Rapid Purification of Fucoxanthin from Phaeodactylum tricornutum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
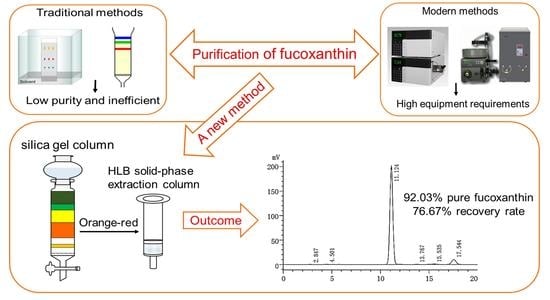
2.1. Purification and Identification of Fucoxanthin
2.2. Characterization of Fucoxanthin by ESI-MS
2.3. NMR Analysis of Fucoxanthin
2.4. Antioxidant Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Cultivation and Collection of Microalgae
3.3. Extraction of Total Pigments from Phaeodactylum Tricornutum
3.4. Isolate the Crude Pigment Extracts of Fucoxanthin by SGCC
3.5. Purification of Fucoxanthin by HLB Solid-Phase Extraction Column
3.6. HPLC Analysis of Fucoxanthin
3.7. ESI-MS Analysis of Fucoxanthin
3.8. Identification of Fucoxanthin by NMR
3.9. Assay for Antioxidant Activity of Fucoxanthin
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Mikami, K.; Hosokawa, M. Biosynthetic Pathway and Health Benefits of Fucoxanthin, an Algae-Specific Xanthophyll in Brown Seaweeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 13763–13781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Chuyen, H.; Eun, J.-B. Marine carotenoids: Bioactivities and potential benefits to human health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2600–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengarajan, T.; Rajendran, P.; Nandakumar, N.; Balasubramanian, M.P.; Nishigaki, I. Cancer Preventive Efficacy of Marine Carotenoid Fucoxanthin: Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Nutrients 2013, 5, 4978–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qu, J.; Wang, X.; Kong, R.; Han, C.; Liu, Z. Fucoxanthin: A Promising Medicinal and Nutritional Ingredient. Evid.-Based Complement. Complement. Med. 2015, 2015, 723515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-K.; Pangestuti, R. Biological Activities and Potential Health Benefits of Fucoxanthin Derived from Marine Brown Algae. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 64, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço-Lopes, C.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Carpena, M.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Pereira, A.; Prieto, M.; Simal-Gandara, J. Scientific Approaches on Extraction, Purification and Stability for the Commercialization of Fucoxanthin Recovered from Brown Algae. Foods 2020, 9, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, E.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Optimisation of fucoxanthin extraction from Irish seaweeds by response surface methodology. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 29, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrushkina, M.; Gusev, E.; Sorokin, B.; Zotko, N.; Mamaeva, A.; Filimonova, A.; Kulikovskiy, M.; Maltsev, Y.; Yampolsky, I.; Guglya, E.; et al. Fucoxanthin production by heterokont microalgae. Algal Res. 2017, 24, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Yuan, J.-P.; Wu, C.-F.; Wang, J.-H. Fucoxanthin, a Marine Carotenoid Present in Brown Seaweeds and Diatoms: Metabolism and Bioactivities Relevant to Human Health. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1806–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Jung, Y.-J.; Kwon, O.-N.; Cha, K.H.; Um, B.-H.; Chung, D.; Pan, C.-H. A Potential Commercial Source of Fucoxanthin Extracted from the Microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovan, A.; Seraglia, R.; Bresin, B.; Caniato, R.; Filippini, R. Fucoxanthin from Undaria pinnatifida: Photostability and Coextractive Effects. Molecules 2013, 18, 6298–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raji, V.; Loganathan, C.; Sadhasivam, G.; Kandasamy, S.; Poomani, K.; Thayumanavan, P. Purification of fucoxanthin from Sargassum wightii Greville and understanding the inhibition of angiotensin 1-converting enzyme: An in vitro and in silico studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Loredo, A.; Benavides, J.; Rito-Palomares, M. Partition behavior of fucoxanthin in ethanol-potassium phosphate two-phase systems. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Si, X.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, G. Isolation of fucoxanthin from edible brown algae by microwave-assisted extraction coupled with high-speed countercurrent chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 2313–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Wang, K.; Wan, L.; Li, A.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, C. Production, Characterization, and Antioxidant Activity of Fucoxanthin from the Marine Diatom Odontella aurita. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2667–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira-Júnior, R.G.; Grougnet, R.; Bodet, P.