Magnetic Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction Using a Novel Carbon-Based Composite Coupled with HPLC–MS/MS for Steroid Multiclass Determination in Human Plasma
Abstract
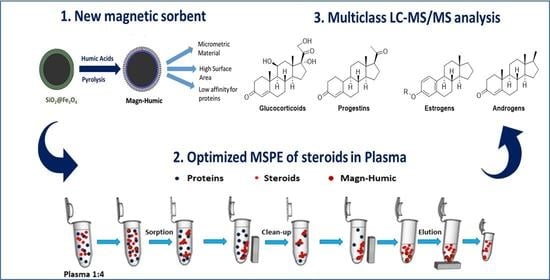
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Magn-Humic Characterizations
2.2. Protein Exclusion and Explorative Extraction Tests
2.3. Development of the MSPE Procedure in BSA Solution Using Magn-Humic
2.4. Optimization and Evaluation of MSPE in Biological Matrices
2.5. Analytical Evaluation of the Method and Application to Bioanalysis
2.6. Comparison with Literature and Critical Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of HA-C@SiO2@Fe3O4 (Magn-Humic)
3.3. Biological Samples
3.4. MSPE Procedure for Simultaneous Extraction, Clean-Up, and Pre-concentration of Multiclass Steroids in Human Plasma
3.5. MSPE Followed by HPLC–ESI-MS/MS: Analytical Parameters
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Appendix A
A.1. Preparation of SiO2@Fe3O4
A.2 HPLC–UV
A.3 HPLC–ESI-MS/MS
References
- Speltini, A.; Sturini, M.; Maraschi, F.; Profumo, A. Recent trends in the application of the newest carbonaceous materials for magnetic solid-phase extraction of environmental pollutants. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2016, 10, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, I.; Fernandes, C. Magnetic solid phase extraction for determination of drugs in biological matrices. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.L.; Li, N.; Cui, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, R.S. Recent application of magnetic solid phase extraction for food safety analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 120, 115632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rehim, M.; Pedersen-Bjergaard, S.; Abdel-Rehim, A.; Lucena, R.; Moein, M.M.; Cárdenas, S.; Miró, M. Microextraction approaches for bioanalytical applications: An overview. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1616, 460790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarzycki, P.K.; Kulhanek, K.M.; Smith, R.; Clifton, V.L. Determination of steroids in human plasma using temperature-dependent inclusion chromatography for metabolomics investigations. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1104, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiraghi, A.; Pourghazi, K.; Amoli-Diva, M. Au nanoparticle grafted thiol modified magnetic nanoparticle solid phase extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for determination of steroid hormones in human plasma and urine. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudl, A.; Kratzsch, J.; Bae, Y.J.; Kiess, W.; Thiery, J.; Ceglarek, U. Liquid chromatography quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometry for quantitative steroid hormone analysis in plasma, urine, saliva and hair. J. Chromatogr. A. 2016, 1464, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisser, J.J.; Hansen, C.H.; Poulsen, R.; Weber Larsen, L.; Cornett, C.; Styrishave, B. Two simple clean-up methods combined with LC-MS/MS for quantification of steroid hormones in in vivo and in vitro assays. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 4883–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.G.; Patel, D.P.; Sanyal, M.; Singhald, P.; Shrivastav, P.S. Simultaneous analysis of glucocorticosteroid fluticasone propionate and its metabolite fluticasone propionate 17β-carboxylic acid in human plasma by UPLC–MS/MS at sub pg/mL level. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 135, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataei, M.M.; Yamini, Y.; Nazaripour, A.; Karimi, M. Novel generation of deep eutectic solvent as an acceptor phase in three phase hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction for extraction and preconcentration of steroidal hormones from biological fluids. Talanta 2018, 178, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belka, M.; Konieczna, L.; Okonska, M.; Pyszka, M.; Ulenberg, A.; Bączek, T. Application of 3D-printed scabbard-like sorbent for sample preparation in bioanalysis expanded to 96-wellplate high-throughput format. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1081, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denver, N.; Khan, S.; Stasinopoulos, I.; Church, C.; Homer, N.Z.M.; MacLean, M.R.; Andrew, R. Derivatization enhances analysis of estrogens and their bioactive metabolites in human plasma by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1054, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque-Córdoba, D.; López-Bascón, M.A.; Priego-Capote, F. Development of a quantitative method for determination of steroids in human plasma by gas chromatography-negative chemical ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2020, 220, 121415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veen, A.; van Faassen, M.; de Jong, W.H.A.; van Beek, A.P.; Dijck-Brouwer, D.A.J.; Kema, I.P. Development and validation of a LC-MS/MS method for the establishment of reference intervals and biological variation for five plasma steroid hormones. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 68, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Nuland, M.; Venekamp, N.; Wouters, W.M.E.; van Rossum, H.H.; Rosing, H.; Beijnen, J.H. LC–MS/MS assay for the quantification of testosterone, dihydrotestosterone, androstenedione, cortisol and prednisone in plasma from castrated prostate cancer patients treated with abiraterone acetate or enzalutamide. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 170, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tircova, B.; Bosakova, Z.; Kozlik, P. Development of an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of anabolic steroids currently available on the black market in the Czech Republic and Slovakia. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Renterghem, P.; Viaene, W.; Van Gansbeke, W.; Barrabin, J.; Iannone, M.; Polet, M.; T’Sjoen, G.; Deventer, K.; Van Eenoo, P. Validation of an ultra-sensitive detection method for steroid esters in plasma for doping analysis using positive chemical ionization GC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1141, 122026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speltini, A.; Merlo, F.; Maraschi, F.; Sturini, M.; Contini, M.; Calisi, N.; Profumo, A. Thermally condensed humic acids onto silica as SPE for effective enrichment of glucocorticoids from environmental waters followed by HPLC-HESI-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1540, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speltini, A.; Pastore, M.; Merlo, F.; Maraschi, F.; Sturini, M.; Dondi, D.; Profumo, A. Humic acids pyrolyzed onto silica microparticles for solid-phase extraction of benzotriazoles and benzothiazoles from environmental waters. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, F.; Speltini, A.; Maraschi, F.; Sturini, M.; Profumo, A. HPLC-MS/MS multiclass determination of steroid hormones in environmental waters after preconcentration on the carbonaceous sorbent HA-C@silica. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speltini, A.; Merlo, F.; Maraschi, F.; Villani, L.; Profumo, A. HA-C@silica sorbent for simultaneous extraction and clean-up of steroids in human plasma followed by HPLC-MS/MS multiclass determination. Talanta 2021, 221, 121496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.; Chai, W.; Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Ding, G. A bioinspired polydopamine approach toward the preparation of gold-modified magnetic nanoparticles for the magnetic solid-phase extraction of steroids in multiple samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 2774–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Yu, X.; Ruan, Z.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Hanagata, N. Magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles coated with thermo-responsive copolymer for potential chemo—and magnetic hyperthermia therapy. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 256, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Yao, J.; Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, G.; Wu, H.; Deng, C. Magnetic mesoporous silica of loading copper metal ions for enrichment and LC-MS/MS analysis of salivary endogenous peptides. Talanta 2020, 207, 120313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.F.; Barbosa, V.M.P.; Bettini, J.; Luccas, P.O.; Figueiredo, E.C. Restricted access carbon nanotubes for direct extraction of cadmium from human serum samples followed by atomic absorption spectrometry analysis. Talanta 2015, 131, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipe de Faria, H.; Tosin Bueno, C.; Krieger, J.E.; Moacyr Krieger, E.; Costa Pereira, A.; Lima Santos, P.C.J.; Figueiredo, E.C. Online extraction of antihypertensive drugs and their metabolites from untreated human serum samples using restricted access carbon nanotubes in a column switching liquid chromatography system. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1528, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipe de Faria, H.; Azevedo Rosa, M.; Thalison Silveira, A.; Figueiredo, E.C. Direct extraction of tetracyclines from bovine milk using restricted access carbon nanotubes in a column switching liquid chromatography system. Food Chem. 2017, 225, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullett, W.M.; Pawliszyn, J. Direct LC analysis of five benzodiazepines in human urine and plasma using an ADS restricted access extraction column. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2001, 26, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leardi, R.; Melzi, C.; Polotti, G. CAT, Cchemometric Agile Tool. Freely. Available online: http://gruppochemiometria.it/index.php/software (accessed on 18 February 2021).
