Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Phyto-Fabricated from the Obscure Morning Glory Plant Ipomoea obscura (L.) Ker Gawl
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
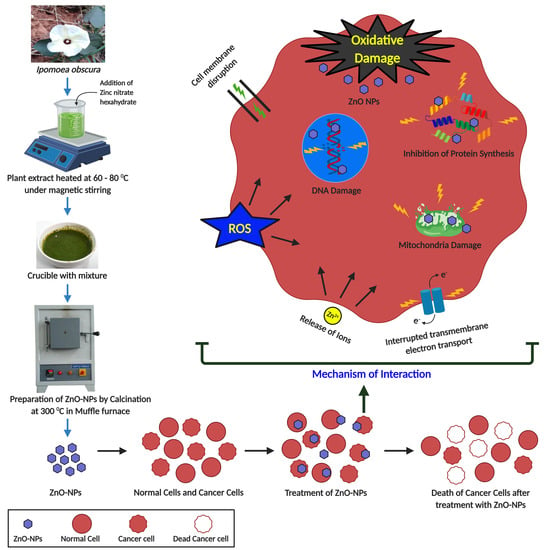
2.1. Collection and Phyto-Fabrication of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from I. obscura
2.2. Physico-Chemical Characterization of ZnO-NPs
2.3. Evaluation of Phyto-Fabricated ZnO-NPs for Biological Potentialities
2.3.1. 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Radical Scavenging Activity
2.3.2. Genotoxic Analysis of Phyto-Fabricated ZnO-NPs by the Allium cepa Method
2.3.3. Cytotoxic Analysis of Phyto-Fabricated ZnO-NPs
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) Assay
Cell Cycle Analysis
Annexin V-FITC Staining Assay
Analysis of Cell Morphology
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physico-Chemical Characterization of Phyto-Fabricated ZnO-NPs
3.2. Evaluation of Phyto-Fabricated ZnO-NPs for Biological Potentialities
3.2.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
3.2.2. Genotoxic Analysis of Phyto-Fabricated ZnO-NPs by the Allium cepa Method
3.2.3. Cytotoxic Analysis of Phyto-Fabricated ZnO-NPs
MTT Assay
Cell Cycle Analysis
Annexin V-FITC Staining Assay
Morphological Evaluation HT-29 Cells by Phase-Contrast Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Nagajyothi, P.; Cha, S.J.; Yang, I.J.; Sreekanth, T.; Kim, K.J.; Shin, H.-M. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using Polygala tenuifolia root extract. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 146, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra, C.; Chandra, M.N.; Murali, M.; Abhilash, M.; Singh, S.B.; Satish, S.; Sudarshana, M. Phyto-fabricated ZnO nanoparticles from Canthiumdicoccum (L.) for antimicrobial, anti-tuberculosis and antioxidant activity. Process. Biochem. 2020, 89, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunalan, S.; Sivaraj, R.; Rajendran, V. Green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2012, 22, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Annu, A.A.; Ahmed, S. Green Synthesis of Metal, Metal Oxide Nanoparticles, and Their Various Applications. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Martínez, L., Kharissova, O., Kharisov, B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.K.H.; Murali, M.; Satish, A.; Singh, S.B.; Gowtham, H.G.; Mahesh, H.M.; Lakshmeesha, T.R.; Amruthesh, K.N.; Jagannath, S. Bioactive and Biocompatible Nature of Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Simaroubaglauca DC.: An Endemic Plant to Western Ghats, India. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Murali, M.; Nagabhushana, H.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Almatroudi, A.; Alomary, M.N.; Udayashankar, A.C.; Singh, S.B.; Asiri, S.M.M.; Ashwini, B.S.; et al. Cinnamomumverum Bark Extract Mediated Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Potentiality. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, D.; Sabela, M.I.; Kanchi, S.; Mdluli, P.S.; Singh, G.; Stenström, T.A.; Bisetty, K. Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Jacaranda mimosifolia flowers extract: Synergistic antibacterial activity and molecular simulated facet specific adsorption studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 162, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murali, M.; Mahendra, C.; Rajashekar, N.; Sudarshana, M.S.; Raveesha, K.A.; Amruthesh, K.N. Antibacterial and antioxidant properties of biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles from Ceropegia candelabrum L.—An endemic species. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 179, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, S.; Murali, M.; Ansari, M.A.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; FarhaSiraj, S.; HaluguddeNagaraja, S.; Chikkamadaiah, M.; ThimappaRamachandrappa, L.; Krishnappa, N.K.H.; et al. Biosynthesized ZnO-NPs from Morusindica Attenuates Methylglyoxal-Induced Protein Glycation and RBC Damage: In-Vitro, In-Vivo and Molecular Docking Study. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suresh, D.; Nethravathi, P.C.; Rajanaika, H.; Nagabhushana, H.; Sharma, S.C. Green synthesis of multifunctional zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using Cassia fistula plant extract and their photodegradative, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 31, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žūkienė, R.; Snitka, V. Zinc oxide nanoparticle and bovine serum albumin interaction and nanoparticles influence on cytotoxicity in vitro. