Understanding the Palatability, Flavor, Starch Functional Properties and Storability of Indica-Japonica Hybrid Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Rice Quality
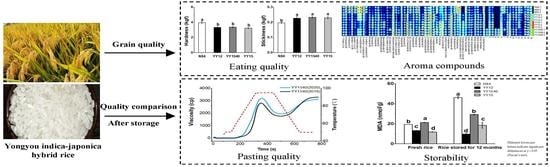
2.1.1. Rice Nutritional and Eating Quality
2.1.2. The Appearance and Textural Characteristic
2.1.3. PCA of Rice Quality
2.2. Analysis of Aroma Components of YY-IJHR
2.2.1. Odor Description of Detected Aroma Components
2.2.2. Differential Aroma Compounds
2.2.3. Key Aroma Compounds
2.2.4. PCA of Aroma Compounds
2.3. Starch Functional Properties of YY-IJHR
2.3.1. Starch Digestive Property
2.3.2. The Pasting Properties
2.3.3. PCA of Pasting Properties
2.4. The Cooking Quality
2.4.1. The Cooking Quality of Fresh Rice
2.4.2. Comparison of the Changes in Cooking Quality during Storage
2.5. The Rice Storability
2.5.1. The Content of FFA and MDA
2.5.2. The Activity of CAT and POD
2.5.3. PCA of Storability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Rice Flour
3.3. Determination of Rice Amylose and Protein Content
3.4. Determination of Eating Quality, Length and Head Rice Rate of Rice Grain
3.5. Determination of Rice Hardness and Stickiness
3.6. Determination of Rice Characteristic Aroma Components
3.7. Determination of Rice Pasting Properties
3.8. Determination of Rice Cooking Quality
3.8.1. Rice Cooking Expansion and Elongation Rate Measurement
3.8.2. Rice Water Absorption Rate Measurement
3.9. Determination of Rice FFA and MDA Content
3.10. Determination of Rice Catalase (CAT) and Peroxidase (POD) Activity
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Qu, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Xia, X.; Cao, J.; Lin, Q.; Wang, L. Preliminary study on quality and storability of giant hybrid rice grain. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 95, 103078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Xu, J.; Shao, Z.; Ge, M.; Zhang, H.; Wei, H.; Dai, Q.; Huo, Z.; Xu, K.; Guo, B.; et al. Advantages and their formation characteristics of the highest population productivity of nitrogen fertilization in Japonica/Indica hybrid rice of Yongyou series. Acta Agron. Sin. 2015, 41, 1711–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.-H.; Li, C.; Xing, Z.-P.; Wang, W.-T.; Dai, Q.-G.; Zhou, G.-S.; Wang, L.; Xu, K.; Huo, Z.-Y.; Guo, B.-W.; et al. Suitable growing zone and yield potential for late-maturity type of Yongyou japonica/indica hybrid rice in the lower reaches of Yangtze River, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.-F.; Han, C.; Hu, L.; Qiu, S.; Wu, P.; Liu, G.-D.; Wei, H.-Y.; Zhang, H.-C. Yield characteristics of japonica/indica hybrids rice in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2394–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L. Effect of ozone stress on yield characteristics of indica-japonica hybrid rice Yongyou 538 in two consecutive growing seasons. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 186, 104447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-M.; Liang, K.-J.; Zhang, S.-G.; Shang, W.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wei, X.-Y.; Ke, B. Analysis of Indica-Japonica Differentiation in Rice Parents and Derived Lines Using ILP Markers. Agric. Sci. China 2009, 8, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.Y.; Li, Z.K.; Li, E.P.; Wang, W.L.; Yuan, L.M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Gu, J.F.; Yang, J.C. Optimization of nitrogen fertilization improves rice quality by affecting the structure and physicochemical properties of starch at high yield levels. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 1576–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B.; Xu, K.; Dai, Q.; Wei, C.; Zhou, G.; Huo, Z. Physicochemical properties of indica-japonica hybrid rice starch from Chinese varieties. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.-L.; Ren, G.-L.; Han, C.; Xu, F.-F.; Qiu, S.; Tang, J.-H.; Zhang, H.-C.; Wei, H.-Y.; Gao, H. Comparative analysis on grain quality and yield of different panicle weight indica-japonica hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Fang, C.; Qian, Z.; Guo, B.; Huo, Z. Differences in starch structure, physicochemical properties and texture characteristics in superior and inferior grains of rice varieties with different amylose contents. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.A.; Singh, P.; Shah, M.A.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Gul, K.; Wani, I.A. Rice Starch Diversity: Effects on Structural, Morphological, Thermal, and Physicochemical Properties-A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2012, 11, 417–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.Y.; Oh, S.K.; Kim, H.S.; Chung, H.J. Influence of molecular structure on physicochemical properties and digestibility of normal rice starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 77, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Zhu, P.; Sui, Z.; Bao, J. Physicochemical properties of starches from diverse rice cultivars varying in apparent amylose content and gelatinisation temperature combinations. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Mao, B.; Zhang, C.; Shao, Y.; Wu, T.; Hu, L.; Hu, Y.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; Tang, W.; et al. Influence of physicochemical properties and starch fine structure on the eating quality of hybrid rice with similar apparent amylose content. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Chen, X.; Meng, L.; Wei, Z.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Cheng, Q. Characteristic Fingerprint Analysis of the Moldy Odor in Guangxi Fragrant Rice by Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry (GC-IMS). Anal. Lett. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruq, G.; Prodhan, Z.H.; Nezhadahmadi, A. Effects of Ageing on Selected Cooking Quality Parameters of Rice. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruq, G.; Mohamad, O.; Hadzim, M.; Meisner, C.A. Optimization of Aging Time and Temperature for Four Malaysian Rice Cultivars. Pak. J. Nutr. 2003, 2, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Robards, K.; Helliwell, S.; Blanchard, C. Ageing of Stored Rice: Changes in Chemical and Physical Attributes. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 35, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, C.-E.; Kim, Y.-S.; Park, K.-J.; Kim, B.-K. Changes in physicochemical characteristics of rice during storage at different temperatures. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2012, 48, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, M.C.; Cuevas, R.P.; Ynion, J.; Laborte, A.G.; Velasco, M.L.; Demont, M. Rice quality: How is it defined by consumers, industry, food scientists, and geneticists? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fitzgerald, M.A.; Prakash, S.; Nicholson, T.M.; Gilbert, R.G. The molecular structural features controlling stickiness in cooked rice, a major palatability determinant. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Mao, B.; Zhang, C.; Shao, Y.; Wu, T.; Hu, L.; Hu, Y.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; et al. Correlations between Parental Lines and Indica Hybrid Rice in Terms of Eating Quality Traits. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 583997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, H.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; Hu, Q.; Ding, C. Effect of dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma treatments on flavor fingerprints of brown rice. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Chen, T.; Chen, M.; Lu, D.; Chen, B. Application of Gas Chromatography—Ion Migration Spectrometry (GC—IMS) to Evaluate the Degree of Mildew in Rice. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2019, 34, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Burdock, G.A. Fenaroli’s Handbook of Flavor Ingredients, 6th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.X.; Yi, C.; Xiao, T.; Qin, W.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, F.; Tong, L.T. Volatile compounds, bacteria compositions and physicochemical properties of 10 fresh fermented rice noodles from southern China. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150 Pt A, 110787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Xiang, X.; Tan, H.; Zhang, Q.; Shan, Y.; Yang, H. Potential correlation between volatiles and microbiome of Xiang xi sausages from four different regions. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J. Rice starch. In Rice; AACC International Press: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2019; pp. 55–108. [Google Scholar]
- Englyst, H.N.; Kingman, S.M.; Cummings, J.H. Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 46 (Suppl. 2), S33–S50. [Google Scholar]
- Arp, C.G.; Correa, M.J.; Ferrero, C. Resistant starches: A smart alternative for the development of functional bread and other starch-based foods. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 121, 106949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ying, Y.; Hu, B.; Pang, Y.; Bao, J. Physicochemical properties and digestibility of endosperm starches in four indica rice mutants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, T.; Nishiba, Y.; Sato, T.; Suda, I. Properties of Starches from Several Low-Amylose Rice Cultivars. Cereal Chem. 2003, 80, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cong, S.; Zhang, H. Comparison of the Grain Quality and Starch Physicochemical Properties between Japonica Rice Cultivars with Different Contents of Amylose, as Affected by Nitrogen Fertilization. Agriculture 2021, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, J.L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lee, L.F.; McPherson, A.E.; Wong, K.S.; Radosavljevic, M.; Kasemsuwan, T. Effects of amylopectin branch chain length and amylose content on the gelatinization and pasting properties of starch. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.G.; Yoshida, T.; Uchimura, Y. Genetic Effect on Amylose and Protein Contents in the Crossed Rice Seeds. Plant Prod. Sci. 2002, 5, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wu, G.