- González, A.G.; Herrador, M.A. A practical guide to analytical method validation, including measurement uncertainty and accuracy profiles. Trend Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SANCO/12571/2013, Guidance Document on Analytical Quality Control and Validation Procedures for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Food and Feed. Available online: https://www.eurl-pesticides.eu/library/docs/allcrl/AqcGuidance_Sanco_2013_12571.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2021).
- Rochester 2021 Interpretive Handbook; Mayo clinic laboratories: Rochester, USA. Available online: https://www.mayocliniclabs.com/test-catalog/pod/MayoTestCatalog-Rochester--SortedByTestName-duplex-interpretive.pdf (accessed on 18 February 2021).
- Koniecza, L.; Belka, M.; Okonska, M.; Pyszka, M.; Bączec, T. New 3D-printed sorbent for extraction of steroids from human plasma preceding LC-MS analysis. J. Chromatogr. A. 2018, 1545, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márta, Z.; Bobály, B.; Fekete, J.; Magda, B.; Imre, T.; Mészáros, K.V.; Bálint, M.; Szabó, P.T. Simultaneous determination of thirteen different steroid hormones using micro UHPLC-MS/MS with on-line SPE system. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 150, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Lu, L.; Gao, D.; Wang, M.; Wang, D.; Xia, Z. Rapid synthesis of three-dimensional sulfur-doped porous graphene via solid-state microwave irradiation for protein removal in plasma sample pretreatment. Talanta 2018, 185, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manousi, N.; Rosenberg, E.; Deliyanni, E.; Zachariadis, G.A.; Samanidou, V. Magnetic solid-phase extraction of organic compounds based on graphene oxide nanocomposites. Molecules 2020, 25, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghorbani, M.; Aghamohammadhassan, M.; Chamsaz, M.; Akhlaghi, H.; Pedramrad, T. Dispersive solid phase microextraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 793–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreda-Piñeiro, J.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. Combined assisted extraction techniques as green sample pre-treatments in food analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material | Surface Area (m2 g−1) |
|---|---|
| c-SiO2@Fe3O4 | 305 |
| c-Magn-Humic | 169 |
| SiO2@Fe3O4 | 81 |
| Magn-Humic | 183 |
| Sorbent | % BSA Exclusion 1 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Magn-Humic | 90(5) | This work |
| c-Magn-Humic | 95(3) | This work |
| RACNTs | 90(3) | [21] |
| HA-C@silica | 86(2) | [21] |
| Exp. | FBS Volume (µL), x1 | Magn-Humic Amount (mg), x2 | Recovery (%) | Residual Proteins (µg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 250 | 10 | 55 | 57 |
| 2 | 1250 | 10 | 28 | 123 |
| 3 | 250 | 50 | 81 | 133 |
| 4 | 1250 | 50 | 65 | 237 |
| Mean Recovery (%) 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spike (ng mL−1) | 100 | 25 | 5 | 1 2 | |
| PREDLO | 95 | 84 | 87 | 65 | |
| PRED | 109 | 98 | 97 | 107 | |
| H-CORT | 80 | 80 | 71 | 70 | |
| CORT | 91 | 87 | 97 | 70 | |
| BETA | 97 | 94 | 104 | 122 | |
| DEXA | 97 | 96 | 80 | 75 | |
| TRIAM | 100 | 95 | 110 | 104 | |
| E2 | 106 | 115 | 109 2 | n.q. 3 | |
| TST | 84 | 81 | 95 | 92 | |
| EPI | 84 | 82 | 94 | 94 | |
| EE2 | 89 | 82 | 88 | 97 | |
| E1 | 86 | 89 | 105 | 90 | |
| H-PROG | 105 | 90 | 84 | 96 | |
| FLUO | 75 | 91 | 97 | 106 | |
| PROG | 88 | 89 | 80 | 84 | |
| M-PROG | 98 | 101 | 99 | 82 | |
