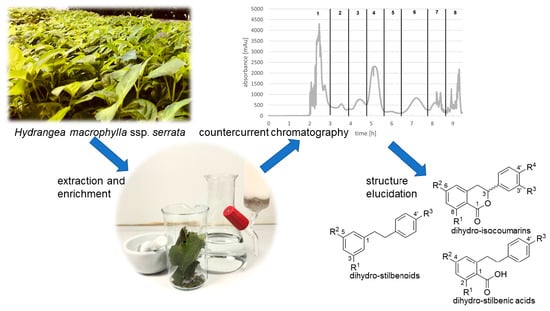
Separation of Dihydro-Isocoumarins and Dihydro-Stilbenoids from Hydrangea macrophylla ssp. serrata by Use of Counter-Current Chromatography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. HPCCC Separation of the XAD-16 Purified Methanol Fraction
2.2. HSCCC Separation of the Purified Ethyl Acetate Fraction
2.3. Dihydro-Isocoumarins
2.4. Dihydro-Stilbenic Acids
2.5. Dihydrostilbenoids and Related Substance
2.6. Cyanogenic Glycoside
2.7. Secoiridoid Glycoside
2.8. Flavonols
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Material
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Extraction
3.4. Purification of the Crude Extract
3.5. Separation of XAD-16 Enriched Methanol Extract by Use of High-Performance Counter-Current Chromatography (HPCCC)
3.6. Separation of Enriched Ethyl Acetate Extract by Use of High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography (HSCCC)
3.7. Preparative HPLC
3.8. Structure Elucidation
3.8.1. UPLC-ESI-IMS-QToF
3.8.2. NMR
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, M.-J.; Yoo, S.-H.; Kim, Y.; Hong, J.-H. Relative sweetness and sweetness quality of phyllodulcin (3R)-8-Hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-1H-isochromen-1-one. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujihara, M.; Shinozaki, M.; Kato, M. Accumulation of phyllodulcin in sweet-leaf plants of Hydrangea serrata and its neutrality in the defence against a specialist leafmining herbivore. Res. Popul. Ecol. 1995, 37, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahina, Y.; Asano, J. Über die Konstitution von Hydrangenol und Phyllodulcin. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. A/B 1929, 62, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahina, Y.; Asano, J. Über die Konstitution von Hydrangenol und Phyllodulcin (II. Mitteil.). Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. A/B 1930, 63, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.-R.; Lee, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.-L.; Hsieh, P.-W.; Khalil, A.T.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wu, Y.-C. Secoiridoid glycoside and alkaloid constituents of Hydrangea chinensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1245–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.S.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zheng, X.K.; Zhu, B.; Yang, L.G.; Li, Z. A new flavonol glycoside from Hydrangea macrophylla (Thunb.) Seringe. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2010, 21, 690–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Tori, M.; Asakawa, Y. Three dihydroisocoumarin glucosides from Hydrangea macrophylla subsp. serrata. Phytochemistry 1987, 26, 3323–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouye, H.; Takeda, Y.; Uesato, S.; Uobe, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Shingu, T. A novel type secoiridoid glucoside, hydrangenoside a from Hydrangea macrophylla. Tetrahedron Lett. 1980, 21, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.T.; Chang, F.R.; Lee, Y.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Liaw, C.C.; Ramesh, P.; Yuan, S.S.; Wu, Y.C. Chemical Constituents from the Hydrangea chinensis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003, 26, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, M.; Kakuda, R.; Kikuchi, M.; Yaoita, Y. Three new glycosides from the leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla subsp. serrata (THUNB.) MAKINO. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 610–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kikuchi, M.; Kakuda, R.; Yaoita, Y. Macropyllanosides A–D, Secoiridoid Glycosides from Hydrangea macrophylla subsp. serrata. Heterocycles 2008, 76, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Nakamura, S.; Matsuda, H.; Yoshikawa, M. Hydrangeamines A and B, novel polyketide-type pseudoalkaloid-coupled secoiridoid glycosides from the flowers of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii1. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Nakamura, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Yoshikawa, M.; Hussein, G.M.E.; Matsuo, K.; Matsuda, H. Medicinal flowers. XXXX. Structures of dihydroisocoumarin glycosides and inhibitory effects on aldose reducatase from the flowers of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 61, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Li, C.-J.; Yang, J.-Z.; Li, Y.; Bao, X.-Q.; Chen, N.-H.; Zhang, D.-M. Three new coumarin glycosides from the stems of Hydrangea paniculata. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 19, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, C.