-E.; Bonnet, A.; Nicolau, E.; Jebali, A.; Rumin, J.; Picot, L. Updated pigment composition of Tisochrysis lutea and purification of fucoxanthin using centrifugal partition chromatography coupled to flash chromatography for the chemosensitization of melanoma cells. Algal Res. 2020, 51, 102035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Cui, W.; Hou, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Yan, X. Isolation and Purification of Fucoxanthin from Brown Seaweed Sargassum horneri Using Open ODS Column Chromatography and Ethanol Precipitation. Molecules 2021, 26, 3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Loredo, A.; Gonzalez-Valdez, J.; Rito-Palomares, M. Insights on the downstream purification of fucoxanthin, a microalgal carotenoid, from an aqueous two-phase system stream exploiting ultrafiltration. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 27, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Kang, S.-W.; Kwon, O.-N.; Chung, D.; Pan, C.-H. Fucoxanthin as a major carotenoid in Isochrysis aff. galbana: Characterization of extraction for commercial application. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2012, 55, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim-Carrilho, K.T.; Cepeda, A.; Fente, C.; Regal, P. Review of methods for analysis of carotenoids. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 56, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Keum, Y.-S. Carotenoid extraction methods: A review of recent developments. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque, N.; Rubio, S. Extraction and stability of pesticide multiresidues from natural water on a mixed-mode admicellar sorbent. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1248, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Quan, L.; Pei, P.; Lin, Y.; Feng, C.; Guan, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, T.; Wu, J.; Huo, J. Simultaneous determination of Vitamin A, 25-hydroxyl vitamin D 3 α-tocopherol in small biological fluids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1079, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, F.; Qian, L.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Lu, L.; Xu, Q. A high-throughput nanofibers mat-based micro-solid phase extraction for the determination of cationic dyes in wastewater. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1460, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarek, W.; Listwan, S.; Pagacz, J.; Leśniak, P.; Latowski, D. Column chromatography as a useful step in purification of diatom pigments. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2016, 63, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, F.-F.; Ma, T.-Y.; Fan, Y.-M.; Chu, L.-L.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y. Nanoparticle-based polyacrylonitrile monolithic column for highly efficient micro solid-phase extraction of carotenoids and vitamins in human serum. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1635, 461755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Quirós, A.R.-B.; Frecha-Ferreiro, S.; Vidal-Pérez, A.M.; López-Hernández, J. Antioxidant compounds in edible brown seaweeds. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 231, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, T.; Baskaran, V.; Tsuzuki, W.; Nagao, A. Brown Algae Fucoxanthin Is Hydrolyzed to Fucoxanthinol during Absorption by Caco-2 Human Intestinal Cells and Mice. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.M.; Shang, Y.F.; Um, B.-H. A preparative method for isolation of fucoxanthin from Eisenia bicyclis by centrifugal partition chromatography. Phytochem. Anal. 2011, 22, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-S.; Song, M.J. Analysis of cyanoacrylate ultraviolet absorbers using liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry: Influence of fragmentor voltage and solvent on ionization and fragmentation behaviors. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 2580–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajauria, G.; Foley, B.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Characterization of dietary fucoxanthin from Himanthalia elongata brown seaweed. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, S.; Canela, R. Influence of Sample Processing on the Analysis of Carotenoids in Maize. Molecules 2012, 17, 11255–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Kim, S.-M.; Pan, C.-H.; Chung, D. Effects of heating, aerial exposure and illumination on stability of fucoxanthin in canola oil. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Wong, C.-C.