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Qi, X. Investigation on molecular and morphology changes of protein and starch in rice kernel during cooking. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Han, F.; Wu, Z.; Lan, T.; Wu, W. Estimation of Free Fatty Acids in Stored Paddy Rice Using Multiple-Kernel Support Vector Regression. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsue, Y.; Uchimura, Y.; Sato, H.; Ogata, T. An Efficient Method for Evaluating the Palatability Deterioration during Storage in Rice. Plant Prod. Sci. 2015, 6, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, C. Analysis of the Storage Property, Physiological, Biochemical Indicators Parameters and the Pasting Characteristics of Rice in Different Storage Time. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2020, 35, 108–114, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Ban, X.; Gu, Z.; Hong, Y. Pasting properties and multi-scale structures of Spirodela starch and its comparison with normal corn and rice starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 132, 107865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Shen, Q. Application of GC-IMS Technology Combined with Chemometrics Method in Classification of Hulless Barley. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2020, 35, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, D.-H.; Zhou, S.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, L.; Lin, Z.; Qin, W.; Liu, L.; Tong, L.-T. Effects of slight milling combined with cellulase enzymatic treatment on the textural and nutritional properties of brown rice noodles. LWT 2020, 128, 109520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Rice Varieties | N84 | YY12 | YY1540 | YY15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh Rice | ||||
| PV (cp) | 2428 ± 39.3 d | 3356 ± 37.6 b | 3238 ± 26.1 c | 3574 ± 63.9 a |
| TV (cp) | 1549 ± 35.6 b | 1677 ± 43.5 b | 2040 ± 58.5 a | 1660 ± 86.9 b |
| BD (cp) | 878 ± 10.8 d | 1678 ± 14.5 b | 1199 ± 73.8 c | 1915 ± 52.8 a |
| FV (cp) | 2484 ± 35.1 c | 2670 ± 41.1 b | 3287 ± 68.6 a | 2608 ± 73.3 bc |
| SB (cp) | 934 ± 4.1 c | 993 ± 2.6 b | 1247 ± 13.1 a | 948 ± 14.2 c |
| PT (°C) | 75.5 ± 0.1 d | 80.3 ± 0.1 b | 74.3 ± 0.1 c | 81.2 ± 0.2 a |
| Rice Stored for 12 Months | ||||
| PV (cp) | 2930 ± 42.0 b | 3589 ± 52.9 a | 2819 ± 72.5 b | 3655 ± 9.7 a |
| TV (cp) | 1690 ± 76.0 ab | 1640 ± 10.6 ab | 1763 ± 61.5 a | 1581 ± 38.7 b |
| BD (cp) | 1240 ± 40.9 c | 1948 ± 56.0 b | 1056 ± 31.7 d | 2074 ± 40.8 a |
| FV (cp) | 2926 ± 55.5 c | 2918 ± 6.9 b | 3286 ± 68.3 a | 2784 ± 40.4 b |
| SB (cp) | 1236 ± 20.5 c | 1278 ± 16.7 b | 1523 ± 8.2 a | 1202 ± 8.7 c |
| PT (°C) | 71.1 ± 0.1 c | 80.7 ± 0.1 b | 86.1 ± 0.4 a | 80.2 ± 0.8 b |
| Rice Varieties | N84 | YY12 | YY1540 | YY15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh Rice | ||||
| Cooking expansion rate (%) | 268 ± 5.7 c | 355 ± 1.4 a | 364 ± 5.7 a | 322 ± 5.7 b |
| Cooking elongation rate (%) | 62.4 ± 0.5 b | 77.5 ± 1.4 a | 80.2 ± 2.8 a | 55.5 ± 7.8 b |
| Heating water absorption rate (%) | 141.6 ± 0.4 b | 145.9 ± 1.2 b | 143.4 ± 2.8 b | 151.8 ± 2.3 a |
| Soaked water absorption rate (%) | 16.1 ± 0.1 c | 23.9 ± 0.4 b | 26 ± 4.4 ab | 30.9 ± 0.4 a |
| Rice Stored for 12 Months | ||||
| Cooking expansion rate (%) | 460 ± 0.4 a | 338 ± 2.8 b | 361 ± 1.4 b | 367 ± 1.4 b |
| Cooking elongation rate (%) | 53.1 ± 0.1 b | 90 ± 2.8 a | 67.5 ± 10.1 b | 56.6 ± 3.5 b |
| Heating water absorption rate (%) | 344.3 ± 0.2 a | 146.4 ± 2.6 b | 146.6 ± 0.6 b | 148.3 ± 1.8 b |
| Soaked water absorption rate (%) | 14.7 ± 0.1 b | 26.0 ± 1.3 a | 27.3 ± 4.1 a | 30.2 ± 2.8 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, A.; Xi, H.; Nie, M.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, F.; Tong, L. Understanding the Palatability, Flavor, Starch Functional Properties and Storability of Indica-Japonica Hybrid Rice. Molecules 2022, 27, 4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134009
Gong X, Zhu L, Wang A, Xi H, Nie M, Chen Z, He Y, Tian Y, Wang F, Tong L. Understanding the Palatability, Flavor, Starch Functional Properties and Storability of Indica-Japonica Hybrid Rice. Molecules. 2022; 27(13):4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134009
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Xue, Lin Zhu, Aixia Wang, Huihan Xi, Mengzi Nie, Zhiying Chen, Yue He, Yu Tian, Fengzhong Wang, and Litao Tong. 2022. "Understanding the Palatability, Flavor, Starch Functional Properties and Storability of Indica-Japonica Hybrid Rice" Molecules 27, no. 13: 4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134009
APA StyleGong, X., Zhu, L., Wang, A., Xi, H., Nie, M., Chen, Z., He, Y., Tian, Y., Wang, F., & Tong, L. (2022). Understanding the Palatability, Flavor, Starch Functional Properties and Storability of Indica-Japonica Hybrid Rice. Molecules, 27(13), 4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134009