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahendra, C.; Murali, M.; Manasa, G.; Ponnamma, P.; Abhilash, M.R.; Lakshmeesha, T.R.; Satish, A.; Amruthesh, K.N.; Sudarshana, M.S. Antibacterial and antimitotic potential of bio-fabricated zinc oxide nanoparticles of Cochlospermumreligiosum (L.). Microb. Pathog. 2017, 110, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnappa, H.K.N.; Andia, J.D.; Manjunatha, S.; Murali, M.; Amruthesh, K.; Jagannath, S.; Andia, D. Antimitotic and DNA-binding potential of biosynthesized ZnO-NPs from leaf extract of Justiciawynaadensis (Nees) Heyne—A medicinal herb. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 101024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, L.; Yao, L.; Peng, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, T.; Kuang, H. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using radish root extract for effective wound dressing agents for diabetic foot ulcers in nursing care. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joel, C.; Badhusha, M.S.M. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Phyllanthusembilica stem extract and their antibacterial activity. Pharm. Lett. 2016, 8, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Satpathy, S.; Patra, A.; Ahirwar, B.; Hussain, M.D. Antioxidant and anticancer activities of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of tubers of Puerariatuberosa. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, S71–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rana, N.; Chand, S.; Gathania, A.K. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nano-sized spherical particles using Terminaliachebula fruits extract for their photocatalytic applications. Int. Nano Lett. 2016, 6, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundaraselvan, S.; Quine, S.D. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles using Seed Extract of Murrayakoenigii and their antimicrobial activity against Some Human Pathogens. J. Nanosci. Tech. 2017, 3, 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Pereda-Miranda, R.; Bah, M. Biodynamic constituents in the Mexican morning glories: Purgative remedies transcending boundaries. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2003, 3, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, R.; Rangga, A. Determination of carotenoids in Chinese vegetables. Food Chem. 1996, 56, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateasan, A.; Prabakaran, R.; Sujatha, V. Phytoextract-mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using aqueous leaves extract of Ipomoea pes-caprae (L).R. br revealing its biological properties and photocatalytic activity. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2017, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumaran, M.; Pisarcik, D.A.; Bao, R.; Yeung, A.T.; Hamilton, T.C. Enhanced cisplatin cytotoxicity by disturbing the nucleotide excision repair pathway in ovarian cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity Mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakshmeesha, T.R.; Sateesh, M.K.; Prasad, B.D.; Sharma, S.C.; Kavyashree, D.; Chandrasekhar, M.; Nagabhushana, H. Reactivity of Crystalline ZnO Superstructures against Fungi and Bacterial Pathogens: Synthesized Using Nerium oleander Leaf Extract. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 4068–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvakkumar, R.; Suresh, J.; Saravanakumar, B.; Nathanael, A.J.; Hong, S.I.; Venkatachalam, R. Rambutan peels promoted biomimetic synthesis of bioinspired zinc oxide nanochains for biomedical applications. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 137, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stan, M.; Popa, A.; Toloman, D.; Silipas, T.-D.; Vodnar, D.C. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Extracts of Allium sativum, Rosmarinusofficinalis and Ocimumbasilicum. Acta Met. Sin. Engl. Lett. 2016, 29, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabir, S.; Arshad, M.; Chaudhari, S.K. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Revolutionizing Agriculture: Synthesis and Applications. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tapadiya, G.G.; Lamale, J.J.; Khadabadi, S.S.; Saboo, S.S. Phytochemical screening and antioxidant, antimitotic, and antiproliferative activities of Trichodesmaindicum shoot. Anc. Sci. Life 2014, 34, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tettey, C.; Shin, H.