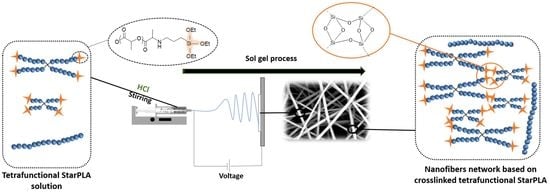
Creation of a Stable Nanofibrillar Scaffold Composed of Star-Shaped PLA Network Using Sol-Gel Process during Electrospinning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Functionalization of StarPLA
2.2. Creation of StarPLA-PTES Nanofibers by Sol-Gel Process during Electrospinning
2.3. Nanofibers Behavior in a Physiological Environment-Like over Time
2.4. Biological Evaluation In Vitro
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Linear and 4-Arm Star Poly(Lactide)
3.3. Functionalization of 4-Arm Starpoly(Lactide) with Triethoxysilane
3.4. Electrospinning
3.5. Characterization Methods
3.6. Gel Fraction
3.7. Tensile Tests
3.8. Nanofibers Behavior in a Physiological Environment-Like over Time
3.9. Biological Evaluation In Vitro
3.9.1. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.9.2. Proliferation Assay
3.9.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Garlotta, D. A Literature Review of Poly(Lactic Acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramot, Y.; Haim-Zada, M.; Domb, A.J.; Nyska, A. Biocompatibility and safety of PLA and its copolymers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, D.; Kaduri, M.; Poley, M.; Adir, O.; Krinsky, N.; Shainsky-Roitman, J.; Schroeder, A. Biocompatibility, biodegradation and excretion of polylactic acid (PLA) in medical implants and theranostic systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasprilla, A.J.R.; Martinez, G.A.R.; Lunelli, B.H.; Jardini, A.L.; Filho, R.M. Poly-lactic acid synthesis for application in biomedical devices—A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dürselen, L.; Dauner, M.; Hierlemann, H.; Planck, H.; Claes, L.E.; Ignatius, A. Resorbable polymer fibers for ligament augmentation: Resorbable Polymer Fibers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 58, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutu, D.L.; Yousefi, A.-M.; Galipeau, J. Three-dimensional porous scaffolds at the crossroads of tissue engineering and cell-based gene therapy. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 108, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellomäki, M.; Niiranen, H.; Puumanen, K.; Ashammakhi, N.; Waris, T.; Törmälä, P. Bioabsorbable scaffolds for guided bone regeneration and generation. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2495–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.J.; Son, B.; Hwang, T.S.; Hwang, E.-H. Increase of degradation and water uptake rate using electrospun star-shaped poly(d,l-lactide) nanofiber. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2011, 17, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikos, A.G.; Thorsen, A.J.; Czerwonka, L.A.; Bao, Y.; Langer, R.; Winslow, D.N.; Vacanti, J.P. Preparation and characterization of poly(l-lactic acid) foams. Polymer 1994, 35, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, I.; Shastri, V.P.; Padera, R.F.; Yang, J.; Mackay, A.J.; Langer, R.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Freed, L.E. Selective differentiation of mammalian bone marrow stromal cells cultured on three-dimensional polymer foams. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 55, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Murugan, R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.-X.; Wang, S. Fabrication of nano-structured porous PLLA scaffold intended for nerve tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumbar, S.G.; Nukavarapu, S.P.; James, R.; Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Electrospun poly(lactic acid-co-glycolic acid) scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4100–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumbar, S.G.; James, R.; Nukavarapu, S.P.; Laurencin, C.T. Electrospun nanofiber scaffolds: Engineering soft tissues. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 34002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geng, X.; Kwon, O.; Jang, J. Electrospinning of chitosan dissolved in concentrated acetic acid solution. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5427–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, E.; Phan, T.; Lim, I.; Zhang, Y.; Bay, B.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lim, C. Evaluation of electrospun PCL/gelatin nanofibrous scaffold for wound healing and layered dermal reconstitution. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kang, H.; Shen, J.; Zhang, L.; Nishi, T.; Ito, K.; Zhao, C.; Coates, P. Highly toughened polylactide with novel sliding graft copolymer by in situ reactive compatibilization, crosslinking and chain extension. Polymer 2014, 55, 4313–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalermpanaphan, V.; Choochottiros, C. Synthesis of unsaturated aliphatic polyester-based copolymer: Effect on the ductility of PLA blend and crosslink. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J. Research progress in toughening modification of poly(lactic acid). J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 1051–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarek, M.; Borska, K.; Kubisa, P. New Polylactide-Based Materials by Chemical Crosslinking of PLA. Polym. Rev. 2021, 61, 493–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarek, M.; Borska, K.; Kubisa, P. Crosslinking of Polylactide by High Energy Irradiation and Photo-Curing. Molecules 2020, 25, 4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamura, M.; Sugimoto, M.; Kawaguchi, S.; Takahashi, T.; Koyama, K. Influence of extrusion temperature on molecular architecture and crystallization behavior of peroxide-induced slightly crosslinked poly(L-lactide) by reactive extrusion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 1468–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, Z.-H.; Yang, W.; Yang, M.-B. Thermal and mechanical properties of chemical crosslinked polylactide (PLA). Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-L.; Wu, Z.-H.; Meng, B.; Yang, W. The effects of dioctyl phthalate plasticization on the morphology and thermal, mechanical, and rheological properties of chemical crosslinked polylactide: Effects of Dioctyl Phthalate Plasticization. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2009, 47, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, R.F.; Warren, S.C.; Allison, C.J.; Wiggins, J.S.; Puckett, A.D. Synthesis of bioabsorbable networks from methacrylate-endcapped polyesters. Polymer 1993, 34, 4365–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helminen, A.O.; Korhonen, H.; Seppälä, J.V. Structure modification and crosslinking of methacrylated polylactide oligomers: Methacrylated Polylactide Oligomers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 3616–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooyan, S.; Box, P.O. Sol-gel process and its application in Nanotechnology. J. Polym. Eng. Technol. 2005, 5, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, G.J.; Singh, R.K.; Foroutan, F.; Alqaysi, M.; Han, C.-M.; Mahapatra, C.; Kim, H.-W.; Knowles, J.C. Sol–gel based materials for biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 77, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livage, J.; Sanchez, C.; Henry, M.; Doeuff, S. The chemistry of the sol-gel process. Solid State Ion. 1989, 32–33, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echalier, C.; Pinese, C.; Garric, X.; Van Den Berghe, H.; Jumas Bilak, E.; Martinez, J.; Mehdi, A.; Subra, G. Easy Synthesis of Tunable Hybrid Bioactive Hydrogels. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echalier, C.; Levato, R.; Mateos-Timoneda, M.A.; Castaño, O.; Déjean, S.; Garric, X.; Pinese, C.; Noël, D.; Engel, E.; Martinez, J.; et al. Modular bioink for 3D printing of biocompatible hydrogels: Sol–gel polymerization of hybrid peptides and polymers. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 12231–12235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arsenie, L.V.; Pinese, C.; Bethry, A.; Valot, L.; Verdie, P.; Nottelet, B.; Subra, G.; Darcos, V.; Garric, X. Star-poly(lactide)-peptide hybrid networks as bioactive materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 139, 109990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinese, C.; Jebors, S.; Echalier, C.; Licznar-Fajardo, P.; Garric, X.; Humblot, V.; Calers, C.; Martinez, J.; Mehdi, A.; Subra, G. Simple and Specific Grafting of Antibacterial Peptides on Silicone Catheters. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2016, 5, 3067–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; McCann, J.T.; Xia, Y.; Marquez, M. Electrospinning: A Simple and Versatile Technique for Producing Ceramic Nanofibers and Nanotubes. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-S.; Lee, S.G.; Im, S.S.; Kim, S.H.; Joo, Y.L. Silica nanofibers from electrospinning/sol-gel process. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2003, 22, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fu, B.; Dai, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Q. Study the Mechanism of Enhanced Li Storage Capacity through Decreasing Internal Resistance by High Electronical Conductivity via Sol-gel Electrospinning of Co 3O4 Carbon Nanofibers. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 3542–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmohammad Sadeghi, S.; Vaezi, M.; Kazemzadeh, A.; Jamjah, R. 3D networks of TiO2 nanofibers fabricated by sol-gel/electrospinning/calcination combined method: Valuation of morphology and surface roughness parameters. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 271, 115254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzada, T.; Arvidson, S.A.; Saquing, C.D.; Shah, S.S.; Khan, S.A. Hybrid Carbon Silica Nanofibers through Sol–Gel Electrospinning. Langmuir 2014, 30, 15504–15513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzada, T.; Arvidson, S.A.; Saquing, C.D.; Shah, S.S.; Khan, S.A. Hybrid Silica–PVA Nanofibers via Sol–Gel Electrospinning. Langmuir 2012, 28, 5834–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejob, L.; Toury, B.; Tadier, S.; Grémillard, L.; Gaillard, C.; Salles, V. Electrospinning of in situ synthesized silica-based and calcium phosphate bioceramics for applications in bone tissue engineering: A review. Acta Biomater. 