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Mao, X.; Wu, T.; Ren, Y.; Chen, F. A novel strategy for isolation and purification of fucoxanthinol and fucoxanthin from the diatom Nitzschia laevis. Food Chem. 2018, 277, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, A.; Hamid, N.; Lu, J. Fucoxanthin content and antioxidant properties of Undaria pinnatifida. Food Chem. 2012, 136, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachindra, N.M.; Sato, E.; Maeda, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Niwano, Y.; Kohno, M.; Miyashita, K. Radical Scavenging and Singlet Oxygen Quenching Activity of Marine Carotenoid Fucoxanthin and Its Metabolites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8516–8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, W.; Sies, H. Photoprotection by dietary carotenoids: Concept, mechanisms, evidence and future development. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, N.; Gemello, E.; Gammone, M.A.; De Girolamo, M.; Ficoneri, C.; Riccioni, G. Fucoxantin: A Treasure from the Sea. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.R.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin: A Marine Carotenoid Exerting Anti-Cancer Effects by Affecting Multiple Mechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 5130–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, T.-B.; Yang, Y.-F.; Balamurugan, S.; Li, D.-W.; Yang, W.-D.; Li, H.-Y. Enrichment of f/2 medium hyperaccumulates biomass and bioactive compounds in the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Algal Res. 2020, 47, 101872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Chen, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, G. Protective Effect of Fucoxanthin Isolated from Laminaria japonica against Visible Light-Induced Retinal Damage Both In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, B.C.; Walter, C.; Lange, H.A.; Buchholz, R. Microalgae as natural sources for antioxidative compounds. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 24, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.; Fröhlich, K.; Böhm, V. Comparative antioxidant activities of carotenoids measured by ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), ABTS bleaching assay (αTEAC), DPPH assay and peroxyl radical scavenging assay. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, H.; Rahim, A.A.; Isa, N.M.; Bakhir, N.M. Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Content of Paederia foetida and Syzygium aqueum. Molecules 2009, 14, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Position | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) | Position | δC, Type | δH (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35.89, C | 1′ | 35.27, C | ||
| 2 | 47.17, CH2 | 1.42, m 1.61, m | 2′ | 45.56, CH2 | 1.49, m 2.07, m |
| 3 | 64.42, CH | 3.80, m | 3′ | 68.20, CH | 5.37, m |
| 4 | 41.74, CH2 | 1.77, m 2.29, m | 4′ | 45.36, CH2 | 1.67, m 2.33, m |
| 5 | 66.31, C | 5′ | 72.80, C | ||
| 6 | 67.26, C | 6′ | 117.60, C | ||
| 7 | 40.91, CH2 | 2.59, d (18.3) 3.65, d (18.4) | 7′ | 202.49, C | |
| 8 | 198.02, C=O | 8′ | 103.49, CH | 6.05, s | |
| 9 | 134.63, C | 9′ | 132.63, C | ||
| 10 | 139.26, CH | 7.14, d (10.8) | 10′ | 128.64, CH | 6.12, d (11.3) |
| 11 | 123.49, CH | 6.64, m | 11′ | 125.81, CH | 6.74, d (11.5) |
| 12 | 145.18, CH | 6.70, d (11.1) | 12′ | 137.22, CH | 6.34, d (15.0) |
| 13 | 138.20, C | 13′ | 135.54, C | ||
| 14 | 136.77, CH | 6.40, d (11.5) | 14′ | 132.29, CH | 6.26, d (11.5) |
| 15 | 129.54, CH | 6.56, dd (14.8, 11.0) | 15′ | 132.65, CH | 6.78, m |
| 16 | 25.16, CH3 | 1.02, s | 16′ | 29.31, CH3 | 1.34, s |
| 17 | 28.24, CH3 | 0.95, s | 17′ | 31.36, CH3 | 1.25, s |
| 18 | 21.26, CH3 | 1.21, s | 18′ | 32.20, CH3 | 1.37, s |
| 19 | 11.94, CH3 | 1.94, s | 19′ | 14.13, CH3 | 1.81, s |
| 20 | 12.88, CH3 | 1.98, s | 20′ | 13.03, CH3 | 1.98, s |
| 21′ | 170.66, C=O | ||||
| 22′ | 21.54, CH3 | 2.03, s |
| Regression Equation | Correlation Coefficient | Linearity Range |
|---|---|---|
| Y = −388,741.28 + 215,585.34X | R2 = 0.9994 | 10~200 μg·mL−1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Gao, L.; Zhao, X. Rapid Purification of Fucoxanthin from Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Molecules 2022, 27, 3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103189
Zhao X, Gao L, Zhao X. Rapid Purification of Fucoxanthin from Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Molecules. 2022; 27(10):3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103189
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xinjie, Liwei Gao, and Xiangzhong Zhao. 2022. "Rapid Purification of Fucoxanthin from Phaeodactylum tricornutum" Molecules 27, no. 10: 3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103189
APA StyleZhao, X., Gao, L., & Zhao, X. (2022). Rapid Purification of Fucoxanthin from Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Molecules, 27(10), 3189. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103189