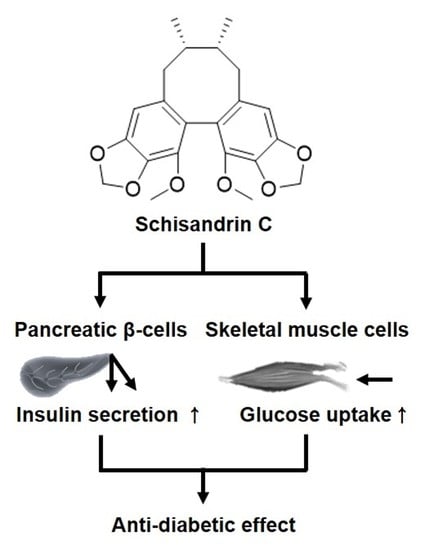
Schisandrin C Affects Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic β-Cells and Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Three Lignans on Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion
2.2. Effect of Schisandrin C on the Protein Expression of PPARγ, P-IRS-2, IRS-2 (Ser731), P-PI3K, PI3K, p-Akt (Ser473), Akt, and PDX-1
2.3. Effect of Schisandrin C on ATP/ADP Ratio and Involvement of L-Type Ca2+ and K+ Channels
2.4. Effect of Schisandrin C on Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Chemicals
4.2. Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion (GSIS) Assay
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. ADP/ATP Ratio Assay
4.6. Glucose Uptake Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khawandanah, J. Double or hybrid diabetes: A systematic review on disease prevalence, characteristics and risk factors. Nutr. Diabetes 2019, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Takei, M.; Ishii, H.; Sato, Y. Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion: A newer perspective. J. Diabetes Investig. 2013, 4, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.V.; Joseph, J.W.; Ronnebaum, S.M.; Burgess, S.C.; Sherry, A.D.; Newgard, C.B. Metabolic cycling in control of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E1287–E1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sylow, L.; Jensen, T.E.; Kleinert, M.; Højlund, K.; Kiens, B.; Wojtaszewski, J.; Prats, C.; Schjerling, P.; Richter, E.A. Rac1 signaling is required for insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and is dysregulated in insulin-resistant murine and human skeletal muscle. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-García, C.; Sánchez-Quesada, C.; Toledo, E.; Delgado-Rodríguez, M.; Gaforio, J.J. Naturally lignan-rich foods: A dietary tool for health promotion? Molecules 2019, 24, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, A.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Ye, X.; Li, H.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gu, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X. Effects of a flaxseed-derived lignan supplement in type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized, double-blind, cross-over trial. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganescu, D.; Andritoiu, C.; Hritcu, D.; Dodi, G.; Popa, M.I. Flaxseed Lignans and Polyphenols Enhanced Activity in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Biology 2021, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fofana, B.; Roy, M.; Ghose, K.; Yao, X.-H.; Nixon, M.-S.; Nair, S.; Nyomba, G.B. Flaxseed lignan secoisolariciresinol diglucoside improves insulin sensitivity through upregulation of GLUT4 expression in diet-induced obese mice. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-G.; Rodriguez, I.; Nam, Y.H.; Gwag, J.E.; Woo, S.H.; Kim, H.-G.; Ko, J.-H.; Hong, B.N.; Kang, T.H.; Baek, N.-I. Recovery effect of lignans and fermented extracts from Forsythia koreana flowers on pancreatic islets damaged by alloxan in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Yang, H.J.; Park, S. The lignan-rich fractions of Fructus Schisandrae improve insulin sensitivity via the PPAR-γ pathways in in vitro and in vivo studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 135, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, L.L.; Zheng, Y.N. Dibenzocyclooctadiene lignans from Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis improve glucose uptake in vitro. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1934578X1000500212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Bae, D.S.; Um, B.H.; Pan, C.-H.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.K. Anti-inflammatory effects of gomisin N, gomisin J, and schisandrin C isolated from the fruit of Schisandra chinensis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, M.; An, F.; Wei, X.; Hong, M.; Lu, Y. Comparative effects of schisandrin A, B, and C on acne-related inflammation. Inflammation 2017, 40, 2163–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.-H.; Liang, X.-H.; Wei, D.-Z.; Wang, Z.-T. Activity of Schisandrin C Isolated from Schisandra chinensis against Human Cancer Cell Lines. Pharm. Biol. 2008, 46, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-S.; Yi, H.-K. Schisandrin C enhances mitochondrial biogenesis and autophagy in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells: Potential involvement of anti-oxidative mechanisms. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2018, 391, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Gao, S.; Liu, J.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, M.; Sun, X.; Guo, P. Extracts and lignans of Schisandra chinensis fruit alter lipid and glucose metabolism in vivo and in vitro. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, M.; Shao, Y.; Dong, X. Schisandrin C attenuates renal damage in diabetic nephropathy by regulating macrophage polarization. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pel, P.; Chae, H.-S.; Nhoek, P.; Yeo, W.; Kim, Y.-M.; Chin, Y.-W. Lignans from the fruits of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill inhibit proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 expression. Phytochemistry 2017, 136, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seino, S. Cell signalling in insulin secretion: The molecular targets of ATP, cAMP and sulfonylurea. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2096–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusunoki, M.; Hayashi, M.; Shoji, T.; Uba, T.; Tanaka, H.; Sumi, C.; Matsuo, Y.; Hirota, K. Propofol inhibits stromatoxin-1-sensitive voltage-dependent k+ channels in pancreatic β-cells and enhances insulin secretion. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, Z. Nifedipine protects INS-1 β-cell from high glucose-induced ER stress and apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 7569–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bardy, G.; Virsolvy, A.; Quignard, J.; Ravier, M.; Bertrand, G.; Dalle, S.; Cros, G.; Magous, R.; Richard, S.; Oiry, C. Quercetin induces insulin secretion by direct activation of L-type calcium channels in pancreatic beta cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santini, E.; Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Masoni, A.; Antonelli, A.; Ferrannini, E. Effect of PPAR-γ activation and inhibition on glucose-stimulated insulin release in INS-1e cells. Diabetes 2004, 53, S79–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yajima, K.; Hirose, H.; Fujita, H.; Seto, Y.; Fujita, H.; Ukeda, K.; Miyashita, K.; Kawai, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ogawa, T. Combination therapy with PPARγ and PPARα agonists increases glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in db/db mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 284, E966–E971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-S.; Hwang, Y.-C.; Koo, S.-H.; Park, K.S.; Lee, M.-S.; Kim, K.-W.; Lee, M.-K. PPAR-γ activation increases insulin secretion through the up-regulation of the free fatty acid receptor GPR40 in pancreatic β-cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e50128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, J.M.D.; Leal, A.E.B.P.; Silva, J.C.; Almeida, J.R.; de Oliveira, H.P. Influence of flavonoids on mechanism of modulation of insulin secretion. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, 639. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balcazar Morales, N.; Aguilar de Plata, C. Role of AKT/mTORC1 pathway in pancreatic β-cell proliferation. Colomb. Méd. 2012, 43, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, Z.; Sun, J.; Ling, J.; Lv, J.; Zhu, D.; Chen, Q.; Sun, Y.; Han, X. Prostaglandin E 2 regulates Foxo activity via the Akt pathway: Implications for pancreatic islet beta cell dysfunction. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, P.; Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Li, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, K.; Niu, Y. Role and mechanism of PI3K/AKT/FoxO1/PDX-1 signaling pathway in functional changes of pancreatic islets in rats after severe burns. Life Sci. 2020, 258, 118145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brissova, M.; Shiota, M.; Nicholson, W.E.; Gannon, M.; Knobel, S.M.; Piston, D.W.; Wright, C.V.; Powers, A.C. Reduction in pancreatic transcription factor PDX-1 impairs glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11225–11232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gauthier, B.R.; Wiederkehr, A.; Baquié, M.; Dai, C.; Powers, A.C.; Kerr-Conte, J.; Pattou, F.; MacDonald, R.J.; Ferrer, J.; Wollheim, C.B. PDX1 deficiency causes mitochondrial dysfunction and defective insulin secretion through TFAM suppression. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, V.; Saravanan, R. Glucose uptake through translocation and activation of GLUT4 in PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by asiatic acid in diabetic rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2015, 34, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świderska, E.; Strycharz, J.; Wróblewski, A.; Szemraj, J.; Drzewoski, J.; Śliwińska, A. Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in insulin-mediated glucose uptake. Blood Glucose Levels 2018, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Schultze, S.M.; Hemmings, B.A.; Niessen, M.; Tschopp, O. PI3K/AKT, MAPK and AMPK signalling: Protein kinases in glucose homeostasis. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2012, 14, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, C.E.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, J.H.; Min, B.-I.; Bae, H.; Choe, W.; Kim, S.-S.; Ha, J. Resveratrol stimulates glucose transport in C2C12 myotubes by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Exp. Mol. Med. 2007, 39, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenbit, A.E.; Burcelin, R.; Katz, E.B.; Tsao, T.-S.; Gautier, N.; Charron, M.J.; Le Marchand-Brustel, Y. Diverse effects of Glut 4 ablation on glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis in red and white skeletal muscle. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.R.; Kang, H.; Yoo, M.J.; Yu, J.S.; Lee, S.; Yi, S.A.; Beemelmanns, C.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.H. Anti-adipogenic pregnane steroid from a Hydractinia-associated fungus, Cladosporium sphaerospermum SW67. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2020, 26, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, M.; Yi, Y.S. Regulatory roles of ginseng on inflammatory caspases, executioners of inflammasome activation. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.; Lee, D.; Park, Y.H.; Choi, H.; Han, J.; Park, D.H.; Choi, Y.-K.; Kwak, J.; Yang, M.-K.; Yoo, J.-W. Discovery and optimization of novel 3-benzyl-N-phenyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxamides as bifunctional antidiabetic agents stimulating both insulin secretion and glucose uptake. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 217, 113325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, H.W.; Choi, Y.-K.; Park, B.J.; Joo, S.H.; Kang, K.S. Schisandrin C Affects Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic β-Cells and Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 6509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216509
Lee D, Kim Y-M, Kim HW, Choi Y-K, Park BJ, Joo SH, Kang KS. Schisandrin C Affects Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic β-Cells and Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle Cells. Molecules. 2021; 26(21):6509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216509
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dahae, Young-Mi Kim, Hyun Woo Kim, You-Kyoung Choi, Bang Ju Park, Sang Hoon Joo, and Ki Sung Kang. 2021. "Schisandrin C Affects Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic β-Cells and Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle Cells" Molecules 26, no. 21: 6509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216509
APA StyleLee, D., Kim, Y. -M., Kim, H. W., Choi, Y. -K., Park, B. J., Joo, S. H., & Kang, K. S. (2021). Schisandrin C Affects Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic β-Cells and Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Muscle Cells. Molecules, 26(21), 6509. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216509