Acacetin Inhibits the Growth of STAT3-Activated DU145 Prostate Cancer Cells by Directly Binding to Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Acacetin Suppresses the Proliferation of DU145 Cancer Cells by Reducing STAT3 Phosphorylation
2.2. Acacetin Reduces the Expression of STAT3 Target Genes and Induces Apoptosis
2.3. Acacetin Induces ROS Generation
2.4. Acacetin Does Not Inhibit Upstream Kinases of STAT3
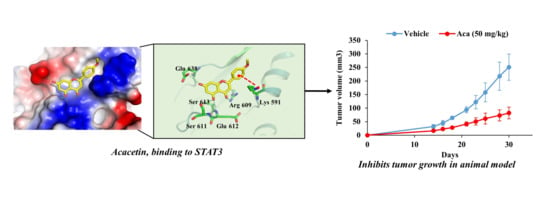
2.5. Acacetin Inhibits STAT3 Activity by Directly Binding to STAT3
2.6. Acacetin Suppresses Tumor Growth in a Mouse DU145 Cell Xenograft Model
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
3.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
3.4. Colony Formation Assay
3.5. Western Blot Analysis
3.6. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) Analyses
3.7. Apoptosis Assay Using Annexin V Staining
3.8. ROS Measurement
3.9. Synthesis of Biotin-Apigenin
3.10. Pull-Down Assay
3.11. Drug Affinity Responsive Target Stability (DARTS)
3.12. Cellular Thermal Shift Assay (CETSA)
3.13. Kinase Assay
3.14. Immunocytochemistry
3.15. In Vivo Xenograft Assay
3.16. Computational Molecular Docking
3.17. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolomeo, M.; Cascio, A. The multifaced role of STAT3 in cancer and its implication for anticancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Tong, Q.; Liu, B.; Huang, W.; Tian, Y.; Fu, X. Targeting STAT3 in cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Cheng, X.D.; Zhang, W.D.; Qin, J.J. Recent update on development of small-molecule STAT3 inhibitors for cancer therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 8884–8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, S.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, X. The role of STAT3 in leading the crosstalk between human cancers and the immune system. Cancer Lett. 2018, 415, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Medicinals for the millennia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 953, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, S.; Mahalanobish, S.; Saha, S.; Ghosh, S.; Sil, P.C. Natural products: An upcoming therapeutic approach to cancer. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 128, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hui, C.; Xie, Y. Natural STAT3 inhibitors: A mini perspective. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 115, 105169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Lim, C. Anticancer activity of flavonoids accompanied by redox state modulation and the potential for a chemotherapeutic strategy. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Gupta, P.; Meena, A.; Luqman, S. Acacetin, a flavone with diverse therapeutic potential in cancer, inflammation, infections and other metabolic disorders. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.H.; Huang, S.H.; Yin, L.T.; Huang, C.S.; Chao, C.H.; Liu, C.L.; Shih, Y.W. Acacetin, a flavonoid, inhibits the invasion and migration of human prostate cancer DU145 cells via inactivation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2010, 333, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.W.; Ho, J.J.; Fu, R.Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.N.; Deng, Q.; Luo, Q.S.; et al. Flavonoids inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis and autophagy through downregulation of PI3Kγ mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K/ULK signaling pathway in human breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, T.A.; Nambiar, D.; Tailor, D.; Pal, A.; Agarwal, R.; Singh, R.P. Acacetin inhibits In vitro and In vivo angiogenesis and downregulates STAT signaling and VEGF expression. Cancer Prev. Res. 2013, 6, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Kim, M.C.; Kim, S.M.; Nam, D.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Ahn, K.S. Lee, E.H.; Jung, S.H.; Ahn, K.S. Chrysanthemum indicum L. extract Induces apoptosis through suppression of constitutive STAT3 activation in human prostate cancer DU145 cells. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, D.; Jia, L.; Guo, J.; Zho, T.; Nordlund, P. Target identification and validation of natural products with label-free methodology: A critical review from 2005 to 2020. Pharmcol. Ther. 2020, 216, 107690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomenick, B.; Jung, G.; Wohlschlegel, J.A.; Huang, J. Target identification using drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS). Curr. Protoc. Chem. Biol. 2011, 3, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, L.; Prabhu, N.; Yu, L.Y.; Bacanu, S.; Ramos, A.D.; Nordlund, P. Horizontal cell biology: Monitoring global changes of protein interaction states with the proteome-wide cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA). Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 383–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.S.; Kim, H.N.; Shin, K.D.; Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, S.J.; Han, D.C.; Kwon, B.M. Cryptotanshinone inhibits constitutive signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 function through blocking the dimerization in DU145 prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, N.; Sharma, J.R.; Yadav, U.C.S. Induction of growth cessation by acacetin via β-catenin pathway and apoptosis by apoptosis inducing factor activation in colorectal carcinoma cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Jove, R. The STATs of cancer--new molecular targets come of age. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flowers, L.O.; Subramaniam, P.S.; Johnson, H.M. A SOCS-1 peptide mimetic inhibits both constitutive and IL-6 induced activation of STAT3 in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, R.L.; Lo, H.W. STAT3 Target Genes Relevant to Human Cancers. Cancers 2014, 6, 897–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onoue, S.; Yamada, S.; Chan, H.K. Nanodrugs: Pharmacokinetics and safety. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Jakstas, V.; Savickas, A.; Bernatoniene, J. Flavonoids as anticancer agents. Nutrients 2020, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chae, I.G.; Kim, D.H.; Kundu, J.; Jeong, C.H.; Kundu, J.K.; Chun, K.S. Generation of ROS by CAY10598 leads to inactivation of STAT3 signaling and induction of apoptosis in human colon cancer HCT116 cells. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.C.; Lee, M.Y.; Shin, D.S.; Jeon, S.B.; Kim, J.M.; Son, K.H.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, H.M.; Kwon, B.M. 2’-Benzoyloxycinnamaldehyde induces apoptosis in human carcinoma via reactive oxygen species. J. Biol Chem. 2004, 279, 6911–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Choi, J.; Kim, C.-H.; Han, D.C.; Kwon, B.-M. 2′-Hydroxycinnamaldehyde inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis via signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 inactivation and reactive oxygen species generation. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, B.; Xu, S.; Neamati, N. Small molecule inhibitors of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) protein. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6645–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohmer, F.D.; Friedrich, K. Protein tyrosine phosphatases as wardens of STAT signaling. JAKSTAT 2014, 3, e28087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Kim, S.H.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Farnesol inhibits tumor growth and enhances the anticancer effects of bortezomib in multiple myeloma xenograft mouse model through the modulation of STAT3 signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2015, 360, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Yoon, Y.J.; Jeon, J.J.; Choi, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.; Nash, O.; Han, D.C.; Kwon, B.M. Geranylnaringenin (CG902) inhibits constitutive and inducible STAT3 activation through the activation of SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 142, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.K.; Lee, H.; Park, C.G.; Jeong, A.J.; Lee, S.H.; Noh, K.H.; Park, J.B.; Lee, C.G.; Paek, S.H.; Kim, H.; et al. STAT3 Inhibitor ODZ10117 Suppresses glioblastoma malignancy and prolongs survival in a glioblastoma xenograft model. Cells 2020, 9, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lomenick, B.; Olsen, R.W.; Huang, J. Identification of direct protein targets of small molecules. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attarha, S.; Reithmeier, A.; Busker, S.; Desroses, M.; Page, B.D.G. Validating signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) Protein-inhibitor interactions using biochemical and cellular thermal shift assays. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Tu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Hua, A.; Geng, P.; Che, F.; Han, A.; Liu, J.; Dai, D.; Wang, S.; et al. Evaluation of acacetin inhibition potential against cytochrome P450 in vitro and in vivo. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 329, 109147. [Google Scholar]













Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yun, S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Choi, J.; Kim, N.D.; Han, D.C.; Kwon, B.-M. Acacetin Inhibits the Growth of STAT3-Activated DU145 Prostate Cancer Cells by Directly Binding to Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3). Molecules 2021, 26, 6204. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26206204
Yun S, Lee Y-J, Choi J, Kim ND, Han DC, Kwon B-M. Acacetin Inhibits the Growth of STAT3-Activated DU145 Prostate Cancer Cells by Directly Binding to Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3). Molecules. 2021; 26(20):6204. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26206204
Chicago/Turabian StyleYun, Sun, Yu-Jin Lee, Jiyeon Choi, Nam Doo Kim, Dong Cho Han, and Byoung-Mog Kwon. 2021. "Acacetin Inhibits the Growth of STAT3-Activated DU145 Prostate Cancer Cells by Directly Binding to Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3)" Molecules 26, no. 20: 6204. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26206204
APA StyleYun, S., Lee, Y. -J., Choi, J., Kim, N. D., Han, D. C., & Kwon, B. -M. (2021). Acacetin Inhibits the Growth of STAT3-Activated DU145 Prostate Cancer Cells by Directly Binding to Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3). Molecules, 26(20), 6204. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26206204