullivan, T.M.; Lee, P.; Franklin, M.; Klein, K.; Taylor, P.J.; Ferguson, M. Resveratrol does not benefit patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 2092–2103.e2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, R.; Howe, P.; Buckley, J.; Coates, A.; Kunz, I.; Berry, N. Acute resveratrol supplementation improves flow-mediated dilatation in overweight/obese individuals with mildly elevated blood pressure. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 21, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howitz, K.T.; Bitterman, K.J.; Cohen, H.Y.; Lamming, D.W.; Lavu, S.; Wood, J.G.; Zipkin, R.E.; Chung, P.; Kisielewski, A.; Zhang, L.-L. Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature 2003, 425, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, T.; Almeida, L.; Rocha, J.F.; Falcão, A.; Fernandes-Lopes, C.; Loureiro, A.I.; Wright, L.; Vaz-da-Silva, M.; Soares-da-Silva, P. Pharmacokinetics of trans-resveratrol following repeated administration in healthy elderly and young subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 49, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.R.; Scott, E.; Brown, V.A.; Gescher, A.J.; Steward, W.P.; Brown, K. Clinical trials of resveratrol. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoliga, J.M.; Vang, O.; Baur, J.A. Challenges of translating basic research into therapeutics: Resveratrol as an example. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biomed. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, A.V.; Martinez, M.; Stamos, M.J.; Moyer, M.P.; Planutis, K.; Hope, C.; Holcombe, R.F. Results of a phase I pilot clinical trial examining the effect of plant-derived resveratrol and grape powder on Wnt pathway target gene expression in colonic mucosa and colon cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2009, 1, 25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pallag, A.; Rosca, E.; Tit, D.M.; Mutiu, G.; Bungau, S.G.; Pop, O.L. Monitoring the effects of treatment in colon cancer cells using immunohistochemical and histoenzymatic techniques. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2015, 56, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Howells, L.M.; Berry, D.P.; Elliott, P.J.; Jacobson, E.W.; Hoffmann, E.; Hegarty, B.; Brown, K.; Steward, W.; Gescher, A.J. Phase I randomized, double-blind pilot study of micronized resveratrol (SRT501) in patients with hepatic metastases—Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smoliga, J.M.; Baur, J.A.; Hausenblas, H.A.J.M.N. Resveratrol and health–A comprehensive review of human clinical trials. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V. Treatment of cardiovascular pathology with epigenetically active agents: Focus on natural and synthetic inhibitors of DNA methylation and histone deacetylation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 227, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjær, T.N.; Ornstrup, M.J.; Poulsen, M.M.; Stødkilde-Jørgensen, H.; Jessen, N.; Jørgensen, J.O.L.; Richelsen, B.; Pedersen, S.B. No beneficial effects of resveratrol on the metabolic syndrome: A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 1642–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bird, J.M.; Owen, R.G.; D’Sa, S.; Snowden, J.A.; Pratt, G.; Ashcroft, J.; Yong, K.; Cook, G.; Feyler, S.; Davies, F. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of multiple myeloma 2011. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 154, 32–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iggo, N.; Winearls, C.; Davies, D. The development of cast nephropathy in multiple myeloma. QJM Mon. J. Assoc. Physicians 1997, 90, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- la Porte, C.; Voduc, N.; Zhang, G.; Seguin, I.; Tardiff, D.; Singhal, N.; Cameron, D.W. Steady-state pharmacokinetics and tolerability of trans-resveratrol 2000mg twice daily with food, quercetin and alcohol (ethanol) in healthy human subjects. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2010, 49, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Koenig, L.; Gjyrezi, A.; Giannakakou, P.; Shin, E.H.; Tighiouart, M.; Chen, Z.; Nie, S. A folate receptor-targeting nanoparticle minimizes drug resistance in a human cancer model. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6184–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, P.; Walpole, S.; Morelli, L.; Lambert, P.; Lunsmann, W.; Westphal, C.; Lavu, S. Resveratrol/SRT-501. Drugs Fut 2009, 34, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.R.; Brown, V.A.; Jones, D.J.; Britton, R.G.; Hemingway, D.; Miller, A.S.; West, K.P.; Booth, T.D.; Perloff, M.; Crowell, J.A. Clinical pharmacology of resveratrol and its metabolites in colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7392–7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, S.; Verma, S.S.; Rai, V.; Awasthee, N.; Chava, S.; Hui, K.M.; Kumar, A.P.; Challagundla, K.B.; Sethi, G.; Gupta, S.C. Long non-coding RNAs are emerging targets of phytochemicals for cancer and other chronic diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 1947–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amri, A.; Chaumeil, J.; Sfar, S.; Charrueau, C. Administration of resveratrol: What formulation solutions to bioavailability limitations? J. Control. Release 2012, 158, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhad, A.; Chopra, K. Highlights from the 3rd International Conference on Polyphenols and Health. Drugs Future 2008, 33, 249–287. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akter, R.; Rahman, M.H.; Kaushik, D.; Mittal, V.; Uivarosan, D.; Nechifor, A.C.; Behl, T.; Karthika, C.; Stoicescu, M.; Munteanu, M.A.; et al. Chemo-Preventive Action of Resveratrol: Suppression of p53—A Molecular Targeting Approach. Molecules 2021, 26, 5325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175325
Akter R, Rahman MH, Kaushik D, Mittal V, Uivarosan D, Nechifor AC, Behl T, Karthika C, Stoicescu M, Munteanu MA, et al. Chemo-Preventive Action of Resveratrol: Suppression of p53—A Molecular Targeting Approach. Molecules. 2021; 26(17):5325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175325
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkter, Rokeya, Md. Habibur Rahman, Deepak Kaushik, Vineet Mittal, Diana Uivarosan, Aurelia Cristina Nechifor, Tapan Behl, Chenmala Karthika, Manuela Stoicescu, Mihai Alexandru Munteanu, and et al. 2021. "Chemo-Preventive Action of Resveratrol: Suppression of p53—A Molecular Targeting Approach" Molecules 26, no. 17: 5325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175325
APA StyleAkter, R., Rahman, M. H., Kaushik, D., Mittal, V., Uivarosan, D., Nechifor, A. C., Behl, T., Karthika, C., Stoicescu, M., Munteanu, M. A., Bustea, C., & Bungau, S. (2021). Chemo-Preventive Action of Resveratrol: Suppression of p53—A Molecular Targeting Approach. Molecules, 26(17), 5325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175325