-M. Evaluation of the antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using scutellariabaicalensis root. Sci. Afr. 2019, 6, e00157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, P.; McMillan, T.J. Use of the tetrazolium assay in measuring the response of human tumor cells to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 1392–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Umar, H.; Kavaz, D.; Rizaner, N. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Albizialebbeck stem bark, and evaluation of its antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities on human breast cancer cell lines. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 14, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaja, F.; Guran, C.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A.; Oprea, O. Cytotoxic effects of ZnO nanoparticles incorporated in mesoporous silica. UPB Sci. Bull. 2014, 76, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, G.I.; Harper, J.W. Anticancer drug targets: Cell cycle and checkpoint control. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminskyy, V.; Lootsik, M.D.; Stoika, R. Correlation of the cytotoxic activity of four different alkaloids, from Chelidoniummajus (greater celandine), with their DNA intercalating properties and ability to induce breaks in the DNA of NK/Ly murine lymphoma cells. Open Life Sci. 2006, 1, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraste, A. Morphologic and biochemical hallmarks of apoptosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 45, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadok, V.; Voelker, D.R.; Campbell, P.A.; Cohen, J.J.; Bratton, D.L.; Henson, P.M. Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of apoptotic lymphocytes triggers specific recognition and removal by macrophages. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 2207. [Google Scholar]
- Van Engeland, M.; Nieland, L.J.; Ramaekers, F.C.; Schutte, B.; Reutelingsperger, C.P. Annexin V-affinity assay: A review on an apoptosis detection system based on phosphatidylserine exposure. Cytom. J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 1988, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hu, X.; Gao, Y.; Ji, Y. ZnO Nanoparticles Treatment Induces Apoptosis by Increasing Intracellular ROS Levels in LTEP-a-2 Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 423287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, D.-P.; Zhang, X.-F.; Zhang, G.-L.; Huang, Y.-F.; Gurunathan, S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis and autophagy in human ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 6521–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vijayakumar, S.; Vaseeharan, B.; Malaikozhundan, B.; Shobiya, M. Laurusnobilis leaf extract mediated green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: Characterization and biomedical applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, F.H.; Li, L.; Sun, Z. Role of the dissolved zinc ion and reactive oxygen species in cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 199, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murali, M.; Anandan, S.; Ansari, M.A.; Alzohairy, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Asiri, S.M.M.; Almatroudi, A.; Thriveni, M.C.; Singh, S.B.; Gowtham, H.G.; et al. Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Phyto-Fabricated from the Obscure Morning Glory Plant Ipomoea obscura (L.) Ker Gawl. Molecules 2021, 26, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040891
Murali M, Anandan S, Ansari MA, Alzohairy MA, Alomary MN, Asiri SMM, Almatroudi A, Thriveni MC, Singh SB, Gowtham HG, et al. Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Phyto-Fabricated from the Obscure Morning Glory Plant Ipomoea obscura (L.) Ker Gawl. Molecules. 2021; 26(4):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040891
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurali, Mahadevamurthy, Satish Anandan, Mohammad Azam Ansari, Mohammad A. Alzohairy, Mohammad N. Alomary, Sarah Mousa Maadi Asiri, Ahmad Almatroudi, M. C. Thriveni, Sudarshana Brijesh Singh, Hittanahallikoppal Gajendramurthy Gowtham, and et al. 2021. "Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Phyto-Fabricated from the Obscure Morning Glory Plant Ipomoea obscura (L.) Ker Gawl" Molecules 26, no. 4: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040891
APA StyleMurali, M., Anandan, S., Ansari, M. A., Alzohairy, M. A., Alomary, M. N., Asiri, S. M. M., Almatroudi, A., Thriveni, M. C., Singh, S. B., Gowtham, H. G., Aiyaz, M., Srinivasa, C., Urooj, A., & Amruthesh, K. N. (2021). Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Phyto-Fabricated from the Obscure Morning Glory Plant Ipomoea obscura (L.) Ker Gawl. Molecules, 26(4), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040891