2021, 123, 123–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, R.F.; Wiggins, J.S.; Mauritz, K.A.; Puckett, A.D. Bioabsorbable composites. I: Fundamental design considerations using free radically crosslinkable matrices. Polym. Compos. 1993, 14, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helminen, A.; Korhonen, H.; Seppälä, J.V. Biodegradable crosslinked polymers based on triethoxysilane terminated polylactide oligomers. Polymer 2001, 42, 3345–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, R.F.; Hickey, T.P. Degradable polyurethane networks based on d,l-lactide, glycolide, ε-caprolactone, and trimethylene carbonate homopolyester and copolyester triols. Polymer 1994, 35, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, A.; Brzezinski, M.; Lapienis, G.; Biela, T. Star-shaped and branched polylactides: Synthesis, characterization, and properties. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 89, 159–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Han, Y.-K.; Kim, Y.H.; Hong, S.I. Multifunctional initiation of lactide polymerization by stannous octoate/pentaerythritol. Makromol. Chem. 1992, 193, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.L.; Bates, W.D.; Frisch, H.L.; Wnek, G.E. Role of chain entanglements on fiber formation during electrospinning of polymer solutions: Good solvent, non-specific polymer–polymer interaction limit. Polymer 2005, 46, 3372–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Kim, K.; Fang, D.; Ran, S.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes. Polymer 2002, 43, 4403–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, V.; Anandjiwala, R.D.; Maaza, M. The influence of electrospinning parameters on the structural morphology and diameter of electrospun nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 3130–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Ran, S.; Kim, K.-S.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Structure and Morphology Changes during in Vitro Degradation of Electrospun Poly(glycolide-co-lactide) Nanofiber Membrane. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percec, V. (Ed.) Hierarchical Macromolecular Structures: 60 Years after the Staudinger Nobel Prize II; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 262, ISBN 978-3-319-03718-9. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Zhu, L.; Huang, X.; Zheng, S.; Tang, X. Synthesis, characterization and degradation of hexa-armed star-shaped poly(l-lactide)s and poly(d,l-lactide)s initiated with hydroxyl-terminated cyclotriphosphazene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 87, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzi, I.; Garreau, H.; Li, S.; Vert, M. Hydrolytic degradation of devices based on poly(dl-lactic acid) size-dependence. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Samples | Degradation Time (Months) | Gel Fraction (%) | Mass Loss (%) | Young Modulus E (Mpa) | Glass Transition (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 0 | 27.5 ± 3 | / | 19.1 ± 5 | 60.7 |
| 1 | 76.2 ± 2 | 5.5 ± 4 | 27.8 ± 7 | 49.5 | |
| 3 | 80 ± 3 | 0 | 23 ± 1 | 52.6 | |
| 6 | 84.7 ± 5 | 7.9 ± 5 | 19.8 ± 8 | 54.2 | |
| G | 0 | 40 ± 4 | / | 37.9 ± 19 | 54.8 |
| 1 | 85.2 ± 9 | 5.8 ± 4 | 31.5 ± 9 | 48.3 | |
| 3 | 81.8 ± 1 | 1.2 ± 2.1 | 82.3 ± 7 | 48.4 | |
| 6 | 81.9 ± 7 | 1.7 ± 0.6 | 35.2 ± 3 | 48 | |
| H | 0 | 61 ± 6 | / | 20.8 ± 4 | 52.1 |
| 1 | 65.3 ± 14 | 8.7 ± 7 | 20.3 ± 3 | 48.8 | |
| 3 | 65.7 ± 3 | 1.5 ± 2.2 | 32.8 ± 11 | 50 | |
| 6 | 72.3 ± 5 | 1.0 ± 1 | 37.1 ± 11 | 48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belabbes, K.; Pinese, C.; Leon-Valdivieso, C.Y.; Bethry, A.; Garric, X. Creation of a Stable Nanofibrillar Scaffold Composed of Star-Shaped PLA Network Using Sol-Gel Process during Electrospinning. Molecules 2022, 27, 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134154
Belabbes K, Pinese C, Leon-Valdivieso CY, Bethry A, Garric X. Creation of a Stable Nanofibrillar Scaffold Composed of Star-Shaped PLA Network Using Sol-Gel Process during Electrospinning. Molecules. 2022; 27(13):4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134154
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelabbes, Karima, Coline Pinese, Christopher Yusef Leon-Valdivieso, Audrey Bethry, and Xavier Garric. 2022. "Creation of a Stable Nanofibrillar Scaffold Composed of Star-Shaped PLA Network Using Sol-Gel Process during Electrospinning" Molecules 27, no. 13: 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134154
APA StyleBelabbes, K., Pinese, C., Leon-Valdivieso, C. Y., Bethry, A., & Garric, X. (2022). Creation of a Stable Nanofibrillar Scaffold Composed of Star-Shaped PLA Network Using Sol-Gel Process during Electrospinning. Molecules, 27(13), 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27134154