-J.; Yang, J.-Z.; Sun, H.; Zhang, D.-M. New Phenylpropanoid and Coumarin Glycosides from the Stems of Hydrangea paniculata Sieb. Molecules 2017, 22, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Sun, H.; Li, C.-J.; Yang, J.-Z.; Chen, F.-Y.; Zhang, D.-M. Chemical constituents from the stems of Hydrangea paniculata. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 19, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, H.; Shimoda, H.; Uemura, T.; Ueda, T.; Yamahara, J.; Yoshikawa, M. Chemical constituents from the leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii (III): Absolute stereostructures of hydramacrosides A and B, secoiridoid glucoside complexes with inhibitory activity on histamine release. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 1753–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murakami, N.; Mostaqul, H.M.; Tamura, S.; Itagaki, S.; Horii, T.; Kobayashi, M. New anti-malarial flavonol glycoside from hydrangeae dulcis folium. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 2445–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Wang, Z.; Xu, F.; Matsuda, H.; Wu, L.; Yoshikawa, M. The absolute stereostructures of cyanogenic glycosides, hydracyanosides A, B, and C, from the leaves and stems of Hydrangea macrophylla. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 4639–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnam, R.; Chang, F.R.; Chen, C.Y.; Kuo, R.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Wu, Y.C. Hydrachine A, a novel alkaloid from the roots of Hydrangea chinensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 948–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, C.-J.; Yang, J.-Z.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, D.-M. Monoterpenes from the leaves of Hydrangea paniculata and their hepatoprotective activities. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 17, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Li, C.-J.; Yang, J.-Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, C.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, D.-M. Hepatoprotective coumarins and secoiridoids from Hydrangea paniculata. Fitoterapia 2014, 96, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, H.; Kakuda, R.; Yaoita, Y.; Kikuchi, M. Secoiridoid glycosides from the leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla subsp. serrata. J. Nat. Med. 2007, 61, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, C.-J.; Yang, J.-Z.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Chen, N.-H.; Zhang, D.-M. Coumarin glycosides and iridoid glucosides with neuroprotective effects from Hydrangea paniculata. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.-S.; Han, H.-S.; Lee, S.-B.; Myung, D.-B.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, K.-T. Chemical Constituents from Leaves of Hydrangea serrata and Their Anti-photoaging Effects on UVB-Irradiated Human Fibroblasts. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Kisaki, T.; Noguchi, M. Isolation and Identification of Two Novel Glycosides from the Fresh Leaves of Amacha (Hydrangea macrophylla Sering var. Thunbergii Makino). Agric. Biol. Chem. 1979, 43, 1785–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Noguchi, M. Polyphenol Components in the Leaves of Amacha (Hydrangea macrophylla Seringe var. Thunbergii Makino). Agric. Biol. Chem. 1979, 43, 653–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uesato, S.; Hashimoto, T.; Takeda, Y.; Uobe, K.; Inouye, H. Novel type secoiridoid glucosides, hydrangenosides B, C and D from Hydrangea macrophylla. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981, 29, 3421–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uesato, S.; Takeda, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Uobe, K.; Inouye, H.; Taguchi, H.; Endo, T. Studies on Monoterpene Glucosides and Related Natural Products Part 51. Absolute Structures of Hydrangenosides A, B, C, D, E, F, and G. Novel Type Secoiridoid Glucosides from TwoHydrangea Plants. Helv. Chim. Acta 1984, 67, 2111–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-B.; Gao, H.-Y.; Yang, C.-J.; Sun, Z.; Wu, L.-J. Novel Cyanoglucosides from the Leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla. Helv. Chim. Acta 2011, 94, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-J.; Wang, Z.-B.; Zhu, D.-L.; Yu, Y.; Lei, Y.