Development of Ferromagnetic Materials Containing Co2P, Fe2P Phases from Organometallic Dendrimers Precursors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Syntheses and Characterization of Homometallic Dendrimers
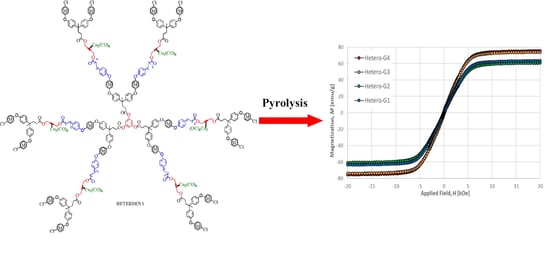
2.2. Synthesis of Heterometallic Dendrimers
2.3. Characterization of Magnetic Particles Containing TMPs Phases
2.3.1. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)
2.3.2. Electron Microscopy Studies
2.3.3. Magnetic Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Instrumentation
3.2. Instrumentation
3.2.1. Morphological Characterization
3.2.2. X-ray Diffraction
3.2.3. Magnetometry
3.3. Synthesis and Characterization
3.3.1. General Procedure
3.3.2. Synthesis of Complex 2, from 2-Butyne-1,4-Diol (a) with Complex 1
3.3.3. Carboxylic-Terminated G1-Homometallic Dendrimer (G1–D2)
3.3.4. Chloro-Terminated G2-Homometallic Dendrimer (G2–D3)
3.3.5. Carboxylic Acid-Terminated G2-Homometallic Dendrimer (G2–D4)
3.3.6. Chloro-Terminated G3-Homometallic Dendrimer (G3–D5)
3.3.7. Carboxylic Acid-Terminated G3-Homometallic Dendrimer (G3–D6)
3.3.8. Chloro-Terminated G4-Homometallic Dendrimer (G4–D7)
3.3.9. Carboxylic Acid-Terminated G4-Homometallic Dendrimer (G4–D8)
3.3.10. Chloro-Terminated G5-Homometallic Dendrimer (G5–D9)
3.3.11. Heterometallic Dendrimer Co/Fe-dendrimerd3 (HETERODEN 1)
3.3.12. Formation of Magnetic Materials Containing TMPs Phases
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Leslie-Pelecky, D.L.; Rieke, R.D. Magnetic properties of nanostructured materials. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1770–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.; Seo, J.; Cheon, J. Nanoscaling laws of magnetic nanoparticles and their applicabilities in biomedical sciences. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrani, A.; Morsali, A. One-dimensional Coordination Polymer as New Precursor for Preparation of Fe2O3 Nano-particles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2011, 21, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Maddikeri, R.R.; Gido, S.P.; Tew, G.N. Magnetic properties of cobalt-containing diblock copolymers with cylindrical morphology of different domain sizes. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2013, 23, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, Z.; Zeng, J.; Deng, M.; Yin, G.; Liao, X.; Gu, J. Histidine-Assisted Synthesis and Cellular Compatibility of Magnetic Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles at Room Temperature. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2012, 22, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myung, N.V.; Park, D.; Yoo, B.; Sumodjo, P.T. Development of electroplated magnetic materials for MEMS. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 265, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayour, H.; Abdellahi, M.; Nejad, M.G.; Khandan, A.; Saber-Samandari, S. Study of the effect of the Zn2 content on the anisotropy and specific absorption rate of the cobalt ferrite: The application of Co1−xZnxFe2O4 ferrite for magnetic hyperthermia. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 54, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiles, D.C. Recent advances and future directions in magnetic materials. Acta. Mater. 2003, 51, 5907–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Badri, Z.M.; Maddikeri, R.R.; Zha, Y.; Thaker, H.D.; Dobriyal, P.; Shunmugam, R.; Russell, T.P.; Tew, G.N. Room temperature magnetic materials from nanostructured diblock copolymers. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schipper, D.E.; Zhao, Z.; Thirumalai, H.; Leitner, A.P.; Donaldson, S.L.; Kumar, A.; Qin, F.; Wang, Z.; Grabow, L.C.; Bao, J. Effects of catalyst phase on the hydrogen evolution reaction of water splitting: Preparation of phase-pure films of FeP, Fe2P, and Fe3P and their relative catalytic activities. J. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 3588–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Liao, J.P.; Wang, Y.F. Solvothermal synthesis and magnetic properties of β-Co2P nanorods. Mater. Sci.-Pol. 2015, 33, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Koo, B.; Yoon, K.Y.; Hwang, Y.; Kang, M.; Park, J.G.; Hyeon, T. Generalized synthesis of metal phosphide nanorods via thermal decomposition of continuously delivered metal− phosphine complexes using a syringe pump. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8433–8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, R.; Bussell, M.E. Metal phosphides: Preparation, characterization and catalytic reactivity. Catal. Lett. 2012, 142, 1413–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Wu, C.; Tian, X.; Wang, K.; Pei, W.; Wang, Q. Magnetic field assisted synthesis of Co2P hollow nanoparticles with controllable shell thickness for hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 330, 135191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, S.T. Novel catalysts for advanced hydroprocessing: Transition metal phosphides. J. Catal. 