| Steroids, Analysed Number and Classes | Plasma Volume (µL) | Protein Precipitation | Centrifugation | Dilution | Extraction Technique | Sorbent (amount, mg) | Elution | Derivatization | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | MQLs (ng mL−1) | Analysis | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10: 4 estrogens, 1 androgen, 3 progestagens, 2 glucocorticoids | 2000 | MeOH | n.a. 1 | H2O (+36 mL) | SPE | C18 (500 mg) | 2 mL MeOH | - | 85.3–99.9 | 0.2–8.3 | 4–157 (MDLs) | HPLC–UV | [5] |
| 19: 3 estrogens, 6 androgens, 4 progestagens, 6 glucocorticoids | 400 | - | - | H2O (+4 mL) | SPE | C18 (500 mg) | 5 mL MeOH- H2O (80:20) | - | 93.9–137.3 | 1.5–15.6 | 0.055–0.530 | HPLC–MS | [8] |
| 7: 2 estrogens, 4 androgens, 1 progestagen | 495 | 0.1 % FA | 20,220× g, 10 min, 4 °C | H2O (to 2 mL) | SPE | C18 (500 mg) | 3 mL ethylacetate | Step 1. 30 min, 30 °C Step 2. 30 min, 40 °C | 69.2–100 | 1.6–35.5 | 0.01–5 | GC-MS | [13] |
| 16: 3 estrogens, 2 androgens, 3 progestagens, 8 glucocorticoids | 250 | - | - | PBS (to 2 mL) | SPE | HA-C@silica 2 (100 mg) | 1 mL MeOH-ACN (1:1) | - | 64–118 | < 15 | 2–10 (15 for E2) | HPLC–MS | [21] |
| 7: 1 estrogen, 3 androgens, 2 glucocorticoids, 1 mineralcorticoid | n.a. | - | - | n.a. | dispersive SPE | 3D-printed LayFOMM 60® | ACN-H2O (80:20), 75 min, 750 rpm | - | 19.3–84.9 | 1.44–9.46 | 3-10 | HPLC–MS | [33] |
| 5: 1 estrogen, 2 androgens, 1 glucocorticoid, 1 mineralcorticoid | 300 | - | - | PBS (to 1.5 mL) | 96-well plate SPE | 3D-printed LayFOMM 60® | ACN-H2O (80:20), 75 min | - | 2.05–38.07 | 3.02–18.14 | n.a. | HPLC–MS | [11] |
| 2: 1 androgen, 1 progestagen | n.a. | ACN | 3000 rpm, 30 min | H2O (to 50 mL) | MSPE | TMSPT-MNP@Au 3 (50 mg) | 1 mL MeOH, 3 min | - | 94.5–99.1 | 3.49–4.19 | 0.05–0.07 (MDLs) | HPLC–UV | [6] |
| 16: 3 estrogens, 2 androgens, 3 progestagens, 8 glucocorticoids | 250 | - | - | PBS (to 1 mL) | MSPE | Magn-Humic (50 mg) | 0.5 mL MeOH-ACN (1:1) + 0.5 mL MeOH (vortex, 1400 rpm, 3 min) | - | 65–122 | 5–14 | 0.07–1 (2.5 for E2) | HPLC–MS | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Speltini, A.; Merlo, F.; Maraschi, F.; Marrubini, G.; Faravelli, A.; Profumo, A. Magnetic Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction Using a Novel Carbon-Based Composite Coupled with HPLC–MS/MS for Steroid Multiclass Determination in Human Plasma. Molecules 2021, 26, 2061. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26072061
Speltini A, Merlo F, Maraschi F, Marrubini G, Faravelli A, Profumo A. Magnetic Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction Using a Novel Carbon-Based Composite Coupled with HPLC–MS/MS for Steroid Multiclass Determination in Human Plasma. Molecules. 2021; 26(7):2061. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26072061
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpeltini, Andrea, Francesca Merlo, Federica Maraschi, Giorgio Marrubini, Anna Faravelli, and Antonella Profumo. 2021. "Magnetic Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction Using a Novel Carbon-Based Composite Coupled with HPLC–MS/MS for Steroid Multiclass Determination in Human Plasma" Molecules 26, no. 7: 2061. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26072061
APA StyleSpeltini, A., Merlo, F., Maraschi, F., Marrubini, G., Faravelli, A., & Profumo, A. (2021). Magnetic Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction Using a Novel Carbon-Based Composite Coupled with HPLC–MS/MS for Steroid Multiclass Determination in Human Plasma. Molecules, 26(7), 2061. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26072061