-T.; Liu, Y. Two new cyanogenic glucosides from the leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla. Molecules 2012, 17, 5396–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Uchida, E.; Chatani, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Naitoh, Y.; Okuno, Y.; Matsuda, H.; Yamahara, J.; Murakami, N. Thunberginols C, D, and E, new antiallergic and antimicrobial dihydroisocoumarins, and thunberginol G 3′-O-glucoside and (-)-hydrangenol 4′-O-glucoside, new dihydroisocoumarin glycosides, from Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1992, 40, 3352–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Uchida, E.; Chatani, N.; Murakami, N.; Yamahara, J. Thunberginols A, B, and F, new antiallergic and antimicrobial principles from hydrangeae dulcis folium. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1992, 40, 3121–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Ueda, T.; Matsuda, H.; Yamahara, J.; Murakami, N. Absolute stereostructures of hydramacrosides A and B, new bioactive secoiridoid glucoside complexes from the leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla Seringe var. thunbergii Makino. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 1691–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Murakami, N.; Ueda, T.; Shimoda, H.; Yahamara, J.; Matsuda, H. Absolute Stereostructures of 3S-Phyllodulcin, 3R- and 3S-Phyllodulcin Glycosides, and 3R- and 3S-Thunberginol H Glycosides from the Leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla SERINGE var. thunbergii MAKINO. Heterocycles 1999, 50, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Ueda, T.; Shimoda, H.; Murakami, N.; Yahamara, J.; Matsuda, H. Dihydroisocoumarin Constituents from the Leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii. (2).: Absolute Stereostructures of Hydrangenol, Thunberginol I, and Phyllodulcin Glycosides and Isomerization Reaction at the 3-Positions of Phyllodulcin and Its Glycosides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Wang, Z.; Nakamura, S.; Matsuda, H.; Wu, L. New Cyanoglycosides, Hydracyanosides D, E, and F, from the Leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla. Heterocycles 2010, 81, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y. New continous extraction method with a coil planet centrifuge. J. Chromatogr. A 1981, 207, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Sandlin, J.; Bowers, W.G. High-speed preparative counter-current chromatography with a coil planet centrifuge. J. Chromatogr. A 1982, 244, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y. Golden rules and pitfalls in selecting optimum conditions for high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1065, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, A.S.; McConvey, I.F.; Shering, P. An Evalution of the Performance of a Preparative CCC Machine for the Separation of an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. 2001, 24, 1811–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAmicis, C.; Edwards, N.A.; Giles, M.B.; Harris, G.H.; Hewitson, P.; Janaway, L.; Ignatova, S. Comparison of preparative reversed phase liquid chromatography and countercurrent chromatography for the kilogram scale purification of crude spinetoram insecticide. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 6122–6127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bórquez, J.; Bartolucci, N.L.; Echiburú-Chau, C.; Winterhalter, P.; Vallejos, J.; Jerz, G.; Simirgiotis, M.J. Isolation of cytotoxic diterpenoids from the Chilean medicinal plant Azorella compacta Phil from the Atacama Desert by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2832–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerz, G.; Elnakady, Y.A.; Braun, A.; Jäckel, K.; Sasse, F.; Al Ghamdi, A.A.; Omar, M.O.M.; Winterhalter, P. Preparative mass-spectrometry profiling of bioactive metabolites in Saudi-Arabian propolis fractionated by high-speed countercurrent chromatography and off-line atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass-spectrometry injection. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1347, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerz, G.; Gebers, N.; Szot, D.; Szaleniec, M.; Winterhalter, P.; Wybraniec, S. Separation of amaranthine-type betacyanins by ion-pair high-speed countercurrent chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1344, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.-B.; Qin, Y.-H.; Yun, Y.-H.; Lu, H.-M.; Chen, X.-Q.; Liang, Y.