2003, 216, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Refaei, S.M.; Russo, P.A.; Pinna, N. Recent Advances in Multimetal and Doped Transition-Metal Phosphides for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction at Different pH values. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 22077–22097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhu, M.; Lv, X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, C.; Dai, Y.; Wang, A.; Majima, T. Insight into iron group transition metal phosphides (Fe2P, Co2P, Ni2P) for improving photocatalytic hydrogen generation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 246, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Galvan, M.C.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L. Transition metal phosphides for the catalytic hydrodeoxygenation of waste oils into green diesel. Catalysts 2019, 9, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oyama, S.T.; Gott, T.; Zhao, H.; Lee, Y. Transition metal phosphide hydroprocessing catalysts: A review. Catal. Today 2009, 143, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hao, Y.; Chien, C.; Searson, P.C. Tuning the properties of magnetic nanowires. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2005, 49, 79–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, S.C.; Tsoi, G.; Wenger, L.E.; Brock, S.L. Synthesis of MnP nanocrystals by treatment of metal carbonyl complexes with phosphines: A new, versatile route to nanoscale transition metal phosphides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13960–13961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, S.C.; Fodor, P.S.; Tsoi, G.M.; Wenger, L.E.; Brock, S.L. Application of de-silylation strategies to the preparation of transition metal pnictide nanocrystals: The case of FeP. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 4034–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamm, K.L.; Garno, J.C.; Liu, G.; Brock, S.L. A general methodology for the synthesis of transition metal pnictide nanoparticles from pnictate precursors and its application to iron−phosphorus phases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4038–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Su, H.L.; Qian, X.F.; Liu, X.M.; Qian, Y.T. A mild one-step solvothermal route to metal phosphides (metal = Co, Ni, Cu). J. Solid State Chem. 2000, 149, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Shao, M.; An, C.; Yu, W.; Qian, Y. Surfactant-aided solvothermal synthesis of dinickel phosphide nanocrystallites using red phosphorus as starting materials. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 252, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Cheng, N.; Liu, Q.; Xing, W.; Sun, X. Cobalt phosphide nanowires: Efficient nanostructures for fluorescence sensing of biomolecules and photocatalytic evolution of dihydrogen from water under visible light. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 5583–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Lv, B.; Li, J.; Xiao, M.; Wang, X.; Du, P. Core–shell amorphous cobalt phosphide/cadmium sulfide semiconductor nanorods for exceptional photocatalytic hydrogen production under visible light. J. Mater. Chem A 2016, 4, 1598–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Yan, J.; Wulan, B.; Li, S.; Liu, K.; Jiang, Q. Noble-metal-free cobalt phosphide modified carbon nitride: An efficient photocatalyst for hydrogen generation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 200, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fu, W. Highly efficient and selective photocatalytic reduction of nitroarenes using the Ni2P/CdS catalyst under visible-light irradiation. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 13217–13220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indra, A.; Acharjya, A.; Menezes, P.W.; Merschjann, C.; Hollmann, D.; Schwarze, M.; Aktas, M.; Friedrich, A.; Lochbrunner, S.; Thomas, A. Boosting visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen evolution with an integrated nickel phosphide–carbon nitride system. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1653–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. Cobalt phosphide-based electrocatalysts: Synthesis and phase catalytic activity comparison for hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 4745–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulbaba, K.; Cheng, A.; Bartole, A.; Greenberg, S.; Resendes, R.; Coombs, N.; Safa-Sefat, A.; Greedan, J.E.; Stöver, H.D.; Ozin, G.A. Polyferrocenylsilane microspheres: Synthesis, mechanism of formation, size and charge tunability, electrostatic self-assembly, and pyrolysis to spherical magnetic ceramic particles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12522–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenbaum, A.; Ginzburg-Margau, M.; Coombs, N.; Lough, A.J.; Safa-Sefat, A.; Greedan, J.E.; Ozin, G.A.; Manners, I. Ceramics containing magnetic Co–Fe alloy nanoparticles from the pyrolysis of a highly metallized organometallic polymer precursor. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astruc, D.; Boisselier, E.; Ornelas, C. Dendrimers designed for functions: From physical, photophysical, and supramolecular properties to applications in sensing, catalysis, molecular electronics, photonics, and nanomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1857–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourani, R.; Kakkar, A. Advances in the elegance of chemistry in designing dendrimers. Macromol. Rapid. Commun. 2010, 31, 947–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminade, A.; Yan, D.; Smith, D.K. Dendrimers and hyperbranched polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3870–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-El-Aziz, A.S.; Abdelghani, A.A.; Mishra, A.K. Optical and biological properties of metal-containing macromolecules. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Tong, B.; Li, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhao, W.; Fu, H.; Zhi, J.; Dong, Y.; Häussler, M.; Lam, J.W. Hyperbranched poly (ferrocenylphenylenes): Synthesis, characterization, redox activity, metal complexation, pyrolytic ceramization, and soft ferromagnetism. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 8195–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-El-Aziz, A.S.; Agatemor, C.; Etkin, N.; Bissessur, R. Toward a new family of bifunctional organoiron dendrimers: Facile synthesis, redox, and photophysical fingerprints. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2015, 216, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-El-Aziz, A.S.; Agatemor, C.; Etkin, N.; Overy, D.P.; Lanteigne, M.; McQuillan, K.; Kerr, R.G. Antimicrobial organometallic dendrimers with tunable activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3694–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-El-Aziz, A.S.; Agatemor, C.; Etkin, N.; Bissessur, R. Tunable room-temperature soft ferromagnetism in magnetoceramics of organometallic dendrimers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 2268–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-El-Aziz, A.S.; Winram, D.J.; Shipman, P.O.; Bichler, L. Polynorbornenes Containing Ferrocene Derivatives and Alkyne-bis (tricarbonylcobalt). Macromol. Rapid. Commun. 2010, 31, 1992–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-El-Aziz, A.S.; Winram, D.J.; Shipman, P.O.; Rock, C.L.; Vandel, M.S.; Patrick, B.O. Post-Modification of Organoiron Poly (alkynyl methacrylate) s with Dicobalt Hexacarbonyl. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2012, 213, 2136–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiowitz, E.; Ron, E.; Mathiowitz, G.; Amato, C.; Langer, R. Morphological characterization of bioerodible polymers. 1. Crystallinity of polyanhydride copolymers. Macromolecules 1990, 23, 3212–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Switzer, J.A. Growth of cerium (IV) oxide films by the electrochemical generation of base method. J. Alloy. Compd. 1996, 237, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, A.C. Advanced Transition Metal Phosphide Materials from Single-Source Molecular Precursors. Ph.D. Thesis, Rice University, Houston, TX, USA, 2011; p. 3524516. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, H.; Hokabe, T.; Kamigaichi, T.; Okamoto, T. Magnetic properties of Fe2P single crystal. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1977, 43, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Salabas, E.; Schüth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaresan, A.; Rao, C. Ferromagnetism as a universal feature of inorganic nanoparticles. Nano Today 2009, 4, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruntu, D.; Caruntu, G.; O’Connor, C.J. Magnetic properties of variable-sized Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized from non-aqueous homogeneous solutions of polyols. J. Phys. D 2007, 40, 5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, B.; Hom, W.L.; Chen, X.; Yu, P.; Pavelka, L.C.; Kisslinger, K.; Parise, J.B.; Bhatia, S.R.; Grubbs, R.B. Magnetic Hydrogels from alkyne/cobalt carbonyl-functionalized ABA triblock copolymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 4616–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, Y.; Thaker, H.D.; Maddikeri, R.R.; Gido, S.P.; Tuominen, M.T.; Tew, G.N. Nanostructured block-random copolymers with tunable magnetic properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14534–14541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.F.; Diehl, M.R.; Beverly, K.C.; Richman, E.K.; Tolbert, S.H. Controlling magnetic coupling between cobalt nanoparticles through nanoscale confinement in hexagonal mesoporous silica. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 5475–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-El-Aziz, A.S.; May, L.J.; Hurd, J.A.; Okasha, R.M. First ring-opening metathesis polymerization of norbornenes containing cationic iron moieties. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2001, 39, 2716–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-El-Aziz, A.S.; Carruthers, S.A.; Todd, E.K.; Afifi, T.H.; Gavina, J.M. Cationic organoiron polyelectrolyte three-arm stars. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 1382–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-El-Aziz, A.S.; Abdelghani, A.A.; El-Ghezlani, E.G.; El-ezz, D.A.; Abdel-Rahman, L.H. Pharmacological Evaluation of Novel Organoiron Dendrimers as Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Agents. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 2000242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neises, B.; Steglich, W. Simple method for the esterification of carboxylic acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1978, 17, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Clendenning, S.B.; Friebe, L.; Chan, W.Y.; Zhu, X.; Freeman, M.R.; Yang, G.C.; Yip, C.M.; Grozea, D.; Lu, Z. Pyrolysis of highly metallized polymers: Ceramic thin films containing magnetic CoFe alloy nanoparticles from a polyferrocenylsilane with pendant cobalt clusters. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 2591–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundqvist, S. X-ray investigations of the ternary system Fe-PB. Some features of the systems Cr-PB, Mn-PB, Co-PB and Ni-PB. Acta Chem. Scand. 1962, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinek, F.; Rundqvist, S. The structures of Ni6Si2B, Fe2P and related phases. Acta Chem. Scand. 1959, 13, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fylking, K.E. Phosphides and Arsenides with modified Nickel-Arsenide Structure. Ark. Kem. Miner. Geol. B 1934, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kostiner, E.; Rea, J.R. Crystal structure of ferrous phosphate, Fe3(PO4)2. Inorg. Chem. 1974, 13, 2876–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, T.; Nord, A.G. The crystal structure of iron(II) diphosphate, Fe2P2O7. Z. Kristallogr. 1982, 159, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skala, R.; Drabek, M. The crystal structure of Co2P from X-ray powder diffraction data and its mineralogical applications. Bull. Czech. Geol. Surv. 2001, 76, 209–216. Available online: http://www.geology.cz/bulletin/contents/art2001.04.209 (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Ellner, M.; Mittemeijer, E.J. The Reconstructive Phase Transformation β-Co2P α-Co2P and the Structure of the High-Temperature Phosphide β-Co2P. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2001, 627, 2257–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Homometallic Films | Fe3P | Fe2P | FeP | Fe | Fe3(PO4)2 | Fe2(P2O7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOMO-G1 | 27.6 | 25.9 | 1.4 | 4.5 | 31.4 | 9.1 |
| HOMO-G2 | 26.8 | 38.4 | 8.9 | 2.9 | 16.1 | 9.7 |
| HOMO-G3 | - | 46.0 | 40.7 | - | - | 13.3 |
| HOMO-G4 | - | 44.6 | 24.9 | - | - | 30.5 |
| Heterometallic Films | Co2P | Fe-FCC | Co-FCC | Co-HCP | Fe-BCC | Co2P-β |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HETERO-G1 | 21.7 | 16.9 | 32.6 | - | 3.6 | 25.2 |
| HETERO-G2 | 24.2 | 26.0 | 12.4 | - | 9.1 | 28.3 |
| HETERO-G3 | 36.9 | 28.2 | 31.2 | 0.6 | 3.1 | - |
| HETERO-G4 | 40.5 | 44.2 | 10.5 | 0.5 | 4.2 | - |
| Sample | Remanence Mr (emu/g) | Coercitivity Hc (Oe) | Saturation Ms (emu/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HOMO-G1 | 1.64 | 175 | 9.7 |
| HOMO-G2 | 1.07 | 131 | 9.1 |
| Sample | Remanence Mr (emu/g) | Coercitivity Hc (Oe) | Saturation Ms (emu/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HETERO-G1 | 1.08 | 73 | 63.4 |
| HETERO-G2 | 1.32 | 89 | 60.8 |
| HETERO-G3 | 1.71 | 81 | 74.0 |
| HETERO-G4 | 1.19 | 64 | 75.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abd-El-Aziz, A.S.; Benaaisha, M.R.; Abdelbaky, M.S.M.; Martinez-Blanco, D.; García-Granda, S.; Abdelghani, A.A.; Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Bissessur, R. Development of Ferromagnetic Materials Containing Co2P, Fe2P Phases from Organometallic Dendrimers Precursors. Molecules 2021, 26, 6732. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216732
Abd-El-Aziz AS, Benaaisha MR, Abdelbaky MSM, Martinez-Blanco D, García-Granda S, Abdelghani AA, Abdel-Rahman LH, Bissessur R. Development of Ferromagnetic Materials Containing Co2P, Fe2P Phases from Organometallic Dendrimers Precursors. Molecules. 2021; 26(21):6732. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216732
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbd-El-Aziz, Alaa S., Maysun R. Benaaisha, Mohammed S. M. Abdelbaky, David Martinez-Blanco, Santiago García-Granda, Amani A. Abdelghani, Laila H. Abdel-Rahman, and Rabin Bissessur. 2021. "Development of Ferromagnetic Materials Containing Co2P, Fe2P Phases from Organometallic Dendrimers Precursors" Molecules 26, no. 21: 6732. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216732
APA StyleAbd-El-Aziz, A. S., Benaaisha, M. R., Abdelbaky, M. S. M., Martinez-Blanco, D., García-Granda, S., Abdelghani, A. A., Abdel-Rahman, L. H., & Bissessur, R. (2021). Development of Ferromagnetic Materials Containing Co2P, Fe2P Phases from Organometallic Dendrimers Precursors. Molecules, 26(21), 6732. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216732