-Z. Using nonrandom two-liquid model for solvent system selection in counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1355, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rivera, M.P.; Lugo-Cervantes, E.; Winterhalter, P.; Jerz, G. Metabolite profiling of polyphenols in peels of Citrus limetta Risso by combination of preparative high-speed countercurrent chromatography and LC-ESI-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.N.; Winterhalter, P.; Jerz, G. Flavonoids from the flowers of Impatiens glandulifera Royle isolated by high performance countercurrent chromatography. Phytochem. Anal. 2016, 27, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Kim, S.J.; Shin, J.M.; Kim, S.H. Structure-taste correlations in sweet dihydrochalcone, sweet dihydroisocoumarin, and bitter flavone compounds. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 4325–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiçek, S.S.; Vitalini, S.; Zidorn, C. Natural Phenyldihydroisocoumarins: Sources, Chemistry and Bioactivity. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 1934578X1801300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos, F.A.; Takaishi, Y.; Shirotori, M.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Shibata, H.; Higuti, T.; Tadokoro, T.; Takeuchi, M. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of quercetin oxidation products from yellow onion (Allium cepa) skin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3551–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Cao, X.; Kuang, H.-X.; Zheng, X. A new stilbene glycoside from Dryopteris sublaeta. Yao Xue Xue Bao = Acta Pharm. Sin. 2005, 40, 1131–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T.; Ito, H.; Iinuma, M. Absolute configuration of resveratrol oligomer glucosides isolated from the leaves of Upuna borneensis. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 20, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.K.; Wang, X.-T.; Liu, P.-P.; Chi, Y.-X.; Wang, B.-J.; Dou, D.-Q.; Kang, T.-G.; Xiong, W. Cytotoxic constituents from the leaves of Broussonetia papyrifera. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Qian, X.-P.; Guo, Y.-G.; Li, T.; Yan, S.-K.; Jin, H.-Z.; Zhang, W.-D. Two new phenanthrene glycosides from Liparis regnieri Finet and their antibacterial activities. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 18, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, J. A family of plant-specific polyketide synthases: Facts and predictions. Trends Plant Sci. 1997, 2, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, B.; Debnath, S.; Banik, R. Naturally occurring iridoids and secoiridoids. An updated review, part 4. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 59, 803–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldansaz, S.M.; Festa, C.; Pagano, E.; de Marino, S.; Finamore, C.; Parisi, O.A.; Borrelli, F.; Sonboli, A.; D’Auria, M.V. Phytochemical and Biological Studies of Nepeta asterotricha Rech. f. (Lamiaceae): Isolation of Nepetamoside. Molecules 2019, 24, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hvattum, E.; Ekeberg, D. Study of the collision-induced radical cleavage of flavonoid glycosides using negative electrospray ionization tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 38, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Song, F.-R.; Tsao, R.; Jin, Y.-R.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Liu, S.-Y. Studies on the homolytic and heterolytic cleavage of kaempferol and kaempferide glycosides using electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wellmann, J.; Hartmann, B.; Schwarze, E.-C.; Hillebrand, S.; Brueckner, S.I.; Ley, J.; Jerz, G.; Winterhalter, P. Separation of Dihydro-Isocoumarins and Dihydro-Stilbenoids from Hydrangea macrophylla ssp. serrata by Use of Counter-Current Chromatography. Molecules 2022, 27, 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113424
Wellmann J, Hartmann B, Schwarze E-C, Hillebrand S, Brueckner SI, Ley J, Jerz G, Winterhalter P. Separation of Dihydro-Isocoumarins and Dihydro-Stilbenoids from Hydrangea macrophylla ssp. serrata by Use of Counter-Current Chromatography. Molecules. 2022; 27(11):3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113424
Chicago/Turabian StyleWellmann, Johannes, Beate Hartmann, Esther-Corinna Schwarze, Silke Hillebrand, Stephan I. Brueckner, Jakob Ley, Gerold Jerz, and Peter Winterhalter. 2022. "Separation of Dihydro-Isocoumarins and Dihydro-Stilbenoids from Hydrangea macrophylla ssp. serrata by Use of Counter-Current Chromatography" Molecules 27, no. 11: 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113424
APA StyleWellmann, J., Hartmann, B., Schwarze, E. -C., Hillebrand, S., Brueckner, S. I., Ley, J., Jerz, G., & Winterhalter, P. (2022). Separation of Dihydro-Isocoumarins and Dihydro-Stilbenoids from Hydrangea macrophylla ssp. serrata by Use of Counter-Current Chromatography. Molecules, 27(11), 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113424